Market Overview
The US aviation infrastructure market current size stands at around USD ~ million and reflects a complex ecosystem spanning airside, terminal, security, and air traffic management assets. Capital flows into runway rehabilitation, terminal modernization, navigation systems upgrades, and digital airport platforms continue to shape deployment priorities across hubs and regional facilities. Investment momentum is guided by safety mandates, capacity constraints, sustainability objectives, and resilience requirements, with funding streams channeled through multi-year infrastructure programs and airport authority capital plans.
Activity is concentrated across large hub airports and high-density metropolitan corridors where passenger throughput, cargo handling, and aircraft movements converge. Coastal gateways and logistics-intensive regions benefit from mature supplier networks, EPC capacity, and digital integration capabilities. Federal policy alignment accelerates modernization in strategically significant nodes, while state and municipal authorities prioritize landside connectivity and terminal experience improvements. Regions with established aerospace clusters exhibit faster adoption of advanced navigation, security automation, and asset management platforms.
Market Segmentation
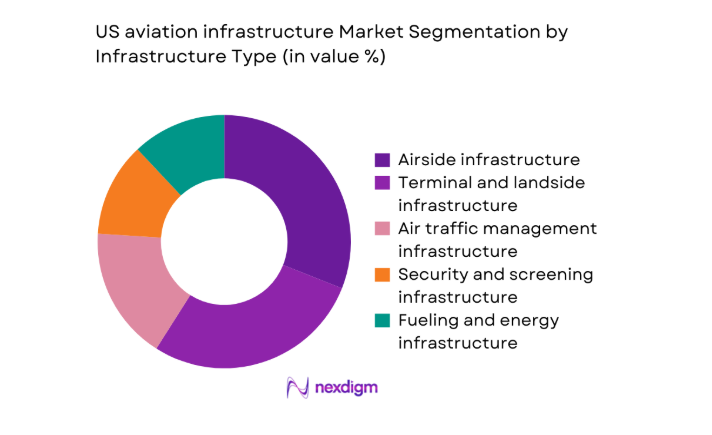
By Infrastructure Type
Airside, terminal, and air traffic management assets dominate allocation priorities due to safety compliance cycles, capacity enhancement mandates, and lifecycle replacement of aging runways, aprons, and navigation systems. Security and screening infrastructure is expanding alongside passenger processing automation, while fueling and energy systems are being reconfigured to accommodate electrification of ground operations and alternative fuels logistics. Maintenance facilities are prioritized at hubs with dense aircraft rotations and overnight parking demand. The segmentation reflects regulatory-driven capex planning, operational resilience needs, and technology refresh cycles aligned with multi-year capital improvement programs and modernization roadmaps.
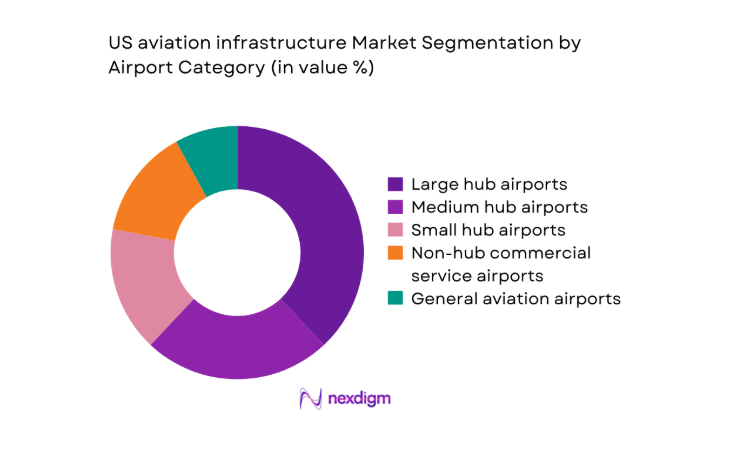
By Airport Category
Large and medium hubs capture a disproportionate share of infrastructure activity due to passenger density, international connectivity, and airline network concentration. These airports anchor multi-phase terminal expansions, runway rehabilitation programs, and advanced navigation deployments, supported by robust financing mechanisms and established delivery partners. Small hubs and non-hub airports prioritize targeted upgrades focused on safety compliance, apron rehabilitation, and terminal efficiency. General aviation facilities focus on runway maintenance, lighting systems, and landside access improvements. The segmentation mirrors demand concentration, funding access disparities, and differentiated modernization pathways across airport classes.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by integrated engineering, construction, systems integration, and digital platform capabilities aligned to regulatory compliance and multi-year capital programs. Providers differentiate through delivery track record, lifecycle support depth, and coordination across federal, state, and local stakeholders.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Bechtel | 1898 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Fluor | 1912 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Jacobs | 1947 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AECOM | 1990 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Kiewit | 1884 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
US aviation infrastructure Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Federal infrastructure funding through AIP and bipartisan infrastructure programs
Federal programs expanded capital allocation cycles during 2022–2025 through multi-year authorization windows, increasing project pipelines for runway rehabilitation, terminal modernization, and navigation upgrades. In 2024, over 450 airports advanced capital plans aligned to safety and capacity mandates. The FAA processed 980 project approvals in 2023, accelerating construction starts across hubs and regional facilities. TSA compliance updates in 2022 and 2024 triggered equipment refresh across 220 terminals. Air traffic modernization milestones completed 38 system deployments in 2025, improving throughput reliability. These institutional signals stabilized procurement calendars, shortened bid cycles, and sustained contractor utilization rates across metropolitan gateways.
Modernization of aging runways, terminals, and navigation systems
Aging asset profiles drove rehabilitation cycles across pavement, lighting, and terminal systems during 2022–2025. Condition assessments completed at 310 airports in 2023 identified priority resurfacing for 1,420 runway segments and replacement of 6,800 lighting fixtures. Terminal retrofits addressed capacity bottlenecks, adding 94 new gates and refurbishing 128 baggage systems in 2024. Navigation modernization advanced with 26 NextGen-related deployments in 2025, reducing separation constraints and improving reliability. Institutional safety audits issued 1,140 corrective actions in 2022, reinforcing compliance-driven capex. These operational imperatives sustained steady project flows and contractor backlogs.
Challenges
Lengthy permitting and environmental clearance timelines
Environmental reviews and permitting processes extended project lead times during 2022–2025, constraining delivery schedules. In 2023, environmental assessments for 160 airport projects exceeded planned timelines by 9 months on average, delaying mobilization. Noise and air quality consultations required coordination across 42 state agencies and 310 local jurisdictions in 2024. Litigation affected 18 large hub expansions in 2022, adding redesign cycles and documentation burdens. Federal consultation queues processed 2,400 filings in 2025, stretching approval windows. These institutional frictions elevated schedule risk, compressed construction seasons, and increased idle equipment days across brownfield upgrades.
Cost overruns and construction delays due to labor shortages
Workforce constraints tightened delivery capacity during 2022–2025 as specialized trades faced persistent shortages. In 2024, certified airfield electricians filled 71 percent of planned rosters across major projects, extending installation schedules. Skilled equipment operators availability declined by 18 in 2023 relative to prior baselines, affecting paving productivity across 640 runway work packages. Contractor vacancy rates averaged 12 during peak seasons in 2022, increasing shift premiums and coordination complexity. Safety training throughput reached 24,000 certifications in 2025, insufficient to offset retirements. These constraints slowed commissioning milestones and increased reliance on phased construction sequencing.
Opportunities
Digital air traffic management and NextGen system upgrades
NextGen modernization created pathways for system integration, analytics, and automation across 2022–2025. The FAA commissioned 14 trajectory-based operations nodes in 2023, enabling tighter sequencing at congested hubs. Data fusion pilots covered 22 metro airspaces in 2024, integrating surveillance feeds from 3 sensor networks. Controller decision-support tools deployed at 9 centers in 2025 improved throughput stability during peak banks. Institutional performance targets tracked 120 operational metrics, driving demand for integration services and cybersecurity hardening. These deployments support scalable digital platforms, lifecycle services, and interoperability frameworks across airport and airspace stakeholders.
Smart terminal technologies and passenger processing automation
Terminal digitization programs expanded during 2022–2025 through biometrics, self-service, and queue optimization. In 2024, 76 terminals implemented biometric boarding lanes, reducing manual processing steps across 3 checkpoints per terminal on average. Passenger flow analytics covered 48 high-density concourses in 2023, integrating data from 5 operational systems. Automated baggage handling retrofits added 112 high-speed sorters in 2025, improving transfer reliability. Federal technology certification cycles approved 9 new screening configurations in 2022, opening standardized procurement pathways. These shifts enable modular deployments, recurring software services, and operations analytics partnerships.
Future Outlook
The market trajectory emphasizes phased modernization across airside, terminals, and digital systems as policy alignment and capacity pressures persist. Infrastructure resilience and sustainability integration will shape capital prioritization through the planning horizon. Regional gateways are expected to accelerate digital adoption and multimodal connectivity. Public–private delivery models will expand to de-risk large redevelopment programs. Execution will hinge on permitting efficiency and workforce availability.
Major Players
- Bechtel
- Fluor
- Jacobs
- AECOM
- Kiewit
- Skanska USA
- Turner Construction
- Parsons Corporation
- HNTB
- HDR
- WSP USA
- Black & Veatch
- Tetra Tech
- Honeywell
- Siemens
Key Target Audience
- Airport authorities and port authorities
- Federal Aviation Administration
- Transportation Security Administration
- State departments of transportation
- City and municipal aviation departments
- Airlines and airport operators
- Engineering, procurement, and construction contractors
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Asset classes, regulatory compliance requirements, lifecycle stages, and delivery models were mapped across airside, terminal, security, and air traffic systems. Demand drivers were structured around capacity constraints, safety mandates, and resilience priorities. Institutional procurement cycles and capital planning horizons were defined to frame project pipelines.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Project pipelines were constructed using approved capital programs, phased delivery schedules, and modernization roadmaps. Technology adoption pathways were analyzed across navigation, security automation, and terminal digitization. Supply chain dependencies and delivery capacity constraints were integrated into scenario construction.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Operational assumptions were validated through consultations with airport program managers, system integrators, and regulatory specialists. Delivery risks were stress-tested against permitting timelines, workforce availability, and commissioning protocols. Technology readiness and interoperability assumptions were refined through pilot deployment learnings.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into thematic insights covering drivers, constraints, and deployment pathways. Segment-level implications were aligned with institutional priorities and delivery models. Strategic implications were structured to support capital planning, partnership design, and phased modernization roadmaps.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and airport infrastructure asset boundaries, FAA capital improvement program data triangulation, airport authority capex and opex disclosures analysis, TSA and DHS security infrastructure procurement tracking, air traffic management modernization program interviews, EPC and systems integrator contract mapping, passenger traffic and aircraft movement demand modeling)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and operational pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising passenger traffic and aircraft movements driving capacity expansion
Federal infrastructure funding through AIP and bipartisan infrastructure programs
Modernization of aging runways, terminals, and navigation systems
Growth of low-cost carriers and regional connectivity expansion
Security and safety compliance upgrades mandated by TSA and FAA
Sustainability investments for electrification and SAF infrastructure - Challenges
Lengthy permitting and environmental clearance timelines
Cost overruns and construction delays due to labor shortages
Funding constraints at smaller and non-hub airports
Complex stakeholder coordination across federal, state, and local agencies
Operational disruptions during brownfield expansions
Supply chain volatility for specialized aviation-grade materials and systems - Opportunities
Digital air traffic management and NextGen system upgrades
Smart terminal technologies and passenger processing automation
Public–private partnerships for large-scale terminal redevelopment
Electrification of ground support equipment and charging infrastructure
Resilient infrastructure investments for climate adaptation
Regional airport revitalization to support domestic connectivity - Trends
Adoption of biometrics and contactless passenger processing
Integration of digital twins for airport planning and operations
Modular and prefabricated construction for terminals
Expansion of sustainable aviation fuel storage and blending facilities
Data-driven asset management and predictive maintenance
Increased use of private capital in airport redevelopment projects - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Infrastructure Type (in Value %)
Airside infrastructure
Terminal and landside infrastructure
Air traffic management infrastructure
Security and screening infrastructure
Fueling and energy infrastructure
Maintenance, repair and overhaul facilities - By Airport Category (in Value %)
Large hub airports
Medium hub airports
Small hub airports
Non-hub commercial service airports
General aviation airports - By Ownership and Operator Type (in Value %)
Public airport authorities
City and state-owned airports
Port authorities
Private airport operators
Public–private partnership operated airports - By Project Type (in Value %)
New airport development
Runway and taxiway expansion
Terminal expansion and modernization
Digital and smart airport upgrades
Sustainability and energy transition projects - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (project delivery capability, regulatory compliance expertise, integrated EPC offerings, digital systems integration depth, sustainability and ESG credentials, financial strength and bonding capacity, long-term O&M support, geographic project footprint)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Bechtel
Fluor
Jacobs
AECOM
Kiewit
Skanska USA
Turner Construction
Parsons Corporation
HNTB
HDR
WSP USA
Black & Veatch
Tetra Tech
Honeywell
Siemens
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


