Market Overview
The UAE Remote Diagnosis market (captured within the UAE telemedicine market) is valued at USD ~ million in the latest year, after generating USD ~ million in the prior year. Demand is driven by the need to optimize specialist availability, accelerate diagnostic turnaround time, and reduce physical infrastructure dependency. Remote diagnosis integrates imaging, pathology, cardiology signals, and chronic disease indicators into virtual workflows, allowing healthcare providers to manage higher patient volumes while maintaining clinical continuity. The market is structurally important due to its direct linkage with hospital efficiency, insurance cost management, and outcome-based care delivery.
Within the UAE, Abu Dhabi and Dubai dominate remote diagnosis adoption due to the concentration of large hospital groups, advanced diagnostic infrastructure, and strong digital health governance frameworks. These emirates host the majority of tertiary care centers, imaging hubs, and health data exchange platforms, enabling seamless diagnostic collaboration. On the supply and technology side, global medical technology leaders influence platform capabilities through advanced imaging, AI algorithms, and enterprise health IT systems, shaping clinical standards and accelerating innovation across the UAE healthcare ecosystem.
Market Segmentation
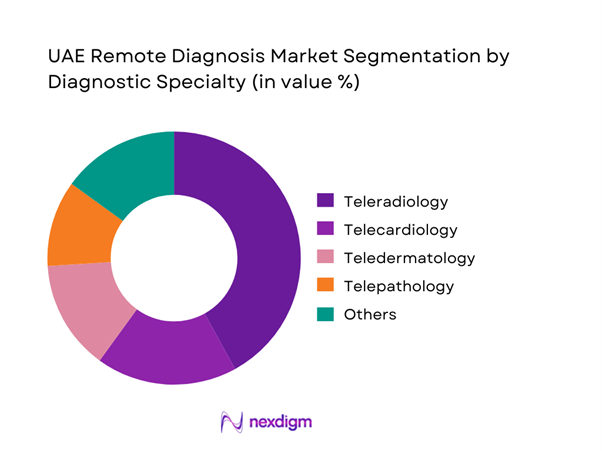
By Diagnostic Specialty
Within diagnostic specialties, teleradiology dominates the UAE Remote Diagnosis Market due to its high compatibility with digital workflows and critical role in acute and chronic care pathways. Imaging diagnostics such as CT, MRI, and X-ray can be generated locally and interpreted remotely without compromising clinical accuracy. Hospitals rely on teleradiology to manage specialist shortages, enable after-hours reporting, and support sub-specialty reads. The dominance is reinforced by rising imaging volumes, increasing chronic disease incidence, and emergency care demand. Additionally, radiology integrates seamlessly with AI triage tools, improving prioritization and efficiency, which further strengthens its leadership position in remote diagnosis adoption across UAE healthcare providers.
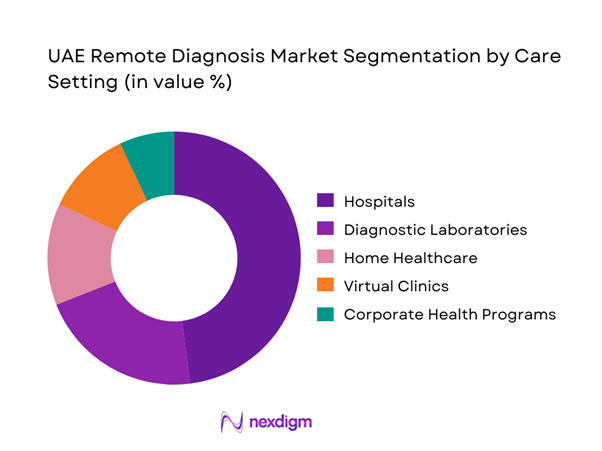
By Care Setting
Hospitals represent the dominant care setting in the UAE Remote Diagnosis Market, driven by their role as primary diagnostic hubs and referral centers. Large hospital networks integrate remote diagnosis to extend specialist coverage across multiple facilities, reduce patient transfer requirements, and improve inpatient and outpatient workflow efficiency. Hospitals also lead in adopting AI-assisted diagnostics, advanced imaging platforms, and integrated clinical decision support systems. Their financial capacity, regulatory readiness, and alignment with insurance reimbursement models enable faster scaling compared to smaller providers. As a result, hospitals continue to account for the largest share of remote diagnostic service consumption in the UAE.
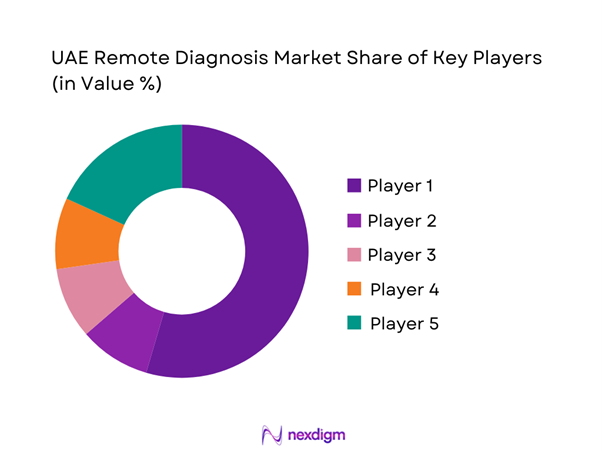
Competitive Landscape
The UAE Remote Diagnosis Market is dominated by a few major players, including PureHealth and global or regional brands like Philips Healthcare, Siemens Healthineers, and GE HealthCare. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Established year | Headquarters | UAE footprint strength | Core remote diagnosis focus | Clinical integration | Data & security posture | Key partnerships / ecosystem |
| PureHealth | 2006 | Abu Dhabi, UAE | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Malaffi (Abu Dhabi Health Information Exchange) | 2018 | Abu Dhabi, UAE | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Philips Healthcare | 1891 | Amsterdam, Netherlands | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Siemens Healthineers | 1847 | Erlangen, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Teladoc Health | 2002 | Purchase, New York, US | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
UAE Remote Diagnosis Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Digital Health Policy Enablement
UAE healthcare policies actively promote the adoption of digital health and remote clinical services, creating a structurally supportive environment for remote diagnosis. National and emirate-level regulators have established clear licensing pathways for telehealth providers, defined clinical governance requirements, and enabled secure cross-facility data exchange. This policy clarity allows hospitals, diagnostic centers, and virtual care providers to integrate remote diagnostic workflows without regulatory ambiguity. Unified electronic medical records, health information exchanges, and standardized telemedicine practice guidelines further reduce operational friction. As a result, healthcare organizations can scale remote diagnosis programs with confidence, align them with insurance and reimbursement frameworks, and deploy enterprise-grade diagnostic services across both public and private healthcare networks.
Rising Chronic Disease Burden
The increasing burden of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, respiratory disorders, and long-term metabolic illnesses is a major driver for remote diagnosis adoption in the UAE. These conditions require frequent monitoring, repeat diagnostics, and early identification of clinical deterioration, which traditional hospital-centric models struggle to deliver efficiently. Remote diagnosis enables clinicians to review diagnostic indicators more frequently without requiring physical visits, supporting proactive care management and timely intervention. This approach reduces avoidable hospital admissions, improves continuity of care, and supports long-term disease control. As chronic disease prevalence continues to rise alongside population aging and lifestyle changes, remote diagnosis is increasingly viewed as a core clinical capability rather than an optional digital add-on.
Challenges
Clinical Accuracy and Liability Risks
Maintaining high diagnostic accuracy in remote environments remains a critical challenge, particularly for complex cases that require multi-disciplinary collaboration or nuanced clinical judgment. Providers face concerns around misinterpretation of diagnostic data, limitations of remote assessments, and unclear liability in cases of adverse outcomes. Variability in clinician experience, inconsistent diagnostic protocols, and reliance on patient-generated data can further complicate clinical accountability. To address these risks, healthcare organizations must implement rigorous quality assurance frameworks, standardized diagnostic pathways, credentialing requirements, and continuous clinical performance audits. Without these safeguards, hesitation around legal exposure and reputational risk may slow adoption among risk-averse providers.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Concerns
Remote diagnosis depends heavily on the digital transmission and storage of sensitive patient information, including imaging files, diagnostic reports, and longitudinal health records. This increased data flow expands the attack surface for cybersecurity threats such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and system disruptions. Compliance with healthcare data protection regulations requires strong encryption, access control, secure identity management, and continuous monitoring. Healthcare providers must also manage third-party risks associated with cloud platforms, device integrations, and external diagnostic vendors. Failure to address cybersecurity and privacy concerns can undermine patient trust, expose organizations to regulatory penalties, and create operational vulnerabilities that hinder large-scale deployment.
Opportunities
AI-Driven Early Diagnosis
Artificial intelligence presents a significant opportunity to enhance the effectiveness and scalability of remote diagnosis. AI-enabled tools can analyze diagnostic images, physiological signals, and longitudinal patient data to identify anomalies, prioritize urgent cases, and support clinician decision-making. This capability improves diagnostic consistency, reduces interpretation time, and helps address specialist capacity constraints. AI-assisted triage allows clinicians to focus attention on high-risk patients while routine cases are managed more efficiently. As clinical validation improves and regulatory acceptance increases, AI-driven remote diagnosis can move beyond decision support to become a foundational component of preventive care and early intervention strategies.
Integration with Home Healthcare
The expansion of home healthcare services creates strong alignment with remote diagnosis capabilities. As more patients receive care in home settings, clinicians require reliable diagnostic visibility without physical examinations. Remote diagnosis enables healthcare professionals to assess patient data collected at home, including vital parameters, imaging results, and symptom reports, supporting timely clinical decisions. This model reduces unnecessary hospital visits, improves patient comfort, and supports aging-in-place initiatives. Integration between home healthcare providers and remote diagnostic platforms also enables coordinated care planning, reduces system-level costs, and aligns with patient preferences for convenient, home-based healthcare delivery.
Future Outlook
The UAE Remote Diagnosis Market is expected to strengthen its role as a foundational element of digital healthcare delivery. Strategic focus will shift toward deeper AI integration, interoperability across care settings, and outcome-driven diagnostic pathways. Providers that combine clinical accuracy, regulatory compliance, and scalable platforms will shape the next phase of market evolution.
Major Players
- PureHealth
- SEHA
- VPS Healthcare
- NMC Healthcare
- Aster DM Healthcare
- Burjeel Holdings
- Mediclinic Middle East
- Philips Healthcare
- Siemens Healthineers
- GE HealthCare
- Oracle Health
- Microsoft Healthcare
- Teladoc Health
Key Target Audience
- Hospitals and integrated healthcare networks
- Diagnostic laboratories and imaging center chains
- Health insurance providers and TPAs
- Home healthcare service providers
- Digital health platform operators
- Medical device and diagnostic technology manufacturers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with mapping stakeholders, care settings, and diagnostic workflows relevant to remote diagnosis. Key demand, supply, and regulatory variables are defined through structured secondary research.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical adoption patterns, service mix, and provider utilization are analyzed using a bottom-up framework. Data is structured by diagnostic specialty and care setting.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights are validated through expert discussions with clinicians, digital health executives, and healthcare administrators to refine assumptions and ensure practical relevance.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All findings are triangulated and synthesized into a coherent market model. Final outputs are reviewed for consistency, accuracy, and client usability.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Inclusions/Exclusions, Abbreviations, Topic-Specific Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Revenue Attribution Logic Across Use Cases or Care Settings, Primary Interview Program Design, Data Triangulation and Validation, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Remote Diagnosis Care-Continuum Mapping
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- UAE Healthcare Delivery Architecture
- Growth Drivers
Digital Health Policy Enablement
Rising Chronic Disease Burden
Specialist Capacity Optimization
Insurance Acceptance of Remote Diagnosis
Healthcare Cost Rationalization - Challenges
Clinical Accuracy and Liability Risks
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Concerns
Interoperability Gaps
Physician Adoption Resistance
Reimbursement Complexity - Opportunities
AI-Driven Early Diagnosis
Remote Diagnosis for Medical Tourism
Integration with Home Healthcare
Population Health Analytics Enablement
Employer-Led Preventive Care Programs - Trends
Advanced Imaging AI Adoption
Convergence of RPM and Diagnosis
Cloud-Based Diagnostic Platforms
Outcome-Based Care Models
Platform Consolidation - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Revenue Contribution, 2019–2024
- By Diagnostic Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Revenue per Diagnostic Interaction, 2019–2024
- By Diagnostic Specialty (in Value %)
Teleradiology
Telecardiology
Teledermatology
Telepathology
Chronic Disease Remote Diagnosis
General Medicine Remote Diagnosis - By Care Setting (in Value %)
Hospitals
Diagnostic Laboratories
Home Healthcare
Virtual Clinics
Corporate Health Programs - By Technology Platform Type (in Value %)
AI-Assisted Diagnostic Platforms
Clinical Decision Support Systems
Remote Monitoring Integrated Diagnostics
Imaging Interpretation Platforms
EHR-Integrated Diagnostic Modules - By Delivery Model (in Value %)
Real-Time Diagnosis
Store-and-Forward Diagnosis
Hybrid Diagnosis Models - By End-Use Customer Type (in Value %)
Public Healthcare Providers
Private Hospital Groups
Insurance-Linked Care Networks
Employers and Corporate Buyers
Individual Consumers - By Region (in Value %)
Abu Dhabi
Dubai
Sharjah
Northern Emirates
- Competition ecosystem overview
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Diagnostic Accuracy, AI Integration Depth, Platform Interoperability, Regulatory Readiness, Data Security Architecture, Specialty Coverage Breadth, Scalability Across Emirates, Integration with Payers)
- SWOT analysis of major players
Pricing and commercial model benchmarking - Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
PureHealth
SEHA
VPS Healthcare
NMC Healthcare
Aster DM Healthcare
Burjeel Holdings
Mediclinic Middle East
Philips Healthcare
Siemens Healthineers
GE HealthCare
Oracle Health
Microsoft Healthcare
Teladoc Health
Cerner Middle East
InstaPract
- Buyer personas and decision-making units
- Procurement and contracting workflows
- KPIs used for evaluation
- Pain points and adoption barriers
- By Revenue Contribution, 2025–2030
- By Diagnostic Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Revenue per Diagnostic Interaction, 2025–2030


