Market Overview
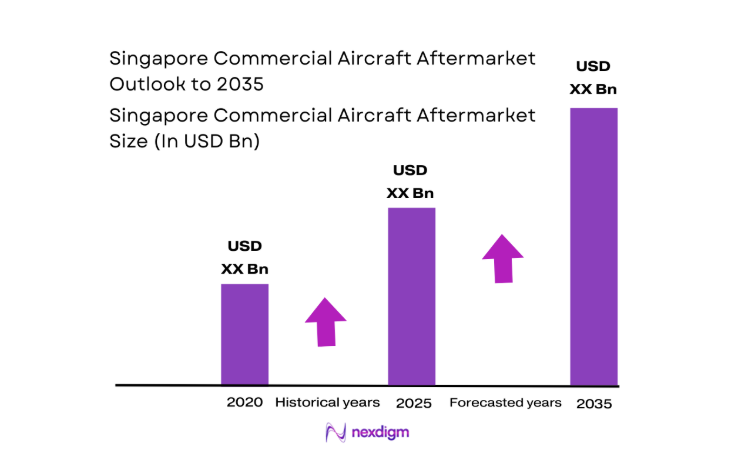
The Singapore Commercial Aircraft Aftermarket market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting a mature, service-intensive aviation support ecosystem anchored by comprehensive maintenance, repair, and overhaul capabilities. The market is characterized by high utilization of narrowbody and widebody fleets, dense component repair networks, and strong OEM-aligned service programs. Demand is sustained by continuous airframe and engine maintenance cycles, reliability-driven spares provisioning, and lifecycle management practices embedded across airline operations and lessor requirements.
Singapore concentrates demand across Changi-based airline engineering operations, clustered engine shops in Seletar, and component MRO parks integrated with logistics free zones. The city-state’s advanced hangar infrastructure, bonded warehousing, and airside access enable rapid turnaround. A dense ecosystem of airframe, engine, and component specialists co-locates with lessors and logistics providers, supported by streamlined certification pathways and a pro-aviation policy environment that prioritizes safety oversight, skills development, and digital aviation initiatives.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
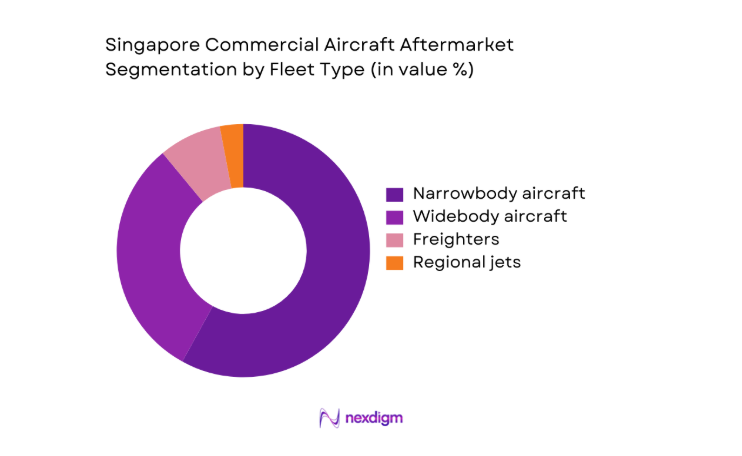
Narrowbody aircraft dominate aftermarket activity due to higher flight cycle intensity, dense regional route networks, and frequent line maintenance events concentrated in Singapore. The operational tempo of short-haul fleets increases component removal rates and consumables usage, driving consistent shop visits for wheels, brakes, avionics, and APU systems. Widebody aircraft contribute larger workscope values during heavy checks and engine shop visits but with longer intervals. Freighters add countercyclical stability through cargo demand continuity. Regional jets represent a smaller installed base yet generate steady component repair demand linked to feeder networks and wet-lease operations.
By Application
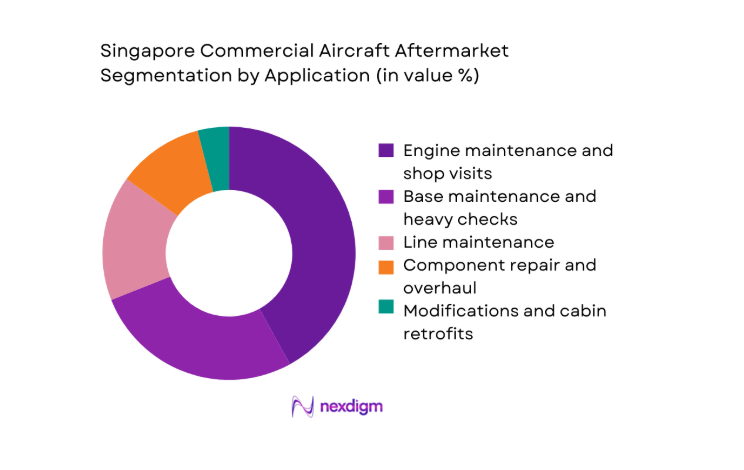
Engine maintenance and shop visits account for the largest value concentration due to complex disassembly, parts replacement, and testing requirements that extend turnaround cycles. Base maintenance and heavy checks remain value-dense but episodic, driven by scheduled C and D checks across Singapore’s hangar network. Line maintenance sustains high-frequency activity with rapid-response teams and night-stop checks. Component repair and overhaul benefit from specialization in avionics, landing gear, and composite structures. Modifications and cabin retrofits grow with connectivity upgrades, cabin densification, and regulatory-driven enhancements linked to safety and operational efficiency.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape reflects a hub-centric ecosystem combining OEM-aligned service providers, independent MRO specialists, and airline engineering arms. Competitive differentiation centers on certifications breadth, engine platform depth, turnaround reliability, digital MRO maturity, and access to pooled spares. Proximity to airside infrastructure and bonded logistics underpins service velocity, while regulatory readiness shapes addressable workscopes. Partnerships with lessors and airlines influence contract tenures and capacity planning.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| ST Engineering Aerospace | 1970 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SIA Engineering Company | 1992 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lufthansa Technik | 1955 | Hamburg | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SR Technics | 1997 | Zurich | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| StandardAero | 1911 | Scottsdale | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore Commercial Aircraft Aftermarket Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising fleet utilization and post-pandemic recovery of flight cycles
Singapore’s flight activity rebounded as annual aircraft movements reached 346000 in 2024, compared with 312000 in 2022, increasing maintenance event frequency across line and base checks. Regional route density expanded as weekly departures exceeded 4600 in 2025, driving higher cycles per narrowbody aircraft and accelerating component removals for wheels, brakes, and avionics. Engine shop visits rose with 118 scheduled inductions in 2024 versus 91 in 2022, reflecting higher thrust setting utilization. Institutional capacity approvals increased hangar slots to 28 in 2025, reducing bottlenecks and enabling sustained throughput growth.
Expansion of Asia-Pacific hub operations centered in Singapore
Changi’s role as a hub intensified with transit passengers exceeding 59 million in 2024, supporting higher aircraft rotations and overnight line maintenance demand. Singapore-based carriers expanded regional frequencies across 14 additional city pairs during 2023 to 2025, increasing A-check occurrences per tail number. Air traffic management enhancements reduced average ground time to 92 minutes in 2025 from 104 minutes in 2022, compressing maintenance windows and elevating reliance on predictive scheduling. Institutional approvals for 6 new hangar bays in 2024 increased base-check capacity, strengthening hub-centric aftermarket utilization and shop visit routing decisions across Southeast Asia.
Challenges
Skilled labor shortages and rising technician wages
Licensed engineer headcount across Singapore-based MROs increased to 8700 in 2024 from 7900 in 2022, yet vacancy rates persisted at 9 in 2025 due to retirements exceeding 1200 technicians over three years. Training throughput expanded with 2600 certifications issued in 2024, but engine type ratings lagged demand for GTF and LEAP platforms, creating schedule risk. Overtime hours rose to 6.2 million in 2024, elevating fatigue management burdens. Regulatory duty-time limits constrained shift flexibility, reducing effective labor availability during peak heavy-check seasons and elongating turnaround cycles.
Capacity constraints at engine and component shops
Engine test cell utilization averaged 91 in 2024, up from 84 in 2022, limiting induction slots for unscheduled removals. Component backlogs for landing gear and avionics exceeded 7400 units awaiting bench time in 2025 due to specialized tooling bottlenecks. Shop floor expansion approvals added 42000 square meters in 2024, but equipment commissioning timelines of 14 months delayed throughput gains. Logistics dwell times at bonded warehouses rose to 6.8 days in 2025 from 5.1 in 2022, reflecting congestion during peak maintenance seasons and complicating parts availability synchronization with induction schedules.
Opportunities
Expansion of engine MRO capacity for new-generation engines
New-generation engine inductions increased from 38 in 2022 to 77 in 2025, driven by higher utilization across narrowbody fleets operating dense regional schedules. Type-certified technicians for GTF and LEAP platforms reached 1460 in 2024, enabling deeper workscopes beyond light maintenance. Institutional approvals for 2 additional test cells in 2025 and 12 engine bays expanded induction capacity, reducing queue times by 9 weeks. Digital borescope inspection adoption reached 420 units deployed across shops in 2024, improving defect detection cycles and increasing successful on-wing time extensions that optimize shop visit planning.
Growth in cabin retrofits and connectivity upgrades
Cabin modification events increased from 112 aircraft in 2022 to 196 in 2025 as airlines prioritized densification, premium economy reconfigurations, and inflight connectivity upgrades. Supplemental type certificates issued for 24 connectivity configurations in 2024 accelerated modification lead times. Linefit and retrofit coordination improved with 38 approved modification teams in 2025, reducing aircraft downtime by 11 days per event compared with 2022 baselines. Institutional safety mandates for enhanced fire-resistant materials drove component replacements across 640 aircraft seats in 2024, expanding specialized repair demand within component MRO shops.
Future Outlook
The market outlook through 2035 reflects sustained hub-centric demand supported by fleet renewal cycles, higher utilization of narrowbody platforms, and growing complexity of engine maintenance. Policy continuity and skills development programs underpin capacity expansion, while digital MRO workflows and predictive maintenance deepen service intensity. Regional competition will intensify, encouraging partnerships and specialization. Sustainability compliance and cabin modernization will shape work scopes, reinforcing Singapore’s role as a premium aftermarket hub.
Major Players
- ST Engineering Aerospace
- SIA Engineering Company
- Lufthansa Technik
- SR Technics
- Rolls-Royce
- GE Aerospace
- Pratt & Whitney
- Safran Aircraft Engines
- AFI KLM Engineering & Maintenance
- Hong Kong Aircraft Engineering Company
- GMF AeroAsia
- AAR Corp
- Delta TechOps
- StandardAero
- Barnes Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airlines and airline engineering divisions
- Aircraft leasing companies and asset managers
- Engine and component OEM service organizations
- Independent MRO service providers
- Airport authorities and aviation infrastructure operators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore and Ministry of Transport
- Logistics and bonded warehousing operators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study identifies fleet composition, utilization cycles, maintenance intervals, regulatory approvals, and shop capacity as core variables. Platform mix across narrowbody, widebody, and freighter fleets defines workscope intensity. Component removal drivers and engine shop visit triggers are mapped to operational tempo and reliability requirements.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Bottom-up construction aligns maintenance events with certified capacity across airframe, engine, and component shops. Utilization patterns are cross-mapped to induction slots, test cell availability, and technician certifications. Digital MRO adoption and predictive maintenance penetration are incorporated to adjust effective throughput assumptions.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions are validated through structured consultations with airline engineering leaders, MRO planners, and regulatory auditors operating in Singapore. Cross-functional workshops test turnaround time constraints, skills availability, and parts logistics frictions. Divergent views are reconciled through evidence from operational records and compliance audits.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are synthesized into coherent narratives linking operational drivers to capacity dynamics and service intensity. Triangulation reconciles fleet utilization, shop throughput, and regulatory approvals. Scenario framing evaluates resilience under utilization volatility, supply chain constraints, and skills pipeline variability to ensure robust conclusions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Singapore-based commercial aircraft aftermarket scope, fleet and component taxonomy aligned to MRO work scopes, bottom-up sizing from flight cycles and maintenance intervals, revenue attribution by line maintenance and heavy check events, primary validation with airline engineering heads and MRO planners in Singapore, triangulation across CAAS records airline fleet data and shop-visit logs, assumptions on utilization recovery widebody narrowbody mix and shop capacity constraints)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Maintenance and repair pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and parts distribution channels
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising fleet utilization and post-pandemic recovery of flight cycles
Expansion of Asia-Pacific hub operations centered in Singapore
Growth of cargo operations and freighter conversions
OEM service agreements and long-term maintenance contracts
Digitalization of maintenance planning and predictive analytics
Singapore’s positioning as a premium MRO hub - Challenges
Skilled labor shortages and rising technician wages
Capacity constraints at engine and component shops
High dependence on OEM parts pricing and availability
Supply chain disruptions and long lead times for rotable spares
Regulatory compliance costs and certification timelines
Intensifying competition from lower-cost regional MRO hubs - Opportunities
Expansion of engine MRO capacity for new-generation engines
Growth in cabin retrofits and connectivity upgrades
Adoption of additive manufacturing for non-critical spares
Partnerships with lessors for end-of-lease maintenance programs
Third-party PMA and DER repair approvals
Sustainability-driven modifications and lightweighting - Trends
Shift toward power-by-the-hour and total care contracts
Increased use of aircraft health monitoring and predictive maintenance
Consolidation among independent component MROs
Rising share of freighter conversions and lifecycle extensions
Digital twins and AI-driven maintenance planning
Sustainability compliance in MRO operations - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft
Widebody aircraft
Regional jets
Freighters - By Application (in Value %)
Line maintenance
Base maintenance and heavy checks
Engine maintenance and shop visits
Component repair and overhaul
Modifications and cabin retrofits - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Conventional scheduled maintenance programs
Predictive maintenance enabled by aircraft health monitoring
Digital MRO and paperless workflows
Additive manufacturing for spares and tooling
Advanced materials repair technologies - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Full-service airlines
Low-cost carriers
Cargo airlines and express operators
Aircraft leasing companies
Business and charter operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
On-aircraft health monitoring systems
Ground-based MRO information systems
OEM digital platforms and portals
Integrated airline-MRO data exchanges
Third-party analytics platforms - By Region (in Value %)
Singapore domestic MRO demand
Regional Southeast Asia transit MRO
Asia-Pacific inbound MRO demand
Intercontinental ferry-in MRO
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (service portfolio breadth, engine and component capabilities, turnaround time performance, regulatory approvals and certifications, digital MRO maturity, geographic network coverage, pricing and contract flexibility, customer portfolio diversity)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Bench marketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
ST Engineering Aerospace
SIA Engineering Company
Lufthansa Technik
SR Technics
Rolls-Royce
GE Aerospace
Pratt & Whitney
Safran Aircraft Engines
AFI KLM Engineering & Maintenance
Hong Kong Aircraft Engineering Company
GMF AeroAsia
AAR Corp
Delta TechOps
StandardAero
Barnes Aerospace
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


