Market Overview
The Singapore commercial aircraft collision avoidance system market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady institutional procurement cycles, mandated avionics upgrades, and sustained safety investments across commercial fleets. Demand is supported by continuous airworthiness directives, fleet renewal programs, and integration of collision avoidance within broader avionics modernization initiatives. Aftermarket service contracts, software lifecycle management, and certification-driven upgrades reinforce recurring adoption, while operational safety imperatives sustain replacement cycles across in-service aircraft.
Activity concentrates in Singapore due to dense airspace management, a mature maintenance ecosystem, and strong regulatory oversight supporting high compliance levels. Changi-centric fleet operations anchor demand through concentrated airline bases, integrated maintenance, repair, and overhaul facilities, and established certification pathways. The presence of regional operations management centers, specialized avionics service providers, and structured procurement frameworks accelerates deployment cycles. Policy stability and safety-first governance further reinforce adoption across passenger and cargo operators.
Market Segmentation
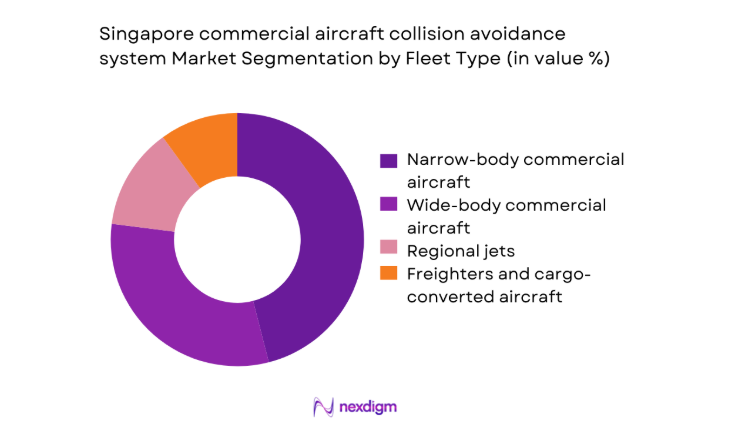
By Fleet Type
Fleet composition shapes adoption dynamics as narrow-body aircraft dominate regional traffic intensity, driving higher upgrade frequency and retrofit volumes due to dense short-haul operations. Wide-body aircraft contribute through long-haul safety compliance requirements and integrated avionics refresh cycles aligned with heavy maintenance checks. Regional jets sustain niche demand linked to feeder routes and cross-border connectivity, while freighters exhibit rising retrofit needs driven by fleet conversions and extended utilization cycles. Operational tempo, aircraft age profiles, and maintenance scheduling windows influence procurement timing. Airlines prioritize standardized configurations across mixed fleets to reduce training complexity and certification overheads. Fleet harmonization strategies increasingly favor common collision avoidance architectures to streamline spares provisioning, software updates, and airworthiness documentation across heterogeneous aircraft portfolios.
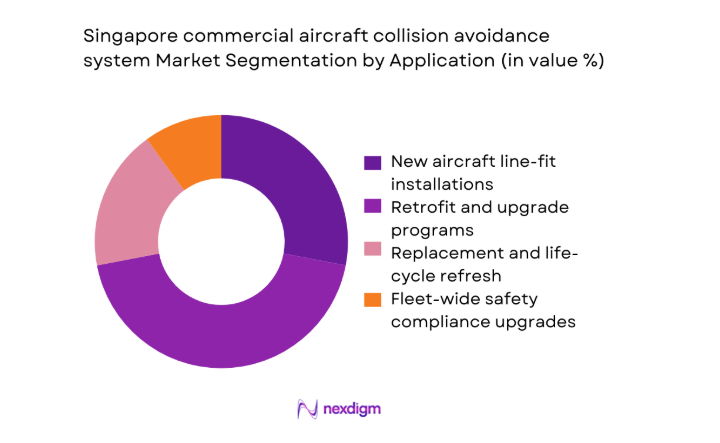
By Application
Application-led segmentation reflects procurement cycles anchored in new aircraft line-fit installations and lifecycle-driven retrofits. Line-fit demand aligns with fleet renewal and lease transitions, embedding collision avoidance within integrated avionics suites. Retrofit programs dominate value capture due to mandated upgrades, obsolescence management, and regulatory harmonization across mixed fleets. Replacement cycles are influenced by component life limits and software support timelines, while fleet-wide compliance upgrades are triggered by evolving airspace safety mandates. Airlines coordinate application strategies with maintenance windows to minimize downtime and optimize aircraft availability. Bundled procurement with flight deck modernization reduces installation complexity and supports standardized training, documentation, and continuing airworthiness management across operating certificates and maintenance organizations.
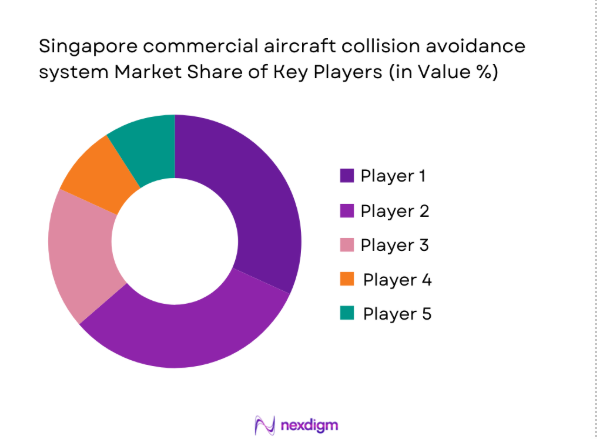
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is shaped by technology compliance depth, certification readiness, and integration capability with existing avionics architectures. Players differentiate through lifecycle support, retrofit execution capacity, and alignment with regulatory requirements governing commercial operations in Singapore’s controlled airspace.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Honeywell International | 1906 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Collins Aerospace | 2018 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Group | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Garmin | 1989 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Technologies | 2019 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore commercial aircraft collision avoidance system Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Mandated upgrades to ACAS standards for commercial fleets
Singapore’s regulator aligned certification with ICAO ACAS standards during 2023 and 2024, driving compliance across operators managing 130 registered commercial aircraft and 92 additional aircraft on long-term wet lease. In 2024, 47 aircraft entered heavy maintenance checks requiring avionics updates, while 29 aircraft underwent software conformity reviews linked to ACAS Xa/Xo readiness. The Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore issued 14 airworthiness notices clarifying interoperability requirements for mixed TCAS and ADS-B In environments. Singapore FIR recorded 1,120 daily movements in 2025, increasing collision risk management emphasis. Maintenance approvals expanded to 38 certified avionics workshops, accelerating mandated upgrades across scheduled maintenance cycles.
Rising air traffic density in Singapore FIR driving mid-air conflict risk mitigation
Air traffic movements in Singapore FIR averaged 1,060 daily operations in 2024 and increased to 1,120 in 2025, driven by route recovery across Southeast Asia corridors. Changi handled 380 scheduled departures daily in 2024, intensifying terminal maneuvering area complexity and vertical separation management. ATC introduced revised separation minima procedures across 22 high-density routes in 2023, requiring enhanced airborne situational awareness integration. In 2025, 18 near-miss incident reports triggered safety audits across operator fleets. Controller training hours reached 46,000 in 2024, reinforcing systemic reliance on airborne collision avoidance to complement procedural separation under constrained airspace conditions.
Challenges
High retrofit and certification costs for legacy aircraft
Legacy fleets operating aircraft delivered before 2012 face complex avionics integration constraints, with 41 aircraft in Singapore-registered fleets requiring structural wiring modifications during 2024 maintenance cycles. Certification documentation updates averaged 9 compliance submissions per aircraft in 2025, increasing administrative burden for operators. Maintenance downtime extended by 6 additional days per retrofit event due to concurrent conformity checks and flight test scheduling. Approved design organization capacity remained limited to 12 active approvals in 2024, constraining throughput. Training requirements expanded to 480 technician-hours per fleet transition program, straining maintenance planning windows and complicating fleet availability for peak seasonal schedules.
Downtime and operational disruption during system upgrades
Scheduled heavy checks in 2024 required coordinated avionics installations across 33 aircraft, causing cumulative ground time of 214 aircraft-days for operators managing narrow-body intensive schedules. In 2025, supply chain delays affected 19 installation kits, extending maintenance slots by 3 to 5 days per aircraft. Simulator reconfiguration for updated collision avoidance logic required 8 weeks of validation per fleet type, delaying crew currency programs. Engineering change approvals averaged 27 working days, compressing turnaround targets. Operational recovery plans required temporary wet-lease capacity of 6 aircraft equivalents to maintain network reliability during clustered retrofit windows.
Opportunities
Fleet-wide ACAS Xa/Xo upgrade programs
Fleet harmonization initiatives scheduled for 2024 and 2025 target 58 aircraft for ACAS Xa/Xo alignment across narrow-body and wide-body types. Regulatory acceptance testing protocols introduced in 2023 reduced re-certification steps from 11 to 7, improving program velocity. Simulator update cycles aligned with 24-month recurrent training windows, enabling synchronized software adoption across pilot cohorts numbering 2,600 in 2024. Maintenance planning integrated 16 dedicated installation slots per quarter at Singapore-based facilities, increasing throughput capacity. Cross-fleet configuration commonality reduces spares variability across 9 active aircraft types, supporting operational resilience and standardized safety management system documentation.
Retrofit demand for cargo-converted aircraft
Cargo conversion programs added 14 aircraft to Singapore-based operations during 2024 and 2025, extending utilization cycles beyond 20 service years and triggering mandatory avionics upgrades. Night operations increased to 210 weekly movements in 2025, elevating conflict detection reliance in constrained airspace corridors. Engineering change approvals for freighter configurations averaged 18 days in 2024, enabling faster retrofit sequencing. Maintenance organizations allocated 6 dedicated bays for cargo avionics workstreams, improving slot availability. Integration with upgraded flight management systems across 11 converted aircraft supports harmonized safety logic, creating bundled retrofit opportunities aligned with extended operational lifecycles.
Future Outlook
Through 2035, regulatory convergence with ICAO safety frameworks and continuous fleet modernization will sustain structured upgrade cycles across Singapore-registered commercial aircraft. Technology transitions toward ACAS-aligned architectures and deeper avionics integration will shape procurement timing. Regional traffic recovery and airspace complexity will reinforce collision avoidance as a core safety investment, supported by stable policy direction.
Major Players
- Honeywell International
- Collins Aerospace
- Thales Group
- Garmin
- L3Harris Technologies
- BAE Systems
- Leonardo
- Indra Sistemas
- Saab AB
- Elbit Systems
- Cobham Aerospace Communications
- ACSS
- Diehl Aviation
- Safran Electronics & Defense
- RTX
Key Target Audience
- Commercial passenger airlines operating Singapore-registered fleets
- Dedicated cargo airlines and ACMI operators
- Aircraft leasing companies with Asia-Pacific portfolios
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul organizations in Singapore
- Aircraft modification and certification organizations
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
- Aviation safety compliance and certification agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables were defined around fleet composition, avionics configuration baselines, regulatory compliance pathways, maintenance cycles, and certification dependencies within Singapore’s controlled airspace. Operational parameters across passenger and cargo fleets were mapped to installation windows and training requirements. Regulatory mandates and airworthiness directives were scoped to establish technology alignment needs.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
The market construct was built around line-fit and retrofit demand flows aligned with fleet renewal and maintenance scheduling patterns. Value capture logic focused on lifecycle support intensity, certification processes, and configuration commonality across fleets. Supply-side capacity across certified avionics facilities informed throughput constraints.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on adoption timing, retrofit clustering, and certification bottlenecks were validated through consultations with fleet engineering leads and certified avionics technicians. Operational data from maintenance planning teams informed downtime assumptions. Regulatory interpretations were reconciled with compliance officers overseeing airworthiness programs.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized to align regulatory timelines, operational constraints, and technology transition pathways. Cross-validation reconciled maintenance capacity with fleet upgrade schedules. The final output reflects realistic deployment cycles and ecosystem readiness across Singapore’s commercial aviation safety environment.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for commercial aircraft collision avoidance systems in Singapore, fleet and technology taxonomy mapping across TCAS and ADS-B based solutions, bottom-up market sizing using avionics shipment and retrofit program data, revenue attribution by OEM contracts and aftermarket service agreements)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage pathways across commercial aviation operations
- Ecosystem structure across OEMs, airlines, MROs, and regulators
- Avionics supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment and safety certification framework
- Growth Drivers
Mandated upgrades to ACAS standards for commercial fleets
Rising air traffic density in Singapore FIR driving mid-air conflict risk mitigation
Fleet renewal programs by Singapore-based carriers
Increased regulatory scrutiny on airborne safety systems
Integration of collision avoidance with next-generation avionics suites
Post-pandemic recovery in commercial flight operations - Challenges
High retrofit and certification costs for legacy aircraft
Downtime and operational disruption during system upgrades
Interoperability issues between legacy TCAS and new ACAS standards
Limited skilled avionics technicians for complex installations
Regulatory approval timelines for new technology architectures
Cost sensitivity among low-cost carriers - Opportunities
Fleet-wide ACAS Xa/Xo upgrade programs
Retrofit demand for cargo-converted aircraft
Bundling collision avoidance with broader avionics modernization
Regional MRO hubs positioning Singapore as retrofit center
Aftermarket service and long-term maintenance contracts
Adoption of data-driven safety analytics integrated with collision avoidance - Trends
Transition from TCAS II to ACAS-compliant systems
Increased integration with ADS-B In surveillance capabilities
Preference for modular, software-upgradable architectures
Growth in predictive conflict detection algorithms
Alignment with ICAO and CAAS evolving safety mandates
Shift toward long-term service agreements with OEMs - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrow-body commercial aircraft
Wide-body commercial aircraft
Regional jets
Freighters and cargo-converted aircraft - By Application (in Value %)
New aircraft line-fit installations
Retrofit and upgrade programs
Replacement and life-cycle refresh
Fleet-wide safety compliance upgrades - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
TCAS II
ACAS Xa/Xo
ADS-B In enhanced conflict detection
Hybrid TCAS and ADS-B integrated systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Scheduled passenger airlines
Low-cost carriers
Dedicated cargo airlines
Charter and ACMI operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone airborne collision avoidance systems
Integrated avionics suite connectivity
Ground-assisted situational awareness integration
Satellite-enabled surveillance augmentation - By Region (in Value %)
Singapore domestic fleet operations
Singapore-registered aircraft operating in Asia-Pacific
International long-haul operations based in Singapore
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology compliance level, certification portfolio, installed base in Asia-Pacific, retrofit capability, software upgrade roadmap, after-sales support footprint, integration with avionics suites, pricing and contract flexibility)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Honeywell International
Collins Aerospace
Thales Group
Garmin
L3Harris Technologies
BAE Systems
Indra Sistemas
Saab AB
Leonardo
Elbit Systems
RTX
Cobham Aerospace Communications
ACSS
Diehl Aviation
Safran Electronics & Defense
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


