Market Overview
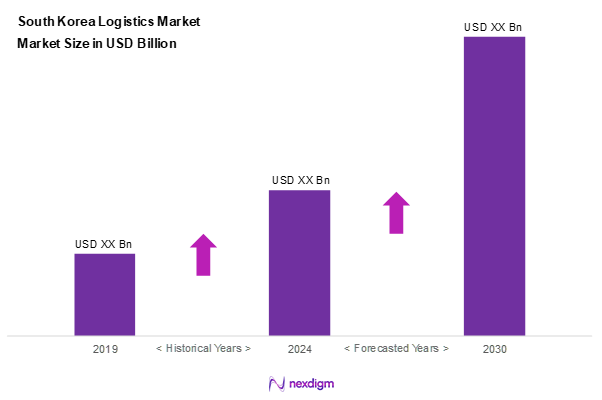
As of 2024, the South Korea logistics market is valued at USD ~ billion, with a growing CAGR of 3.6% from 2024 to 2030, reflecting growth driven by a robust manufacturing sector and a surge in e-commerce activities. With the increased reliance on efficient supply chains to meet rapid consumer demands, logistics service providers are capitalizing on technological advancements to enhance operational efficiencies. Continuous advancements in infrastructure further support this growth trajectory, making the logistics sector increasingly critical to the national economy.
Dominant cities in the South Korea logistics market include Seoul, Busan, and Incheon, primarily due to their strategic locations, well-established transport networks, and significant economic activities. Seoul, as the capital, serves as a vital commerce and consumption hub, while Busan’s major port enhances maritime logistics capabilities. Incheon benefits from its proximity to international airports and extensive road networks, facilitating swift movement of goods across borders.
Market Segmentation
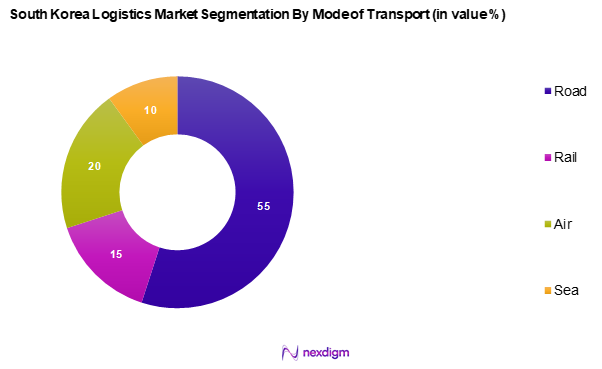
By Mode of Transport
The South Korea logistics market is segmented into road, rail, air, and sea. The road segment dominates, holding a significant market share due to the extensive road network and the efficiency of trucking services in meeting domestic transportation needs. Road transport’s flexibility in scheduling and routes makes it the preferred choice for many logistics companies. The ability to provide last-mile delivery services efficiently further enhances this segment’s popularity among both businesses and consumers.
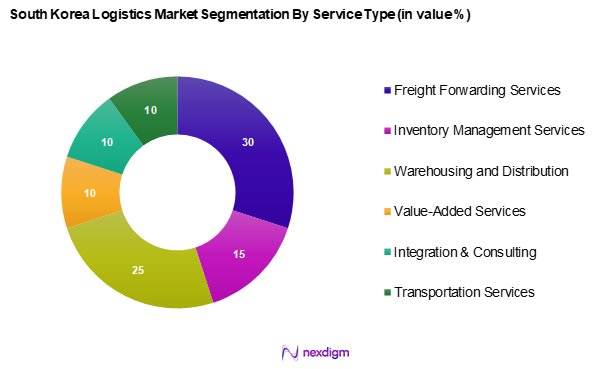
By Service Type
The South Korea logistics market is segmented into freight forwarding services, inventory management services, warehousing and distribution services, value-added services, integration and consulting services, and transportation services. Freight forwarding services dominate this market segment, accounting for the largest share due to the globalization of trade and the increasing demand for efficient logistics solutions that can handle international shipping complexities. Major freight forwarders in South Korea leverage advanced tech solutions to optimize supply chains, ensuring timely delivery and cost-effectiveness.
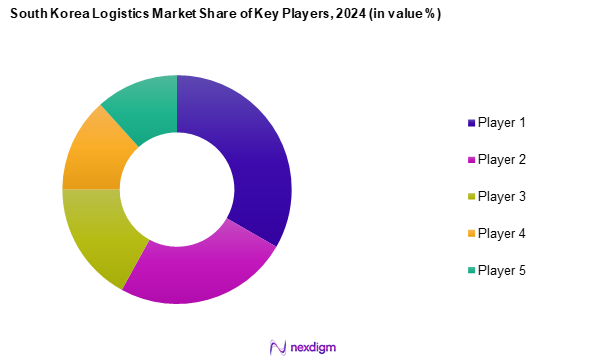
Competitive Landscape
The South Korea logistics market is characterized by the presence of several major players, including CJ Logistics, Lotte Global Logistics, and Hanjin Transportation. These companies have established a solid foothold due to their extensive networks, innovative service offerings, and commitment to leveraging technology in logistics operations.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Market Share | Service Type | Revenue (USD) | Strength |
| CJ Logistics | 1930 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
| Lotte Global Logistics | 1996 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
| Hanjin Transportation | 1945 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
| SEBANG | 1965 | Incheon, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
| DAEWOO | 1967 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
South Korea Logistics Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increased E-commerce Boom
The e-commerce sector in South Korea has experienced remarkable growth, with online retail sales reaching USD 157.0 billion in 2022, significantly bolstered by the ongoing shift toward digital shopping. This boom is driven by factors such as high internet penetration, reported at 99% in 2022, and a tech-savvy population. The convenience of e-commerce is leading to higher demand for efficient logistics solutions, with the logistics industry adapting to meet the challenges of fast delivery times and complex order fulfilment. Additionally, an increase in mobile commerce transactions supports this sector’s expansion, contributing to the overall growth of the logistics market.
Urbanization and Population Growth
Urbanization in South Korea is a significant driver of logistics demand, with approximately 82.5% of the population residing in urban areas as of 2022. This high urban concentration facilitates greater logistical efficiencies and necessitates improved distribution networks to cater to the densely populated cities. Moreover, the population is projected to be around 51.6 million in 2025. The demand for goods in urban environments is rising, leading to increased pressure on logistics providers to enhance their services. This growth in urban population exemplifies the need for streamlined logistics operations to ensure efficient delivery systems are in place.
Market Challenges
Infrastructure Limitations
Despite significant advancements in logistics, South Korea faces infrastructure challenges that hinder seamless supply chain operations. According to the Korea Transport Institute, outdated facilities and insufficient investment have led to congestion in key logistics hubs, particularly in metropolitan areas. For instance, traffic congestion costs the economy around USD 1.5 billion annually, affecting delivery efficiency and increasing operational costs for logistics companies. The need for infrastructure upgrades is crucial to enhance logistics functionalities and ensure optimal performance across the supply chain.
Regulatory Hurdles
The South Korean logistics market grapples with stringent regulatory frameworks that can pose challenges for businesses operating in this sector. Compliance with regulations regarding transport safety, environmental standards, and labor laws can create operational complexities. Reports indicate that the logistics sector incurs approximately USD 500 million annually due to compliance with various regulations. The processes involved in securing licenses and navigating bureaucratic challenges can delay logistics operations, impacting overall market performance and competitiveness.
Opportunities
Expansion of Green Logistics
The increasing emphasis on sustainability presents a vital opportunity for growth in green logistics within South Korea. Reports indicate that around 60% of consumers prefer environmentally friendly options when it comes to transportation and logistics services. This shift is driving logistics providers to adopt greener practices, such as electric vehicles and sustainable packaging solutions. The ongoing governmental support for green technology investments and initiatives further highlights the potential for growth in this segment, ensuring logistics firms remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market focused on sustainability.
Growth in Warehousing Technologies
Advancements in warehousing technologies offer substantial growth opportunities in the South Korean logistics market. With the 4th Industrial Revolution bringing forth innovations such as automation, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT), warehouses can achieve increased efficiency and reduced operational costs. The total warehouse space was approximately 12 million square meters in 2022, with projections indicating a continued increase as businesses seek to optimize logistics systems. The adoption of smart warehousing solutions will enable businesses to enhance order accuracy and streamline inventory management, fueling market growth.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the South Korea logistics market is projected to experience significant growth, driven by the expansion of e-commerce, urbanization, and advancements in logistics technologies. The increasing demand for quick delivery timelines and enhanced customer experience will push logistics providers to adopt automation, artificial intelligence, and sustainable practices, ultimately shaping a more efficient supply chain landscape.
Major Players
- CJ Logistics
- Lotte Global Logistics
- Hanjin Transportation
- SEBANG
- DAEWOO
- Sunjin Logistics
- KCTC
- Pantos Logistics
- Logos Global
- SF Express
- GEFCO
- KGL Network
- Woojung Air
- Samil Logistics
- Leschaco
Key Target Audience
- Investors and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport)
- Logistics Companies
- Manufacturers
- E-commerce Companies
- Retail Chains
- Supply
- Chain Management Consultants
- Technology Providers for Logistics Industry
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map encompassing all major stakeholders within the South Korea logistics market. This step relies on extensive desk research using a combination of secondary data sources, proprietary databases, and government reports to gather comprehensive information. The primary objective here is to identify and define the critical variables that influence market dynamics and sector performance.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, we compile and analyze historical and current data related to the South Korea logistics market. This includes evaluating market penetration levels, the ratio of service providers to demand, and resulting revenue generation trends. Additionally, we analyze service quality metrics to assure the accuracy of our revenue estimates and market forecasts.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses will be developed and subsequently validated through structured interviews with industry experts representing various sectors within the logistics landscape. This consultation process utilizes both telephone and in-person interviews to derive insights directly from practitioners, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of operational and financial metrics.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves synthesizing findings from multiple data sources and validating them through direct engagement with logistics providers. This allows for the acquisition of detailed insights into service performance, consumer behavior, technology usage, and other factors critical to understanding market dynamics. The goal is to deliver a well-rounded and validated analysis, ensuring the report’s reliability and depth.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Overview Genesis
- Timeline of Major Players
- Business Cycle
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Increased E-commerce Boom
Urbanization and Population Growth - Market Challenges
Infrastructure Limitations
Regulatory Hurdles - Opportunities
Expansion of Green Logistics
Growth in Warehousing Technologies - Trends
Adoption of AI and Automation
Rise of Omni channel Logistics - Government Regulation
Transportation Policies
Environmental Regulations - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Price, 2019-2024
- By Mode of Transport, (In Value %)
Road
Rail
Air
Sea - By Service Type, (In Value %)
Freight Forwarding Services
Inventory Management Services
Value-Added Services
Integration & Consulting Services
Warehousing and Distribution Services
Transportation Services - By End-User Vertical, (In Value %)
Manufacturing
Consumer Goods
Retail
Food and Beverages
IT Hardware
Chemicals
Construction
Automotive
Telecom
Others - By Model, (In Value %)
1PL
2PL
3PL
4PL - By Category, (In Value %)
Conventional Logistics
E-Commerce Logistics - By Customer Type, (In Value %)
B2B
B2C
- Market Share of Major Players on the Basis of Value/Volume, 2024
Market Share of Major Players by Mode of Transport Segment, 2024 - Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Recent Developments, Strengths, Weaknesses, Revenue Analysis, Service Offerings, Technology Adoption)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis Basis SKUs for Major Players
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Leschaco
CJ Logistics
SEBANG
OOCL
DAEWOO
Sunjin
LOTTE GLOBAL LOGISTICS
JBG Logistics
KCTC
Pantos Logistics
Logos Global
SF Express
GEFCO in South Korea
KBE
ILYANG Express
KGL Network
Woojung Air
- Market Demand and Utilization Patterns
- Purchasing Power Analysis
- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
- Needs and Pain Point Analysis
- Decision Making Process
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Mode of Transport, 2025-2030


