Market Overview
As of 2024, the Singapore cold chain market is valued at USD ~ billion, with a growing CAGR of 22.1% from 2024 to 2030, driven primarily by the increasing demand for perishable goods such as food and pharmaceuticals. This robust demand is further fueled by stringent safety regulations, technological advancements, and the growing e-commerce sector for chilled goods. Leading cities like Singapore play a dominant role in the region due to their superior infrastructure and advanced logistics capabilities, which facilitate efficient transportation and storage.
Prominent players like Mandai and CWT Logistics have established logistics hubs that cater to a wide range of temperature-controlled products. Singapore’s strategic location serves as a key transhipment point in Asia, leveraging its connectivity to expand its cold chain operations beyond domestic borders, making it a crucial player in the global marketplace.
Market Segmentation
By Application
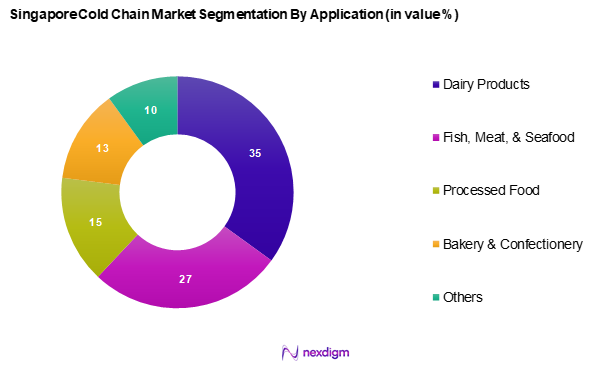
The Singapore cold chain market is segmented into food & beverages and pharmaceuticals. Food & beverages have a dominant market share due to high consumer demand for fresh and quality products. Sub-segments like dairy products and fish, meat, & seafood continue to grow, driven by increasing consumption trends and dietary shifts towards protein-rich diets. Dairy Products hold a significant share, backed by a strong network of refrigerated storage facilities ensuring product safety and compliance with health standards.
By Technology
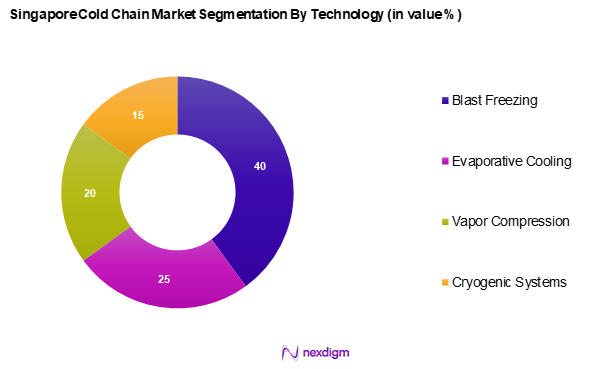
The Singapore cold chain market is segmented into blast freezing, evaporative cooling, vapor compression, and cryogenic systems. Blast freezing stands out due to its efficiency in rapidly reducing the temperature of perishable items, preserving nutritional value and quality. The increasing demand for frozen food products necessitates the use of advanced freezing techniques, thus securing a larger share for Blast Freezing in the market.
Competitive Landscape
The Singapore cold chain market is competitive, dominated by a few major players who have established a firm foothold due to their comprehensive service offerings and robust infrastructure.
| Company Name | Year Established | Headquarters | Market Share (%) | Technology Use | Service Spectrum | Key Clients | Innovation Focus |
| CWT Logistics | 1970 | Singapore | – | – | – | – | – |
| Mandai / Lineage Link | 1967 | Singapore | – | – | – | – | – |
| StorBest Holdings | 1987 | Singapore | – | – | – | – | – |
| Sharikat Logistics | 2000 | Singapore | – | – | – | – | – |
| Keppel Logistics | 1965 | Singapore | – | – | – | – | – |
Singapore Cold Chain Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing Perishable Products Demand
The demand for perishable products in Singapore has been on a consistent rise, particularly driven by the increasing urban population and changing consumer preferences for fresh food. As of 2023, Singapore’s food import volume reached approximately 4.8 million metric tons, with an anticipated growth of about 3% annually in the food sector, driven by the steady influx of expatriates and tourists. The Ministry of Trade and Industry has projected that domestic food consumption will increase, making effective cold chain logistics essential to ensure product freshness and safety in an increasingly crowded marketplace. This sustained demand for fresh and quality perishable goods significantly boosts the cold chain sector in Singapore.
Stringent Food Safety Regulations
In Singapore, food safety regulations are among the strictest, reinforcing the need for a robust cold chain system. The Agri-Food & Veterinary Authority of Singapore (AVA) asserts that compliance with its food safety standards protects public health and ensures consumer confidence in food products. The Food Agency of Singapore estimated that in 2023, approximately 79% of foodborne illness cases were linked back to improper food handling and storage. Consequently, businesses in the cold chain sector must invest in temperature-controlled storage and transport solutions to comply with these laws, reinforcing the market’s growth outlook as more companies seek to meet these stringent standards.
Market Challenges
High Operational Costs
High operational costs, particularly in energy consumption, continue to pose significant challenges for the cold chain market in Singapore. Around 40% of logistics-related expenses come from energy use, especially for refrigeration, which is essential for maintaining temperature-sensitive products. Additionally, the energy price per kilowatt-hour has increased by approximately 25% from 2022 to 2023, affecting profit margins for cold chain operators. The Singapore government has initiated energy efficiency programs; however, significant investments in technology and infrastructure are still needed to mitigate these high costs, impacting competitiveness in the market.
Infrastructure Limitations
Despite advancements, Singapore’s cold chain infrastructure faces limitations that hinder market growth. The World Bank reported that while Singapore ranks high in logistics performance globally, its cold storage facilities are under pressure due to rapid urbanization and population growth. As of 2023, the number of cold storage spaces was estimated at 3.2 million cubic meters, which lacks scalability to meet the increasing demand for chilled and frozen foods adequately. The current infrastructure expansion is not keeping pace with projected demand increases, leading to a potential shortfall in capacity that may disrupt supply chains.
Opportunities
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements present a considerable opportunity for the cold chain market in Singapore. The integration of IoT technologies has enabled real-time tracking and monitoring of temperature-sensitive goods, leading to enhanced efficiency and reduced spoilage rates. Currently, around 30% of cold chain companies have implemented IoT solutions, with benefits seen in improved logistics management and data analytics capacity. As more technology partners emerge, the expansion of smart cold chain solutions is expected, which will streamline operations and promote market growth by ensuring high-quality standards in product delivery.
Expansion in E-commerce of Chilled Goods
The rise of e-commerce in chilled goods offers significant growth potential for Singapore’s cold chain sector. In 2023, online food and grocery sales reached approximately USD 2.1 billion, with chilled and fresh food segments showing robust growth driven by customer preference for convenience. Current delivery platforms emphasize fast and convenient service, necessitating efficient cold chain logistics to maintain product integrity during delivery. As the e-commerce trend continues to grow, cold chain logistics partners who can support this demand trajectory will significantly benefit, positioning themselves well for future opportunities.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Singapore cold chain market is forecasted to experience notable growth, driven by continuous advancements in storage and transportation technologies, and the ever-increasing demand for temperature-sensitive products. With a projected CAGR of 22.1% for the period 2024 to 2030, market expansion is anticipated due to the integration of IoT and AI for better monitoring and efficiency, along with expanding cold chain capacities to accommodate the growing needs of e-commerce and retail.
Major Players
- CWT Logistics
- Mandai / Lineage Link
- Seo Eng Joo
- WLNA
- StorBest
- Agility
- Jurong Cold Store
- NCS Cold Store
- Sharikat Logistics Pte Ltd.
- Atlas Ice Ptd Ltd
- QAF Fruits Cold Store
- Commonwealth Kokubu Logistics Pte Ltd
- Keppel Logistics
- ITC Cold Chain Logistics
- Alliance Cold Store
Key Target Audience
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Enterprise Singapore)
- Food Retail Chains
- Pharmaceutical Companies
- Cold Storage Service Providers
- Large-scale Food and Beverage Manufacturers
- Technology Solution Providers Specializing in Cold Chain Logistics
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves creating an ecosystem map including all major stakeholders within the Singapore cold chain market. This process is driven by extensive desk research, utilizing a combination of secondary and proprietary databases to gather comprehensive industry-level information. The primary aim is to identify and define the critical variables influencing market dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data on the Singapore cold chain market is compiled and analyzed. This includes assessing market penetration, the ratio of service providers, and the resultant revenue generation. Additionally, service quality statistics are evaluated to ensure the reliability and accuracy of revenue estimates.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are developed and validated through computer-assisted telephone interviews (CATIS) with industry experts from a range of companies. These consultations provide valuable operational and financial insights directly from industry practitioners, which are instrumental in refining and corroborating market data.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase engages multiple cold chain service providers to acquire detailed insights into services, operations, consumer preferences, and other factors. This interaction helps verify and complement statistics from the bottom-up approach, ensuring a comprehensive, accurate analysis of the Singapore cold chain market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Overview Genesis
- Timeline of Major Players
- Business Cycle
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Increasing Perishable Products Demand
Stringent Food Safety Regulations - Market Challenges
High Operational Costs
Infrastructure Limitations - Opportunities
Technological Advancements
Expansion in E-commerce of Chilled Goods - Trends
Adoption of IoT in Cold Chain Logistics
Increasing Use of Blockchain for Greater Transparency - Government Regulation
Food Safety Standards - SWOT Analysis
- Stake Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Price, 2019-2024
- By Application, (In Value %)
Food & Beverages
Dairy Products
Fish, Meat, and Seafood
Pharmaceuticals
Others - By Temperature Range, (In Value %)
Chilled
Frozen
Ambient - By Mode of Transportation, (In Value %)
Road
Rail
Air
Sea - By Market Structure, (In Value %)
Organized
Unorganized - By Service, (In Value %)
Storage
Transportation
Value-added Services - By Technology, (In Value %)
Blast Freezing
Evaporative Cooling
Vapor Compression
Cryogenic Systems
Programmable Logic Controller
- Market Share of Major Players on the Basis of Value/Volume, 2024
Market Share of Major Players by Type of Application Segment, 2024 - Cross-Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Recent Developments, Strength, Weakness, Market Share, Technological Capabilities, Customer Base, Revenue, Distribution Networks, and Others)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis Basis SKUs for Major Players
- Profiles of Major Companies
CWT Logistics
Mandai / Lineage Link
Seo Eng Joo
WLNA
StorBest
Agility
Jurong Cold Store
NCS Cold Store
Sharikat Logistics Pte Ltd.
Atlas Ice Ptd Ltd
QAF Fruits Cold Store
Commonwealth Kokubu Logistics Pte Ltd
Keppel Logistics
ITC Cold Chain Logistics
Alliance Cold Store
Logistics Solution Hub
DB Schenker
- Consumer Demand and Behaviour
- Industry-Specific Requirements and Budget Allocations
- Needs Assessment of Key Stakeholders
- Decision-Making Processes in Procurement
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Price, 2025-2030


