Market Overview
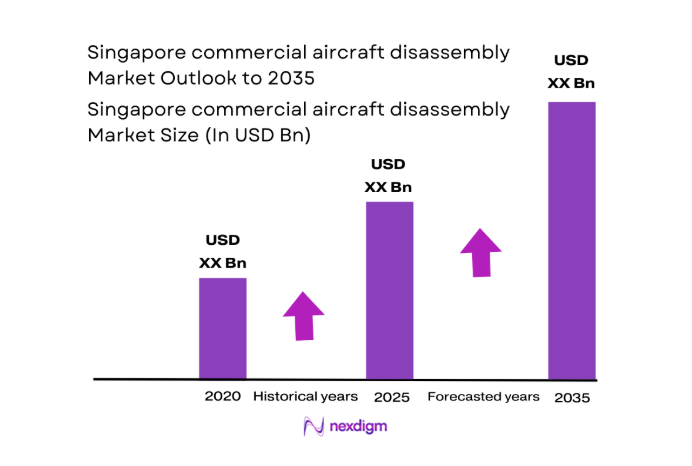
The Singapore commercial aircraft disassembly market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting a specialized ecosystem anchored by certified teardown operations, bonded logistics zones, and component traceability practices. The market is shaped by structured end-of-life aircraft processing, component harvesting workflows, and environmentally compliant material recovery. Value creation concentrates on demanufacturing services, preservation-to-teardown transitions, and circulation of serviceable components through global distribution channels, supported by regulatory approvals and maintenance standards that ensure airworthiness documentation integrity.
Operational activity is concentrated around Changi and Seletar, where proximity to maintenance clusters, bonded storage, and export logistics accelerates teardown throughput. Demand concentrates around lessor-managed portfolios and regional airline fleets transitioning through storage-to-teardown cycles. The ecosystem benefits from mature certification regimes, digital part traceability, and established component trading networks. Policy alignment on environmental compliance, hazardous waste handling, and customs facilitation reinforces Singapore’s role as a preferred regional hub for structured aircraft demanufacturing.
Market Segmentation
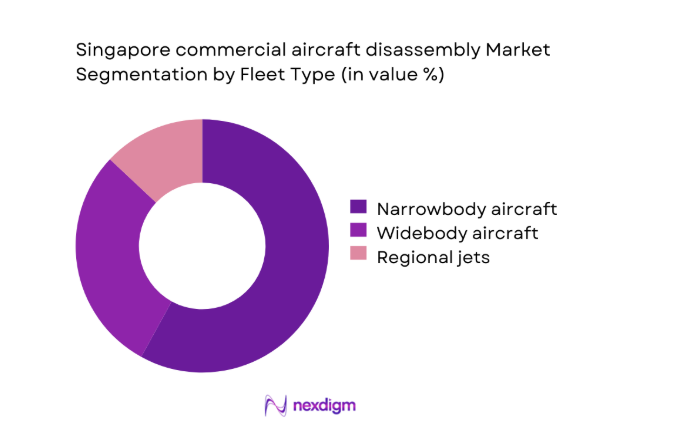
By Fleet Type
Narrowbody aircraft dominate disassembly activity due to accelerated fleet renewal cycles and high secondary demand for serviceable components. Regional airlines and short-haul operators contribute consistent narrowbody feedstock into teardown pipelines, supporting predictable harvesting of avionics, landing gear, and interiors. Widebody disassembly remains episodic, driven by portfolio rationalization and engine program transitions, while regional jets form a smaller but specialized niche aligned with selective part demand. The concentration of narrowbody platforms in storage and conversion programs sustains operational utilization across teardown facilities, logistics providers, and certification workflows, reinforcing process standardization and inventory turnover across component categories.
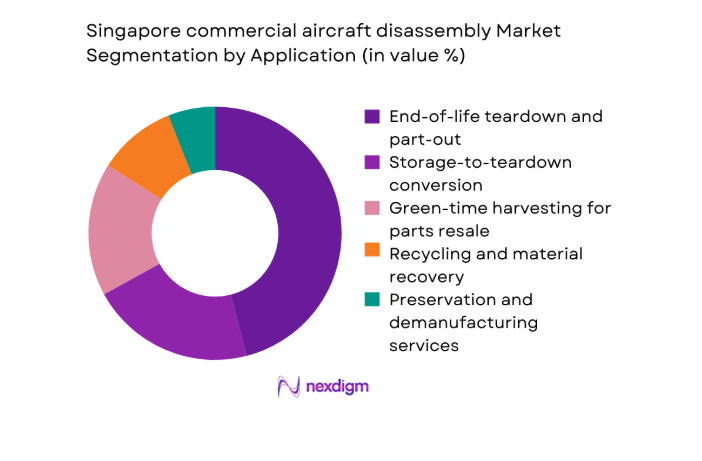
By Application
End-of-life teardown and part-out accounts for the largest share, supported by lessor-driven asset optimization and airline fleet transitions. Storage-to-teardown conversion represents a growing pathway as parked aircraft are released into demanufacturing pipelines following lease returns. Green-time harvesting remains opportunistic, targeting high-rotation components for near-term resale. Recycling and material recovery are expanding as composite handling capabilities mature, while preservation and demanufacturing services address compliance-led requirements for hazardous material handling. Application mix reflects the maturity of certification processes, digital traceability, and alignment with global component trading platforms that improve liquidation velocity and operational predictability.
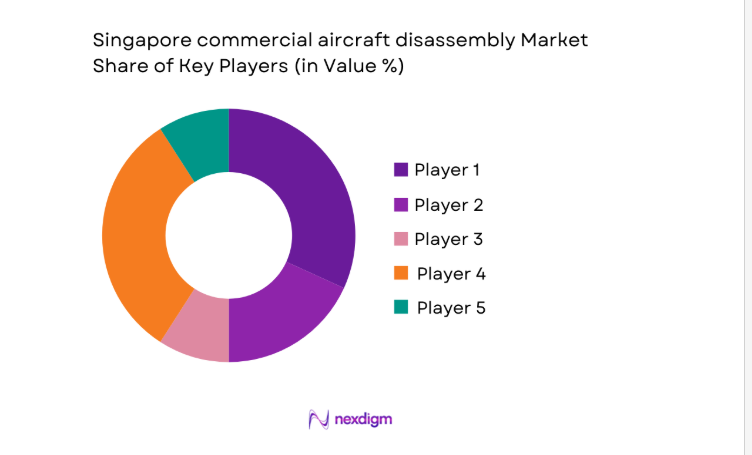
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment features certified teardown operators integrated with maintenance clusters and component trading networks, supported by logistics and regulatory readiness.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| ST Engineering Aerospace | 1970 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SIA Engineering Company | 1992 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| HAECO Singapore | 2006 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lufthansa Technik Asia | 2003 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SR Technics | 1997 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore commercial aircraft disassembly Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising end-of-life retirements of aging narrowbody and widebody fleets in Asia-Pacific
Aircraft retirement flows intensified across Asia-Pacific during 2024 and 2025 as fleets introduced newer models, increasing feedstock into teardown pipelines. Regional civil aviation registries recorded 612 aircraft withdrawn from active service in 2024, compared with 489 in 2023, reflecting accelerated fleet turnover. Storage inventories in proximate markets averaged 184 aircraft during 2025, sustaining steady conversion into disassembly programs. Engine shop visit deferrals in 2024 increased parked aircraft dwell time by 63 days on average, improving timing flexibility for teardown planning. Regulatory airworthiness lifecycle limits imposed on legacy platforms in 2025 further increased removals. Logistics throughput at bonded facilities processed 146 outbound component consignments weekly in 2025.
Singapore’s positioning as a global MRO and parts trading hub
Singapore’s maintenance cluster supports disassembly through certified facilities, bonded logistics, and component traceability infrastructure. In 2024, 37 CAAS-approved maintenance organizations operated within Changi and Seletar zones, enabling integrated teardown workflows. Customs processing times for controlled aviation parts averaged 2 days in 2025, supporting rapid export cycles. Digital part traceability systems registered 128,000 serialized components processed through accredited databases during 2024. Regional connectivity handled 1,900 weekly cargo movements supporting aviation supply chains in 2025. Skilled technical manpower numbered 21,400 licensed engineers across 2024, ensuring capacity for inspection, documentation, and certification. Environmental compliance audits conducted 214 inspections in 2025, reinforcing operational continuity.
Challenges
Limited airfield and apron space for large-scale aircraft parking and teardown
Physical constraints around Changi and Seletar limit large-scale parking, constraining feedstock staging for teardown programs. Apron allocation records in 2024 showed average occupancy of 92, restricting dwell capacity during peak fleet transition periods. Temporary parking approvals averaged 18 days in 2025, compressing teardown scheduling windows. Competing demands from active maintenance and cargo operations increased slot contention, with 74% utilization reported during 2024. Ground handling equipment availability declined during peak months, extending aircraft repositioning by 11 days on average in 2025. Regulatory safety buffers require 25 meters clearance around parked aircraft, reducing usable space. Seasonal weather disruptions caused 9 operational suspensions during 2024, compounding space limitations for staged demanufacturing workflows.
High labor and compliance costs relative to regional teardown hubs
Labor intensity and compliance requirements elevate operational burdens. In 2024, licensed technician density averaged 3.6 per teardown line, increasing manpower needs for concurrent programs. Mandatory certification checks added 14 procedural steps per aircraft in 2025, extending cycle times. Environmental audits conducted quarterly resulted in 27 corrective actions across facilities in 2024, increasing administrative load. Safety training mandates required 24 hours annually per technician in 2025, diverting productive time. Hazardous material handling protocols required 6 certified handlers per teardown event in 2024. Documentation requirements generated 1,200 pages per aircraft file set in 2025, slowing processing velocity relative to regional alternatives with fewer procedural layers.
Opportunities
Conversion of parked aircraft into teardown programs during fleet transitions
Parked aircraft inventories create conversion opportunities as fleet transitions accelerate. Regional storage pools recorded 201 aircraft in 2024, with 143 transitioning to teardown pathways during 2025 following lease expiries. Average storage duration reached 312 days in 2025, aligning with optimized teardown scheduling windows. Conversion planning frameworks reduced idle dwell by 47 days in 2024 through coordinated release triggers. Institutional policies promoting asset lifecycle optimization resulted in 26 portfolio-level conversion approvals during 2025. Engine preservation thresholds reached 9 months for parked units in 2024, incentivizing timely harvesting. Integrated logistics routing enabled 84 aircraft repositioning into Singapore-linked teardown programs in 2025, strengthening feedstock reliability for local operators.
Partnerships with lessors to anchor long-term teardown pipelines
Long-term partnerships with lessors stabilize feedstock and scheduling. Portfolio management offices overseeing 4,200 leased aircraft in 2024 adopted structured end-of-life frameworks incorporating regional teardown hubs. Contractual teardown pipeline agreements averaged 18 months in 2025, improving facility utilization planning. Asset lifecycle audits conducted 2 times annually per portfolio in 2024 identified early retirement candidates. Data-sharing agreements enabled pre-teardown part demand mapping for 3,600 components per aircraft in 2025, improving harvesting yields. Compliance coordination reduced documentation cycle time by 21 days in 2024. Regional repositioning corridors enabled 62 cross-border transfers into Singapore-linked programs during 2025, enhancing throughput predictability.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to benefit from sustained fleet renewal cycles through 2035, with increasing conversion of parked aircraft into structured teardown programs. Digital traceability and circular aviation initiatives will deepen component recovery and recycling integration. Policy alignment on environmental compliance will further professionalize demanufacturing practices. Regional connectivity and logistics efficiency will continue to anchor Singapore’s hub role.
Major Players
- ST Engineering Aerospace
- SIA Engineering Company
- HAECO Singapore
- Lufthansa Technik Asia
- SR Technics
- Safran Aircraft Engines Singapore
- Pratt & Whitney Singapore
- Rolls-Royce Singapore
- AAR Corp
- GA Telesis
- AerSale
- AJ Walter Aviation
- AFI KLM E&M
- Magellan Aviation Services
- Ascent Aviation Services
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airlines fleet management divisions
- Aircraft lessors and asset management offices
- MRO and teardown service providers
- Component traders and distribution networks
- Logistics and bonded warehouse operators
- Recycling and materials recovery firms
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore and National Environment Agency
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core variables were defined around aircraft lifecycle stages, teardown workflows, certification requirements, component traceability, and environmental compliance. Demand drivers were mapped across fleet renewal cycles, storage-to teardown conversion triggers, and component reuse pathways. Stakeholder roles were delineated across operators, lessors, logistics providers, and regulators.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
The analytical framework integrated disassembly capacity, operational throughput, and certification processes within maintenance clusters. Segmentation logic was constructed around fleet type and application pathways. Ecosystem mapping aligned logistics corridors, bonded storage, and digital traceability systems with operational flow constraints.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses were validated through structured consultations with teardown program managers, maintenance engineers, logistics coordinators, and compliance specialists. Operational assumptions were stress-tested against regulatory audits, certification workflows, and observed storage-to-teardown conversion cycles to ensure practical relevance.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized to align ecosystem dynamics, operational constraints, and partnership models. Insights were consolidated into actionable themes covering drivers, challenges, and opportunities, with emphasis on compliance-led process maturity, digital enablement, and regional logistics integration.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and teardown scope for end-of-life commercial aircraft in Singapore MRO zones, Fleet and component taxonomy aligned to narrowbody and widebody teardown outputs, Bottom-up sizing from disassembly throughput and part-out yields across Changi and Seletar facilities, Revenue attribution across teardown labor, storage, harvesting and material recovery streams)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage pathways for end-of-life and parked fleet teardown
- Ecosystem structure across MROs, lessors, part traders and recyclers
- Supply chain and channel structure for harvested components and materials
- Regulatory environment under CAAS, customs and environmental compliance
- Growth Drivers
Rising end-of-life retirements of aging narrowbody and widebody fleets in Asia-Pacific
Singapore’s positioning as a global MRO and parts trading hub
Strong demand for serviceable used material from operators managing fleet costs
Availability of bonded storage and logistics infrastructure for part export
Increased lessor-led portfolio optimization and part-out programs
Favorable air connectivity and trade facilitation for harvested components - Challenges
Limited airfield and apron space for large-scale aircraft parking and teardown
High labor and compliance costs relative to regional teardown hubs
Stringent environmental and waste handling regulations increasing processing costs
Volatility in used serviceable material pricing cycles
Supply chain complexity for certification and traceability of harvested parts
Competition from lower-cost teardown locations in Southeast Asia - Opportunities
Conversion of parked aircraft into teardown programs during fleet transitions
Partnerships with lessors to anchor long-term teardown pipelines
Investment in advanced composite recycling capabilities
Digital marketplaces to improve liquidation velocity of harvested parts
Development of green teardown certifications to attract ESG-focused lessors
Regional consolidation of teardown logistics through Singapore free trade zones - Trends
Shift toward narrowbody teardown volumes driven by fleet renewal programs
Increased digitization of part traceability and certification workflows
Growth in composite material recovery and circular aviation initiatives
Longer storage-to-teardown cycles aligned to market timing for parts demand
Integration of teardown planning with lessor asset management platforms
Rising demand for engines and avionics from parted-out fleets - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft
Widebody aircraft
Regional jets - By Application (in Value %)
End-of-life teardown and part-out
Storage to teardown conversion
Green-time harvesting for parts resale
Recycling and material recovery
Aircraft preservation and demanufacturing services - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Manual disassembly and inspection workflows
Digitized teardown planning and asset tracking
RFID and part traceability systems
Advanced materials separation and recycling technologies
Predictive analytics for part demand forecasting - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Aircraft lessors
Commercial airlines
MRO and teardown service providers
Aircraft part traders and distributors
Metals and composites recyclers - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
On-premise asset management systems
Cloud-based teardown management platforms
Integrated airline and lessor IT connectivity
Third-party parts marketplace integrations
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (teardown throughput capacity, turnaround time per aircraft, certification and traceability coverage, engine and avionics harvesting capability, recycling and material recovery rates, geographic export reach, digital asset management maturity, ESG and environmental compliance performance)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
ST Engineering Aerospace
SIA Engineering Company
HAECO Singapore
Lufthansa Technik Asia
Safran Aircraft Engines Singapore
Pratt & Whitney Singapore
Rolls-Royce Singapore
SR Technics
AAR Corp
GA Telesis
AerSale
AJ Walter Aviation
AFI KLM E&M
Magellan Aviation Services
Ascent Aviation Services
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


