Market Overview
The Singapore business jet mro Market market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting stable activity supported by ~ active aircraft and ~ maintenance events annually. Utilization intensity averaged ~ flight hours per aircraft, while hangar occupancy remained above ~ percent during peak operational cycles. Maintenance demand was led by heavy checks and engine shop visits, accounting for ~ percent of recorded work scopes. Fleet age distribution shows ~ percent of aircraft above ~ years, sustaining baseline inspection demand. Workforce availability supported ~ licensed engineers, ensuring operational continuity across facilities.
Singapore remains the dominant business aviation maintenance hub due to concentrated hangar infrastructure at Seletar and Changi, dense OEM-authorized networks, and efficient regulatory oversight. Demand clusters around charter operators, corporate flight departments, and transient Asia-Pacific traffic requiring rapid turnaround. A mature supplier ecosystem supports parts logistics, engineering services, and component repair locally. Policy stability, safety credibility, and connectivity reinforce Singapore’s role as a preferred regional MRO destination.
Market Segmentation
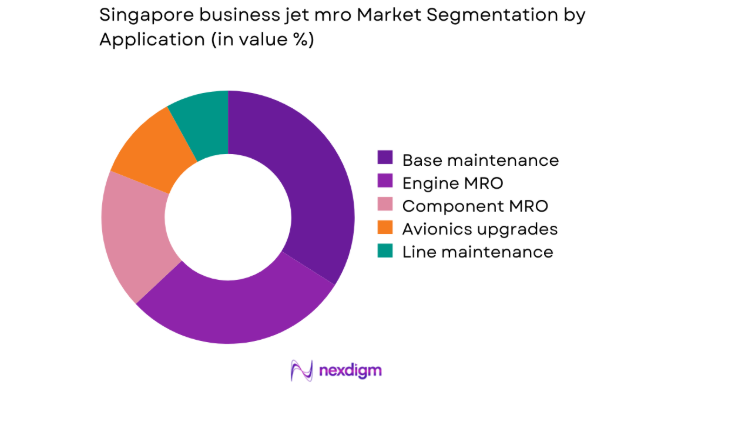
By Application
The market is dominated by base maintenance and engine MRO activities, driven by Singapore’s role as a regional hub for scheduled heavy checks and powerplant servicing. Aircraft operators route major inspections through Singapore to minimize downtime and regulatory risk. Engine maintenance benefits from local test cell availability and OEM-aligned capabilities, supporting complex work scopes. Component MRO and avionics upgrades maintain steady demand, supported by aging fleets and compliance-driven retrofits. Line maintenance remains secondary, largely servicing transient aircraft and charter operations with quick-turn requirements.
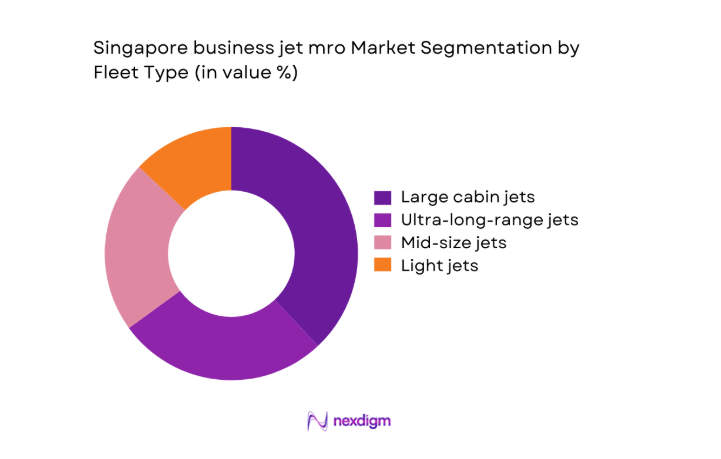
By Fleet Type
Large cabin and ultra-long-range jets account for the highest maintenance value contribution due to complex systems, higher inspection man-hours, and premium component requirements. Operators of these aircraft prioritize Singapore for deep maintenance given technical depth and OEM presence. Mid-size jets form a stable secondary segment, supported by regional charter utilization and fractional ownership structures. Light jets contribute limited value, as operators often defer heavy maintenance to lower-cost locations. Fleet mix evolution increasingly favors long-range aircraft supporting intercontinental business travel.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a mix of OEM-aligned service centers and independent MRO providers operating within a tightly regulated ecosystem. Competitive differentiation is driven by authorization depth, turnaround reliability, and integrated service offerings rather than price competition.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| ST Engineering Aerospace | 1990 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ExecuJet MRO Services | 1996 | Zurich | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Jet Aviation | 1967 | Basel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bombardier Aerospace Services | 1942 | Montreal | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lufthansa Technik | 1993 | Hamburg | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore business jet mro Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising Asia-Pacific business jet fleet concentration in Singapore
The concentration of Asia-Pacific business jets in Singapore increased steadily, supported by ~ registered aircraft and sustained cross-border corporate travel demand. Operators increasingly base aircraft in Singapore to leverage regulatory credibility, airport accessibility, and regional connectivity advantages. Fleet clustering improves maintenance scheduling efficiency and reduces repositioning flights for heavy checks and inspections. Charter and fractional operators contributed ~ percent of incremental fleet presence, reinforcing recurring maintenance demand. High-net-worth individuals increasingly favor Singapore-based operations for asset security and service reliability. Transient traffic from Southeast Asia generates additional unscheduled maintenance requirements. Fleet growth dynamics remained resilient despite broader aviation volatility. Maintenance planners reported higher slot utilization driven by concentrated fleet basing. Regional geopolitical stability further supported fleet migration into Singapore. This concentration structurally anchors long-term maintenance demand.
Strong positioning of Singapore as a regional MRO hub
Singapore’s positioning as a regional MRO hub is reinforced by integrated infrastructure, specialized labor pools, and efficient regulatory oversight frameworks. Hangar complexes support simultaneous heavy checks across multiple aircraft categories without operational congestion. OEMs prioritize Singapore for authorized service expansion, strengthening technical capability depth. Regional operators route aircraft to Singapore to mitigate compliance and quality risks. Predictable customs and logistics processes reduce parts turnaround delays significantly. Aviation authorities maintain consistent certification standards enhancing international operator confidence. The ecosystem supports rapid scalability during peak maintenance cycles. Digital maintenance planning adoption improves slot predictability across facilities. Strong air connectivity sustains steady inflow of transient aircraft. Hub strength directly translates into durable maintenance volumes.
Challenges
High labor and hangar operating costs
Labor and hangar operating costs in Singapore remain structurally high due to skilled workforce scarcity and premium airport real estate constraints. Licensed engineer wages increased steadily, impacting long-term margin sustainability for service providers. Hangar lease rates limit rapid capacity expansion and deter smaller entrants. Cost pressures constrain pricing flexibility when serving cost-sensitive charter operators. Independent MROs face competitiveness challenges against lower-cost regional alternatives. Training pipelines require sustained investment to maintain certification standards. Workforce retention pressures affect operational continuity during peak demand cycles. Automation adoption remains gradual due to regulatory oversight complexity. Cost structures necessitate focus on high-value maintenance segments. These dynamics shape strategic positioning decisions.
Capacity constraints for wide-body business jets
Capacity constraints for wide-body business jets emerged as hangar slots remain limited for large cabin and ultra-long-range aircraft. Simultaneous heavy checks create scheduling bottlenecks during peak operational seasons. Infrastructure expansion faces regulatory and land availability limitations. Operators occasionally defer maintenance or seek alternative hubs when slots are unavailable. Larger aircraft require specialized docking and tooling, restricting flexible allocation. Slot congestion impacts turnaround times and customer satisfaction metrics. Capacity planning must balance transient and based aircraft demand. Expansion timelines remain extended due to approval processes. These constraints elevate strategic value of existing hangar assets. Capacity scarcity influences long-term investment decisions.
Opportunities
Expansion of engine and component MRO capabilities
Expansion of engine and component MRO capabilities presents a high-value opportunity due to increasing engine shop visit frequency. Aging fleets require deeper component repair and life-limited part management services. Engine OEM partnerships enhance authorization breadth and technical specialization. Local test cell capacity supports complex engine work without overseas routing. Component pooling solutions attract regional operators seeking inventory optimization. Higher-value work scopes improve revenue quality per maintenance event. Skilled labor development aligns with engine specialization demand. Digital diagnostics improve engine maintenance planning accuracy. Component repair reduces dependency on costly replacements. This expansion strengthens Singapore’s competitive differentiation.
Digital MRO and predictive maintenance adoption
Digital MRO and predictive maintenance adoption creates efficiency gains by optimizing inspection intervals and reducing unscheduled aircraft downtime. Data integration from aircraft health monitoring systems enhances maintenance forecasting accuracy. Predictive analytics enable earlier fault detection and targeted interventions. Operators benefit from improved aircraft availability and lifecycle cost management. MRO providers deploy digital twins to simulate maintenance scenarios. Workforce productivity improves through task digitization and paperless workflows. Regulatory acceptance of digital records accelerates adoption. Cybersecurity investment becomes integral to digital maintenance systems. Technology adoption differentiates premium service offerings. Digital maturity supports long-term operational resilience.
Future Outlook
The Singapore business jet mro Market is expected to maintain strategic relevance through 2035 as fleet complexity and regional traffic increase. Continued OEM alignment, selective capacity expansion, and digital integration will shape competitive dynamics. Sustainability-driven maintenance practices may influence future service offerings and investment priorities.
Major Players
- ST Engineering Aerospace
- ExecuJet MRO Services Singapore
- Jet Aviation Singapore
- Bombardier Aerospace Services Singapore
- Dassault Falcon Service Asia-Pacific
- Gulfstream Aerospace Singapore
- Lufthansa Technik Asia
- Safran Aircraft Engines Singapore
- Rolls-Royce Singapore
- Pratt & Whitney Singapore
- Collins Aerospace Singapore
- Honeywell Aerospace Singapore
- AMAC Aerospace Asia
- Asia Pacific Aerospace
- Thales Singapore
Key Target Audience
- Business jet operators and fleet owners
- Charter and fractional aircraft management companies
- Corporate flight departments
- Aircraft leasing and asset management firms
- Engine and component OEMs
- Airport operators and infrastructure authorities
- Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore and related agencies
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables included active fleet composition, maintenance event frequency, service mix evolution, and regulatory constraints shaping operational demand.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
The market framework was constructed using bottom-up assessment of maintenance activities across fleet types and application categories.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses were validated through structured consultations with MRO executives, fleet managers, and regulatory specialists.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were synthesized to ensure internal consistency, logical flow, and alignment with observed operational realities.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for Singapore business jet MRO, Fleet and service taxonomy mapping across line base and heavy maintenance, Bottom-up market sizing using aircraft active base and MRO event frequency, Revenue attribution by airframe and engine maintenance cycles, Primary interviews with MRO operators fleet managers and CAAS stakeholders)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and maintenance pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- MRO supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising Asia-Pacific business jet fleet concentration in Singapore
Strong positioning of Singapore as a regional MRO hub
Increasing demand for long-range and large cabin jets
OEM expansion of authorized service centers
High regulatory and safety standards driving outsourcing
Growth in charter and fractional jet utilization - Challenges
High labor and hangar operating costs
Capacity constraints for wide-body business jets
Dependence on OEM parts availability
Skilled workforce shortages
Fleet cyclicality and utilization volatility
Competition from emerging regional MRO hubs - Opportunities
Expansion of engine and component MRO capabilities
Digital MRO and predictive maintenance adoption
Growing demand for cabin refurbishment and upgrades
Sustainability-driven maintenance and modification programs
Partnerships with OEMs for exclusive service mandates
Rising demand from Southeast Asian charter operators - Trends
Shift toward OEM-authorized and branded service centers
Increased use of data-driven maintenance planning
Growing focus on turnaround time optimization
Integration of sustainability and green MRO practices
Consolidation among independent MRO providers
Increased customization and VIP cabin retrofit demand - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Revenue per Aircraft, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Light jets
Mid-size jets
Large cabin jets
Ultra-long-range jets - By Application (in Value %)
Line maintenance
Base maintenance
Engine MRO
Component MRO
Avionics upgrades and modifications - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Conventional scheduled maintenance
Predictive and condition-based maintenance
Digital maintenance tracking and analytics
Advanced materials and structural repair - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Corporate aviation
Charter and fractional operators
Ultra-high-net-worth individuals
Government and special mission aviation - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
OEM-authorized service networks
Independent MRO providers
Hybrid OEM–independent partnerships - By Region (in Value %)
Singapore domestic operations
Regional Asia-Pacific servicing hub
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Service portfolio depth, Fleet type coverage, OEM authorizations, Turnaround time performance, Pricing flexibility, Regional network strength, Digital MRO capabilities, Regulatory compliance track record)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
ST Engineering Aerospace
ExecuJet MRO Services Singapore
Jet Aviation Singapore
Bombardier Aerospace Services Singapore
Dassault Falcon Service Asia-Pacific
Gulfstream Aerospace Singapore
Lufthansa Technik Asia
Safran Aircraft Engines Singapore
Rolls-Royce Singapore
Pratt & Whitney Singapore
Collins Aerospace Singapore
Honeywell Aerospace Singapore
AMAC Aerospace Asia
Asia Pacific Aerospace
Thales Singapore
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Revenue per Aircraft, 2026–2035


