Market Overview
The South Korea BNPL market is valued at USD 2.09 billion, based on detailed research covering historical data through 2023 and validated 2024 estimates. Growth through 2024 reflects rising consumer trust, increased e‑commerce transactions, and adoption of instant‑approval, zero‑interest installment models as standard checkout options.
The market is dominated by major urban economic hubs such as Seoul, Busan, and Incheon, where e‑commerce density, smartphone penetration, and digital wallet usage are among the highest nationwide. These regions benefit from concentrated tech ecosystems, superior logistics infrastructure, and dense retail networks that foster rapid BNPL integration.
Market Segmentation
By Channel
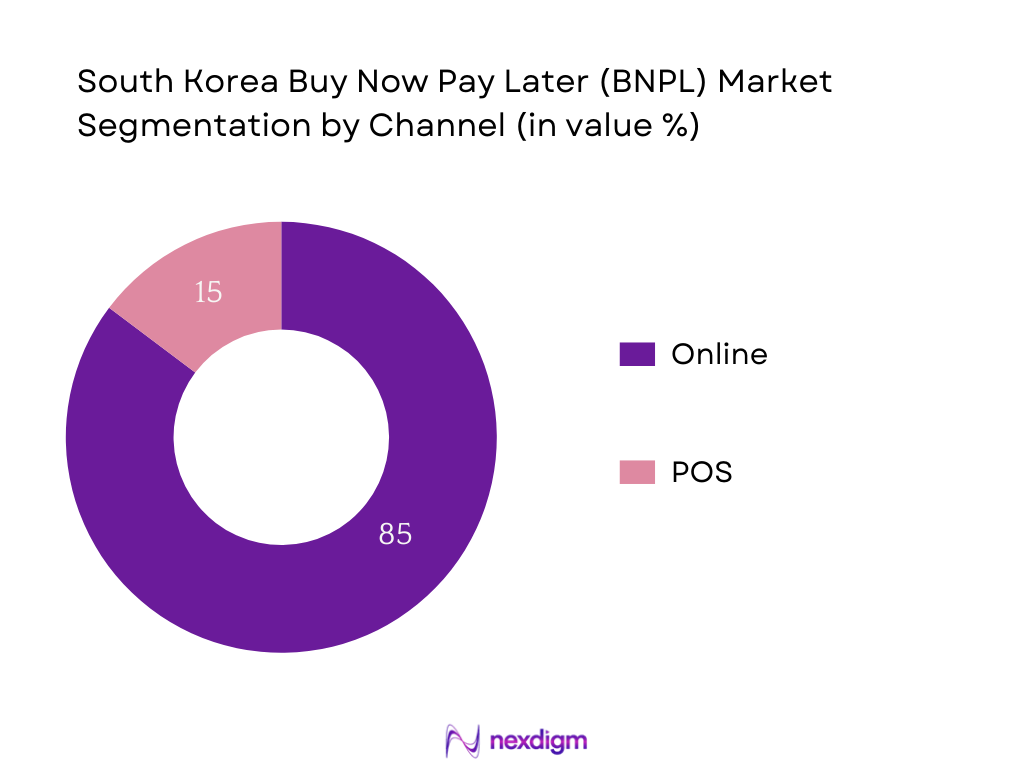
South Korea BNPL market is segmented by channel into online and POS. The online channel holds a dominant market share at 85% in 2024, driven by pervasive smartphone use, seamless integration with e‑commerce platforms like Coupang, Naver, and Kakao, and preference for contactless payments.
By End-Use Sector
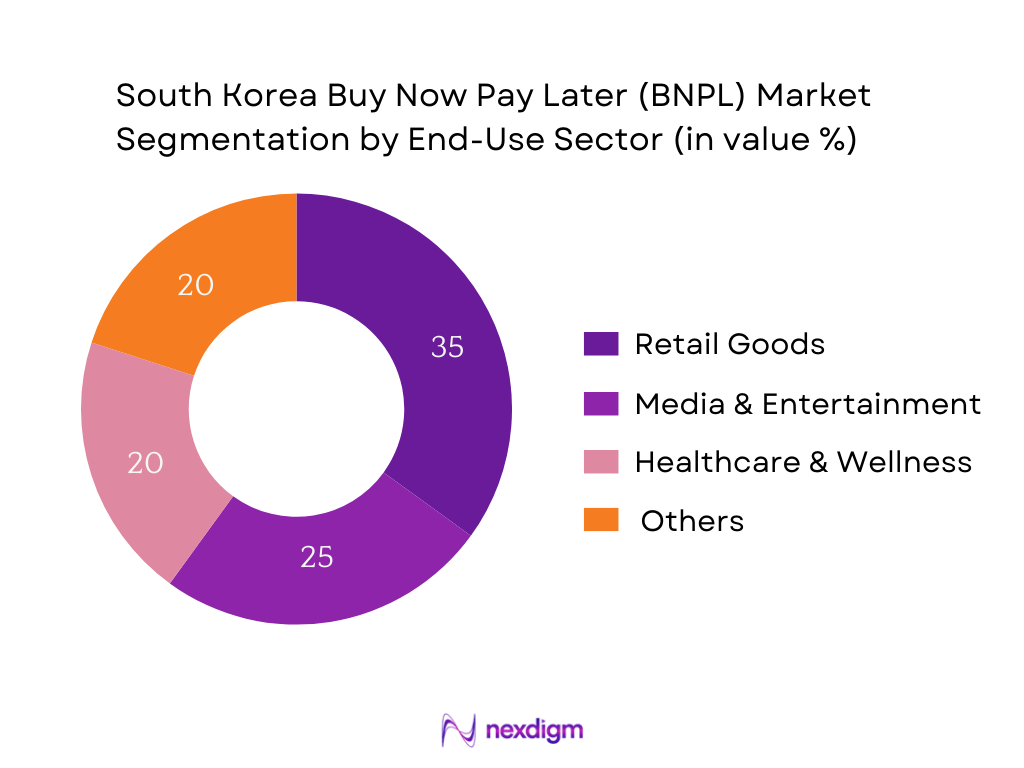
In South Korea’s BNPL market, the Retail Goods segment leads, underpinned by high demand for electronics, fashion, and daily essentials. Consumers favor flexible payments for mid‑ to high‑ticket purchases—such as smartphones, apparel, and home goods—especially within digital marketplaces. The strong digital retail infrastructure, paired with tailored installment plans, reinforces this segment’s prominence.
Competitive Landscape
The South Korea BNPL market is concentrated among a mix of domestic fintech and financial-institution–backed players. Leading platforms include Naver Financial, Coupang Pay‑Later, Toss (Viva Republica), KakaoPay, Hyundai Card, and others. Their integrated digital ecosystems and advanced credit‑assessment technologies confer them dominant influence.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters (City) | Super‑App Integration (Depth) | AI‑Credit Scoring (Y/N) | Merchant Partnerships (Breadth) | Fee Structure (Flexibility) | Regulatory Compliance Capability | Consumer Trust / Brand Equity |
| Naver Financial BNPL | — | Seoul | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Coupang Pay‑Later | — | Seoul | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Toss (Viva Republica) | — | Seoul | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| KakaoPay Later | — | Seoul | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Hyundai Card Installments | — | Seoul | — | — | — | — | — | — |
South Korea BNPL Market Analysis
Key Growth Drivers
Surge in Mobile E‑Commerce Transactions
South Korea’s mobile-first consumer environment is a significant catalyst for BNPL growth. In 2024, 75% of online purchases were completed via mobile devices, illustrating strong smartphone transaction behavior. Furthermore, South Korea’s real-time payments system processed 9.1 billion transactions in 2023, showing extraordinary digital payments infrastructure usage. These numbers indicate that BNPL providers benefit from a frictionless, tech-enabled checkout experience. High smartphone usage and real-time infrastructure emphasize how consumers prefer instant, integrated mobile payment options—a perfect environment for BNPL adoption, allowing seamless installment integration at checkout without friction.
Integration with Super‑App Ecosystems
South Korea’s digital landscape features highly sophisticated super‑apps such as Kakao and Naver, which embed multiple services within a single interface. The underlying digital infrastructure—backed by government e‑governance strategy 2021–2025—supports open APIs, MyData, blockchain-enabled authentication, and public-private collaboration. These digital government initiatives have accelerated private sector integration with platforms, enabling BNPL providers to seamlessly plug into widely used apps. As a result, when consumers use Kakao or Naver, they encounter embedded BNPL options within familiar environments. The technological readiness and regulatory frameworks ensure BNPL offerings are secure, compliant, and frictionless—enhancing uptake and trust through established ecosystem embedding.
Key Market Challenges
Regulatory Oversight under Financial Consumer Protection Act
South Korea enforces robust consumer protection frameworks, including digital finance oversight. As part of its 2021–2025 digital government roadmap, the state advances secure authentication, MyData privacy, and API governance. These layers of regulation ensure data sovereignty and consumer rights. BNPL actors must comply with fintech-specific rules from bodies like the Financial Services Commission (FSC). Meeting the stringent e‑payment, disclosure, and consumer data standards raises operational complexity. Firms are required to invest in compliance systems, legal counsel, and data governance. While these structures enhance trust, they also increase the cost of entry for new BNPL players and slow rapid innovation—creating friction, particularly for fintech startups aiming to iterate quickly within tight regulatory boundaries.
Rising Delinquencies in Non‑Traditional Lending
While specific South Korean BNPL delinquency data is scarce, global trends raise concerns. For instance, LendingTree reports 41% of BNPL users globally made late payments in the past year, up from 34% previously. These patterns pose risks for Korean providers, as non‑traditional consumers may default on installments. Rising delinquency elevates provisioning costs and undermines profitability, challenging BNPL viability. Given South Korea’s high digital engagement and low credit culture, defaults could dampen investor confidence if repayment becomes unpredictable. BNPL players must strengthen repayment monitoring and recovery protocols to mitigate risks in underwritten consumer segments.
Emerging Opportunities
BNPL Expansion into Subscription and Healthcare Financing
BNPL’s application beyond retail—such as subscriptions and healthcare—offers diversification potential. South Korea recorded USD 148.5 billion in retail e‑commerce volume in 2024, indicating mature consumer digital activity. Within this ecosystem, adjacent verticals like online subscriptions (media, streaming) and digital health services (e‑clinics, wellness platforms) account for a growing share of transactions. By leveraging existing digital payment habits, BNPL providers can extend their installment models into recurring charges—for example installment-based gym memberships or digital therapy packages. Although precise stats for healthcare payments are lacking, the robust baseline of digital commerce suggests scalability in these adjacent sectors. Embedding BNPL for subscriptions taps into consumer comfort with recurring payments and the digital ecosystem, fostering retention and expanding provider reach.
Merchant‑Embedded BNPL through POS and APIs
South Korea’s infrastructure supports seamless integration at merchant points: the real-time payments system processed 9.1 billion transactions in 2023. Coupled with widespread API adoption via digital government initiatives, this enables BNPL deployment directly at checkout in both online and physical stores. Retailers can embed BNPL into POS systems through APIs, offering instalment options on the spot. This reduces cart abandonment and enhances acceptance among brick-and-mortar merchants, especially in electronics outlets or lifestyle shops where installment culture is strong. Given consumers’ digital payments dominance (only 7% POS cash in 2024), merchant-embedded BNPL aligns with both retailer and consumer behaviors—creating a compelling expansion avenue.
Future Outlook
South Korea’s BNPL sector is poised for sustained growth, driven by broader fintech adoption, evolving consumer payment preferences, and regulatory support for digital financing models. As super‑apps expand their ecosystems and AI‑powered credit assessment matures, BNPL services will deepen integration across retail channels, further enhancing consumer convenience and market penetration.
Major Players
- Naver Financial BNPL
- Coupang Pay‑Later
- Toss (Viva Republica) BNPL
- KakaoPay Later
- Hyundai Card Installment Service
- KB Kookmin Card (BNPL modules)
- Shinhan Card (BNPL initiatives)
- Woori Card (Fintech adoptions)
- Hana Card (BNPL services)
- NH Nonghyup Card (Fintech offerings)
- Atome Korea
- Sezzle
- Klarna (PULP)
- PayPal BNPL
Key Target Audience
- E‑commerce platform decision‑makers (e.g., heads of digital payments at Coupang, Naver, Kakao)
- Fintech innovation leaders at Toss, KakaoPay, Naver Financial
- Heads of digital strategy at major credit card issuers (Hyundai, KB, Shinhan)
- Investments and venture capitalist firms evaluating SK fintech opportunities (e.g., Korea Investment Partners, SoftBank Ventures Asia)
- Government and regulatory bodies (Financial Services Commission, Financial Supervisory Service)
- Heads of consumer finance divisions at major banks with BNPL initiatives
- Retail chain CFOs exploring embedded finance (e.g., Lotte, Shinsegae)
- Logistics and tech enablers supplying checkout systems
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research commenced with mapping stakeholders in the South Korea BNPL ecosystem—including BNPL providers, e‑commerce platforms, credit issuers, and regulators—using desk research from secondary sources.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compiled historical GMV and revenue data for the BNPL market (2021–2024), segmenting by channel and end‑use sector. Attention was paid to validation through multiple report sources to triangulate market size (e.g., USD 2.09 bn in 2023, USD 3.78 bn GMV in 2024).
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Preliminary market trends and forecasts were reviewed through expert consultations (virtual interviews) with industry analysts familiar with South Korean fintech and BNPL dynamics to refine assumptions—particularly around adoption trends and future growth drivers.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Final validation included cross‑checking numeric projections with updated report data (e.g., CAGR, market size) to ensure accuracy. The outcome is a validated, industry-ready analysis tailored for strategic decision‑makers.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Timeline of Major Player Entry (Naver Financial, Coupang Pay, Toss, Hyundai Card, etc.)
- BNPL Business Cycle in South Korea
- Value Chain and Stakeholder Analysis (Consumer – Platform – BNPL Provider – Regulator)
- Key Growth Drivers
Surge in Mobile E-Commerce Transactions
Integration with Super-App Ecosystems
Increasing Credit Aversion Among Young Adults
Rise of AI-Powered Risk Modeling - Key Market Challenges
Regulatory Oversight under Financial Consumer Protection Act
Rising Delinquencies in Non-Traditional Lending - Emerging Opportunities
BNPL Expansion into Subscription and Healthcare Financing
Merchant-Embedded BNPL through POS and APIs - Trends
Fee-Free Installments as a Standard Expectation
Custom Credit Tenure Offerings by Cohort - Government Regulation
Role of Financial Services Commission (FSC)
Electronic Financial Transactions Act and BNPL Guidelines - SWOT Analysis (Market-Specific SWOT)
- Stake Ecosystem (Consumer, BNPL Tech Providers, Regulators, Merchants)
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Ecosystem (Domestic and Foreign Players in South Korea)
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Ticket Size, 2019-2024
- By Distribution Channel (In Value %)
Online Platforms
POS Retail Partners
Super-Apps (KakaoPay, NaverPay)
Embedded Finance via E-Commerce
Offline Department Stores - By End-Use Sector (In Value %)
Consumer Electronics
Fashion and Lifestyle
Healthcare and Wellness
Travel & Leisure
Digital Content & Subscription Services - By Consumer Demographic (In Value %)
Gen Z (18–25)
Millennials (26–40)
Gen X (41–55)
Baby Boomers (56+)
Students and First-time Credit Users - By Provider Type (In Value %)
Fintech Startups
Traditional Banks
E-Commerce Anchored BNPL Providers
Credit Card Companies
Payment Gateway Aggregators - By Credit Scoring Model (In Value %)
Traditional Bureau-Based
AI/ML Driven Risk Assessment
Alternative Data Model
Hybrid Models
No-Credit Scoring Instant Approval
- Market Share Analysis (By Value and Volume for Leading Players)
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Tech Stack, Super-App Integration Capability, Consumer Trust Score, AI-based Risk Engine, APR & Fee Structure, Merchant Network Breadth, Regulatory Compliance Infrastructure)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis of Leading Providers
- Company Profiles of Major Players
Naver Financial
Coupang Pay
Toss (Viva Republica)
KakaoPay
Hyundai Card
KB Kookmin Card
Shinhan Card
Atome Korea
Sezzle
Klarna
PayPal BNPL (South Korea)
Woori Card
Hana Card
Lotte Card
NH Nonghyup Card
- Adoption Rates and Intent Metrics
- Credit Usage Patterns by Age and Spend Type
- End-User Risk Appetite
- Merchant Onboarding Funnel and API Adoption
- Behavioral Insights and Default Pattern Analysis
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Ticket Size, 2025-2030


