Market Overview
The Singapore commercial aircraft aerostructures market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained demand for structural components, assemblies, and advanced composite repairs across commercial aviation platforms. The market is shaped by Singapore’s role as a regional aerospace hub, strong tier-1 supplier presence, and deep integration with OEM and MRO ecosystems. Value creation is anchored in high-precision manufacturing, certified repair capabilities, and program-linked subassemblies that support fleet renewal and structural modification requirements.
Singapore concentrates aerostructures activity around Seletar Aerospace Park, Changi aviation clusters, and integrated logistics corridors connecting ASEAN production nodes. Demand concentrates where narrowbody utilization is highest and where freighter conversion and heavy checks are performed. The ecosystem benefits from advanced testing infrastructure, proximity to regional airline headquarters, and dense supplier networks. Policy stability, certification rigor, and export-oriented manufacturing frameworks reinforce supply chain resilience and attract sustained program participation from global aerospace partners.
Market Segmentation
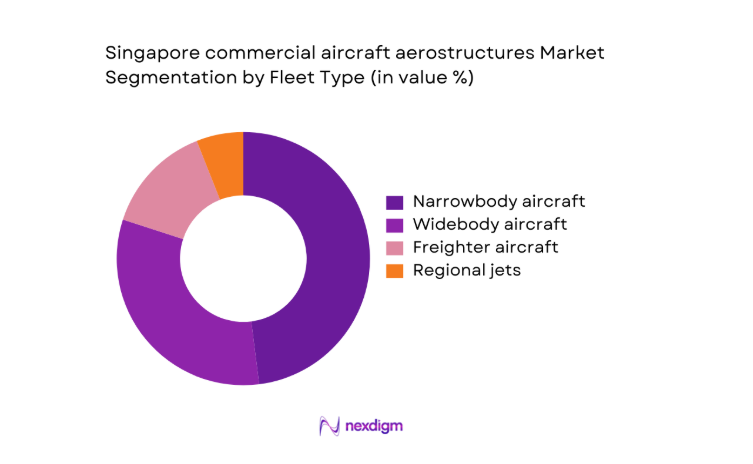
By Fleet Type
Narrowbody aircraft dominate aerostructures demand due to high utilization across short-haul networks and dense MRO throughput in Singapore. Structural replacement panels, doors, and wing subcomponents cycle faster under frequent operations, sustaining steady aftermarket demand. Widebody platforms contribute through heavy checks, composite repairs, and structural modifications linked to cabin reconfigurations. Freighters add incremental demand from cargo door conversions and floor beam reinforcements, while regional jets account for targeted structural repairs tied to feeder operations. The fleet mix favors programs with composite-intensive architectures, supporting investments in automated layup, precision drilling, and certified composite repair cells integrated within regional maintenance schedules.
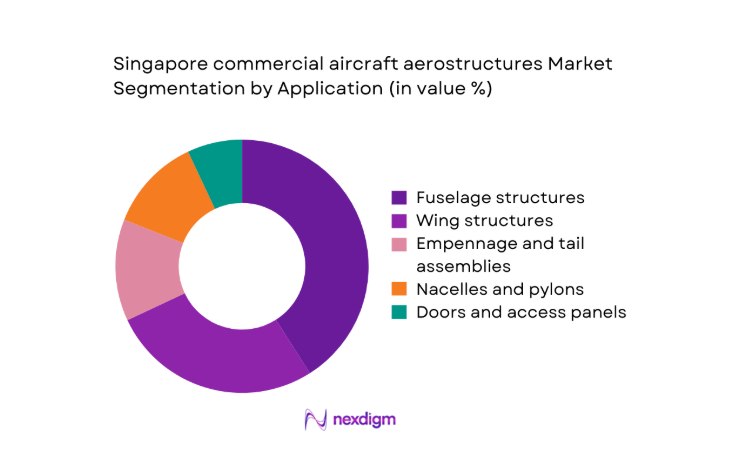
By Application
Fuselage structures account for the largest share as skin panels, frames, and door surrounds experience frequent repair cycles and modification demand linked to cabin densification. Wing structures follow, driven by flap track fairings, ribs, and access panels subject to wear and corrosion in humid operating environments. Empennage assemblies sustain steady demand from structural inspections and life-extension work, while nacelles and pylons benefit from engine shop visits and aerodynamic upgrades. Doors and access panels contribute recurring aftermarket volumes due to line maintenance replacements and retrofit programs aligned with operational reliability targets and turnaround-time reduction initiatives across regional fleets.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is shaped by tier-1 aerostructures integrators, specialized composite manufacturers, and Singapore-based MRO-linked fabricators aligned to OEM programs and regional airline fleets. Competitive differentiation centers on certifications, composite depth, turnaround reliability, and ability to support both line-fit and aftermarket structural work across multiple platforms.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Spirit AeroSystems | 2005 | Wichita, United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GKN Aerospace | 1759 | Solihull, United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo Aerostrutture | 1948 | Pomigliano d’Arco, Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Triumph Group | 1993 | Berwyn, United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ST Engineering Aerospace | 1990 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore commercial aircraft aerostructures Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Singapore’s MRO base for composite aerostructure repair
Singapore’s certified composite repair footprint expanded across Seletar and Changi aviation clusters as regional fleets increased heavy checks between 2022 and 2025. Civil Aviation Authority approvals rose across multiple Part 145 scopes, while training pipelines added 240 certified technicians by 2024. Regional narrowbody cycles averaged 2 major checks annually, increasing demand for bonded repairs, scarf patches, and structural reinforcements. Airport movements exceeded 1,200 daily operations in 2024, intensifying wear on access panels and fairings. Institutional support for advanced manufacturing accelerated autoclave utilization and nondestructive testing capacity, improving turnaround reliability for time-critical structural rectifications.
Rising narrowbody fleet utilization in Southeast Asian networks
Short-haul traffic density across ASEAN corridors increased flight cycles per airframe between 2022 and 2025, raising inspection findings on fuselage skins, floor beams, and wing trailing-edge components. Slot-constrained hubs recorded average turnaround intervals under 60 minutes in 2024, elevating exposure to ramp damage and panel replacements. Airline schedules intensified utilization beyond 9 block hours daily on key routes, accelerating structural fatigue accumulation. Regional aviation authorities approved higher utilization maintenance programs, increasing demand for certified repairs and replacement assemblies. Singapore’s logistics connectivity enabled rapid spares routing within 48 hours, reinforcing its role as a structural repair hub for narrowbody operators.
Challenges
Dependence on global OEM production cycles and delivery volatility
OEM line-rate adjustments between 2022 and 2025 created uneven demand for line-fit aerostructures, complicating capacity planning for Singapore-based suppliers. Program pauses led to batch variability in shipset requirements, while certification change notices delayed part release schedules by up to 90 days in 2024. Supplier lead times for aerospace-grade alloys and prepregs extended beyond 16 weeks during peak periods, constraining throughput. Institutional audits increased documentation workloads per part number, slowing first-article approvals. Volatile delivery sequencing forced buffer inventory accumulation, raising operational complexity and increasing rework risk when engineering revisions were issued mid-cycle.
High capital intensity of composite fabrication and autoclave capacity
Composite aerostructure capability requires autoclaves exceeding 4 meters diameter, precision AFP cells, and Class 100,000 cleanrooms, elevating fixed-asset commitments. Between 2022 and 2025, certification upgrades demanded additional ultrasonic inspection equipment and bonded repair tooling across multiple bays. Technician certification cycles extended to 18 months, constraining workforce ramp-up. Energy reliability standards imposed redundant power systems for curing cycles, increasing facility complexity. Utilization volatility during OEM schedule shifts reduced asset efficiency, pressuring operational planning. Institutional safety audits increased compliance overhead per work order, lengthening average cycle times for complex structural repairs and retrofit assemblies.
Opportunities
Expansion of composite repair capabilities for next-generation aircraft
Composite-intensive fleets operating in Southeast Asia increased structural inspection findings between 2022 and 2025, elevating demand for certified bonded repairs and complex scarf restorations. Regulatory bodies expanded approved repair schemes for advanced laminates, enabling local execution of repairs previously routed overseas. Training cohorts added 180 composite specialists by 2024, supporting higher bay utilization. Airline maintenance programs shortened allowable downtime windows to under 72 hours for AOG events, favoring proximate repair hubs. Singapore’s proximity to dense route networks allows rapid deployment of mobile repair teams within 24 hours, positioning local facilities for higher-value structural interventions.
Participation in freighter conversion programs for widebody platforms
Cargo operators expanded widebody freighter utilization across regional trade lanes between 2022 and 2025, increasing demand for structural modifications such as cargo doors, floor beam reinforcements, and fuselage cut-outs. Certification authorities approved additional conversion STCs, enabling regional execution of complex structural work. Conversion lines processed multiple aircraft concurrently in 2024, increasing throughput requirements for prefabricated kits and reinforced assemblies. Airport cargo tonnage flows recovered strongly, sustaining utilization of converted platforms. Singapore’s heavy-check infrastructure and logistics connectivity support parallel conversion workflows, creating opportunities for tier-1 subassembly participation and specialized composite-metal hybrid fabrication.
Future Outlook
Future growth will be shaped by deeper composite adoption across narrowbody and widebody platforms, tighter certification standards, and rising regional utilization. Singapore is positioned to capture higher-value structural repairs and subassembly work as ASEAN fleets expand. Digital manufacturing and automation will improve turnaround reliability, while policy stability sustains supplier investment confidence. Partnerships with OEM programs will anchor long-term workload visibility through the outlook period.
Major Players
- Spirit AeroSystems
- GKN Aerospace
- Leonardo Aerostrutture
- Triumph Group
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries Aerospace
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Aerospace
- FACC
- Aernnova Aerospace
- Premium AEROTEC
- Korea Aerospace Industries
- ST Engineering Aerospace
- Safran Nacelles
- Collins Aerospace
- Liebherr-Aerospace
- Avcorp Industries
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airlines operating in Southeast Asia
- Cargo and freighter operators
- Aircraft lessors and asset managers
- MRO providers and heavy-check facilities
- OEMs and tier-1 aerostructures integrators
- Tier-2 component and material suppliers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore and Ministry of Transport
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Platform coverage, aerostructure categories, certification scopes, and repair versus line-fit workflows were defined to establish market boundaries. Program participation and aftermarket exposure were mapped across narrowbody, widebody, and freighter use cases. Supply chain nodes across fabrication, inspection, and logistics were delineated to frame scope.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Program-level activity mapping, maintenance event frequency, and facility throughput were analyzed to construct demand logic. Capacity constraints across composite bays and inspection resources were assessed. Regional route density and utilization patterns informed structural wear profiles and service mix requirements.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions on repair mix, certification bottlenecks, and capacity utilization were validated with certified maintenance engineers, quality managers, and regulatory liaison professionals. Program alignment and workflow feasibility were reviewed against operational constraints and approval pathways.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were reconciled across operational data, institutional indicators, and ecosystem mapping to ensure coherence. Contradictions were resolved through triangulation of workflow evidence and regulatory constraints. Final outputs emphasize decision-relevant insights for investment, capacity planning, and program participation.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and airframe aerostructures scope mapping for Singapore MRO and OEM sourcing, Aircraft platform taxonomy across narrowbody widebody freighter and regional jets serving Singapore operators, Bottom-up sizing from shipsets delivered to Singapore final assembly and MRO modification programs, Revenue attribution by tier-1 tier-2 aerostructures contracts linked to Singapore-based production and rework)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of Singapore’s MRO base for composite aerostructure repair
Rising narrowbody fleet utilization in Southeast Asian networks
OEM supply chain localization and nearshoring to Singapore
Growth in freighter conversions and structural modifications
Airline fleet renewal toward composite-intensive aircraft types - Challenges
Dependence on global OEM production cycles and delivery volatility
High capital intensity of composite fabrication and autoclave capacity
Skilled labor shortages in advanced aerostructures manufacturing
Exposure to titanium and aerospace-grade aluminum price volatility
Stringent certification timelines for structural repairs and modifications - Opportunities
Expansion of composite repair capabilities for next-generation aircraft
Participation in freighter conversion programs for widebody platforms
Digital manufacturing and automation for low-volume complex structures
Aftermarket structural retrofits for cabin densification and cargo doors
Partnerships with OEMs for regional aerostructure subassembly hubs - Trends
Shift toward higher composite content in replacement structures
Adoption of automated fiber placement and robotic drilling
Growing demand for rapid-turn structural repair kits
Increased use of digital twins for structural life management
Sustainability-driven lightweighting and material substitution - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft
Widebody aircraft
Freighter aircraft
Regional jets - By Application (in Value %)
Fuselage structures
Wing structures
Empennage and tail assemblies
Nacelles and pylons
Doors and access panels - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Metallic aerostructures
Composite aerostructures
Hybrid metal-composite assemblies
Additively manufactured substructures - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Commercial airlines
Aircraft lessors
Cargo operators
MRO providers
OEM and tier-1 integrators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Line-fit aerostructures
Retrofit and modification kits
Repair and replacement assemblies
Spare aerostructure components - By Region (in Value %)
Singapore domestic demand
Intra-ASEAN supply linkages
East Asia OEM sourcing
Europe and North America trade flows
Middle East hub-linked demand
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (product portfolio breadth, composite manufacturing capability, certifications and regulatory approvals, OEM program participation, regional footprint in Asia-Pacific, aftermarket support capabilities, pricing competitiveness, delivery lead times)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Spirit AeroSystems
GKN Aerospace
Leonardo Aerostrutture
Triumph Group
Kawasaki Heavy Industries Aerospace
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Aerospace
FACC
Aernnova Aerospace
Premium AEROTEC
Korea Aerospace Industries
ST Engineering Aerospace
Safran Nacelles
Collins Aerospace
Liebherr-Aerospace
Avcorp Industries
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


