Market Overview
As of 2024, the South Korea warehousing market is valued at USD ~ billion, with a growing CAGR of 6.8% from 2024 to 2030, driven by exponential growth in e-commerce activities and a strategic push towards automation and technological integration in supply chain processes. The market is experiencing robust growth due to an increasing demand for efficient logistics solutions that enhance supply chain resilience and performance. The warehousing sector is supported by heavy investments in technology and infrastructure to meet these rising demands.
The dominance of major cities such as Seoul, Busan, and Incheon in the South Korean warehousing market is attributed to their significant economic contributions and infrastructural advancements. Seoul, being the capital, houses a large volume of retail and e-commerce activities, while Busan serves as a pivotal port city facilitating international trade. Incheon, with its well-developed logistics hubs and connectivity, complements the overall market dynamics, making these cities critical to warehousing operations.
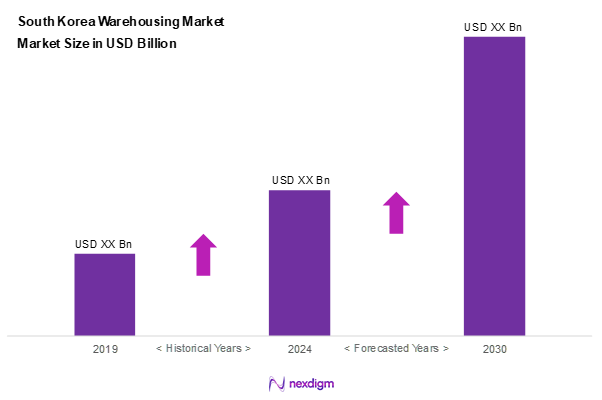
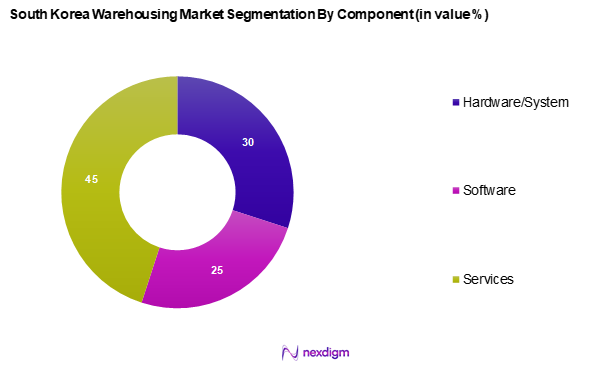
Market Segmentation
By Component
The South Korea warehousing market is segmented into hardware/system, software, and services. The services segment holds a dominant market share due to the increasing need for specialized logistics support, including inventory management, order fulfilment, and transportation services. As businesses continue to seek efficient operations and cost-effective solutions, service providers have adapted to market demands by offering tailored services that align with specific client needs, ensuring their leadership in this segment.
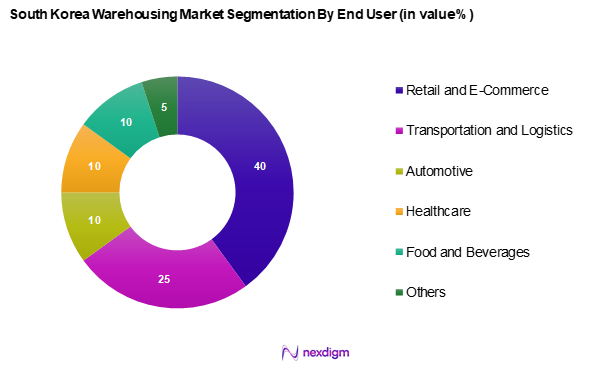
By End User
The South Korea warehousing market is segmented into end user, including retail and e-commerce, transportation and logistics, automotive, healthcare, food and beverages, and others. The retail and e-commerce segment dominates this category, driven by the ongoing boom in online shopping and the necessity for efficient distribution channels. Companies are increasingly investing in warehousing solutions to maintain competitive advantage and ensure timely delivery of goods, which has amplified the need for extensive warehousing capabilities.
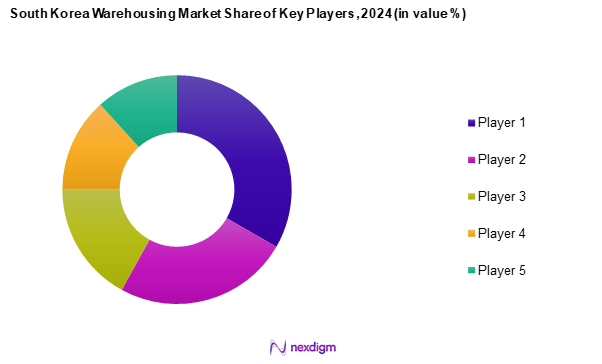
Competitive Landscape
The South Korea warehousing market is dominated by a few major players, each leveraging their strengths to maintain a competitive edge. Companies such as Logos Logistics and LOTTE GLOBAL LOGISTICS, CEVA Logistics, Samil Logistics and ILYANG Express stand out due to their extensive networks and strategic innovations tailored to meet market demands.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Revenue (USD Mn) | Number of Facilities | Employee Count | Technology Utilization |
| Logos Logistics | 2008 | Michigan, U.S.A. | – | – | – | – |
| LOTTE GLOBAL LOGISTICS | 1996 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
| ILYANG Express | 1975 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
| CEVA Logistics | 1946 | Marseillais, French | – | – | – | – |
| Samil Logistics | 1987 | Seoul, South Korea | – | – | – | – |
South Korea Warehousing Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing E-commerce Activities
The surge in e-commerce activities in South Korea significantly drives the warehousing market, with online retail sales reaching approximately USD 180 billion in 2023, highlighting a major shift in consumer behavior. This rapid growth demands efficient warehousing solutions to manage inventory and ensure quick delivery to consumers. Notably, the South Korean e-commerce market is projected to continue scaling, spurred by increased mobile commerce which accounted for 50% of online sales in 2022. This trend necessitates advanced logistics operations and infrastructure investments to support the demand for fast and reliable warehouse services.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a crucial role in the growth of the warehousing market as businesses increasingly invest in automation and AI systems to enhance efficiency. South Korea’s government allocated KRW 777.2 billion (approximately USD 585 million) for AI research and development in 2024, showcasing its commitment to innovation. Additionally, the country ranks among the top in the Global Innovation Index, which fosters an environment for tech-savvy warehousing solutions. Implementations such as automated picking systems and real-time inventory management are vital for improving operational costs and customer satisfaction, solidifying South Korea’s position as a leader in logistics technology.
Market Challenges
Regulatory Hurdles
Strict regulatory frameworks present notable challenges to warehouse operators in South Korea. From building codes and safety standards to environmental compliance, the regulatory environment requires firms to be highly adaptive. Upcoming policy changes are expected to further tighten operational requirements, making it essential for businesses to continuously monitor and adjust to evolving regulations. These compliance demands can lead to increased costs and operational delays, particularly for companies that are not prepared to quickly align with the new rules.
High Operational Costs
High operational costs remain a significant barrier within the warehousing market due to rising labor and real estate prices. In 2023, average wages for logistics workers in South Korea reached approximately 45,780,105 KRW (USD 34,292.73) per year, reflecting a 5% increase from the previous year. Coupled with escalating warehouse rental prices in key locations, this scenario imposes financial pressure on logistics providers.
Opportunities
Sustainability Initiatives
The growing emphasis on sustainability presents a promising avenue for innovation and differentiation in the warehousing market. Government-backed initiatives focused on green logistics are encouraging the adoption of environmentally friendly practices, such as energy-efficient warehouse designs, renewable energy integration, and the use of electric vehicles for last-mile delivery. Companies that proactively align with these sustainability goals are likely to gain a competitive edge, attract environmentally conscious clients, and contribute to long-term environmental targets.
Expansion into Emerging Areas
Efforts to develop logistics infrastructure in less urbanized regions offer untapped potential for market growth. Government strategies are increasingly focused on improving connectivity and supply chain efficiency in rural and semi-urban areas. As businesses expand their presence in these regions, the need for localized warehousing solutions is expected to grow. This opens up new opportunities for logistics providers to cater to underserved markets and establish early-mover advantages in emerging areas.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the South Korea warehousing market is expected to exhibit considerable growth fueled by the integration of advanced technologies, such as automation and AI, enhancing operational efficiencies. The continued rise of e-commerce will drive demand for innovative warehousing solutions, positioning the market for sustained expansion and diversification in service offerings.
Major Players in the Market
- Logos Logistics
- ILYANG Express
- Woojung Air
- LOTTE GLOBAL LOGISTICS
- GEFCO in South Korea
- DAEWOO
- Samil Logistics
- KCTC
- Rhenus Group
- ALPS LOGISTICS CO.,LTD.
- NIPPON EXPRESS KOREA CO., LTD.
- Lamaignere Cargo
- Omni Logistics, LLC
- CTSI Logistics (a Subsidiary of Tan Holdings Corporation)
- Others
Key Target Audience
- Retail and E-commerce Companies
- Transportation and Logistics Firms
- Automotive Manufacturers
- Healthcare Providers
- Food and Beverage Distributors
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, South Korea)
- Industrial Product Manufacturers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map to encompass all major stakeholders within the South Korea warehousing market. Through extensive desk research utilizing a combination of secondary and proprietary databases, the goal is to identify and define critical variables influencing market dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data pertaining to the South Korea warehousing market will be compiled and analyzed. This includes evaluating market penetration, the relationship between service providers and warehouses, and revenue generation. Assessments of service quality statistics will ensure the credibility of the revenue estimates.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses will be developed and validated through computer-assisted telephone interviews (CATI) with industry experts representing a diverse array of companies. These consultations will provide valuable insights into operational practices and financial trends, which are essential in refining and corroborating the obtained market data.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves engaging directly with multiple warehousing companies to gather detailed insights into product segments, sales performance, consumer preferences, and additional pertinent factors. This interaction will serve to verify and complement statistics derived from the bottom-up approach, ensuring a comprehensive, accurate, and validated analysis of the South Korea warehousing market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Data Sources, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Dynamics Through Expert Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Overview Genesis
- Timeline of Major Players
- Business Cycle
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Increasing E-commerce Activities
Technological Advancements - Market Challenges
Regulatory Hurdles
High Operational Costs - Opportunities
Sustainability Initiatives
Expansion into Emerging Areas - Trends
Emphasis on Digital Transformation
Evolution of Shared Warehousing Models - Government Regulation
Building Standards and Safety Regulations
Environmental Policies - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Price, 2019-2024
- By Component, (In Value %)
Hardware/System
Software
Services - By Function, (In Value %)
Inventory Control and Management
Asset Tracking
Yard & Dock Management
Order Fulfilment
Workforce & Task (Process) Management
Shipping
Predictive Maintenance
Others - By Type, (In Value %)
Insource Warehousing
Outsource Warehousing - By Size, (In Value %)
Small
Medium
Large - By Ownership, (In Value %)
Public Warehouses
Private Warehouses
Bonded Warehouses
Consolidated Warehouse - By Warehousing Storage Nature, (In Value %)
Ambient Warehousing (Around 80°F)
Air Conditioned (56°F and 75°F)
Refrigerated (33°F and 55°F)
Cold/Frozen (Of or Below 32°F)
- Market Share of Major Players on the Basis of Value/Volume, 2024
Market Share of Major Players by Type of Component Segment, 2024 - Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Recent Developments, Revenue Analysis, Operational Efficiency, Technology Utilization, Geographic Reach, Client Base)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis Basis SKUs for Major Players
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Logos Logistics
ILYANG Express
Woojung Air
LOTTE GLOBAL LOGISTICS
CEVA Logistics
DAEWOO
Samil Logistics
KCTC
Rhenus Group
ALPS LOGISTICS CO.,LTD.
NIPPON EXPRESS KOREA CO., LTD.
Lamaignere Cargo
Omni Logistics, LLC
CTSI Logistics (a Subsidiary of Tan Holdings Corporation)
- Market Demand and Utilization
- Purchasing Power and Budget Allocations
- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
- Needs, Desires, and Pain Point Analysis
- Decision-Making Process
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Price, 2025-2030


