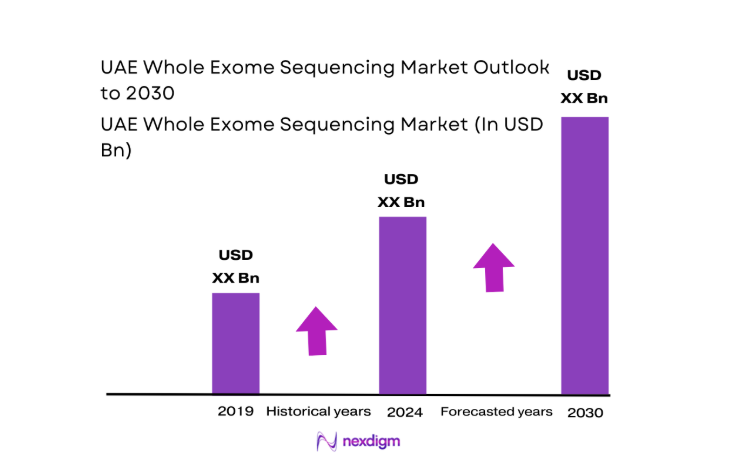
Market Overview
The UAE Whole Exome Sequencing market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by test volumes of ~ units in clinical and research settings and active system installations of ~ systems across major hospitals and laboratories. In recent periods, diagnostic throughput expanded from ~ tests to ~ tests annually, while average revenue per test stabilized near USD ~. Capital inflows of USD ~ million strengthened laboratory automation, bioinformatics capacity, and clinician training programs.
Market activity is concentrated in Abu Dhabi and Dubai, driven by advanced tertiary hospitals, national genomics programs, and dense clusters of diagnostic laboratories. These cities benefit from integrated care pathways, centralized procurement, and mature reimbursement frameworks that accelerate adoption of complex genetic tests. Strong public–private partnerships, sovereign-backed life sciences initiatives, and a policy environment prioritizing precision medicine further reinforce ecosystem maturity, enabling faster translation of sequencing technologies from research to routine clinical practice.
Market Segmentation
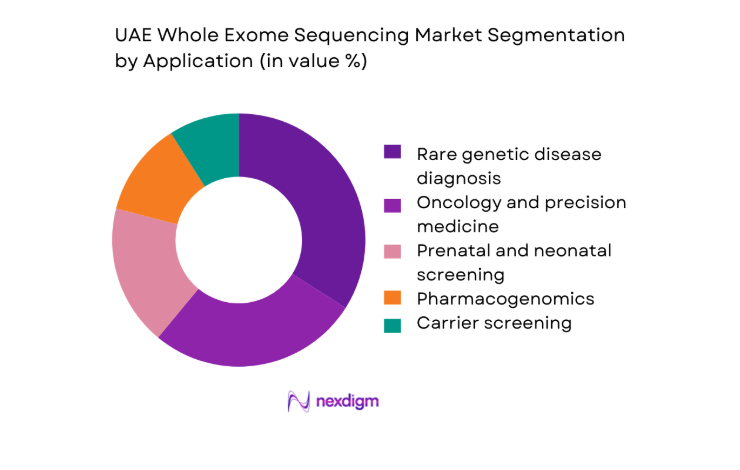
By Application
Clinical diagnostics dominates application demand due to rising utilization in rare disease identification, oncology profiling, and prenatal risk assessment. Hospitals increasingly rely on comprehensive exome-level insights to reduce diagnostic odysseys and improve therapeutic targeting. Research and translational medicine also contribute steadily, supported by national biobanking efforts and population genomics programs. Pharmacogenomics adoption is strengthening within specialty clinics as clinicians seek actionable genetic markers for drug response optimization. The convergence of improved clinician awareness, expanding reimbursement coverage, and streamlined laboratory workflows continues to elevate the role of application-driven uptake in shaping overall market structure.
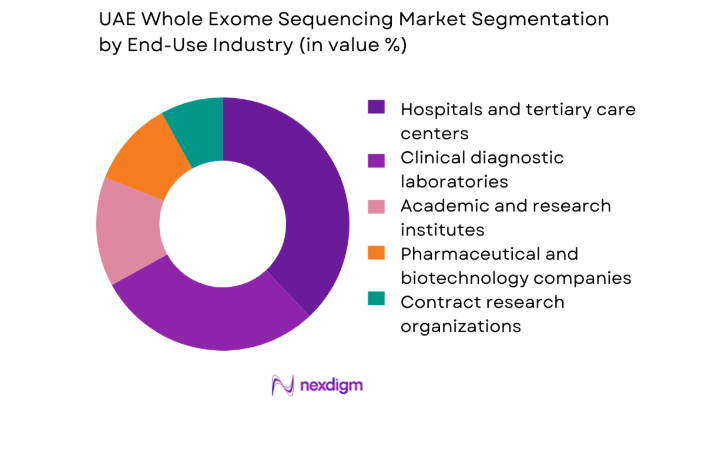
By End-Use Industry
Hospitals and tertiary care centers represent the largest end-use segment, reflecting their role as primary access points for advanced diagnostics and multidisciplinary care teams. Clinical laboratories follow closely, leveraging centralized testing models and high-throughput platforms to serve both public and private healthcare networks. Academic and translational research institutes maintain consistent demand through population studies and clinical trials. Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies increasingly integrate sequencing into companion diagnostics and biomarker discovery, while contract research organizations expand service offerings for regional and international sponsors.
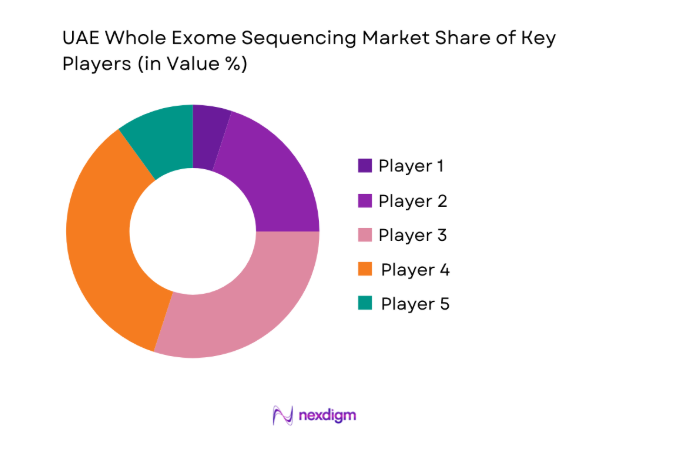
Competitive Landscape
The UAE Whole Exome Sequencing market shows moderate concentration, with a mix of global technology providers and specialized genomics service firms shaping platform availability and testing standards. Competitive dynamics center on technology depth, local service infrastructure, and alignment with national healthcare strategies, creating a landscape where a limited number of players exert strong influence over procurement and long-term partnerships.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Illumina | 1998 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific | 1956 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Roche Diagnostics | 1896 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BGI Genomics | 1999 | China | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| QIAGEN | 1984 | Netherlands | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
UAE Whole Exome Sequencing Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising prevalence of rare genetic disorders and inherited diseases
Clinical demand has accelerated as annual diagnostic referrals increased from ~ cases to ~ cases, driving test volumes from ~ units to ~ units across tertiary centers. Specialized clinics expanded sequencing capacity by ~ systems to address complex phenotypes requiring comprehensive variant detection. Public health programs allocated USD ~ million toward rare disease pathways, supporting earlier intervention and reducing long-term treatment burdens. This structural rise in patient identification and referral intensity continues to anchor sustained utilization of exome sequencing in routine care.
National genomics initiatives and precision medicine strategies
Government-backed genomics platforms expanded sequencing throughput from ~ tests to ~ tests, supported by infrastructure investments of USD ~ million in centralized laboratories and data platforms. Integration with national health records enabled longitudinal analysis across ~ patient profiles, improving diagnostic accuracy and care coordination. These initiatives increased institutional adoption of advanced sequencing workflows, standardizing clinical pathways and accelerating clinician confidence in genomic-guided decision-making.
Challenges
High capital cost of sequencing platforms and laboratory setup
Initial laboratory deployment requires investments of USD ~ million per facility, covering instrumentation, bioinformatics infrastructure, and quality systems. Annual operational outlays of USD ~ million for reagents and maintenance place pressure on smaller providers, limiting geographic expansion. System acquisition cycles of ~ months further delay market entry for new laboratories, constraining overall service availability despite rising clinical demand.
Shortage of skilled genomic scientists and bioinformaticians
The workforce gap remains evident, with only ~ specialists supporting sequencing operations across major centers. Training programs graduate ~ professionals annually, insufficient to match growing test volumes of ~ units. Institutions allocate USD ~ million toward international recruitment and upskilling, yet onboarding timelines of ~ months slow capacity ramp-up and affect turnaround times for complex analyses.
Opportunities
Integration of WES into national newborn and rare disease screening programs
Pilot screening initiatives processed ~ samples annually, demonstrating feasibility for scaled deployment across ~ births each year. Program expansion could channel USD ~ million into standardized testing pathways, improving early diagnosis and long-term care efficiency. Infrastructure readiness across ~ hospitals positions the system to absorb higher screening volumes without proportional increases in per-test resource intensity.
Development of local genomic reference databases for Arab populations
Population genomics projects have sequenced ~ individuals, generating region-specific variant datasets that enhance clinical interpretation accuracy. Continued investment of USD ~ million into biobanking and data governance can expand coverage to ~ participants, strengthening diagnostic yield and positioning the UAE as a regional hub for ethnically relevant genomic insights.
Future Outlook
The UAE Whole Exome Sequencing market is expected to deepen its role in routine diagnostics as precision medicine becomes embedded across care pathways. Continued alignment between healthcare policy, digital health infrastructure, and life sciences investment will support broader access to advanced genetic testing. Collaboration between public institutions and private innovators is likely to accelerate platform localization, workforce development, and data integration, reinforcing long-term sustainability and clinical impact through 2030 and beyond.
Major Players
- Illumina
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Roche Diagnostics
- QIAGEN
- BGI Genomics
- Agilent Technologies
- Oxford Nanopore Technologies
- Pacific Biosciences
- Twist Bioscience
- SOPHiA Genetics
- Revvity
- Eurofins Genomics
- Centogene
- G42 Healthcare
- Pure Health
Key Target Audience
- Public and private hospital networks
- Independent diagnostic laboratories
- Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies
- Contract research organizations
- Health insurance providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Ministry of Health and Prevention
- Department of Health Abu Dhabi
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Defined core market parameters including clinical demand drivers, technology adoption patterns, and regulatory alignment factors. Mapped stakeholder groups across healthcare providers, laboratories, and policy bodies. Established baseline metrics for capacity, utilization, and service coverage to frame subsequent analysis.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Synthesized qualitative and quantitative inputs to structure the market across applications and end-use industries. Assessed infrastructure readiness, procurement dynamics, and reimbursement environments. Built scenario frameworks to capture varying adoption trajectories and institutional investment behaviors.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Engaged domain specialists across clinical genetics, laboratory management, and health policy to validate assumptions. Cross-checked operational realities including workforce availability, data governance practices, and integration challenges within existing care systems.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Integrated validated insights into a coherent market narrative supported by structured segmentation and competitive mapping. Ensured consistency in assumptions, terminology, and analytical rigor to deliver a publication-ready strategic assessment.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, whole exome sequencing service taxonomy across clinical and research use, market sizing logic by test volume and sequencing throughput, revenue attribution across library prep sequencing and bioinformatics services, primary interview program with genetic labs hospitals and research centers, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Clinical care and research usage pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising prevalence of rare genetic disorders and inherited diseases
National genomics initiatives and precision medicine strategies
Expansion of advanced diagnostic infrastructure in tertiary hospitals
Growing adoption of NGS-based oncology and prenatal testing
Increasing investments by government and sovereign funds in life sciences
Improving reimbursement and coverage for advanced genetic tests - Challenges
High capital cost of sequencing platforms and laboratory setup
Shortage of skilled genomic scientists and bioinformaticians
Data privacy, consent management, and genomic data governance concerns
Limited local manufacturing and dependence on imported reagents
Complex regulatory pathways for advanced molecular diagnostics
Uneven awareness among clinicians about WES clinical utility - Opportunities
Integration of WES into national newborn and rare disease screening programs
Development of local genomic reference databases for Arab populations
Public-private partnerships in genomic medicine and biobanking
Expansion of clinical trials and companion diagnostics in oncology
Growth of medical tourism for advanced genetic testing services
Adoption of AI-driven variant interpretation and decision support - Trends
Shift from research-focused to routine clinical adoption of WES
Increasing use of cloud-based bioinformatics and data sharing platforms
Bundling of WES with targeted panels and whole genome sequencing
Rising role of population genomics and preventive healthcare
Standardization of laboratory workflows and accreditation
Consolidation among diagnostic service providers - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Test Volume, 2019–2024
- By Active Sequencing Systems, 2019–2024
- By Revenue per Test, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Public hospitals and government laboratories
Private hospital networks
Independent diagnostic laboratories
Academic and research institutes
Biotechnology companies and CROs - By Application (in Value %)
Rare genetic disease diagnosis
Oncology and precision medicine
Prenatal and neonatal screening
Pharmacogenomics
Carrier screening and inherited disorder testing - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Short-read NGS platforms
Long-read sequencing platforms
Hybrid capture-based WES workflows
Amplicon-based exome sequencing workflows - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Hospitals and tertiary care centers
Clinical diagnostic laboratories
Academic and translational research institutes
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies
Contract research organizations - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
On-premise sequencing and analysis
Cloud-based bioinformatics platforms
Hybrid deployment models
Standalone offline systems - By Region (in Value %)
Abu Dhabi
Dubai
Sharjah
Northern Emirates
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (sequencing accuracy, turnaround time, test menu breadth, bioinformatics capability, data security compliance, local service support, pricing flexibility, partnership ecosystem)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Illumina
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Agilent Technologies
QIAGEN
Roche Diagnostics
BGI Genomics
Pacific Biosciences
Oxford Nanopore Technologies
Twist Bioscience
SOPHiA Genetics
Revvity
Eurofins Genomics
Centogene
G42 Healthcare
Pure Health
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Test Volume, 2025–2030
- By Active Sequencing Systems, 2025–2030
- By Revenue per Test, 2025–2030


