Market Overview
The Singapore inflight catering market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady service demand across international and regional flight operations. Operational activity is shaped by fluctuating flight schedules and evolving service expectations across multiple cabin classes. Production planning prioritizes reliability, hygiene assurance, and timely airside delivery within constrained operational windows. Capacity utilization varies with travel cycles, requiring flexible staffing and workflow coordination. Digital tools increasingly support demand forecasting and inventory visibility. Service consistency remains central to maintaining airline partnerships and passenger experience expectations.
Singapore concentrates inflight catering activity around major airport infrastructure, supported by dense airline networks and mature cold chain logistics capabilities. The ecosystem benefits from clustered suppliers, specialized food safety laboratories, and efficient airside access protocols. Demand concentration follows long haul and premium traffic flows, while regional connectivity sustains base volumes. Policy frameworks emphasize hygiene, halal compliance, and traceability standards, encouraging process investments. The city environment supports rapid supplier coordination, while ecosystem maturity enables consistent service reliability across diverse airline requirements.
Market Segmentation
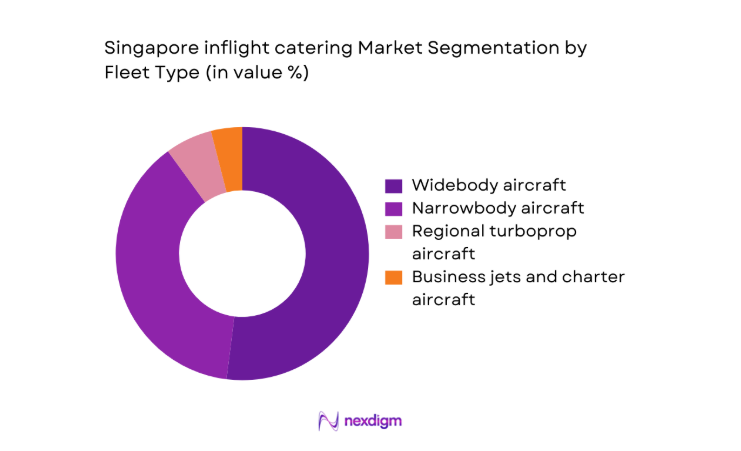
By Fleet Type
Widebody aircraft dominate value contribution because long haul routes require multiple meal services, higher menu complexity, and stricter consistency controls across extended flight durations. Narrowbody aircraft contribute steady baseline demand, yet typically involve simplified service formats and reduced per flight complexity. Business jets and charter operations represent niche demand, but they command premium customization and higher per unit service intensity. Fleet mix decisions by airlines increasingly balance operational efficiency with service differentiation, influencing kitchen scheduling and inventory planning. Standardization across similar aircraft families supports cost control, while mixed fleets require flexible production lines. The dominance of widebody operations therefore reflects both traffic patterns and service architecture, reinforcing their central role in capacity utilization and menu innovation across Singapore facilities.
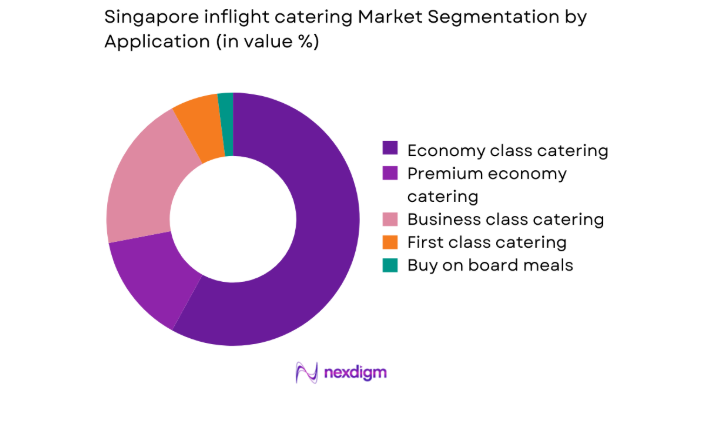
By Application
Economy class catering accounts for the largest service volumes, driven by seat density and frequency across regional and intercontinental routes. Business and first class segments generate disproportionate value through complex menus, premium ingredients, and enhanced presentation standards. Premium economy continues expanding, reflecting airline efforts to bridge service differentiation while maintaining operational efficiency. Buy on board services add incremental volume for low cost carriers, emphasizing packaging efficiency and menu stability. Application mix therefore shapes production workflows, storage requirements, and quality control intensity. The dominance of economy class by volume, combined with premium class by value influence, creates a dual optimization challenge for Singapore kitchens managing throughput and consistency simultaneously.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a small group of scale operators with extensive airline relationships, integrated kitchen infrastructure, and strong compliance capabilities supporting consistent service delivery.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| SATS | 1972 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| dnata | 1959 | Dubai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Gate Gourmet | 1992 | Zurich | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| LSG Sky Chefs | 1942 | Frankfurt | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| DO & CO | 1981 | Vienna | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore inflight catering Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising passenger traffic through Changi Airport
Rising passenger movements increase meal cycles and scheduling complexity, requiring kitchens to optimize throughput while maintaining consistent service reliability. Aircraft rotations in 2024 and 2025 expanded service windows, creating additional production peaks across daily operational timetables. Higher frequencies amplify demand forecasting importance, especially when load factors fluctuate and menu customization requirements differ across route categories. Kitchen utilization metrics improved across 2 successive operational cycles, reflecting better coordination between flight operations and catering logistics. Increased transit flows also raise special meal requests, including medical and cultural preferences, which complicate preparation sequencing. Operational planning teams therefore invest in integrated software tools supporting batch planning and inventory synchronization. Workforce deployment models increasingly rely on flexible shift patterns to accommodate unpredictable scheduling changes. Packaging line optimization becomes critical when multiple aircraft types require simultaneous loading under strict airside security timelines. Rising traffic further elevates scrutiny on hygiene protocols, inspection frequency, and traceability documentation processes. These combined factors structurally reinforce catering demand intensity and elevate operational sophistication requirements across Singapore facilities.
Expansion of premium cabin offerings by full-service carriers
Premium cabin expansion increases menu complexity and ingredient diversity, demanding tighter coordination between procurement teams and culinary development functions. In 2024 and 2025, carriers introduced additional differentiated services, requiring parallel production streams within constrained kitchen footprints. Premium menus involve more assembly steps, elevating labor intensity and extending preparation lead times before flight departures. Quality assurance procedures become stricter, because presentation standards directly influence perceived onboard brand differentiation among high yielding passengers. Storage requirements also expand, since premium ingredients often require segregated temperature-controlled handling and specialized packaging processes. Coordination with airline service design teams becomes more frequent, increasing revision cycles for menus and service concepts. Production scheduling must therefore integrate premium and standard workflows without compromising overall throughput efficiency targets. Training programs for culinary and assembly staff gain importance to maintain consistency across multiple service tiers. Equipment investments focus on precision and repeatability, rather than pure volume handling capabilities. These structural shifts steadily increase the strategic importance of premium focused catering capabilities within Singapore operations.
Challenges
High operating costs and labor constraints in Singapore
Operating environments face persistent labor availability constraints, requiring kitchens to redesign workflows and increase reliance on standardized preparation modules. Staffing models in 2024 and 2025 increasingly incorporate cross training to stabilize productivity during peak flight departure waves. Wage pressure encourages management to prioritize automation, yet implementation cycles remain complex within regulated airside environments. Space limitations further restrict layout optimization, forcing creative scheduling rather than physical expansion of preparation lines. Energy and compliance requirements elevate baseline operational intensity, even when production volumes fluctuate across seasonal travel cycles. Recruitment challenges also influence quality consistency, since frequent onboarding requires extended supervision and retraining periods. Supervisory overhead therefore increases, diverting experienced staff from continuous improvement initiatives and process refinement activities. Outsourcing non core preparation steps becomes tempting, yet integration risks remain significant for time sensitive operations. These constraints collectively reduce operational flexibility during sudden schedule changes or irregular operations. Cost and labor pressures thus remain a structural challenge shaping strategic planning across Singapore inflight catering facilities.
Stringent food safety and halal certification requirements
Regulatory compliance frameworks require continuous documentation, routine audits, and rigorous segregation of preparation zones within production facilities. In 2024 and 2025, inspection cycles intensified, increasing administrative workloads alongside core culinary operations. Halal certification standards impose additional supplier vetting, ingredient traceability, and storage separation requirements across inventory systems. These obligations reduce flexibility in procurement substitutions when supply disruptions occur or menu adjustments become necessary. Training requirements expand, because every operational role must understand contamination risks and procedural control points. Audit readiness also demands parallel record keeping, which consumes managerial attention and information technology resources. Layout changes or process innovations therefore require prior regulatory review, extending implementation timelines for operational improvements. Coordination with airline partners becomes more detailed, since service changes trigger compliance reassessments and documentation updates. The cumulative effect increases process rigidity, even while demand volatility calls for adaptive production responses. Compliance intensity therefore represents a persistent operational constraint alongside quality assurance priorities.
Opportunities
Premiumization of inflight dining experiences
Premiumization initiatives encourage collaboration between culinary teams and airline branding departments, expanding scope for differentiated menu storytelling and presentation design. In 2024 and 2025, several carriers emphasized regional flavors, creating new development cycles and testing protocols. These efforts increase average preparation steps, but also strengthen perceived service value among premium cabin passengers. Kitchens can leverage modular recipe frameworks to balance creativity with repeatability across multiple flight rotations. Supplier partnerships also deepen, as specialty ingredients require coordinated sourcing and quality verification processes. Digital pre selection systems further support premiumization by enabling better demand forecasting and waste reduction strategies. Staff skill development becomes more visible, with plating precision and consistency receiving greater managerial attention. Marketing alignment with onboard service narratives increases cross functional coordination between catering and airline experience teams. These dynamics collectively raise strategic importance of culinary innovation within operational planning structures. Premiumization therefore offers a pathway toward service differentiation without relying solely on volume expansion.
Partnerships with celebrity chefs and local F&B brands
Collaborations with well known culinary brands create marketing visibility while introducing controlled complexity into menu development and production processes. In 2024 and 2025, such partnerships emphasized limited edition offerings, requiring precise forecasting and coordinated promotional scheduling. These programs demand strict recipe adherence, protecting brand integrity while maintaining scalability across flight networks. Kitchens benefit from knowledge transfer, gaining new preparation techniques and presentation standards adaptable to aviation constraints. Supplier ecosystems also expand, as specialty components require integration into existing procurement and quality assurance frameworks. Communication with airline marketing teams intensifies, aligning launch timing with route strategies and cabin positioning objectives. Operational rehearsals become essential, ensuring consistency before broader rollout across multiple flights and aircraft types. Data feedback loops then inform iteration, refining offerings based on passenger acceptance and operational practicality. These partnerships therefore create both differentiation opportunities and structured innovation pipelines. Strategic execution determines whether brand collaborations translate into sustainable service enhancements.
Future Outlook
The Singapore inflight catering market is expected to evolve toward greater service differentiation, operational automation, and deeper integration with airline experience strategies. Regulatory rigor will remain high, encouraging continued investment in compliance systems. Fleet and route adjustments will shape production planning approaches. Collaboration across the aviation ecosystem will increasingly define competitive positioning through service quality rather than scale alone.
Major Players
- SATS
- dnata
- Gate Gourmet
- LSG Sky Chefs
- DO & CO
- Newrest
- Servair
- Flying Food Group
- Royal Holdings Services
- ANA Catering Service
- Emirates Flight Catering
- KLM Catering Services
- Qantas Catering
- Cathay Pacific Catering Services
- AAS Catering
Key Target Audience
- Full-service airlines operating international routes
- Low-cost carriers with buy on board programs
- Charter and ACMI aircraft operators
- Airport authorities and airside operations management bodies
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Aircraft leasing companies managing service specifications
- Inflight service design and experience management teams
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Operational variables were mapped across fleet types, cabin classes, kitchen workflows, and compliance obligations. Service demand patterns were aligned with flight schedules, route structures, and turnaround constraints. Process dependencies were defined across sourcing, preparation, assembly, and airside delivery stages.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Service architecture was constructed around aircraft categories, meal complexity tiers, and volume handling requirements. Capacity utilization patterns were analyzed across peak and off-peak operational cycles within airport infrastructure. Ecosystem linkages between airlines, caterers, suppliers, and regulators were structurally mapped.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Operational assumptions were validated through structured consultations with kitchen managers and logistics coordinators. Culinary development workflows were reviewed to assess scalability under regulatory constraints. Service consistency risks were tested against irregular operations and demand variability scenarios.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into integrated operational and market structure narratives. Cross-sectional insights were reconciled across fleet, application, and service delivery dimensions. Final outputs were structured to reflect strategic, operational, and regulatory interdependencies.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope of inflight catering services across full-service and LCC operations in Singapore, fleet and route-based service taxonomy for narrowbody and widebody operations, bottom-up meal count modeling linked to seat capacity and load factor data, revenue attribution by meal class mix and ancillary buy-on-board penetration, primary interviews with airline catering managers and airport concession operators at Changi)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Service delivery and meal provisioning workflows
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and cold-chain logistics structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising passenger traffic through Changi Airport
Expansion of premium cabin offerings by full-service carriers
Growth in low-cost carrier buy-on-board revenues
Recovery and growth of international long-haul routes
Airline focus on brand differentiation through onboard experience
Increased frequency of regional short-haul flights - Challenges
High operating costs and labor constraints in Singapore
Stringent food safety and halal certification requirements
Volatility in airline capacity deployment
Supply chain disruptions for imported food ingredients
Pressure on catering margins from airline cost controls
Complex airside logistics and security compliance - Opportunities
Premiumization of inflight dining experiences
Partnerships with celebrity chefs and local F&B brands
Sustainable packaging and waste reduction solutions
Digital pre-order and personalization of inflight meals
Expansion of halal-certified premium catering for regional traffic
Outsourced catering growth from foreign carriers operating in Singapore - Trends
Menu localization and seasonal rotation
Shift toward sustainable and recyclable packaging
Increased pre-order and data-driven meal forecasting
Growth of ancillary food and beverage sales on LCCs
Automation in kitchen operations and inventory management
Focus on health-oriented and special-diet meal options - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft
Widebody aircraft
Regional turboprop aircraft
Business jets and charter aircraft - By Application (in Value %)
Economy class catering
Premium economy catering
Business class catering
First class catering
Buy-on-board meals - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Centralized flight kitchens
Commissary-based distributed kitchens
On-board galley preparation systems
Automated meal assembly and packaging systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Full-service carriers
Low-cost carriers
Charter and ACMI operators
Private and business aviation - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Hub-based catering at Changi Airport
Spoke-based regional catering partnerships
Cross-border catering for transit flights
Off-airport production with airside logistics - By Region (in Value %)
Singapore Changi Airport terminals
Seletar Airport
Regional partner kitchens in Southeast Asia
International catering supply corridors
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (fleet coverage, service portfolio breadth, production capacity, quality certifications, pricing competitiveness, sustainability initiatives, airline contract tenure, operational reliability metrics)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
SATSG
dnata
Gate Gourmet
LSG Sky Chefs
Cathay Pacific Catering Services
Flying Food Group
DO & CO
Newrest
AAS Catering
Royal Holdings Services
Servair
KLM Catering Services
ANA Catering Service
Emirates Flight Catering
Qantas Catering
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


