Market Overview
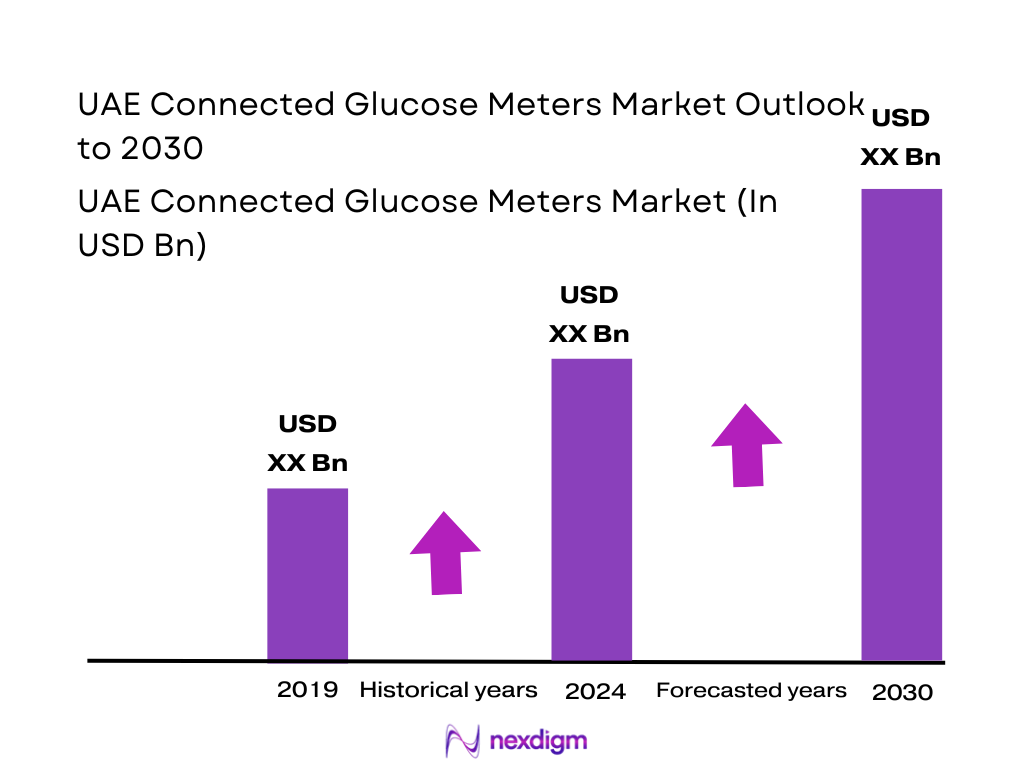
The UAE Connected Glucose Meters market (captured within the UAE blood glucose monitoring devices ecosystem, where connected SMBG meters and connected CGM solutions are key revenue contributors) generated USD ~ million in revenue, rising from USD ~ million, supported by sustained diabetes management demand and increasing adoption of app-connected monitoring workflows in clinics and homecare. Demand is being reinforced by expanding outpatient chronic-care pathways, wider availability of Bluetooth/Wi-Fi enabled devices through pharmacies and e-commerce, and increasing use of data-sharing features that support clinician review and patient adherence.
Dubai and Abu Dhabi dominate connected glucose meter adoption due to the concentration of multi-specialty hospitals, endocrinology networks, and digital-health adoption infrastructure, including telehealth workflows that benefit from device-to-app data continuity. These emirates also serve as the primary commercialization hubs for global manufacturers and local distributors, accelerating product registrations, channel onboarding, and insurer/provider partnerships. In supply terms, the market is heavily shaped by international medtech brands (notably from the US, Switzerland, and Japan) that operate through UAE distributors and hospital procurement frameworks, enabling faster scaling versus smaller emirates.
Market Segmentation
By Connectivity Type
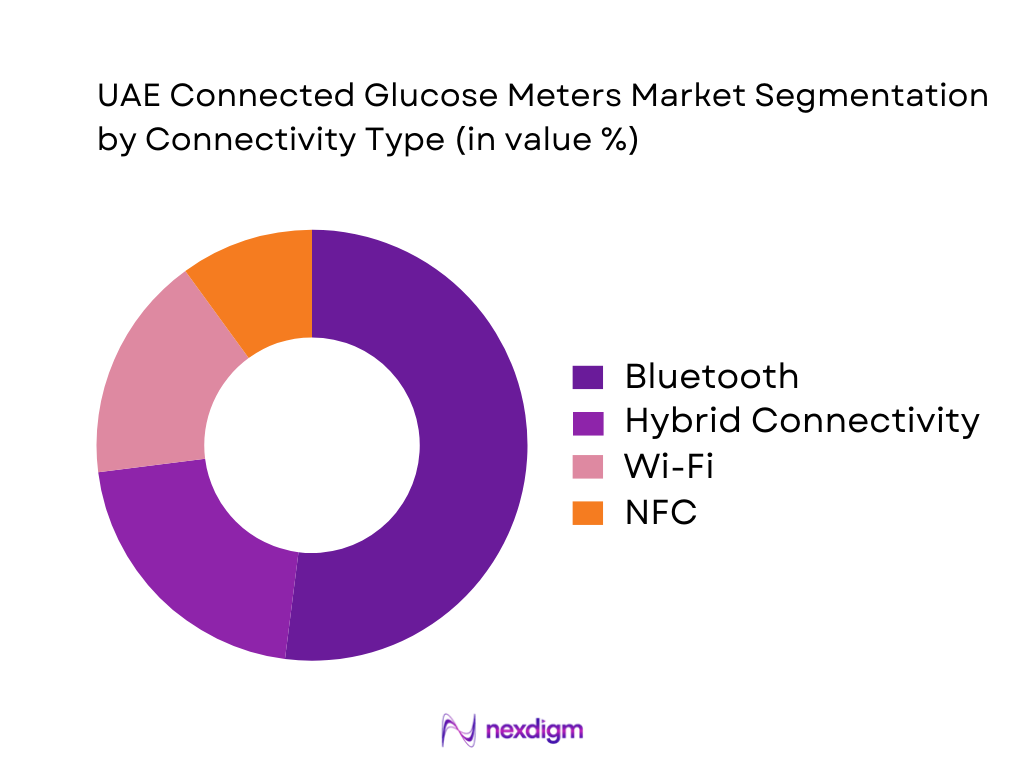
The UAE Connected Glucose Meters market is segmented by connectivity type into Bluetooth, NFC, Wi-Fi, and hybrid connectivity. Bluetooth holds the dominant share because it offers the most practical balance of low power consumption, reliable phone pairing, broad smartphone compatibility, and seamless integration with companion apps used in day-to-day diabetes self-management. Bluetooth-based meters are also easier to commercialize through pharmacy retail because they do not require home Wi-Fi setup or additional infrastructure—important for consistent patient experience and lower product returns. Additionally, Bluetooth connectivity supports fast sharing of readings during teleconsultations and follow-ups, aligning with provider needs for remote monitoring workflows.
By End User
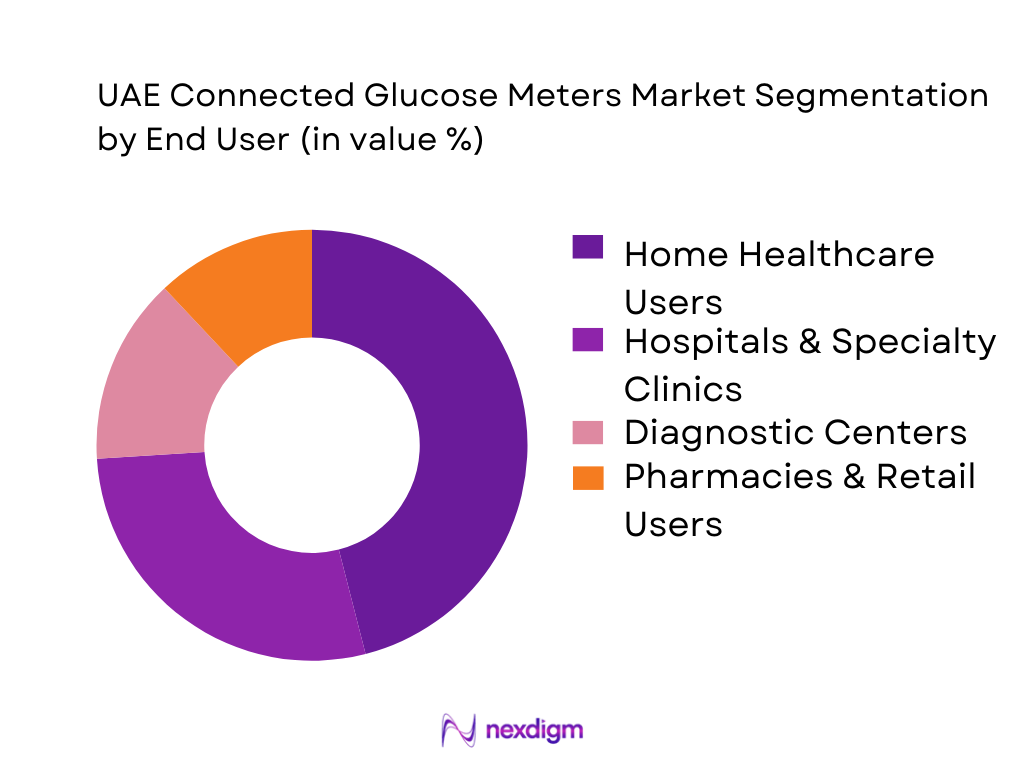
The UAE Connected Glucose Meters market is segmented by end user into hospitals & specialty clinics, diagnostic centers, home healthcare users, and pharmacies & retail users. Home healthcare users dominate because diabetes monitoring is a high-frequency requirement that is increasingly shifting outside hospitals—patients prefer self-testing convenience, app-based logs, reminders, and easier data sharing with clinicians. Retail availability (pharmacy chains and online channels) makes procurement frictionless, while clinicians benefit from more complete longitudinal datasets to adjust therapy. Home use is further reinforced by UAE’s modern digital-health landscape, where connected readings support continuity of care across follow-ups and telehealth interactions.
Competitive Landscape
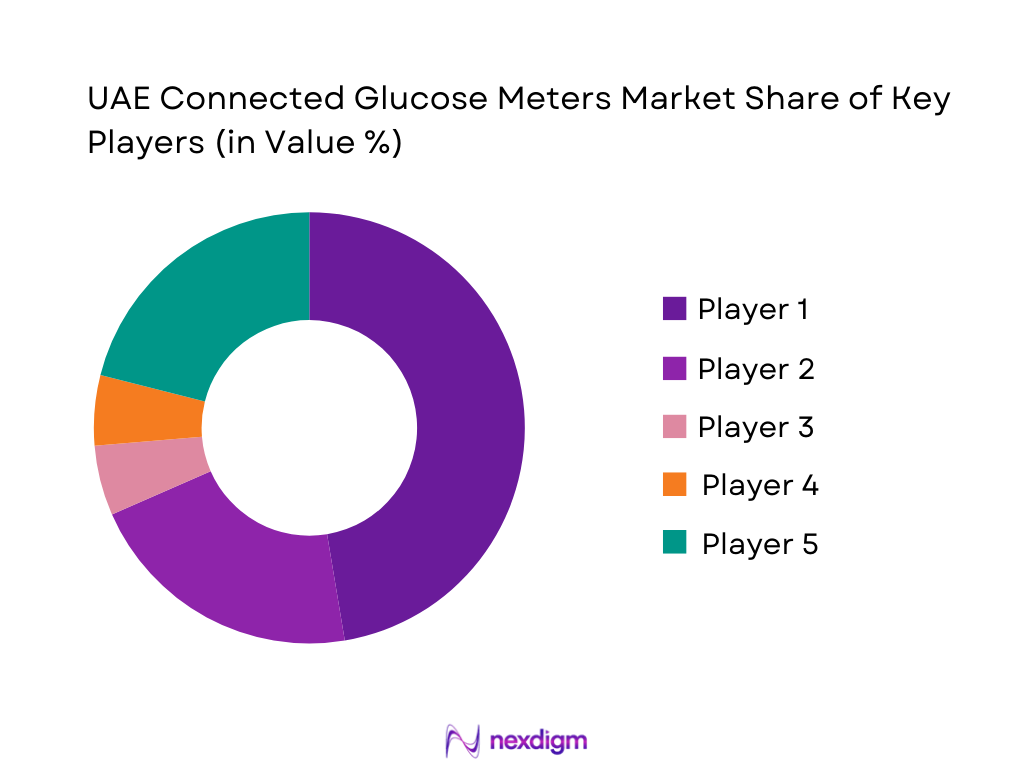
The UAE Connected Glucose Meters market is moderately consolidated, led by global diabetes-care and diagnostics companies with strong device portfolios, established distributor networks, and high trust among clinicians. Competitive differentiation in the UAE centers on connectivity reliability, app ecosystem quality, accuracy credentials, MoHAP-compliant product registration readiness, and the ability to supply both institutional tenders and fast-moving retail channels. Regulatory compliance is a major gating factor, as medical equipment registration under the Ministry of Health and Prevention is integral to commercialization, procurement access, and wider adoption across care settings.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Key Connected Offerings | App/Data Ecosystem Strength | Clinical/Accuracy Positioning | UAE Go-to-Market Strength | Channel Footprint | After-Sales Capability |
| Abbott Diabetes Care | 1888 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Roche Diagnostics | 1896 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Ascensia Diabetes Care | 2016 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Dexcom | 1999 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Medtronic | 1949 | Ireland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
UAE Connected Glucose Meters Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing Diabetes Prevalence
The UAE’s connected glucose meter demand is structurally anchored in the scale of diabetes and dysglycaemia among adults, which expands the recurring need for frequent self-monitoring and clinician-reviewed logs. The International Diabetes Federation estimates ~ adults in the UAE living with diabetes, within a total adult population of ~, and also highlights ~ adults with undiagnosed diabetes—an addressable pool that drives higher screening, earlier diagnosis, and sustained testing intensity once enrolled into care pathways. In parallel, the UAE’s macro capacity to fund chronic-care infrastructure supports uptake of connected monitoring; the World Bank reports national output at ~ with GDP per capita at ~, creating strong ability for payers, providers, and employers to expand disease-management programs and digital follow-up workflows. The combination of a large, clinically active diabetes base, substantial undiagnosed burden that keeps new users entering the monitoring funnel, and high-income macro fundamentals that support ongoing chronic-care investment, keeps connected SMBG attractive because it produces time-stamped, shareable readings usable in therapy titration, medication adherence discussions, and remote follow-ups across Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and the wider federation.
Government Digital Health Push
The UAE’s connected glucose meter market benefits from a healthcare digitalization environment that increasingly expects device-to-app continuity, data capture, and remote documentation as part of routine care. A visible signal is Dubai’s scaled virtual-care throughput: Dubai Health Authority reporting indicates nearly ~ telehealth consultations in ~ and electronic prescriptions exceeding ~, demonstrating real, system-level normalization of remote interactions where connected glucometer readings can be shared during consults and used for follow-up decisioning. This operational scale is supported by national macro strength and the ability to invest in digital health infrastructure; the World Bank lists UAE GDP at ~ and GDP per capita at ~, both enabling sustained spend on interoperability, regulated digital channels, and provider adoption programs. In parallel, Dubai’s health insurance system data shows the payer and claims ecosystem has moved to high-volume digital processing—transactions through the electronic healthcare insurance portal exceeded AED ~ in ~, and ~ individuals were covered under Dubai’s healthcare insurance umbrella, supporting a reimbursement and claims environment that can integrate digital documentation and chronic-care pathways at scale. For connected glucose meters, these digital-health pushes translate into faster pathway integration: onboarding via hospitals and specialty clinics, ongoing refills via pharmacy chains and e-commerce, and continuity of data-sharing through telehealth and e-prescribing flows that require structured patient monitoring records rather than anecdotal reporting.
Challenges
Device Cost Sensitivity
Even in a high-income setting, device cost sensitivity persists because diabetes monitoring is frequent, recurring, and often distributed across mixed payer types (insured, employer-sponsored, and direct retail purchasing). While the World Bank reports UAE GDP per capita at ~, affordability constraints still surface where patients or families face repeated purchase decisions and may trade down from premium connected ecosystems to basic models if insurance coverage is partial or if employer plans prioritize essential benefits over connected add-ons. The World Bank also reports out-of-pocket health expenditure per capita at ~, indicating that a meaningful portion of health spending can still sit with households, which amplifies sensitivity in segments that purchase in retail pharmacies or online channels. In Dubai, the insurance ecosystem is large and digital—~ people are within the insurance umbrella and portal transactions exceeded AED ~—but connected device adoption still depends on whether monitoring devices and related diabetes management workflows are smoothly reimbursed and whether procurement pathways favor connected solutions or standard meters. This sensitivity shapes market dynamics in a very specific way: it rewards suppliers who can keep users inside an ecosystem through reliable connectivity and low-friction app workflows, because if consumers “churn” due to affordability, they often revert to non-connected meters that reduce clinical visibility and weaken the case for remote follow-up. It also pressures distributors and retail channels to manage SKU portfolios that cover multiple income tiers while still meeting regulatory requirements and accuracy expectations. Ultimately, cost sensitivity is not a contradiction of UAE wealth; it is a feature of high-frequency chronic monitoring economics, where household exposure, payer rules, and procurement constraints determine whether connected features are treated as essential clinical infrastructure or optional convenience.
Data Privacy Regulations
Data privacy and compliance obligations create commercialization and scaling friction for connected glucose meters because the product’s value proposition depends on capturing, storing, and transmitting sensitive health data across phones, apps, and cloud dashboards. The UAE’s official digital portal summarizes data protection laws and individuals’ rights around personal data processing, which sets a governance expectation that vendors must operationalize across consent flows, data handling policies, and cross-border data transfer controls for app ecosystems. At the infrastructure level, the World Bank reports ~ secure internet servers per ~ people in the UAE, a measure that reflects the country’s secure digital environment—but it also signals that connected device suppliers are expected to operate at strong baseline security and compliance standards consistent with an advanced digital economy. In healthcare, the compliance bar is reinforced by the scale of digital care activity: Dubai’s telehealth consultations reached nearly ~ in ~, and electronic prescriptions exceeded ~, meaning that digital patient interactions are not niche and that system stakeholders (providers, payers, regulators) have strong incentives to enforce privacy-by-design, audit readiness, and regulated documentation. For connected glucose meters, this translates into operational requirements that go beyond device accuracy: secure pairing and authentication, controlled data-sharing permissions, reliable audit logs, and integration approaches that do not violate local expectations for regulated health information handling. Vendors operating through distributors and pharmacy channels must also ensure that apps and cloud platforms are aligned with UAE compliance expectations, because any breach or regulatory misalignment can disrupt procurement access, delay registrations, or reduce provider willingness to recommend connected solutions. As a result, privacy regulation acts as both a trust enabler and a market barrier: it increases confidence in connected monitoring when executed well, but it raises time-to-scale for players without mature governance, localized compliance practices, and security-grade digital infrastructure.
Opportunities
Integration with Telemedicine
Connected glucose meters have a clear growth pathway through deeper integration with telemedicine workflows that are already operating at scale in Dubai and are increasingly normalized across UAE care delivery. Dubai Health Authority reporting indicates nearly ~ telehealth consultations in ~ and more than ~ electronic prescriptions, which demonstrates that remote interactions are not a pilot activity but an operational channel where clinicians can routinely review patient information and issue prescriptions without in-person visits. This creates a direct opportunity for connected SMBG: device readings can be synced to an app, structured into trend summaries, and shared during teleconsultations, enabling medication adjustments and adherence counseling that are more clinically grounded than verbal recall or paper diaries. The macro foundations support scalable integration: the World Bank reports UAE GDP at ~ and GDP per capita at ~, enabling continued investment in digital care platforms, interoperability, and regulated digital documentation. Additionally, Dubai’s insurance ecosystem processed AED ~ in electronic portal transactions and covers ~ individuals, indicating that telemedicine-supported diabetes pathways can be embedded into payer processes where digital records, remote follow-ups, and chronic-care programs are administratively feasible. The opportunity is not “future demand”; it is present operational readiness: high telehealth volumes, established e-prescribing, and a large insured population create immediate touchpoints where connected glucose meters can become a standard input into remote care. Vendors that align device pairing, app UX, and clinician dashboards to telemedicine workflows—and that support provider education on interpreting shared SMBG logs—can capture growth by becoming the default monitoring infrastructure for remote diabetes visits across hospitals, specialty clinics, and digital health platforms already serving large patient volumes in Dubai and, increasingly, across other emirates.
AI-Based Analytics
AI-based analytics is a near-term commercial opportunity for connected glucose meters in the UAE because the country is building a dense AI ecosystem while healthcare delivery increasingly values data-driven chronic care and remote monitoring. Dubai International Financial Centre reporting notes the Dubai AI Campus has attracted over ~ firms, highlighting ecosystem depth that can accelerate development of regulated analytics capabilities, integration partnerships, and product localization across high-priority sectors including digital health. At the same time, the IDF estimates ~ adults with diabetes in the UAE, and ~ adults with undiagnosed diabetes, which implies a large monitoring base where analytics that translate raw readings into actionable insights can materially improve day-to-day management and clinician follow-up efficiency. The macroeconomic foundation supports this shift: the World Bank reports GDP per capita at ~ and GDP at ~, aligning with a healthcare environment that can invest in advanced digital tools when they support clinical workflows and system efficiency. For connected glucose meters, AI opportunity is not about speculative adoption; it is about leveraging existing data streams to produce value that clinicians and patients can use immediately—pattern detection, adherence flags, and personalized reminders—within the constraints of privacy regulation and regulated medical-device ecosystems. As telehealth volumes are already high, analytics that compress weeks of readings into interpretable summaries can make remote consultations more efficient and clinically decisive. Vendors that deliver analytics as part of a compliant, UAE-ready app ecosystem—supported by local partnership networks and robust data governance—can differentiate beyond connectivity alone and expand usage intensity among both home users and provider-managed chronic-care pathways.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the UAE Connected Glucose Meters market is expected to expand steadily as diabetes management increasingly adopts continuous and connected monitoring models. The UAE blood glucose monitoring devices market is projected to grow at a CAGR of ~%, supported by technology upgrades, greater integration with remote patient monitoring, and rising preference for data-driven chronic care. Product innovation (analytics, alerts, cloud dashboards) and tighter linkage with virtual care pathways will keep connected devices central to both home and clinical monitoring.
Major Players
- Abbott Diabetes Care
- Roche Diagnostics
- Ascensia Diabetes Care
- Dexcom
- Medtronic
- iHealth Labs
- ForaCare
- Omron Healthcare
- ACON Laboratories
- Sinocare
- Terumo Corporation
- B. Braun
- Beurer GmbH
- Ypsomed
Key Target Audience
- Hospital procurement heads and tender committees
- Endocrinology and diabetology specialty clinic owners
- Retail pharmacy chain category heads
- Medical device distributors and importers
- Digital health and telemedicine platform leadership
- Health insurance payer and chronic-care program heads
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies (MOHAP, DHA, Department of Health Abu Dhabi)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with mapping the UAE diabetes-care ecosystem across manufacturers, authorized distributors, hospitals, specialty clinics, pharmacy chains, and digital health platforms. Desk research is conducted using regulator and industry sources to define variables such as device categories (connected SMBG vs connected CGM), pricing bands, channel coverage, and registration requirements.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
A bottom-up model is developed using triangulation across institutional demand (hospital procurement), retail sell-out proxies (pharmacy and e-commerce), and distributor-level inputs. The analysis assesses adoption intensity by end user type, connectivity preference, and product lifecycle replacement trends, ensuring the market is built from measurable commercial pathways rather than single-source assumptions.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are validated through structured interviews (CATI/virtual) with stakeholders such as endocrinologists, diabetes educators, distributor category managers, pharmacy buyers, and digital health operators. This step is used to validate device mix, connectivity preferences, usage behaviors, and the practical barriers to adoption such as onboarding complexity and app experience.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are synthesized and cross-verified with regulatory and commercialization constraints, ensuring that product availability aligns with UAE market realities. Outputs are finalized through consistency checks between top-down references (published market numbers) and bottom-up channel logic to ensure defensible sizing and realistic segment structuring.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Device Classification Framework, Market Sizing Logic, Bottom-Up & Top-Down Validation, Primary Interviews with Endocrinologists & Procurement Heads, Distributor-Level Data Validation, Regulatory Cross-Verification, Limitations & Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of Digital Glucose Monitoring Ecosystem
- Technology Adoption Curve in UAE Healthcare
- Timeline of Connected Glucose Meter Adoption
- Business Cycle Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Increasing Diabetes Prevalence
Government Digital Health Push
Remote Patient Monitoring Adoption
Insurance Coverage for Chronic Care - Challenges
Device Cost Sensitivity
Data Privacy Regulations
Patient Awareness Gaps - Opportunities
Integration with Telemedicine
AI-Based Analytics
Corporate Wellness Programs - Trends
App-Based Monitoring
Cloud Dashboards
Real-Time Alerts - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Smart Glucose Meters (Bluetooth Enabled)
Smartphone-Integrated Glucose Meters
Cloud-Connected Glucose Monitoring Systems
AI-Enabled Glucose Monitoring Devices - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Bluetooth
NFC
Wi-Fi
Hybrid Connectivity - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Hospitals & Specialty Clinics
Diagnostic Centers
Home Healthcare Users
Pharmacies & Retail Users - By Distribution Channel (In Value %)
Hospital Procurement
Medical Device Distributors
Retail Pharmacies
E-Commerce & Digital Health Platforms - By Region (in Value %)
Dubai
Abu Dhabi
Sharjah
Northern Emirates
- Market Share by Value & Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Product Portfolio Breadth, Connectivity & App Ecosystem, UAE Regulatory Approvals, Clinical Accuracy & Certifications, Distribution Footprint in UAE, Integration with Telehealth Platforms, Pricing & Reimbursement Compatibility, After-Sales & Technical Support)
- SWOT of Key Players
- Pricing Analysis by Key SKUs
- Company Profiles of Major Players
Abbott Diabetes Care
Roche Diagnostics
Ascensia Diabetes Care
Dexcom
Medtronic
iHealth Labs
ForaCare
Omron Healthcare
ACON Laboratories
Sinocare
Terumo Corporation
B. Braun
Beurer GmbH
Ypsomed
- Monitoring Frequency
- Purchasing Criteria
- Reimbursement Influence
- Pain Points
- Clinical Decision Flow
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025–2030


