Market Overview
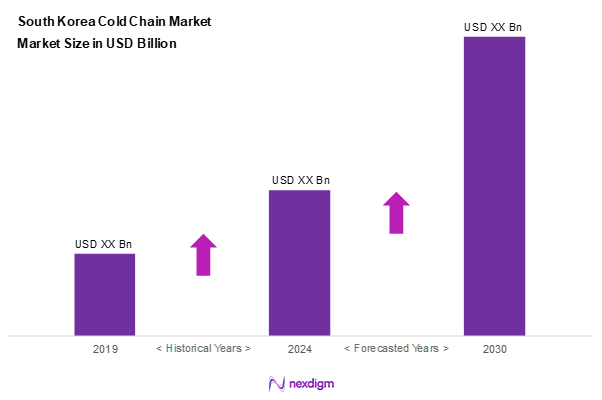
As of 2024, the South Korea cold chain market is valued at USD ~ billion, with a growing CAGR of 10.2% from 2024 to 2030, supported by the increasing demand for perishable goods and the rise in e-commerce. Factors such as technological innovations in logistics and stricter food safety regulations contribute to this growth. The market remains robust as retailers and food producers increasingly invest in efficient supply chain solutions to meet evolving consumer preferences.
Seoul stands out as the dominant city in the South Korean cold chain market, driven by its status as the nation’s capital and a major economic hub. It accounts for a significant portion of the market due to the high population density, extensive logistics infrastructure, and proximity to major suppliers. Other critical cities include Busan, which has significant port facilities, making it an essential node for imports and exports.
Market Segmentation
By Application
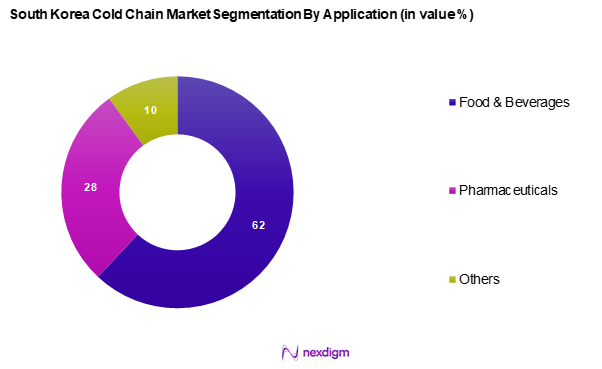
The South Korea cold chain market is segmented into food & beverages, pharmaceuticals, and others. The food & beverages segment holds a dominant market share due to the country’s growing consumer demand for fresh and frozen products. As consumer preferences shift towards healthier meal options and the convenience of frozen foods, companies are increasingly investing in cold chain logistics to preserve product quality. This segment is especially vital in regions with high consumption of perishables, ensuring the food supply chain remains intact.
By Temperature Range
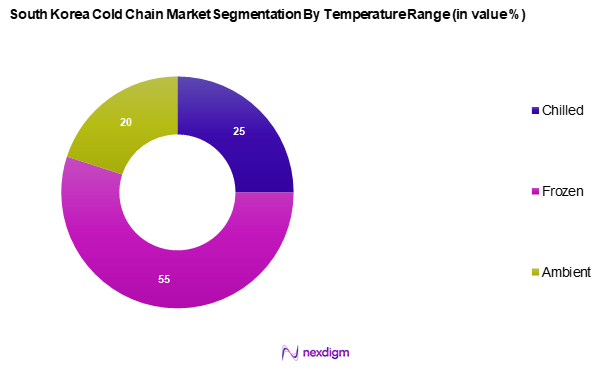
The South Korea cold chain market is segmented into chilled, frozen, and ambient. The frozen segment commands a substantial share as it caters to a variety of consumer needs, including processed foods and ready-to-eat meals. This dominance is attributed to the extended shelf life that frozen products offer, which aligns with consumer preferences for convenience and quality. Frost-free storage techniques and freezer technologies are rapidly improving, further enhancing the frozen segment’s attractiveness.
Competitive Landscape
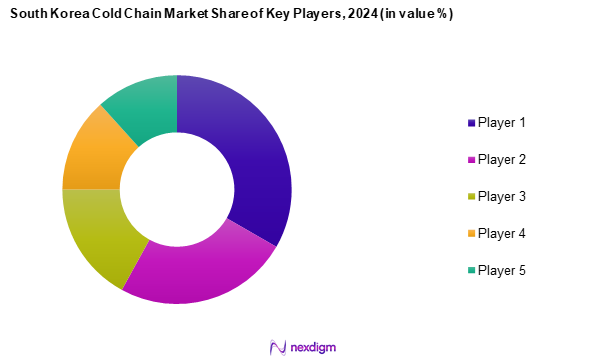
The South Korea cold chain market is dominated by key players such as CJ Logistics, Lotte Logistics, DB Schenker, DHL, and Dongwon Industrial. These companies have leveraged technological advancements to enhance their service offerings and meet the demands of an evolving consumer base. This market consolidation highlights their strong operational capabilities and extensive logistics networks, which contribute to improved efficiency and service reliability. The sector also faces significant competition from both local and international logistics providers. The table below highlights five major companies operating in this market.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Revenue (2024) | Services Offered | Market Focus | Technological Capabilities |
| CJ Logistics | 1930 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
| Lotte Logistics | 1996 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
| DB Schenker | 1872 | Essen, Germany | – | – | – | – |
| DHL | 1969 | Bonn, Germany | – | – | – | – |
| Dongwon Industrial | 1969 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
South Korea Cold Chain Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rise in E-commerce and Online Grocery
The growing prominence of e-commerce platforms in South Korea has significantly reshaped consumer purchasing behavior, particularly in the grocery segment. As more consumers opt for the convenience of ordering perishables online, the cold chain logistics sector has been compelled to evolve in response. Enhanced expectations for rapid delivery and the assurance of freshness have led to heightened investments in cold storage, refrigerated transport, and last-mile temperature-controlled delivery systems. The expanding digital economy and deeper internet penetration are reinforcing the reliance on sophisticated cold chain solutions to meet modern retail demands.
Increasing Demand for Perishable Goods
Consumer preferences in South Korea have shifted notably toward fresh and minimally processed food items, such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Heightened awareness around health and wellness has driven this trend, resulting in greater emphasis on food quality and safety. As consumers increasingly prioritize nutritional value and freshness, there is a growing dependence on cold chain infrastructure to ensure seamless delivery from producers to consumers. This change in consumption patterns underscores the need for an efficient and reliable cold logistics system across the country.
Market Challenges
Regulatory Compliance Issues
Operators in the South Korean cold chain market face considerable challenges in adhering to evolving food safety and pharmaceutical storage regulations. Strict government oversight requires logistics providers to maintain rigorous temperature control and hygiene standards. Compliance with these regulations often demands significant investments in facility upgrades and operational practices. For many small and medium-sized enterprises, meeting these standards presents a financial and technical hurdle, potentially limiting their competitiveness and market participation.
Infrastructure Limitations
Cold chain infrastructure in South Korea still grapples with several limitations, particularly regarding the availability and modernity of cold storage and refrigerated transportation assets. Many distribution companies lack adequate facilities to support the growing demand for perishable goods, particularly in rural or less developed regions. As urban populations expand and consumer expectations evolve, the pressure on logistics networks continues to mount. Without substantial infrastructure development, the sector risks operational bottlenecks and inefficiencies that could impede market growth.
Opportunities
Rise of Smart Cold Chain Solutions
The integration of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled sensors and real-time monitoring systems, is transforming cold chain logistics in South Korea. These innovations are enhancing operational transparency and control, allowing companies to track temperature-sensitive goods throughout the supply chain with greater precision. The adoption of data-driven logistics tools not only improves inventory management and reduces spoilage rates but also builds consumer trust in product quality. As technology becomes more accessible, companies have a strong incentive to modernize and digitize their operations to remain competitive.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
South Korea’s expertise in cold chain management positions its logistics providers well for regional expansion, especially in rapidly urbanizing and economically developing areas of the Asia-Pacific. As demand for quality perishables and temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals increases in these markets, South Korean firms have the opportunity to establish strategic partnerships and extend their services. By capitalizing on this growth potential, companies can diversify their market base and reinforce their leadership in cold chain innovation beyond domestic borders.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the South Korea cold chain market is expected to witness substantial growth driven by technological advancements, increased urbanization, and rising consumer demand for perishable goods. Government support for infrastructure improvement and sustainability initiatives will further bolster the market, ensuring it adapts to future challenges and opportunities.
Major Players
- CJ Logistics
- Lotte Logistics
- DB Schenker
- DHL
- Dongwon Industrial
- Borim Logistics
- Dongbu Express
- Hansol Logistics
- Daelim Corporation
- GS Global
- Ottogi Logistics Service Co., Ltd.
- Pantos Logistics
- Yusen Logistics
- Samsung SDS
- Hanjin Transportation
Key Target Audience
- Investors and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Korea Customs Service)
- Retail Chains
- Food and Beverage Manufacturers
- Pharmaceutical Companies
- Logistics and Distribution Providers
- E-commerce Platforms
- Cold Storage Facility Operators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map encompassing all major stakeholders within the South Korea Cold Chain Market. This step is supported by extensive desk research, utilizing a combination of secondary and proprietary databases to gather comprehensive industry-level information. The aim is to identify and define the critical variables that influence market dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, we compile and analyze historical data pertaining to the South Korea Cold Chain Market. This includes assessing market penetration, the ratio of marketplaces to service providers, and the resultant revenue generation. Additionally, an evaluation of service quality statistics will be conducted to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the revenue estimates.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses will be developed and subsequently validated through computer-assisted telephone interviews (CATIs) with industry experts representing a diverse array of companies. These consultations will provide valuable operational and financial insights directly from industry practitioners, which will be instrumental in refining and corroborating the market data.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves direct engagement with multiple cold chain logistics providers to acquire detailed insights into product segments, sales performance, consumer preferences, and other pertinent factors. This interaction will serve to verify and complement the statistics derived from the bottom-up approach, thereby ensuring a comprehensive, accurate, and validated analysis of the South Korea Cold Chain Market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Overview Genesis
- Timeline of Major Players
- Business Cycle
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Rise in E-commerce and Online Grocery
Increasing Demand for Perishable Goods - Market Challenges
Regulatory Compliance Issues
Infrastructure Limitations - Opportunities
Rise of Smart Cold Chain Solutions
Expansion into Emerging Markets - Trends
Adoption of IoT and AI in Cold Chain
Increased Sustainability Practices - Government Regulation
Food Safety Standards
Environmental Regulations - SWOT Analysis
- Stake Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Price, 2019-2024
- By Application, (In Value %)
Food & Beverages
Dairy Products
Fish, Meat, and Seafood
Pharmaceuticals
Others - By Temperature Range, (In Value %)
Chilled
Frozen
Ambient - By Mode of Transportation, (In Value %)
Road
Rail
Air
Sea - By Market Structure, (In Value %)
Organized
Unorganized - By Service, (In Value %)
Storage
Transportation
Value-added Services - By Technology, (In Value %)
Blast Freezing
Evaporative Cooling
Vapor Compression
Cryogenic Systems
Programmable Logic Controller
- Market Share of Major Players on the Basis of Value/Volume, 2024
Market Share of Major Players by Type of Application Segment, 2024 - Cross-Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Recent Developments, Strength, Weakness, Market Share, Technological Capabilities, Customer Base, Revenue, Distribution Networks, and Others)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis Basis SKUs for Major Players
- Profiles of Major Companies
Lotte Logistics
CJ Logistics
Dongwon Industrial
Borim Logistics
Dongbu Express
Hansol Logistics
DB Schenker
Daelim Corporation
GS Global
DHL
Ottogi Logistics Service Co., Ltd.
Pantos Logistics
Yusen Logistics
Others
- Consumer Demand and Behaviour
- Industry-Specific Requirements and Budget Allocations
- Needs Assessment of Key Stakeholders
- Decision-Making Processes in Procurement
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Price, 2025-2030


