Market Overview
The Singapore commercial aircraft engines market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting a mature aviation services ecosystem anchored by extensive engine maintenance, repair, and overhaul activity, strong airline fleet presence, and deep OEM-certified capabilities. The market is shaped by long-term service agreements, high engine utilization cycles, and dense integration of aftermarket support infrastructure across airlines, lessors, and independent service providers, with value concentrated in installed base sustainment, parts lifecycle management, and engine health monitoring services.
Activity concentrates in Singapore due to Changi’s hub status, dense airline and lessor presence, and a tightly integrated aerospace services cluster. The city hosts advanced engine shops, parts distribution hubs, and digital maintenance operations aligned with regional traffic flows. Policy support for aerospace manufacturing, skilled workforce pipelines, and streamlined certification regimes reinforce ecosystem maturity. Proximity to Southeast Asian carriers, freighter operators, and leasing platforms further consolidates demand concentration and supply chain coordination within Singapore’s aviation services environment.
Market Segmentation
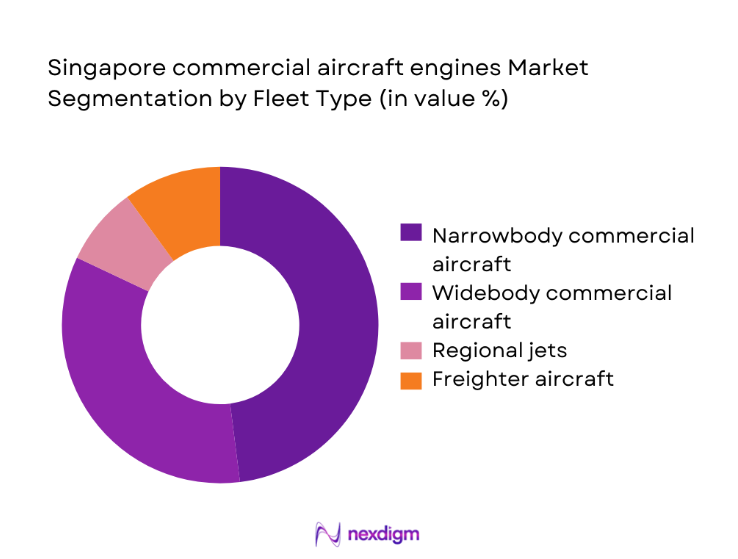
By Fleet Type
Narrowbody aircraft engines dominate value contribution due to high utilization intensity on regional and short-haul routes centered on Southeast Asia. Fleet renewal cycles among hub-and-spoke operators sustain steady shop visits and parts replacement cadence, while narrowbody engine families account for the majority of active flight cycles processed through local MRO facilities. Widebody engines contribute significant aftermarket value per shop visit but lower aggregate frequency. Regional jets and dedicated freighters remain niche but growing, driven by cargo network densification and conversion programs routed through Singapore-based maintenance ecosystems.
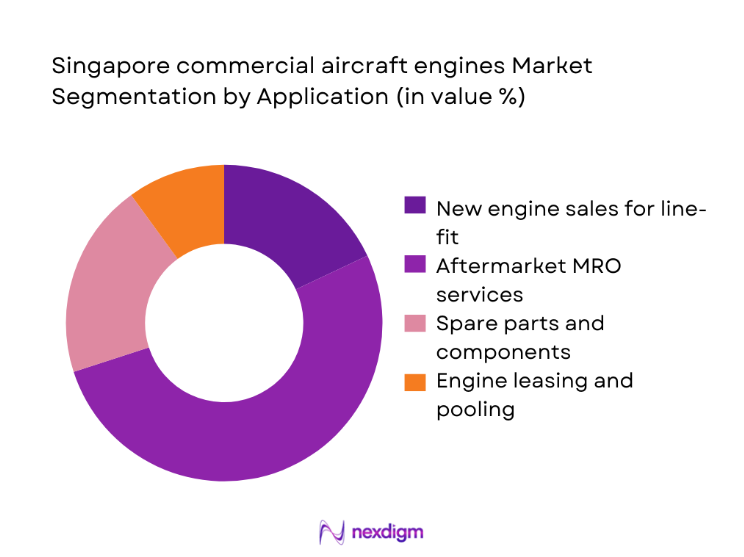
By Application
Aftermarket MRO services account for the largest value pool, reflecting the concentration of heavy shop visits, module exchanges, and parts lifecycle management performed in Singapore. Line-fit new engine sales are limited locally, while spare parts provisioning and component repairs are anchored by regional distribution hubs and OEM-approved part pools. Engine leasing and spare pooling are gaining prominence as airlines seek operational resilience and flexibility amid fleet transitions. The application mix favors recurring service intensity over episodic capital procurement.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape reflects a mix of global engine OEM ecosystems and locally anchored MRO platforms, with Singapore positioned as a regional service hub for Asia-Pacific fleets. Competitive positioning is shaped by certification breadth, shop capacity depth, digital diagnostics integration, and long-term service agreement coverage across narrowbody and widebody platforms.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| GE Aerospace | 1892 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pratt & Whitney | 1925 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rolls-Royce | 1906 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| CFM International | 1974 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ST Engineering Aerospace | 1990 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore commercial aircraft engines Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Fleet renewal by Singapore-based carriers toward fuel-efficient engines
Fleet renewal among Singapore-based carriers accelerated as 62 aircraft deliveries were inducted across narrowbody and widebody fleets during 2024 and 2025, increasing engine utilization cycles processed locally. Engine shop visits rose alongside average flight hours per aircraft reaching 4100 annually in 2024, driven by restored regional connectivity. Changi handled 67 million passengers in 2024, elevating utilization intensity and maintenance demand. The civil aviation authority approved 28 new maintenance capability ratings in 2025, expanding certified scope for next-generation turbofans. Regional route frequencies increased by 214 weekly movements, sustaining higher cycle-driven wear profiles across installed engines in Singapore.
Expansion of Asia-Pacific air travel demand supported by Changi hub connectivity
Changi’s route network expanded to 162 destinations by 2025, enabling higher aircraft rotations and engine cycle accumulation for Singapore-based fleets. Passenger movements rebounded to 67 million in 2024, while cargo throughput reached 1.9 million tonnes, increasing freighter engine utilization. Regional capacity restoration lifted average daily departures to 1020 in 2025, sustaining maintenance throughput. Bilateral air service agreements expanded seat entitlements across 14 country pairs during 2024, raising utilization intensity. Slot utilization averaged 88 per day per runway, reinforcing hub connectivity and sustained demand for engine health monitoring and scheduled shop visits in Singapore.
Challenges
High capital cost of next-generation engines for airline balance sheets
Next-generation engine induction increased technical complexity, with 4 new engine variants entering local maintenance scope during 2024 and 2025, raising tooling and certification burdens. Training pipelines certified 320 additional technicians in 2024, yet skill gaps persist across advanced composites and geared architectures. Engine spare module lead times extended to 140 days in 2025 due to constrained supplier output. Shop capacity utilization averaged 91 during peak months, creating scheduling bottlenecks. Regulatory approval cycles for new repair schemes required 9 months on average, delaying throughput optimization and increasing aircraft ground time within Singapore-based maintenance networks.
Supply chain disruptions affecting engine parts availability and turnaround times
Parts availability constraints persisted as 23 critical component categories experienced backorders in 2024, extending average shop visit durations to 78 days. Global logistics disruptions affected 41 supplier routes feeding Singapore hubs, complicating inventory planning. Local bonded warehouse throughput rose to 19000 consignments in 2025, yet customs clearance variability added 3 to 6 days to cycle times. Approved alternative repair pathways covered only 12 high-failure components, limiting flexibility. Workforce attrition reached 11 in 2024, compounding delays in specialized repairs and inspection throughput across engine modules handled in Singapore.
Opportunities
Localization of advanced engine MRO capabilities in Singapore
Capability localization accelerated as 17 new engine test cells and module lines were commissioned across 2024 and 2025, expanding throughput for next-generation turbofans. Certification approvals covered 9 additional repair schemes for composite fan blades and hot-section components, reducing overseas dependency. Workforce pipelines added 480 specialized technicians across materials science and nondestructive testing disciplines. Turnaround time for complex modules declined by 14 days with localized repairs. Government-supported aerospace initiatives approved 6 capability expansion programs in 2025, enabling Singapore to capture a greater share of regional shop visits and deepen lifecycle service integration.
Partnerships between OEMs and independent MRO providers
Collaborative frameworks expanded as 11 new authorized repair agreements were concluded during 2024 and 2025, widening access to proprietary tooling and repair data. Joint training programs certified 260 technicians on digital diagnostics platforms, improving first-pass yield rates across inspections. Shared spares pools covered 320 high-rotation line-replaceable units, reducing aircraft-on-ground events by 18 days cumulatively per fleet annually. Co-located engineering teams processed 740 repair approvals in 2025, accelerating turnaround decisions. Data-sharing protocols enabled real-time health monitoring across 420 connected engines routed through Singapore service hubs.
Future Outlook
The Singapore commercial aircraft engines market will be shaped by sustained hub connectivity, deeper localization of advanced MRO capabilities, and tighter integration of digital engine health ecosystems through 2035. Fleet transitions will reinforce aftermarket intensity, while policy support for aerospace skills and certification capacity is expected to strengthen Singapore’s regional service hub positioning.
Major Players
- GE Aerospace
- Pratt & Whitney
- Rolls-Royce
- CFM International
- MTU Aero Engines
- Safran Aircraft Engines
- SIA Engineering Company
- ST Engineering Aerospace
- Lufthansa Technik
- SR Technics
- Airbus
- Boeing
- StandardAero
- Chromalloy
- GA Telesis
Key Target Audience
- Commercial passenger airlines operating Singapore-based fleets
- Air cargo and freighter operators in Southeast Asia
- Aircraft leasing companies with regional portfolios
- Engine leasing and spare pooling providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore and Ministry of Transport
- Aerospace MRO service providers and component repair shops
- Engine OEM authorized service network partners
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables included fleet composition in Singapore, active engine families, utilization intensity, shop visit cadence, repair scheme coverage, certification scope, and digital diagnostics penetration. Variables were structured to reflect operational realities across airlines, lessors, and MRO platforms.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Operational throughput indicators, installed base dynamics, and maintenance capability depth were analyzed to construct the market structure. Engine lifecycle stages, module repair flows, and regional routing patterns were mapped to Singapore’s hub-centric ecosystem.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on utilization recovery, capacity constraints, and capability localization were validated through consultations with airline engineering teams, maintenance planners, and regulatory specialists engaged in certification and oversight functions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into coherent market narratives aligned to segmentation, competitive positioning, and operational constraints. Insights were structured to support strategic planning across procurement, capacity investment, and partnership development.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and commercial aircraft engine scope in Singapore civil aviation, Fleet and engine architecture taxonomy aligned to Singapore-based airline operations, Bottom-up market sizing using engine deliveries MRO revenues and leasing disclosures, Revenue attribution by OEM sales aftermarket service contracts and parts lifecycle)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and maintenance pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Fleet renewal by Singapore-based carriers toward fuel-efficient engines
Expansion of Asia-Pacific air travel demand supported by Changi hub connectivity
Growth in engine MRO throughput driven by Singapore’s aerospace services cluster
Rising adoption of engine health monitoring and predictive maintenance
Increase in freighter conversions and dedicated cargo operations
OEM aftermarket revenue growth through long-term service agreements - Challenges
High capital cost of next-generation engines for airline balance sheets
Supply chain disruptions affecting engine parts availability and turnaround times
Skilled labor constraints in advanced engine MRO capabilities
Grounding risks from in-service technical issues and durability concerns
Volatility in airline capacity planning impacting engine utilization
Dependence on OEM-approved parts and repair network constraints - Opportunities
Localization of advanced engine MRO capabilities in Singapore
Partnerships between OEMs and independent MRO providers
Growth in engine leasing and spare engine pooling for fleet flexibility
Sustainable aviation fuel compatibility upgrades driving retrofit demand
Digital twin and AI-based engine performance optimization services
Expansion of Asia-Pacific widebody maintenance demand routed through Singapore - Trends
Shift toward geared turbofan and higher bypass ratio architectures
Long-term power-by-the-hour contracts dominating airline procurement
Increased use of predictive maintenance and remote engine diagnostics
Rising emphasis on lifecycle cost optimization over upfront pricing
Sustainability-driven engine efficiency upgrades and emissions reporting
Consolidation among MRO providers for scale and capability depth - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody commercial aircraft
Widebody commercial aircraft
Regional jets
Freighter aircraft - By Application (in Value %)
New engine sales for line-fit
Aftermarket MRO services
Spare parts and components
Engine leasing and pooling - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
High-bypass turbofan
Geared turbofan
Advanced composite fan blade engines
Next-generation ultra-high bypass concepts - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Commercial passenger airlines
Air cargo operators
Aircraft leasing companies
Charter and ACMI operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
On-wing health monitoring connectivity
Engine health monitoring via ACARS
Satellite-connected engine analytics
Ground-based diagnostic integration
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (engine portfolio breadth, installed base in Singapore fleets, MRO network footprint in Singapore, aftermarket contract coverage, turnaround time performance, digital diagnostics capabilities, pricing flexibility, sustainability and efficiency roadmap)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
GE Aerospace
Pratt & Whitney
Rolls-Royce
CFM International
MTU Aero Engines
Safran Aircraft Engines
SIA Engineering Company
ST Engineering Aerospace
Lufthansa Technik
SR Technics
Airbus
Boeing
StandardAero
Chromalloy
GA Telesis
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


