Market Overview
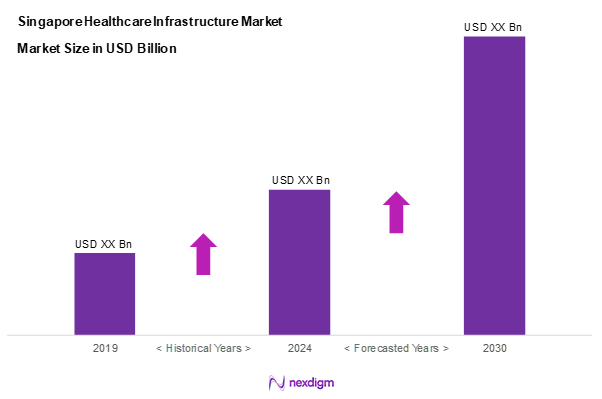
As of 2024, the Singapore healthcare infrastructure market is valued at USD ~ billion, with a growing CAGR of 14.96% from 2024 to 2030, showcasing robust growth driven by increasing healthcare demand, technological advancements, and significant investments in facility expansions and upgrades. The market benefits from a well-established healthcare system that combines public and private sectors catering to the healthcare needs of both local and expatriate populations. Recent initiatives have focused on enhancing healthcare facilities, thereby promoting better patient outcomes and overall efficiency within the healthcare system, making Singapore a leader in Asia’s healthcare landscape.
Key cities, particularly Singapore city, dominate the healthcare infrastructure market owing to their concentration of advanced healthcare facilities and a skilled workforce. The strategic location and status as a financial hub facilitate significant foreign investments, improving healthcare technology and facilities. Singapore’s emphasis on preventive healthcare and the adoption of digital health solutions further strengthen its position in the market, attracting international patients seeking high-quality healthcare services.
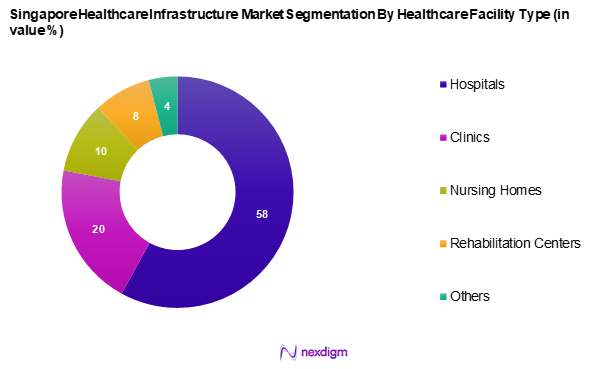
Market Segmentation
By Healthcare Facility Type
The Singapore healthcare infrastructure market is segmented into hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, and others. Hospitals dominate the market owing to their comprehensive services, advanced medical technology, and specialized healthcare professionals. With major establishments such as Singapore General Hospital and Tan Tock Seng Hospital, the hospital segment caters to a diverse patient population, offering both inpatient and outpatient services. Furthermore, the government’s commitment to expanding hospital capacity and introducing advanced healthcare services plays a pivotal role in maintaining the growth trajectory of the hospitals segment.
By Ownership Structure
The Singapore healthcare infrastructure market is segmented into public and private facilities. The public facilities segment holds a significant share, primarily because the Singapore government invests heavily in building and maintaining hospitals to ensure high-quality healthcare accessibility for residents. Public facilities are known for their affordability and range of services that cater to various health needs. Meanwhile, private facilities are expanding their market share, driven by their ability to provide faster services and specialized treatments, appealing to both local and international patients.

Competitive Landscape
The Singapore healthcare infrastructure market is dominated by significant players that influence various dimensions, including service diversity and technological advancements. Major entities, such as the Singapore General Hospital and Tan Tock Seng Hospital, head the competitive landscape by offering comprehensive healthcare solutions and quality patient care. This consolidation highlights the pivotal role that these key organizations play, particularly in terms of innovation and practices that set benchmarks within the industry.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Market Focus | Number of Facilities | Workforce Size | Innovative Services |
| Singapore General Hospital | 1821 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
| Tan Tock Seng Hospital | 1844 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
| KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital | 1858 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
| Mount Elizabeth Hospital | 1979 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
| Raffles Hospital | 1976 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
Singapore Healthcare Infrastructure Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising Aging Population
The increasing proportion of elderly individuals in Singapore is significantly influencing the healthcare infrastructure market. With a growing number of seniors requiring medical care, there is a heightened demand for specialized geriatric and chronic care services. Healthcare facilities are expanding their focus on elder-specific treatments, ensuring adequate hospital and nursing home capacities to meet the needs of this demographic. Global health organizations also emphasize the necessity for systems to adapt to such demographic shifts, reinforcing the need for enhanced medical infrastructure.
Increasing Health Expenditure
Singapore’s healthcare system continues to receive substantial financial investment, reflecting a strong commitment to enhancing medical accessibility and service quality. Government funding allocations have seen consistent growth, supporting the expansion of healthcare facilities, technological advancements, and improved patient care outcomes. The direct correlation between increased spending and better health services has led to the development of modern medical infrastructures that cater to evolving healthcare demands.
Market Challenges
Regulatory Compliance
The regulatory landscape in Singapore imposes stringent requirements on healthcare establishments to ensure high-quality and safe services. Strict compliance measures govern hospitals, clinics, and other medical institutions, necessitating significant investments in legal adherence, training, and infrastructure modifications. Non-compliance with regulations results in considerable penalties, posing a challenge for entities looking to expand their facilities. Additionally, evolving international health standards add complexity, requiring continuous adjustments to operational practices.
High Operational Costs
Running a healthcare facility in Singapore entails significant operational expenses, driven by high labor costs and real estate prices. Healthcare professionals, including doctors and nurses, command competitive salaries, contributing to substantial financial outlays for medical institutions. Urban healthcare hubs also face high rental costs, influencing the overall pricing of medical services. These economic factors may lead to increased service charges, potentially affecting healthcare affordability for different population segments.
Opportunities
Expansion of Private Sector
The private healthcare sector in Singapore continues to experience notable growth, presenting significant opportunities for investment and expansion. A rising preference for specialized and expedited medical services has led to increased demand for private hospitals and boutique clinics. The sector’s development is further supported by growing medical tourism, attracting both local and international patients. Potential government incentives aimed at encouraging private sector growth create an attractive environment for further investment in healthcare infrastructure.
Government Initiatives and Funding
The Singapore government has introduced several initiatives aimed at strengthening public healthcare infrastructure and technological advancements. These efforts include funding programs dedicated to the construction of new hospitals, upgrading existing facilities, and integrating digital health solutions such as telemedicine. Such strategic investments foster a robust healthcare ecosystem, ensuring comprehensive medical access and promoting advancements that align with the evolving needs of the population. These government-backed initiatives create promising opportunities for stakeholders within the healthcare infrastructure sector.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Singapore healthcare infrastructure market is projected to maintain a steady growth trajectory driven by ongoing government support, advancements in healthcare technology, and rising consumer demand for superior healthcare services. The continuous push towards integrating digital health solutions, along with the anticipated increase in healthcare expenditure, will bolster market growth. The country’s strategic vision for healthcare transformation is likely to yield a robust healthcare system that balances efficiency, accessibility, and high-quality care.
Major Players
- Singapore General Hospital
- Tan Tock Seng Hospital
- KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital
- Mount Elizabeth Hospital
- Raffles Hospital
- National University Hospital
- Thomson Medical Centre
- Changi General Hospital
- Parkway Pantai
- Health Promotion Board
- Andrew’s Community Hospital
- JurongHealth Campus
- Ng Teng Fong General Hospital
- Ng Teng Fong Medical Centre
- Singapore Health Services
Key Target Audience
- Hospital Administrators
- Healthcare Facility Owners
- Insurance Providers
- Healthcare Technology Companies
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Ministry of Health, Singapore)
- Investment and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Pharmaceutical Companies
- Non-Profit Health Organizations
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves mapping the ecosystem of stakeholders across the Singapore healthcare infrastructure market. This includes identifying key players, trends, and relationships among various healthcare entities, all supported by extensive desk research utilizing a blend of secondary and proprietary databases. The primary goal is to define and understand the critical variables that shape market dynamics and influences.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, we compile and scrutinize historical and current data regarding the Singapore healthcare infrastructure market. This encompasses analysing healthcare penetration, the ratio of healthcare facilities to service providers, and associated revenue generation. A thorough examination of service quality metrics will also be incorporated to validate the accuracy of revenue and market assessments.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are constructed and validated through structured interviews (CATIs) with industry experts from various healthcare segments. These consultations are integral for gathering operational insights and financial data from practitioners, allowing us to refine and corroborate the data obtained through preliminary research.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase entails engaging with multiple healthcare providers to obtain detailed insights into service offerings, patient demographics, and operational efficiencies. This direct engagement serves to verify and enhance the statistical analysis and ensures a comprehensive understanding of the Singapore healthcare infrastructure market, resulting in an accurate and validated report.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Overview Genesis
- Timeline of Major Players
- Business Cycle
- Supply Chain & Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Rising Aging Population
Increasing Health Expenditure - Market Challenges
Regulatory Compliance
High Operational Costs - Opportunities
Expansion of Private Sector
Government Initiatives and Funding - Trends
Rise in Preventive Healthcare
Growth of Hybrid Healthcare Models - Government Regulation
Healthcare Policies
Quality Assurance Standards - SWOT Analysis
- Stake Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Cost per Bed, 2019-2024
- By Healthcare Facility Type, (In Value %)
Hospitals
Clinics
Nursing Homes
Rehabilitation Centres
Others - By Ownership Structure, (In Value %)
Public
Private - By Service Types, (In Value %)
Inpatient Services
Outpatient Services
Emergency Services
Diagnostic Services - By Region, (In Value %)
Central Region
East Region
North Region
West Region - By Healthcare Technology, (In Value %)
Telemedicine
Electronic Health Records
Health Information Systems
Robotics and Automation
- Market Share of Major Players on the Basis of Value, 2024
Market Share of Major Players by Facility Type, 2024 - Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Recent Developments, Strength, Weakness, Organizational Structure, Revenues, Revenues by Facility Type, Number of Healthcare Professionals, Service Offerings, Unique Value Proposition, and others)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis for Major Players
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Singapore General Hospital
Tan Tock Seng Hospital
KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital
Mount Elizabeth Hospital
Changi General Hospital
National University Hospital
Raffles Hospital
Parkway Pantai
Thomson Medical Centre
Health Promotion Board
Ministry of Health
Singapore Health Services
IHH Healthcare Berhad
AstraZeneca Singapore
Siemens Healthcare
- Market Demand and Utilization
- Purchasing Power and Budget Allocations
- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
- Needs, Desires, and Pain Point Analysis
- Decision Making Process
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Cost per Bed, 2025-2030


