Market Overview
The US ground handling system market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained demand across commercial aviation, cargo operations, and airport service ecosystems. Investment momentum remains anchored in equipment modernization, service outsourcing, and digital fleet management, with capital allocation directed toward electrification, automation, and safety compliance. The market’s present structure is shaped by long-term service contracts, airport concession frameworks, and integrated service delivery models that prioritize aircraft turnaround reliability and operational resilience.
Demand concentration is strongest across major aviation hubs and high-throughput cargo gateways, supported by dense airline networks, intermodal logistics connectivity, and mature service ecosystems. Coastal gateway airports and inland freight corridors benefit from established maintenance clusters, specialized workforce availability, and policy support for low-emission ground operations. Regional hubs exhibit growing activity driven by network optimization strategies, while regulatory alignment, infrastructure readiness, and public funding programs influence deployment pace and service sophistication.
Market Segmentation
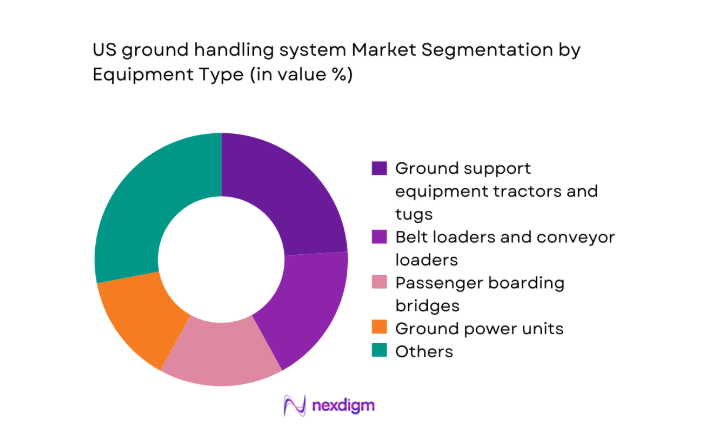
By Equipment Type
The equipment mix is dominated by ground support assets that directly influence aircraft turnaround time and safety compliance. Electric baggage tractors, belt loaders, and ground power units increasingly anchor procurement strategies as operators seek lower emissions and predictable maintenance cycles. Passenger boarding bridges and pre-conditioned air units retain strong relevance at high-traffic terminals due to throughput requirements and passenger experience standards. De-icing systems show heightened utilization in cold-climate regions, while baggage handling systems benefit from terminal automation initiatives. Equipment replacement cycles are driven by operational uptime targets, safety audits, and charging infrastructure availability, shaping procurement prioritization across hub and regional airports.
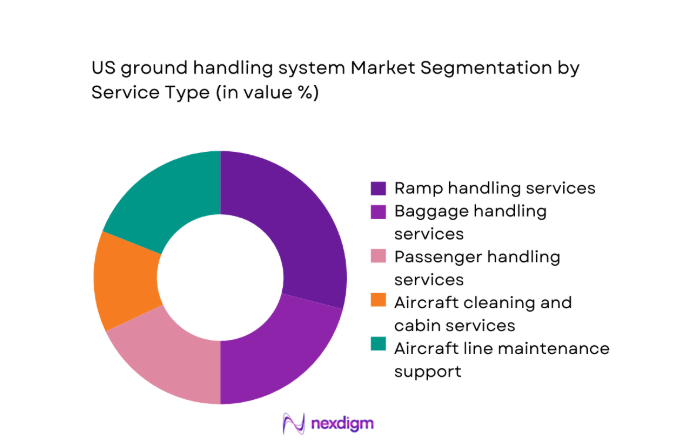
By Service Type
Ramp handling and baggage services form the operational backbone of airport ground activities, accounting for the highest service utilization due to frequency and safety criticality. Passenger handling remains essential at large hubs with complex transfer flows and service-level commitments. Aircraft cleaning and line maintenance support scale with aircraft utilization intensity and turnaround compression mandates. Cargo and mail handling services are expanding with growth in express logistics and belly cargo utilization, reinforcing demand for specialized handling workflows. Service portfolios are increasingly bundled under integrated contracts, emphasizing standardized performance metrics, safety assurance, and digital coordination across multi-operator airport environments.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a mix of integrated service providers and equipment-focused specialists operating under airport concessions and multi-year service contracts. Differentiation centers on operational reliability, safety compliance depth, electrification readiness, and digital fleet coordination capabilities aligned to hub-level performance requirements.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Swissport International | 1996 | Zurich, Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Menzies Aviation | 1833 | Edinburgh, United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| dnata | 1959 | Dubai, United Arab Emirates | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Worldwide Flight Services | 1984 | Paris, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Signature Aviation | 1992 | Orlando, United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
US ground handling system Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising air passenger traffic and aircraft movements at US hubs
Operational throughput at major hubs is rising as scheduled departures increased to 915000 in 2024 from 872000 in 2023 across top metropolitan airports, intensifying ground coordination needs. Average daily movements exceeded 2500 at several hubs during peak seasons, straining turnaround windows. Institutional indicators show terminal capacity utilization approaching 92 at high-density gateways, requiring optimized ramp sequencing and equipment availability. Aircraft utilization cycles rose from 8.6 to 9.1 hours per day between 2023 and 2024, increasing service frequency per aircraft. Federal infrastructure programs expanded gate modernization at 42 facilities in 2024, further driving ground handling activity intensity and reliability requirements.
Airline outsourcing of ground handling to improve cost efficiency
Airline internalization rates declined as 61 carriers expanded third-party service contracts in 2024, up from 53 in 2023, reflecting operational focus on network optimization. Contract tenures extended to 36 months on average, compared with 24 months previously, improving service continuity. Labor availability constraints saw vacancy rates reach 14 in 2024 at large hubs, reinforcing outsourcing incentives. Institutional indicators show procurement cycles compressed from 180 to 120 days for ramp services. Fleet utilization improvements, with narrowbody turnarounds reduced by 6 minutes per cycle in 2024, favored specialized providers with standardized operating procedures and digital dispatch capabilities.
Challenges
High capital expenditure for electrified ground support equipment
Airport electrification programs require dense charging networks, with 420 fast chargers deployed across 18 hubs in 2024, compared with 260 in 2023, stressing power distribution systems. Grid interconnection queues averaged 14 months in 2024, delaying equipment commissioning. Equipment availability lagged as delivery lead times extended to 9 months, up from 6 months in 2023. Institutional permitting cycles for airside electrical upgrades averaged 210 days. Workforce retraining programs reached 3800 technicians in 2024, yet maintenance readiness gaps persist. These constraints slow fleet transition pacing and complicate synchronized deployment across multi-operator terminals.
Operational disruptions from labor shortages and unionization pressures
Ground operations faced staffing volatility as attrition reached 22 in 2024 at large hubs, compared with 17 in 2023, affecting service continuity. Collective bargaining cycles increased work-rule complexity, with 14 major agreements renegotiated in 2024. Training throughput improved to 5200 certifications issued annually, yet onboarding time remained 90 days, constraining peak-season scalability. Institutional safety audits recorded 3100 minor non-conformities in 2024, highlighting process strain. Absenteeism peaks of 11 during adverse weather events disrupted ramp sequencing, requiring contingency staffing models and digital rostering to stabilize operations.
Opportunities
Deployment of fully electric and autonomous ground support fleets
Pilot programs expanded autonomous towing trials to 6 airports in 2024, up from 3 in 2023, supported by updated airside operations guidance. Electric fleet penetration reached 38 at select hubs, compared with 29 the prior year, indicating readiness for scaled deployment. Institutional funding enabled 27 electrification projects in 2024, accelerating charger installation density to 1 unit per 3 gates at leading terminals. Equipment uptime improved to 97 with predictive maintenance integration. Battery lifecycle management frameworks matured as standardized health diagnostics were adopted across 2400 assets, enabling operational confidence for wider autonomous and electric fleet rollouts.
Growth of long-term service contracts with airport authorities
Airport authorities expanded multi-year concession frameworks, with 19 hubs issuing contracts exceeding 60 months in 2024, compared with 11 in 2023, improving planning stability. Institutional procurement reforms reduced tender cycles to 150 days, supporting faster service onboarding. Performance-based clauses linked to 98 on-time departure thresholds incentivized operational excellence. Capital planning alignment improved as 34 terminals synchronized apron upgrades with service contracts. Workforce continuity benefits emerged as annual turnover declined to 18 at airports with longer contracts. These conditions create durable platforms for technology integration, training investment, and service standardization across airport ecosystems.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to advance through accelerated electrification, deeper service outsourcing, and tighter integration of digital fleet coordination across hub and regional airports. Policy alignment around low-emission operations and infrastructure funding will shape deployment timelines. Multi-year concessions and performance-based contracting are likely to stabilize service delivery while enabling technology adoption through 2035.
Major Players
- Swissport International
- Menzies Aviation
- dnata
- Worldwide Flight Services
- Signature Aviation
- Atlantic Aviation
- GAT Airline Ground Support
- PrimeFlight Aviation Services
- Unifi Aviation
- Aviation Facilities Company Management
- TCR Group
- JBT Corporation
- Textron GSE
- Kalmar Motor USA
- Mallaghan
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airlines and network carriers
- Cargo airlines and integrated logistics operators
- Airport authorities and airport operating companies
- Third-party ground handling service providers
- Ground support equipment manufacturers and OEMs
- Electric charging and airside infrastructure providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core variables were defined across equipment categories, service workflows, utilization intensity, airside infrastructure readiness, and regulatory compliance depth. Demand drivers were mapped to hub traffic density, fleet utilization cycles, and cargo throughput patterns. Supply-side variables captured equipment availability, workforce capacity, and maintenance readiness.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Operational datasets were synthesized with airport capacity indicators, fleet deployment footprints, and concession frameworks. Bottom-up modeling mapped equipment installed bases to gate counts and turnaround requirements. Service utilization intensity was aligned to aircraft movements and peak-season variability to construct demand scenarios.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through structured consultations with airport operations leaders, airside safety managers, and fleet maintenance heads. Regulatory interpretations were stress-tested against compliance requirements and operational audits. Scenario testing assessed electrification readiness and service outsourcing feasibility under infrastructure constraints.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were integrated into a coherent market narrative linking infrastructure maturity, policy alignment, and service evolution. Analytical outputs were triangulated across operational indicators and deployment readiness signals. Final insights emphasize practical implications for procurement planning, service integration, and technology adoption.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and service scope mapping for US airport ground handling systems, Primary interviews with US airport operators airlines and ground service providers, Analysis of FAA TSA and DOT operational datasets, Bottom-up fleet and equipment installed base modeling at major US airports, Vendor revenue triangulation from financial disclosures and contracts, RFP tender tracking and concession agreement analysis)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and service workflows
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising air passenger traffic and aircraft movements at US hubs
Airline outsourcing of ground handling to improve cost efficiency
Fleet modernization and replacement of aging ground support equipment
Electrification mandates and sustainability targets at major airports
Expansion of cargo operations driven by e-commerce logistics
Airport infrastructure investments under federal funding programs - Challenges
High capital expenditure for electrified ground support equipment
Operational disruptions from labor shortages and unionization pressures
Infrastructure constraints for charging and power distribution at airports
Stringent safety compliance and certification requirements
Cyclicality of airline traffic and exposure to macroeconomic shocks
Fragmented vendor ecosystem and interoperability issues - Opportunities
Deployment of fully electric and autonomous ground support fleets
Growth of long-term service contracts with airport authorities
Integration of telematics and fleet management software
Public–private partnerships for ground handling infrastructure upgrades
Expansion of cargo-focused ground handling at secondary airports
Performance-based contracting models with airlines - Trends
Rapid adoption of electric baggage tractors and belt loaders
Digitization of turnaround management and resource scheduling
Increased use of IoT sensors for predictive maintenance
Shift toward outsourced integrated ground handling solutions
Standardization of safety and service quality benchmarks across hubs
Consolidation among third-party ground handling service providers - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Equipment Type (in Value %)
Ground support equipment tractors and tugs
Belt loaders and conveyor loaders
Passenger boarding bridges
Ground power units
Pre-conditioned air units
De-icing and anti-icing systems
Baggage handling systems - By Service Type (in Value %)
Ramp handling services
Passenger handling services
Baggage handling services
Aircraft cleaning and cabin services
Aircraft line maintenance support
Cargo and mail handling services - By Powertrain (in Value %)
Electric ground support equipment
Hybrid ground support equipment
Diesel and gasoline ground support equipment - By Airport Category (in Value %)
Large hub airports
Medium hub airports
Small hub airports
Non-hub commercial service airports - By End User (in Value %)
Commercial airlines
Cargo airlines
Airport authorities and operators
Third-party ground handling service providers
Military and government aviation operators
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (service portfolio breadth, equipment electrification readiness, airport footprint and concessions, safety compliance track record, pricing and contract flexibility, digital fleet management capabilities, maintenance and uptime SLAs, financial stability)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Swissport International
Menzies Aviation
dnata
Worldwide Flight Services
Signature Aviation
Atlantic Aviation
GAT Airline Ground Support
PrimeFlight Aviation Services
Unifi Aviation
Aviation Facilities Company Management
TCR Group
JBT Corporation
Textron GSE
Kalmar Motor USA
Mallaghan
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


