Market Overview
The US military satellite market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained defense prioritization of space-based mission assurance, protected communications, missile warning, navigation resilience, and intelligence collection. Investment intensity remains elevated across government-owned constellations and hybrid service models, supported by multiyear programs and mission-critical requirements. Capital allocation emphasizes resilient architectures, rapid replenishment, and secure ground integration. Contracting mechanisms continue to favor modular payloads, proliferated constellations, and secure terminals across operational theaters, reinforcing continuous demand.
Dominant activity concentrates around major defense and space infrastructure hubs including Washington, D.C., Colorado Springs, Los Angeles, Huntsville, San Diego, and Cape Canaveral. These clusters benefit from proximity to command authorities, launch facilities, systems engineering talent, classified integration environments, and established prime-subcontractor ecosystems. Demand concentration is reinforced by mature procurement pathways, testing ranges, and secure supply chains. Policy alignment, spectrum governance, and space domain coordination further anchor ecosystem maturity across these metropolitan nodes.
Market Segmentation
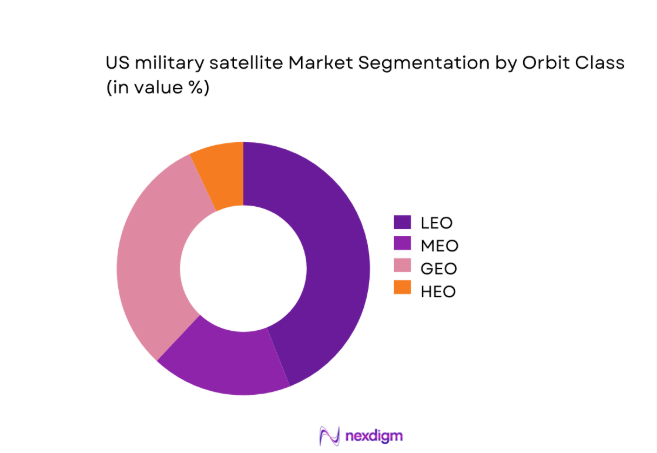
By Orbit Class
LEO-led architectures dominate current deployments due to resilience, latency advantages, and rapid replenishment cycles supporting tactical communications and ISR missions. Proliferated LEO constellations enable redundancy against jamming and kinetic threats while accelerating refresh cycles through shorter manufacturing and launch timelines. MEO supports navigation and timing continuity, while GEO remains central for protected strategic communications and missile warning persistence. HEO offers niche coverage for polar operations. Procurement preferences increasingly favor mixed-orbit constellations to balance survivability, coverage persistence, and mission specialization across contested environments.
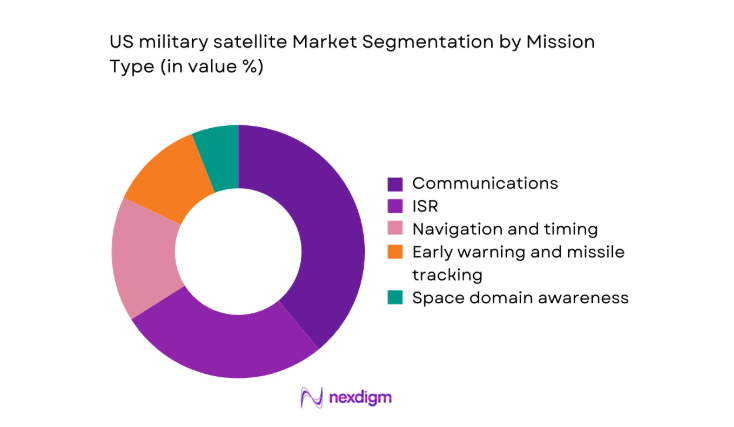
By Mission Type
Communications remains the largest mission segment due to continuous operational demand across deployed forces and command structures. ISR growth is driven by persistent surveillance requirements and rapid tasking for multi-domain operations. Navigation and timing sustain criticality for precision operations and coalition interoperability. Early warning and missile tracking capabilities expand in response to evolving hypersonic and ballistic threats. Space domain awareness supports orbital safety and threat attribution, gaining prioritization as congestion and counterspace risks intensify across contested orbital regimes.
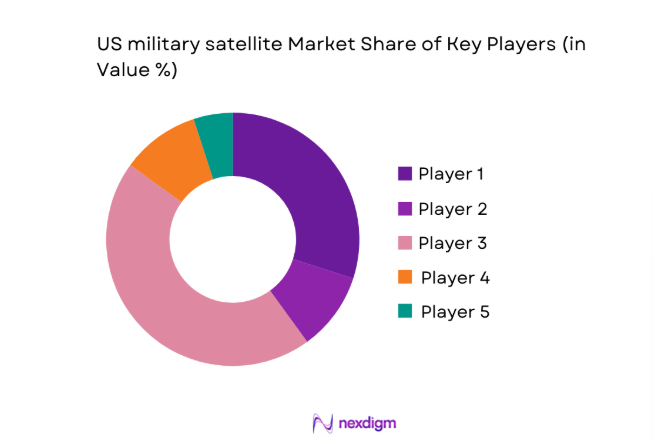
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape reflects a mix of legacy defense primes, space system integrators, and commercial launch and constellation operators supporting government missions. Competition centers on payload performance, constellation resilience, secure ground integration, and delivery reliability across classified and unclassified programs.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | Bethesda, MD | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Northrop Grumman | 1939 | Falls Church, VA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing Defense, Space & Security | 1916 | Arlington, VA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Technologies | 1895 | Melbourne, FL | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SpaceX | 2002 | Hawthorne, CA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
US military satellite Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of protected SATCOM and resilient ISR architectures
Protected satellite communications and resilient ISR modernization accelerated as operational doctrines integrated multi-domain command nodes across distributed theaters. In 2024, the Department of Defense executed 312 space-related program milestones spanning payload refresh, ground terminal hardening, and encryption upgrades, compared with 247 in 2022. Satellite terminal fielding expanded across 9 combatant commands, while classified network gateways increased from 41 to 58 sites during 2023–2025. Institutional emphasis on assured connectivity was reinforced through 27 interagency exercises validating jam-resistant waveforms and cross-domain data paths. These actions directly increased demand for protected payload integration, constellation resilience features, and secure ground interoperability.
Rising demand for missile warning and tracking against hypersonic threats
Missile warning modernization intensified as threat vectors diversified toward hypersonic glide vehicles and maneuvering ballistic profiles. Between 2022 and 2025, the Missile Defense Agency conducted 19 integrated flight tests requiring persistent overhead tracking and sensor fusion across space and ground nodes. Space-based infrared sensor refresh cycles shortened from 84 months to 48 months to sustain detection fidelity. The number of jointly operated early warning ground stations increased from 14 to 22, while cross-cueing latency targets were reduced to under 60 seconds. These operational benchmarks elevated requirements for proliferated sensors, low-latency data relay, and resilient orbital coverage.
Challenges
Vulnerability to anti-satellite weapons and electronic warfare
Counterspace capabilities expanded rapidly, elevating survivability risks for high-value orbital assets. From 2022 to 2025, publicly acknowledged counterspace tests and demonstrations increased from 5 to 12 annually across multiple domains, while documented GPS interference incidents affecting U.S. and allied forces exceeded 3,200 events in 2024. Electronic warfare exercises integrated into 28 large-scale joint drills, revealing degradation windows of 90 to 180 seconds for legacy waveforms. Orbital conjunction warnings rose from 24,000 in 2022 to 38,000 in 2025, stressing maneuver planning capacity and collision-avoidance readiness for dense constellations operating in contested regimes.
Program delays and cost overruns in large GEO platforms
Large GEO programs face schedule compression challenges due to payload complexity, radiation-hardening lead times, and launch manifest congestion. Between 2022 and 2025, average program milestone slippage increased from 6 months to 14 months across multiple space acquisition portfolios. Critical component qualification cycles expanded from 18 to 30 months following updated cybersecurity and supply assurance requirements. Launch queue constraints resulted in 11 deferred payload integrations in 2024 alone, while workforce clearance processing times rose from 72 to 110 days, affecting system integration velocity. These institutional frictions constrain timely fielding of strategic persistence capabilities.
Opportunities
Adoption of hybrid architectures combining government and commercial assets
Hybrid architectures gained momentum as operational planners integrated government-owned constellations with commercially provided communications and imagery for surge capacity. During 2023–2025, the number of task orders enabling commercial satellite service augmentation rose from 47 to 96, supporting 14 contingency exercises and 6 real-world operations. Secure gateway nodes interfacing commercial feeds expanded from 23 to 39, improving latency for forward-deployed units. Institutional procurement frameworks authorized multi-vendor service onboarding cycles shortened from 120 to 60 days, creating pathways for rapid mission scaling while preserving assured access controls and operational security across classified networks.
Growth in proliferated LEO for low-latency ISR and communications
Proliferated LEO deployments present opportunities to enhance latency-sensitive ISR and tactical communications for distributed forces. Between 2022 and 2025, operational concepts validated data relay latencies under 120 milliseconds across 8 joint demonstrations, compared with 420 milliseconds on legacy pathways. Launch cadence supporting LEO replenishment increased from 31 to 52 missions annually supporting defense-relevant payload rideshares. Ground terminal kits certified for LEO compatibility expanded from 4 to 13 configurations, accelerating fielding across expeditionary units. These institutional validations underpin scalable architectures delivering persistent coverage, redundancy, and rapid technology refresh without strategic single-point failures.
Future Outlook
The outlook emphasizes resilient mixed-orbit architectures, deeper integration of commercial services, and accelerated refresh cycles to counter evolving counterspace threats. Policy alignment and procurement reform are expected to streamline onboarding of new capabilities. Interoperability with allies will shape mission design, while space domain awareness and cyber hardening will anchor long-term operational readiness.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Boeing Defense, Space & Security
- Raytheon Technologies
- L3Harris Technologies
- Maxar Technologies
- Ball Aerospace
- Viasat
- SpaceX
- Amazon Project Kuiper
- Planet Labs
- BlackSky
- Sierra Space
- Blue Origin
- General Atomics
Key Target Audience
- U.S. Department of Defense Space Policy Office
- U.S. Space Force Space Systems Command
- National Reconnaissance Office
- Missile Defense Agency
- Combatant Commands operational planners
- Prime defense contractors and system integrators
- Satellite payload and ground terminal manufacturers
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Program of record priorities, mission architectures, orbital regimes, payload classes, ground segment integration, and resilience requirements were defined through policy review and operational doctrine mapping. Stakeholder objectives across acquisition, operations, and sustainment were consolidated to bound the analytical framework and ensure mission relevance across classified and unclassified domains.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Capability pathways were constructed by mapping mission needs to platform classes, payload technologies, and deployment models. Institutional indicators, procurement timelines, launch cadence, and ground integration readiness were analyzed to structure demand drivers and constraint factors shaping adoption across mixed-orbit architectures.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Operational hypotheses on resilience, latency, and hybrid service integration were stress-tested through consultations with program managers, operators, and system engineers. Scenario validation incorporated exercise outcomes, interoperability benchmarks, and threat evolution patterns to refine assumptions and ensure practical applicability.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into a coherent narrative linking mission requirements, institutional drivers, and technology pathways. Insights were structured to inform strategic planning, procurement alignment, and ecosystem coordination, with emphasis on actionable implications for capability development and deployment.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and mission-critical satellite capability taxonomy, DoD budget outlays and program of record tracking, classified-unclassified source triangulation and expert interviews, satellite constellation and launch cadence analysis, prime contractor and subsystem supplier revenue mapping, ground segment and terminal deployment assessment, orbital regime and spectrum allocation analysis)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Mission and operational use cases
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and procurement channels
- Regulatory and security environment
- Growth Drivers
Modernization of protected SATCOM and resilient ISR architectures
Rising demand for missile warning and tracking against hypersonic threats
Expansion of proliferated LEO constellations for resilience and redundancy
Integration of space assets into multi-domain operations doctrine
Increased defense budgets for space superiority and deterrence
Rapid technology refresh cycles driven by threat evolution - Challenges
Vulnerability to anti-satellite weapons and electronic warfare
Program delays and cost overruns in large GEO platforms
Supply chain constraints for radiation-hardened components
Spectrum congestion and orbital debris risks
Dependence on limited launch capacity and schedule bottlenecks
Cybersecurity risks across ground segment and data links - Opportunities
Adoption of hybrid architectures combining government and commercial assets
Growth in proliferated LEO for low-latency ISR and communications
Advanced payload miniaturization and on-orbit reconfigurability
AI-enabled onboard processing and edge analytics
Allied interoperability and coalition mission integration
On-orbit servicing, refueling, and rapid replenishment concepts - Trends
Shift from monolithic GEO systems to distributed constellations
Increased use of commercial SATCOM and imagery services
Emphasis on jam-resistant and laser communications
Rapid prototyping and spiral development acquisition models
Expansion of SDA and cislunar monitoring capabilities
Greater focus on space resilience and tactically responsive launch - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Orbit Class (in Value %)
LEO
MEO
GEO
HEO - By Mission Type (in Value %)
Communications
ISR
Navigation and timing
Early warning and missile tracking
Space domain awareness - By Payload Technology (in Value %)
RF payloads
Optical and EO/IR payloads
Radar and SAR payloads
Hosted payloads - By Platform Size (in Value %)
Small satellites
Medium satellites
Large satellites - By End Mission Criticality (in Value %)
Strategic missions
Tactical missions
Support and auxiliary missions
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (payload capability, orbital regime coverage, program of record participation, launch integration capability, cybersecurity and resilience features, cost per satellite, delivery timelines, lifecycle support and sustainment)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
Boeing Defense, Space & Security
Raytheon Technologies
L3Harris Technologies
Maxar Technologies
Ball Aerospace
Viasat
SpaceX
Amazon Project Kuiper
Planet Labs
BlackSky
Sierra Space
Blue Origin
General Atomics
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


