Market Overview
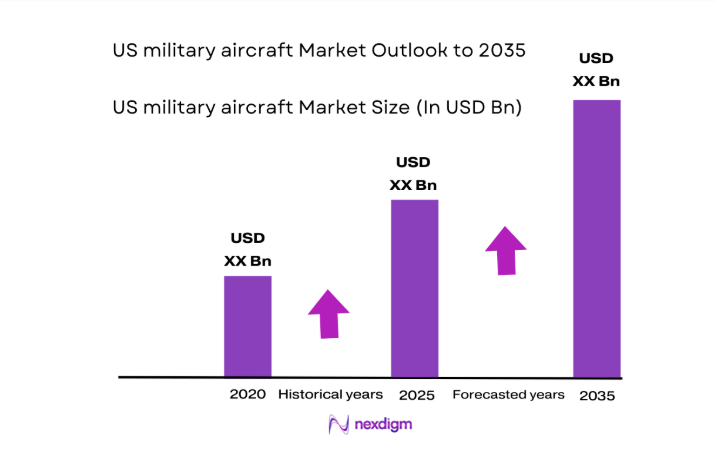
The US military aircraft market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained procurement momentum across fixed-wing and rotary platforms, modernization cycles for aging fleets, and ongoing sustainment demand across training, combat, and support missions. Spending patterns emphasize platform readiness, avionics refresh, propulsion upgrades, and mission system integration, with procurement cadence shaped by multi-year programs, fleet recapitalization priorities, and alignment to operational readiness objectives across air superiority, mobility, and intelligence missions.
Activity concentrates around established aerospace hubs in Southern California, North Texas, the Mid-Atlantic corridor, and the Southeast, supported by dense supplier ecosystems, test ranges, and MRO infrastructure. Proximity to major bases and depots enables faster integration, acceptance testing, and sustainment. The policy environment emphasizes domestic industrial capacity, secure supply chains, and export control compliance, reinforcing localized manufacturing clusters and long-term sustainment networks aligned with operational tempo and readiness targets.
Market Segmentation
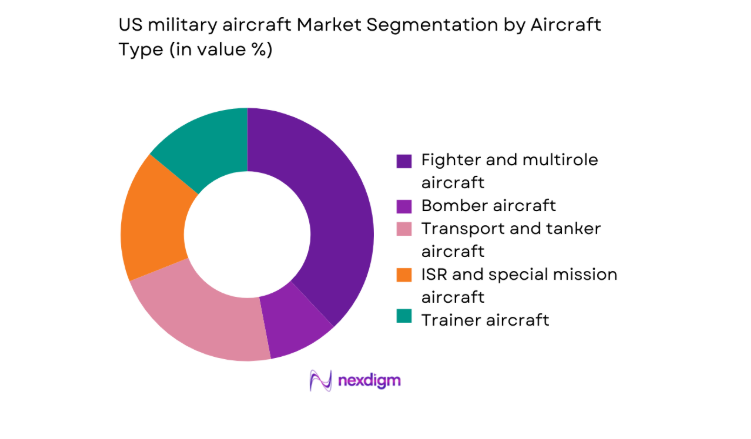
By Aircraft Type
Fighter and multirole aircraft dominate demand due to continuous fleet recapitalization, mission versatility across air superiority and strike roles, and sustained modernization of avionics, sensors, and propulsion. Transport and tanker platforms remain structurally important for mobility and refueling, while ISR and special mission aircraft benefit from persistent demand for surveillance and electronic warfare. Trainers retain steady replacement cycles tied to pilot throughput. Unmanned combat and support aircraft are expanding, driven by operational concepts integrating autonomy, teaming with crewed platforms, and extended endurance requirements across contested environments.
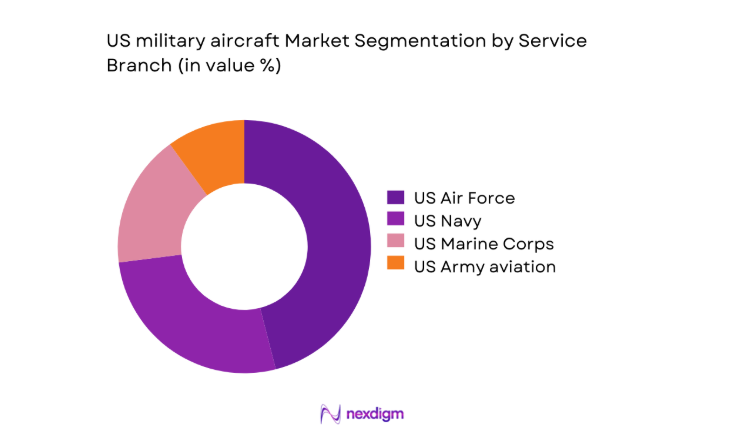
By Service Branch
The US Air Force leads procurement and sustainment intensity due to platform diversity, global deployment commitments, and large-scale modernization programs. The US Navy maintains strong demand for carrier-capable aircraft and maritime strike capabilities, while the US Marine Corps emphasizes expeditionary aviation and short takeoff operations aligned to distributed operations concepts. Army aviation sustains steady demand for support aircraft aligned to lift, reconnaissance, and joint integration, with lifecycle programs driving continuous upgrades, depot maintenance, and interoperability investments across services.
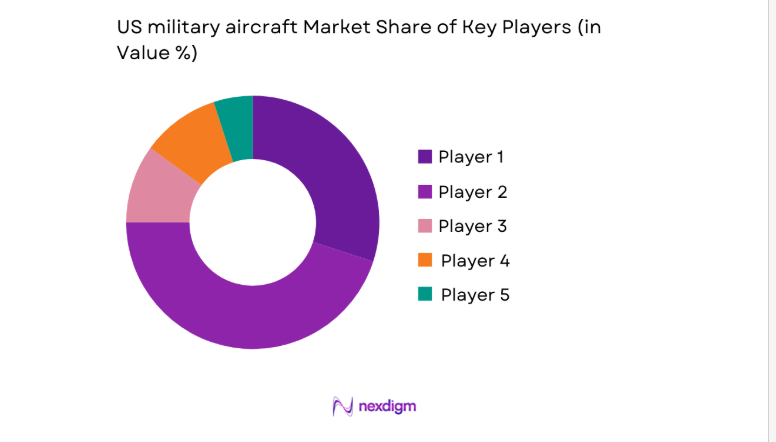
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is shaped by vertically integrated primes, deep-tier supplier ecosystems, and long-cycle platform programs that favor incumbency through certification depth, installed base, and sustainment footprints. Competition centers on program execution, technology readiness, supply chain resilience, and lifecycle support performance aligned to readiness objectives.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing Defense, Space & Security | 2002 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Northrop Grumman | 1939 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| RTX | 2020 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| General Atomics Aeronautical Systems | 1993 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
US military aircraft Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising geopolitical tensions and force modernization mandates
Heightened security competition since 2022 has accelerated readiness objectives and modernization sequencing across air dominance, strike, and mobility missions. Congressional authorization cycles in 2024 and 2025 emphasized recapitalization for contested environments, while operational tempo across Europe and the Indo-Pacific increased sortie requirements. The Department of Defense reported 2 theaters sustaining elevated deployment postures in 2024, with joint exercises increasing to 31 events in 2023 and 34 in 2024. Aircrew training throughput expanded to 9800 pilots in 2024, requiring higher trainer availability. Depot induction slots rose to 46 locations by 2025, supporting accelerated modernization and sustainment rhythms.
Replacement of aging legacy fleets
Fleet age profiles continue to pressure availability and readiness, with multiple platforms exceeding 30 service years by 2024, increasing maintenance downtime and parts obsolescence risks. In 2023, readiness targets prioritized reductions in unscheduled maintenance events recorded at 128000 incidents across major airframes, prompting accelerated replacement decisions. The Air Logistics Complex network expanded component repair lines to 64 in 2024 to stabilize availability. Engine shop visit cycles shortened from 420 days in 2022 to 360 days in 2025, reflecting intensified utilization. Flight hour programs surpassed 1.6 million hours in 2024, reinforcing replacement urgency to sustain mission reliability.
Challenges
Long development cycles and program cost overruns
Complex systems integration extends development timelines, with program milestones slipping across multiple technology domains since 2022. Test and evaluation schedules expanded to 48 months for advanced avionics integration by 2024, while software certification queues grew to 112 packages awaiting verification in 2025. Range availability constraints limited live-fire test windows to 210 days in 2023, delaying acceptance. Workforce certification backlogs affected 3800 engineers in 2024, slowing configuration baselines. Supply chain qualification cycles for new materials averaged 26 months in 2025, compounding schedule risk and compressing delivery windows critical to operational planning.
Supply chain fragility for engines, avionics, and advanced materials
Tier-2 and Tier-3 supplier concentration created bottlenecks in 2022–2025, with single-source dependencies affecting 74 critical components by 2024. Lead times for flight-critical semiconductors extended to 52 weeks in 2023, improving to 41 weeks in 2025 but remaining volatile. Forging capacity utilization reached 92 in 2024, constraining throughput. Qualified casting facilities numbered 18 in 2023, limiting surge options. Depot-level parts fill rates dropped to 83 in 2024, increasing aircraft-on-ground events and compressing readiness buffers during peak training cycles and contingency deployments.
Opportunities
Modernization and upgrade programs for legacy fleets
Incremental upgrades across sensors, mission computers, and survivability suites offer near-term readiness gains without full platform replacement. In 2024, retrofit lines processed 240 aircraft across avionics refresh packages, while electronic warfare updates expanded coverage across 12 wing locations. Open systems interfaces adopted in 2023 enabled 9 new software drops in 2024, accelerating capability insertion cycles. Depot modification kits reduced downtime by 18 days per aircraft in 2025. Fleet utilization metrics showed sortie availability improving across 7 operational wings in 2024, demonstrating modernization pathways that unlock readiness improvements within constrained timelines.
Expansion of unmanned and optionally piloted aircraft programs
Operational concepts integrating crewed–uncrewed teaming advanced through 2023 and 2024 exercises, with 14 large-scale demonstrations conducted across 5 ranges. Autonomy safety releases progressed to level 3 certifications by 2025, enabling expanded mission envelopes. Command-and-control nodes increased to 22 distributed sites in 2024, supporting networked operations. Endurance trials surpassed 48 continuous hours in 2023, validating extended ISR roles. Training pipelines certified 620 operators in 2024, accelerating adoption across reconnaissance and support missions while complementing crewed platforms in high-risk operational environments.
Future Outlook
Through 2035, the market will prioritize readiness, survivability, and interoperability across crewed and uncrewed platforms. Modernization of legacy fleets will coexist with advanced platform introductions, while digital engineering and open architectures compress upgrade cycles. Supply chain resilience and workforce development will shape delivery reliability amid evolving operational demands.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Boeing Defense, Space & Security
- Northrop Grumman
- RTX
- General Atomics Aeronautical Systems
- L3Harris Technologies
- Textron Aviation Defense
- Sierra Nevada Corporation
- Kratos Defense & Security Solutions
- General Dynamics Aerospace
- BAE Systems
- Leonardo
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Rolls-Royce
- GE Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Defense procurement agencies within the Department of Defense
- Program executive offices and lifecycle management commands
- Military air logistics and depot maintenance organizations
- Aerospace component and systems suppliers
- MRO and sustainment service providers
- Prime contractors and platform integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names including the Department of Defense and the Federal Aviation Administration
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Platform classes, mission roles, fleet age profiles, readiness metrics, certification cycles, depot capacities, and supply chain constraints were mapped to define analytical variables. Operational tempo indicators and modernization pathways were structured to capture demand drivers. Policy frameworks and compliance requirements were integrated to bound scope.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Program pipelines, retrofit throughput, training capacity, and sustainment networks were synthesized to construct scenario pathways. Platform lifecycles and integration schedules were aligned with readiness objectives. Interdependencies across suppliers, depots, and operational units were modeled to assess execution risk.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions on readiness improvements, integration timelines, and workforce capacity were tested against operational planning cycles. Feedback loops refined technology insertion pacing and sustainment constraints. Validation emphasized feasibility across certification queues, test availability, and logistics throughput.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into actionable themes linking modernization, supply resilience, and operational readiness. Insights were structured to support strategic planning, procurement sequencing, and capability roadmaps. The synthesis emphasized practical levers for near-term execution and medium-term transformation.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and platform scope validation, DoD budget and POM cycle analysis, SIPRI and USAF/NAVAIR procurement database triangulation, OEM and Tier-1 supplier primary interviews, fleet inventory and readiness rate modeling, contract awards and FMS deal tracking, teardown and cost-curve benchmarking)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Mission usage pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and MRO channel structure
- Regulatory and export control environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising geopolitical tensions and force modernization mandates
Replacement of aging legacy fleets
Next-generation air dominance and sixth-generation program investments
Increased emphasis on ISR and electronic warfare capabilities
Budget prioritization for air superiority and power projection
Allied interoperability and joint operations requirements - Challenges
Long development cycles and program cost overruns
Supply chain fragility for engines, avionics, and advanced materials
Skilled labor shortages in aerospace manufacturing and MRO
Export control constraints affecting industrial scale efficiencies
Platform sustainment costs and readiness rate pressures
Technology integration risks for stealth, AI, and autonomy - Opportunities
Modernization and upgrade programs for legacy fleets
Expansion of unmanned and optionally piloted aircraft programs
Advanced propulsion and adaptive engine development
Open architecture avionics and software-defined upgrades
Increased sustainment, MRO, and lifecycle services contracts
Foreign Military Sales spillover supporting production scale - Trends
Shift toward modular open systems architectures
Integration of AI-enabled mission systems and sensor fusion
Growing use of digital twins and model-based systems engineering
Hybrid crewed-uncrewed teaming concepts
Electrification of subsystems and advanced power management
Increased focus on survivability and low observable enhancements - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Aircraft Type (in Value %)
Fighter and multirole aircraft
Bomber aircraft
Transport and tanker aircraft
ISR and special mission aircraft
Trainer aircraft
Unmanned combat and support aircraft - By Service Branch (in Value %)
US Air Force
US Navy
US Marine Corps
US Army aviation - By Mission Profile (in Value %)
Air superiority and strike
Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance
Strategic airlift and tactical transport
Aerial refueling
Electronic warfare and special operations
Training and test - By Platform Generation (in Value %)
Fourth generation
Fourth generation plus
Fifth generation
Next-generation air dominance and advanced platforms - By Procurement Channel (in Value %)
New aircraft procurement
Mid-life upgrade and modernization
Service life extension programs
Remanufactured and refurbished platforms
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (fleet penetration, contract win rate, technology readiness level, cost per flight hour, production throughput, sustainment footprint, export exposure, upgrade roadmap depth)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
Boeing Defense, Space & Security
Northrop Grumman
RTX (Raytheon Technologies)
General Atomics Aeronautical Systems
L3Harris Technologies
Textron Aviation Defense
Sierra Nevada Corporation
Kratos Defense & Security Solutions
General Dynamics Aerospace
BAE Systems
Leonardo
Airbus Defence and Space
Rolls-Royce
GE Aerospace
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase sustainment and service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


