Market Overview
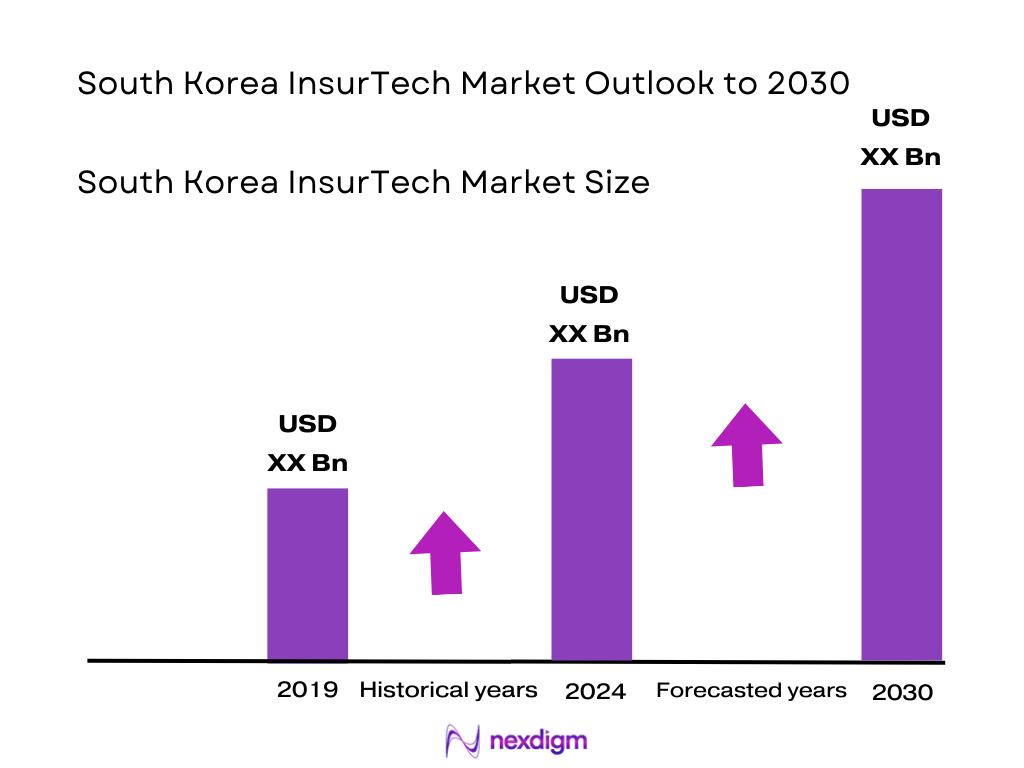
The South Korea InsurTech market is valued at approximately USD 195.70 million in 2024. Growth is underpinned by a rapid rise in demand for microinsurance solutions, increased partnerships between InsurTechs and fintech/e‑commerce platforms, and consumer preference shifting toward digital‑first insurance purchase and claims processing. In the prior period (historical base up to 2023), the market had been growing steadily, with technology enablers (AI, IoT, big data) being adopted by both traditional insurers and start‑ups.
Seoul (Seoul Capital Area) dominates South Korea’s InsurTech market as the central hub for technology firms, financial institutions, and regulatory bodies. Many InsurTech start‑ups, including Carrot General Insurance, and data & monitoring companies like Signal Planner, are headquartered in Seoul, benefiting from proximity to venture capital, regulatory agencies (FSS, FSC), major insurer headquarters, and advanced infrastructure. The concentration of digital infrastructure, high smartphone penetration, and consumer readiness in metropolitan regions (Seoul, Gyeonggi‑do) contribute further to dominance.
Market Segmentation
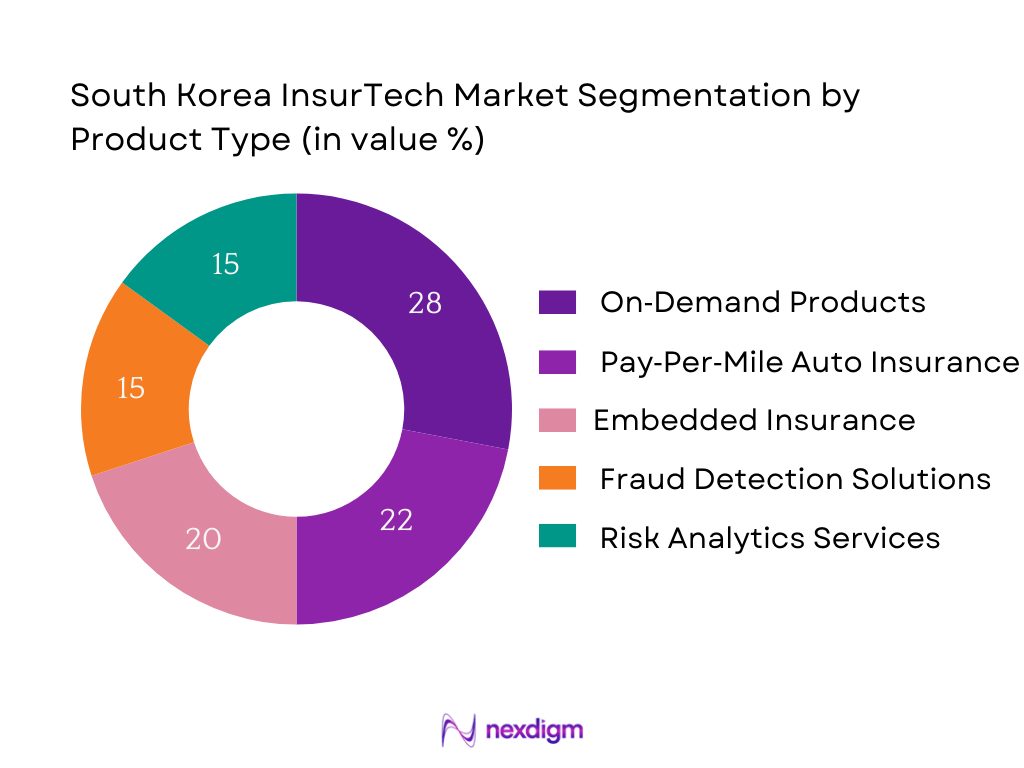
By Product / Service Type
Microinsurance & On‑Demand Products dominate the South Korea InsurTech market because they offer affordable, flexible coverage options aligned with modern consumer preferences, especially among younger, digitally native, or gig economy workers. The friction of traditional insurance (high premiums, cumbersome documentation, less flexibility) leads consumers to prefer smaller, needs‑based products. InsurTech firms are exploiting this by introducing on‑demand coverage that can be purchased immediately (e.g. for travel, pet insurance, device protection) and microinsurance policies that require lower capital or underwriting burdens. Also, regulatory allowances for digital sales and the adoption of mobile apps accelerate distribution.
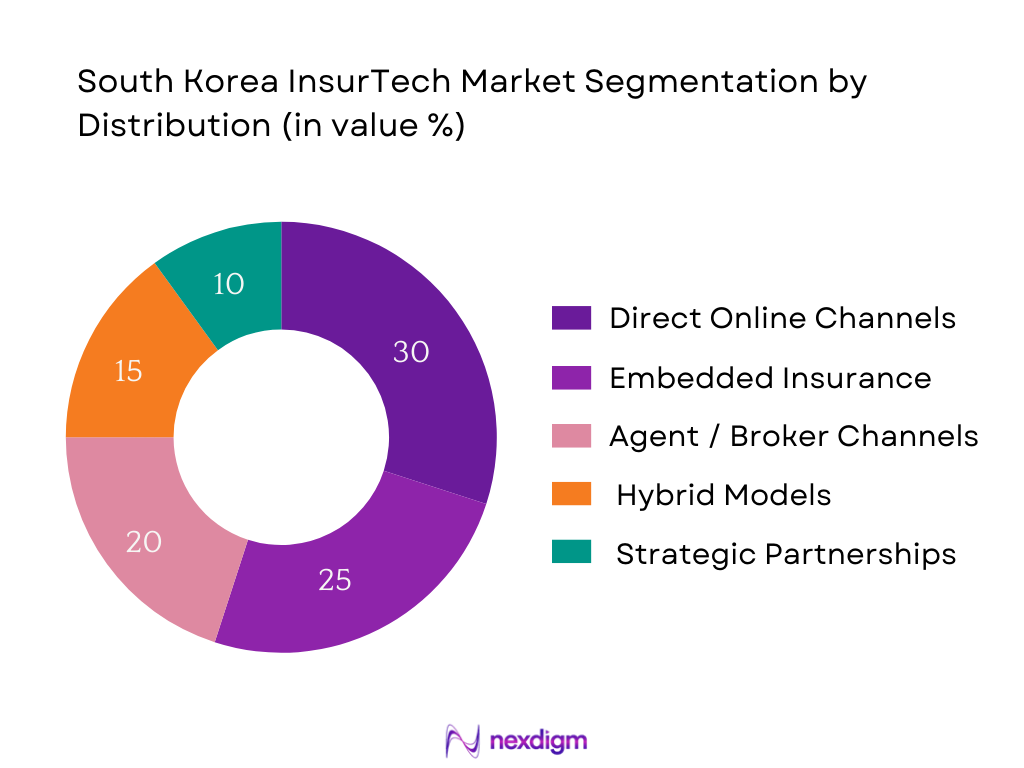
By Distribution / Channel Model
Fully Digital / Direct Online Channels dominate due to an increasing consumer comfort with purchasing insurance via apps or websites, combined with high smartphone penetration and robust e‑KYC and digital identity infrastructure in South Korea. InsurTech start‑ups like Carrot focus on direct digital channels, bypassing intermediaries, allowing for lower customer acquisition costs, faster underwriting and claims, real‑time premium calculation (as in pay‑per‑mile auto insurance), and app‑based policy management. Regulatory flexibility around digital solicitation and the push by consumers for immediacy and transparency also favor direct digital models. These factors give digital direct channels an edge over more traditional agent‑based models.
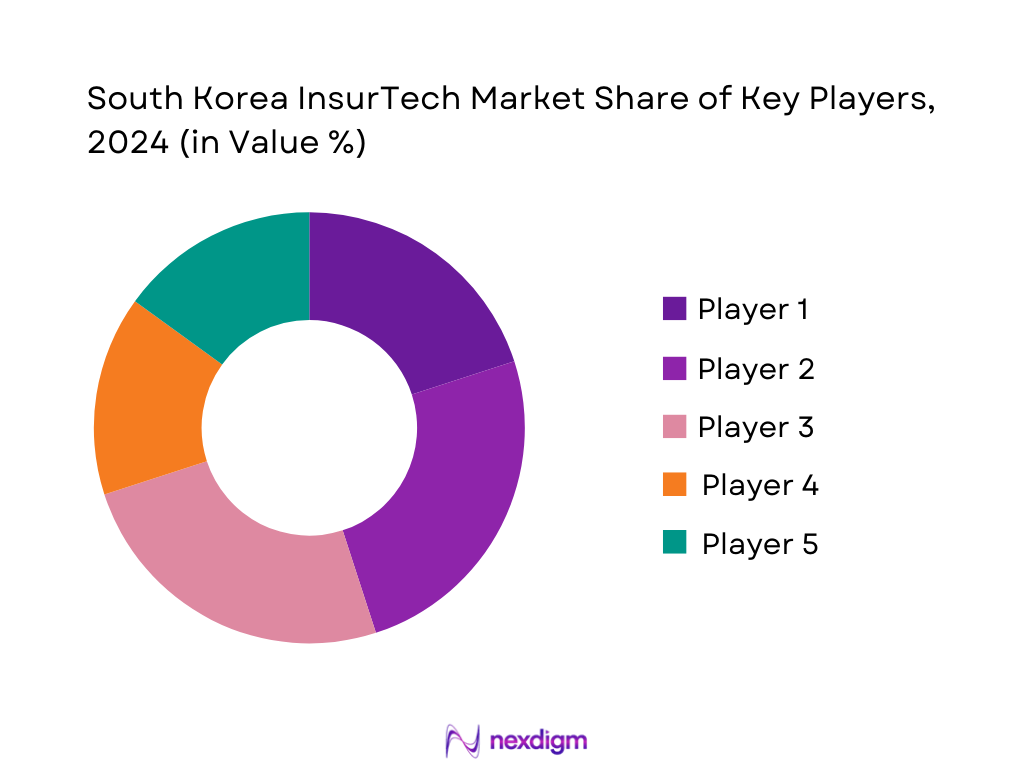
Competitive Landscape
The South Korea InsurTech market features a mix of digital insurgents (start‑ups) and incumbents adapting digitally. Among key players, Carrot General Insurance is prominent as the first fully licensed 100% digital insurance carrier. Signal Planner is notable for its data‑monitoring capabilities. There’s growing competition in embedded insurance, usage‑based auto insurance, and behavior‑based insurance models.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Fully Digital Insurer / Product Focus | Key Technology / Innovation Parameter | Distribution Strategy | Renewal / Retention Rates / Customer Loyalty | Regulatory / Licensing Status | Recent Funding or Valuation Highlights |
| Carrot General Insurance | 2019 | Seoul | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Signal Planner | 2018 | Seoul | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Habit Factory | N/A (startup) | Seoul | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| KB Insurance | Long-standing incumbent | Seoul | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hanwha Insurance / Hanwha Life | Incumbent (non-life / life) | Seoul | – | – | – | – | – | – |
South Korea InsurTech Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rise of Smartphone-Based Distribution
Mobile connectivity in Korea is effectively universal at scale, creating a ready rail for app-first insurance sales and claims. Mobile cellular subscriptions stand at 162.114 per 100 people, indicating multiple lines per person and dense device reach that supports push-notifications, photo claims and telematics uploads. This density sits atop an internet user base that ranks among the world’s highest, and a policy setting prioritizing ubiquitous broadband. These rails translate directly into higher activation for non-face-to-face insurance enrollment and in-app servicing, reducing cycle time for quote-bind-issue and enabling micro-duration covers aligned to on-demand usage.
Regulatory Push for Digital-First Insurance
Korea’s financial authorities have leaned into data portability and digital rails that insurers can plug into. The Financial Services Commission’s regulatory sandbox has cleared 82 innovative financial services over two years, while open banking and loan transfer infrastructure were elevated in the 2024 work plan—all of which insurers leverage for instant eligibility checks and embedded issuance. In parallel, MSIT’s Digital Strategy of Korea and 2024 Work Plan place AI/5G as national infrastructure, with projects to apply 5G and AI “to all sectors of industry,” giving carriers concrete programs to automate underwriting and claims on secure, high-throughput networks.
Market Challenges
High Customer Acquisition Cost (Crowded Digital Commerce Rail)
Although Korea’s digital advertising unit costs are proprietary, macro transaction density signals intense competition for consumer attention where embedded and direct-to-consumer insurers bid for the same checkout moments. KOSTAT reported KRW 21.2147 trillion in monthly online transactions and KRW 16.2048 trillion mobile—large, recurrent baskets concentrated on a few peak platforms. In cross-border channels alone, purchases from China totaled KRW 4.7 trillion, dominated by a single marketplace group—raising the bar for paid placement and partner slotting. For insurers, winning shelf space in these high-velocity rails requires sustained spend and data partnerships.
Price Pressure Among Aggregators & InsurTechs (Concentrated Platforms)
Platform concentration in overseas online shopping magnifies pricing pressure for attached protection products at checkout. The competition regulator highlighted that a proposed JV’s combined control over major marketplaces would command 41% of the overseas online-shopping segment, with Gmarket’s 50 million-customer dataset a focal concern. In such concentrated rails, insurance add-ons face tight take-rate negotiations and standardized price points, compressing margins for both white-label and branded covers. This structurally limits room for premium differentiation in embedded micro-protection unless paired with exclusive data or fulfillment advantages.
Emerging Opportunities
Platform Partnerships for Embedded Products
Korea’s transaction-dense ecommerce creates abundant attach points for micro-covers. In April, online transactions were KRW 19.8027 trillion and mobile KRW 14.8026 trillion; in December, online reached KRW 21.2147 trillion and mobile KRW 16.2048 trillion. These sustained, high-frequency carts support 1-click insurance at payment confirmation, parcel insurance tied to shipment events, and device protection at electronics checkout. Cross-border imports from China at KRW 4.7 trillion add incremental corridors for shipping and warranty-style covers via customs/logistics flows. InsurTechs that can deliver low-latency APIs and instant adjudication can scale via a handful of high-volume partners.
Expansion into Gig-Economy Risk Cover
Traffic intensity and the growing fleet underscore opportunities in per-task, per-mile and per-hour covers for delivery riders, ride-hailing drivers and freelance couriers. Korea had 25,949,000 registered automobiles at year-end, and road traffic volume rose 27.6% over the last decade—conditions that correlate with expanding last-mile logistics and on-demand mobility. With mobile lines at 162.114 per 100 people, gig platforms can continuously stream location and activity data to bind micro-tenor liability and accident covers, and to trigger event-based claims. This hard infrastructure and telemetry footprint is already in place for insurers to model and price episodic risk.
Future Outlook
Over the forecast period from 2025 to 2030, the South Korea InsurTech market is expected to expand substantially, driven by continued demand for digital‑first insurance products, further regulatory enabling (sandbox environments, digital insurer licensing, open insurance / API frameworks), and growth in embedded insurance via e‑commerce, mobility, fintech. Technology advances—especially in AI, IoT, telematics, usage‑based insurance, behavior‑based insurance—are expected to improve underwriting accuracy, reduce fraud, lower costs, and enhance customer experience. Start‑ups will continue to scale, while incumbents will increasingly partner or acquire to stay competitive.
Major Players
- Carrot General Insurance
- Signal Planner
- Habit Factory
- KB Insurance
- Hanwha Insurance / Hanwha Life / Hanwha Group (via Carrot)
- Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance
- DB Insurance
- Meritz Fire & Marine Insurance
- K‑SURE (Korea Trade Insurance Corporation)
- Viva Republica (Toss) [as embedded insurance / fintech partner]
- Balance Hero
- Finda
- Signal Planner (repeat; there are more, e.g. smaller startups)
- Insurance super‑apps or aggregators (where present)
- Underwriting / Risk analytics tech providers
Key Target Audience
- Insurance companies / Carriers (non‑life, life) operating in South Korea looking to expand digital offering
- Digital‑only InsurTech startups in South Korea planning scaling or product diversification
- Embedded insurance providers / Fintech / E‑commerce platforms seeking to partner or offer insurance products
- Auto OEMs / Mobility service providers exploring usage‑based or behavior‑based insurance products
- Health & Wellness technology firms exploring opportunities in wellness, health‑insurance integration
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms (e.g. PE / VC funds investing in InsurTechs in Asia)
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Financial Supervisory Service; Financial Services Commission of Korea; Ministry of Land, Infrastructure & Transport for auto insurance legislation)
- Reinsurers and global insurance firms evaluating entering or expanding in the Korean InsurTech ecosystem
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study begins by mapping the InsurTech ecosystem in South Korea: start‑ups, incumbents, insurers, regulators, technology vendors. Secondary research is used via published reports, regulatory documents, company‑financial disclosures. Key variables include premium value via InsurTech channels, number of policies via digital/usage‑based models, technology adoption rates (AI, IoT, usage data), renewal / retention rates, regulatory status.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Data Compilation
Historical data (from 2019 to 2024) is collected to understand growth patterns, segment shares, product innovation trends. Distribution of digital vs traditional channels is analyzed. Service type segmentation, product type segmentation, technology enabler segmentation are constructed. Data from company reports (e.g. Carrot, KB Insurance etc.) are used to validate market numbers.
Step 3: Expert Interviews and Hypothesis Validation
Interviews are conducted with InsurTech founders, tech‑providers, executives at incumbents, regulators. These provide insight into operational realities (claims process, underwriting innovation, digital identity / KYC challenges). Hypotheses about which sub‑segments will lead growth (e.g. embedded insurance, behavior‑based, microinsurance) are validated against expert opinion.
Step 4: Forecasting & Scenario Modelling
Forecast models are built (bottom‑up and top‑down) to estimate market size growth from 2024 through 2030, applying adoption curves, regulatory trend scenarios, technology maturity, consumer behavior shifts. Sensitivity analysis is included for regulatory risk, technology adoption delays, macroeconomic headwinds, and competition.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of InsurTech Landscape in South Korea
- Timeline of Key Market Events and Regulatory Milestones
- Value Chain and Digital Integration
- Role of FSC, FSS, and MyData Framework in InsurTech
- Growth Drivers
Rise of Smartphone-Based Distribution
Regulatory Push for Digital-First Insurance
Embedded Insurance Integration via E-Commerce & Mobility
MyData Legislation Boosting Open Insurance
High Tech Adoption in Claims Automation
Demand for Microinsurance and Usage-Based Products - Market Challenges
Regulatory Uncertainty under K-ICS and IFRS-17
Low Consumer Trust in Fully Digital Models
Data Privacy Compliance under PIPA
High Customer Acquisition Cost
Integration Barriers for Legacy Players
Price War among Aggregators & InsurTechs - Emerging Opportunities
Platform Partnerships for Embedded Products
Expansion into Gig Economy Risk Cover
Cross-Border Expansion via Reinsurers
Real-Time Risk Monitoring with IoT
Wellness-linked Life & Health Covers - Trends
Shift Towards Parametric Insurance
InsurTechs as B2B API Providers
AI-Powered Claims Fraud Detection
Increase in ReinsurTech Collaboration - Government Regulation
FSS Licensing for Digital-Only Players
Remote Solicitation Guidelines
K-ICS Solvency Guidelines
MyData Authorization Process - SWOT Analysis
- Stake Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Policy Value, 2019-2024
- By Number of Users / Policies Sold via InsurTech Channels, 2019-2024
- By Insurance Type (In Value %)
Auto / Motor Insurance
Health Insurance
Life Insurance
Travel Insurance
Home Insurance
Specialty & Microinsurance
Business / Commercial Insurance - By Distribution Model (In Value %)
Digital Direct
Embedded via Platforms (E-commerce, Fintech, Mobility Apps)
Agents / Brokers
Bancassurance
Hybrid Models - By Service Model (In Value %)
Digital-only Insurer
Embedded Insurance Provider
Aggregator Platforms
Underwriting & Risk Analytics as a Service
Claims Automation & Fraud Detection Providers - By Technology Enabler (In Value %)
AI & Big Data
IoT & Connected Devices
Telematics & Usage-Based Insurance
Blockchain & Smart Contracts
Predictive Analytics
API, Cloud & Platform Infrastructure - By Customer Segment (In Value %)
Individual / Retail Consumers
SMEs and Affinity Groups
Corporate Clients
Gig Economy Workers
Freelancers & Non-Traditional Workforce
- Market Share of Major Players
By Premiums and Digital Policies
By Type of Insurance Offered
By Channel Penetration - Cross Comparison Parameters (Regulatory Status (Digital License, MyData Certified), Product Breadth (Microinsurance, UBI, Parametric), Technology Stack (AI, Telematics, API, IoT), Distribution Reach (Platform Partners, Agent Count, Web/App Traffic), Claims Automation Level, Customer Retention & Renewal Rates, Ecosystem Partnerships, Compliance Framework (PIPA, Cybersecurity)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing & Underwriting Model Comparison
- Detailed Company Profiles
Samsung Fire & Marine
DB Insurance
Meritz Fire & Marine
KB Insurance
Hanwha General Insurance
Hanwha Life
Kyobo Life
Carrot General Insurance
Signal Planner
Habit Factory
K-SURE
Viva Republica (Toss)
Kakao Pay Insurance
Balance Hero
- Demand Patterns by Age and Region
- SME & Corporate Insurance Preferences
- Willingness to Pay Analysis
- Pain Points and Adoption Barriers
- Regulatory Understanding among Consumers
- Decision-Making Journey in Digital Channels
By Value, 2025-2030
By Volume, 2025-2030
By Number of Policies, 2025-2030
By Embedded Insurance Share, 2025-2030


