Market Overview
The Singapore business aviation services market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by approximately ~ active managed aircraft and ~ annual business flight movements. Operational activity reflects ~ percent utilization across charter, management, and maintenance services, with ~ operators licensed and ~ certified maintenance facilities active. Fleet composition remains skewed toward large cabin and ultra-long-range aircraft, accounting for ~ percent of operations. Service revenues are diversified across charter, fixed base operations, and maintenance contracts, reducing cyclicality exposure. Business aviation movements represent ~ percent of total non-commercial traffic at dedicated airports. Demand intensity remains stable, driven by corporate, medical, and government usage patterns.
Singapore serves as the primary hub, with activity concentrated around Seletar Airport due to dedicated infrastructure and regulatory specialization. Strong connectivity to Southeast Asia and North Asia reinforces its regional command role. Demand clusters around multinational headquarters, family offices, and diplomatic missions. The ecosystem benefits from mature maintenance capabilities, skilled workforce availability, and strong safety oversight. Policy clarity and regulatory predictability enhance operator confidence. Supporting logistics, fuel supply, and financing services further strengthen ecosystem depth.
Market Segmentation
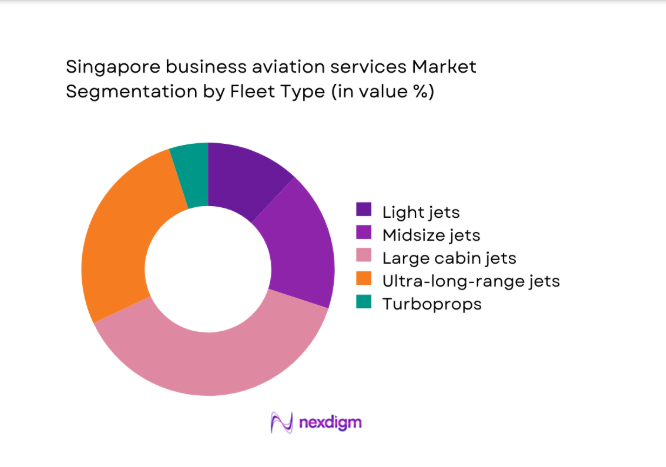
By Fleet Type
Large cabin and ultra-long-range jets dominate the Singapore business aviation services market due to regional geography and mission requirements. Corporate and government users prefer aircraft capable of nonstop intercontinental travel, increasing utilization of long-range platforms. Fleet operators emphasize reliability, cabin comfort, and extended endurance, reinforcing preference for larger aircraft categories. Managed fleet growth favors standardized large-cabin models to optimize maintenance planning and crew scheduling. Charter demand also aligns with these aircraft due to high passenger loads and premium service expectations. Turboprops and light jets remain niche, primarily supporting regional hops and medical missions.
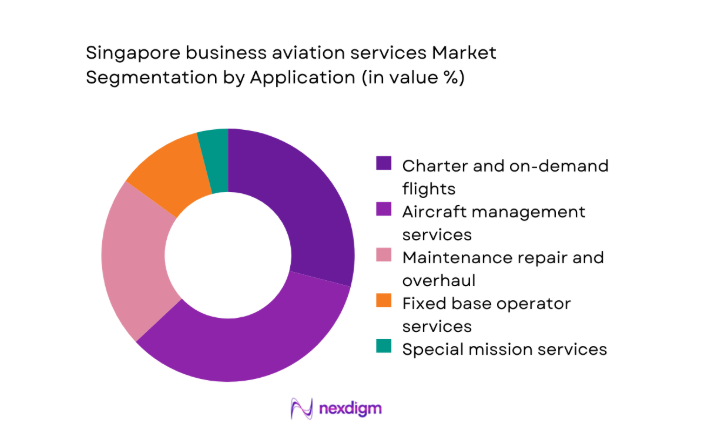
By Application
Aircraft management services represent the most dominant application within the Singapore business aviation services market. Owners increasingly outsource operational oversight, compliance management, and crew administration to specialized providers. Charter and on-demand services maintain strong relevance, particularly for regional executives and private wealth clients. Maintenance, repair, and overhaul services benefit from Singapore’s technical reputation and regulatory rigor. Fixed base operator services add incremental value through concierge handling and ground support. Special mission operations remain limited but strategically important for government and medical users.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is moderately consolidated, with global operators coexisting alongside regional specialists. Market participants differentiate through fleet scale, regulatory certifications, and integrated service depth.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| ExecuJet Aviation Group | 1991 | Zurich | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Jet Aviation | 1967 | Basel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Luxaviation Group | 2008 | Luxembourg | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ST Engineering Aerospace | 1990 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| VistaJet | 2004 | Malta | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore business aviation services Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising regional headquarters and cross-border executive travel
Regional headquarters concentration in Singapore continues driving executive mobility demand across Southeast Asia and North Asia markets. Cross-border travel volumes increased steadily during 2024 and 2025, reinforcing reliance on flexible business aviation services. Executives prioritize time efficiency, privacy, and direct routing, favoring private aviation solutions over scheduled commercial alternatives. Corporate travel policies increasingly allow charter usage for multi-city regional itineraries. Business aviation enables same-day return trips, improving executive productivity metrics. Demand also reflects board-level travel, mergers, and regional oversight responsibilities. Aviation services providers align offerings with corporate scheduling needs. Utilization rates improved consistently across managed fleets. Service contracts expanded in duration during 2025. These factors collectively reinforce sustained demand momentum.
Expansion of ultra-long-range business jet deployments
Ultra-long-range aircraft deployments expanded across Singapore-based fleets to support nonstop intercontinental business missions. Operators added aircraft capable of extended range operations during 2024 and 2025. Demand increased for Asia to Europe and North America direct connectivity. These aircraft enhance Singapore’s attractiveness as a global aviation base. Longer range reduces dependency on intermediate refueling stops. Fleet owners value operational flexibility and passenger comfort improvements. Service providers invested in specialized maintenance and crew training. Infrastructure readiness supports larger aircraft categories efficiently. Utilization intensity rose across premium fleet segments. This expansion structurally elevates service revenue density.
Challenges
High operating and hangarage costs at Seletar Airport
Operating costs at Seletar Airport remain structurally high compared to regional alternatives. Hangarage constraints limit availability and increase competition for space. Operators face elevated fixed costs regardless of utilization levels. Cost pressures affect smaller fleet operators disproportionately. Service providers must optimize scheduling to maintain margins. Owners assess alternative basing strategies within Southeast Asia. Infrastructure expansion remains limited due to land constraints. Regulatory requirements further add compliance-related overheads. Cost management remains a strategic priority during 2024 and 2025. These pressures moderate new market entry rates.
Stringent regulatory and compliance requirements
Singapore maintains stringent regulatory oversight for business aviation operations. Compliance requirements cover safety management, crew licensing, and maintenance documentation. Operators invest heavily in governance frameworks to meet standards. Regulatory audits increase administrative workload for service providers. Smaller operators face higher proportional compliance burdens. Certification timelines influence fleet induction planning. Regulatory clarity supports safety reputation but increases operational complexity. Cross-border operations require multilayer compliance coordination. Regulatory adherence costs remain persistent during 2024 and 2025. This environment favors well-capitalized operators.
Opportunities
Growth in aircraft management outsourcing models
Aircraft owners increasingly adopt outsourcing models to reduce operational complexity. Management providers offer bundled services covering compliance, crew, and maintenance coordination. This model gained traction during 2024 and 2025 among corporate owners. Outsourcing improves cost predictability and risk management. Service providers achieve scale efficiencies through pooled resources. Fleet standardization supports operational optimization. Demand for turnkey solutions continues rising. Contract durations extended reflecting owner confidence. Management penetration deepens across large-cabin fleets. This trend strengthens recurring revenue visibility.
Expansion of digital flight planning and predictive maintenance services
Digitalization transforms operational efficiency across business aviation services. Predictive maintenance platforms reduce unscheduled downtime and improve dispatch reliability. Flight planning software optimizes routing and fuel efficiency. Adoption accelerated during 2024 and 2025 across managed fleets. Operators leverage data analytics for proactive decision-making. Digital tools enhance regulatory reporting accuracy. Service differentiation increasingly depends on digital maturity. Investment focus shifts toward integrated platforms. Digital adoption lowers long-term operational risk. This creates value-added service expansion opportunities.
Future Outlook
The Singapore business aviation services market is expected to maintain steady expansion through 2035. Demand fundamentals remain supported by regional economic integration and executive mobility needs. Sustainability initiatives and digital adoption will shape service differentiation. Regulatory consistency will continue favoring established operators. Singapore’s hub positioning is likely to remain structurally intact.
Major Players
- ExecuJet Aviation Group
- Jet Aviation
- Luxaviation Group
- VistaJet
- ST Engineering Aerospace
- SIA Engineering Company
- Million Air Singapore
- Universal Aviation Singapore
- AMAC Aerospace
- Metrojet Limited
- TAG Aviation Asia
- Hawker Pacific
- Asian Sky Group
- Shell Aviation
- World Fuel Services
Key Target Audience
- Business jet operators and fleet owners
- Corporate enterprises with regional headquarters
- High-net-worth individuals and family offices
- Aircraft leasing and management companies
- Fixed base operator service providers
- Maintenance repair and overhaul providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including civil aviation authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Focused on fleet composition, service categories, operational intensity, and regulatory scope. Primary parameters were defined to reflect Singapore-specific aviation structures.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Involved mapping service workflows, operator models, and utilization patterns. Data normalization ensured consistency across service segments.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Included structured discussions with operators, airport authorities, and service providers. Insights were reconciled to reflect operational realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Integrated qualitative insights with validated data to produce coherent market narratives and forward-looking assessments.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for business aviation services, Fleet and service taxonomy mapping across charter management and MRO, Bottom-up market sizing using flight hours and managed aircraft data, Revenue attribution across FBO handling maintenance and charter operations, Primary interviews with operators regulators and airport authorities, Triangulation using CAAS traffic statistics OEM deliveries and operator disclosures)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission profiles
- Ecosystem structure
- Service delivery and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising regional headquarters and cross-border executive travel
Expansion of ultra-long-range business jet deployments
Singapore’s positioning as a neutral and secure aviation hub
Growth of wealth concentration and family offices
Demand for time-critical medical and government missions - Challenges
High operating and hangarage costs at Seletar Airport
Stringent regulatory and compliance requirements
Limited airport slot availability and capacity constraints
Volatility in fuel prices and operating expenses
Skilled workforce shortages in MRO and flight operations - Opportunities
Growth in aircraft management outsourcing models
Expansion of digital flight planning and predictive maintenance services
Rising demand for sustainable aviation fuel services
Increased use of Singapore as an Asia-Pacific maintenance hub
Private-public collaboration for special mission aviation - Trends
Adoption of ultra-long-range jets for nonstop intercontinental routes
Integration of sustainability reporting and carbon offset services
Growth of subscription-based charter models
Increased use of data analytics in fleet management
Rising demand for concierge-style FBO services - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume (Flight Hours), 2020–2025
- By Installed Base (Managed Aircraft), 2020–2025
- By Revenue per Flight Hour, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Light jets
Midsize jets
Large cabin jets
Ultra-long-range jets
Turboprops - By Application (in Value %)
Charter and on-demand flights
Aircraft management services
Maintenance repair and overhaul
Fixed base operator services
Special mission and medical evacuation - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Conventional avionics platforms
Next-generation integrated avionics
Predictive maintenance and analytics platforms
Digital flight operations management systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Corporate enterprises
High-net-worth individuals
Government and diplomatic missions
Aviation leasing and management firms
Medical and emergency services - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Satellite-based broadband connectivity
Air-to-ground connectivity
Hybrid connectivity solutions
Basic cockpit communication systems - By Region (in Value %)
Singapore domestic operations
Southeast Asia regional operations
North Asia operations
Long-haul intercontinental operations
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Service portfolio breadth, Fleet size under management, regional network coverage, Regulatory approvals and certifications, Pricing and contract flexibility, Digital capabilities, Sustainability offerings, Customer service depth)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
ExecuJet Aviation Group
Jet Aviation
Luxaviation Group
VistaJet
ST Engineering Aerospace
SIA Engineering Company
Million Air Singapore
Universal Aviation Singapore
AMAC Aerospace
Metrojet Limited
TAG Aviation Asia
Hawker Pacific
Asian Sky Group
Shell Aviation
World Fuel Services
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume (Flight Hours), 2026–2035
- By Installed Base (Managed Aircraft), 2026–2035
- By Revenue per Flight Hour, 2026–2035


