Market Overview
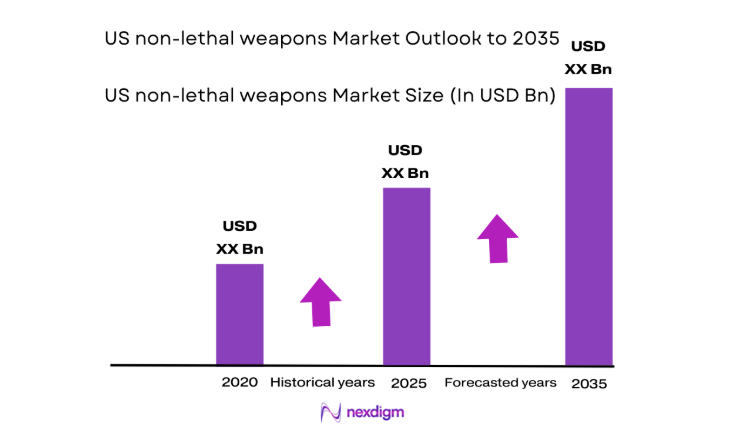
The US non-lethal weapons market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained procurement across law enforcement, corrections, and border security ecosystems. Demand is anchored in institutional mandates to expand de-escalation capabilities, improve officer safety, and diversify use-of-force toolkits. Platform reliability, training integration, and lifecycle serviceability shape purchasing priorities, while interoperability with evidence management systems influences adoption decisions. Channel maturity across federal frameworks and municipal procurement programs supports predictable replenishment cycles and standardized deployment protocols.
Deployment density concentrates in metropolitan corridors with high call volumes, complex crowd management needs, and established training infrastructure. Large coastal cities exhibit higher adoption due to policy-led use-of-force reform, mature procurement frameworks, and dedicated less-lethal training academies. Southern border states show elevated deployment linked to port-of-entry operations and federal agency coordination. Midwestern and Mountain West jurisdictions prioritize corrections modernization and rural law enforcement coverage, supported by regional distributors and integrators embedded within public safety procurement ecosystems.
Market Segmentation
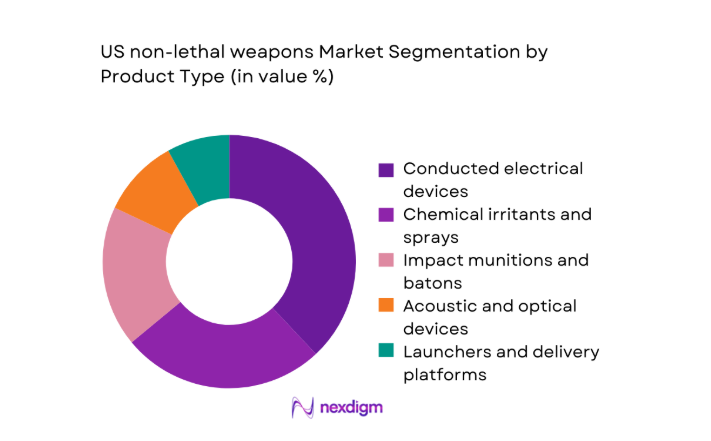
By Product Type
Product type dominance reflects operational versatility and training compatibility across agencies. Conducted electrical devices lead routine patrol adoption due to standardized training curricula and documented safety protocols. Chemical irritants maintain strong presence for personal defense and corrections environments where standoff distance is constrained. Impact munitions and batons retain niche relevance for crowd management and custodial control, while acoustic and optical devices are deployed selectively for perimeter security and maritime interdiction. Launchers and delivery platforms gain traction where modular payload compatibility and inventory standardization streamline logistics across multi-agency task forces, reinforcing procurement alignment with existing training and maintenance frameworks.
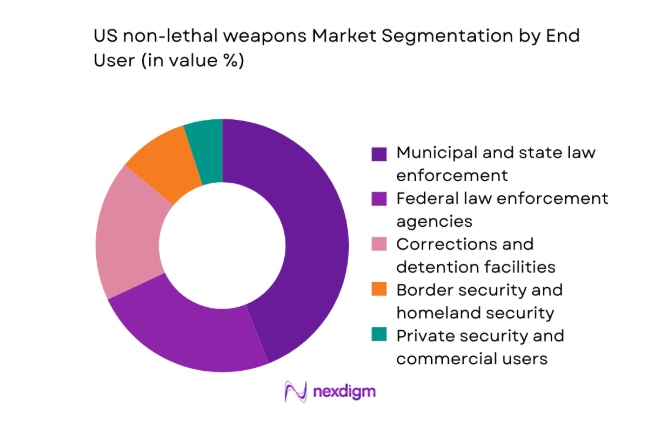
By End User
End-user dominance is shaped by procurement scale, policy mandates, and operational tempo. Municipal and state law enforcement agencies account for the largest share due to continuous replenishment cycles and training-driven standardization. Federal law enforcement adoption is anchored in multi-year framework contracts emphasizing compliance, data governance, and interoperability. Corrections facilities prioritize non-lethal options to reduce custodial injuries and manage confined-space incidents. Border security deployments emphasize standoff tools and compliance devices for ports of entry. Private security adoption remains selective, constrained by regulatory readiness and certification requirements across jurisdictions.
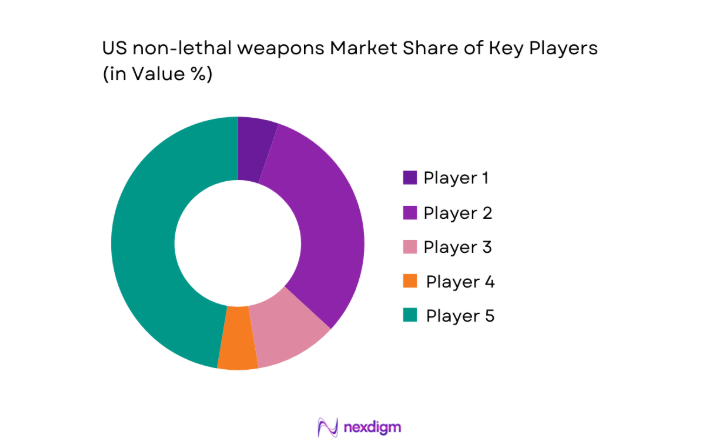
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by strong channel relationships, regulatory readiness, and integrated training ecosystems. Product breadth and service capability differentiate positioning across municipal, federal, and corrections buyers, while distribution reach and compliance track records influence framework eligibility.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Axon Enterprise | 1993 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Safariland Group | 1964 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| PepperBall Technologies | 2002 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Byrna Technologies | 2005 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mace Security International | 1965 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
US non-lethal weapons Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising emphasis on de-escalation and use-of-force reform
Federal guidance updates issued in 2022 accelerated de-escalation training adoption across agencies, with 42000 officers completing revised use-of-force modules during 2023. In 2024, 138 municipal departments implemented standardized less-lethal qualification protocols, increasing certified device issuance. DOJ grant programs supported 260 multi-agency pilots focused on alternatives to lethal force during high-risk encounters. Body-worn camera programs expanded to 410000 active devices by 2025, strengthening accountability frameworks that favor non-lethal deployment. Civil rights consent decrees in 17 jurisdictions mandated expanded toolkits, reinforcing institutional demand for compliant less-lethal options and structured training pipelines nationwide.
Increased federal and state funding for less-lethal modernization
Public safety modernization line items in 2024 authorized 320 procurement programs across states, with 74 statewide framework agreements enabling coordinated purchasing. In 2023, 112 regional task forces received equipment grants tied to training compliance milestones. DHS port-of-entry modernization initiatives in 2025 incorporated non-lethal capability upgrades across 48 facilities, emphasizing standoff options for perimeter control. State corrections departments executed 29 facility refresh programs during 2024, aligning non-lethal deployments with custodial safety benchmarks. Interoperability requirements across 9 federal agencies standardized certification pathways, reducing deployment friction and accelerating multi-jurisdictional adoption through shared compliance criteria and training reciprocity.
Challenges
Public scrutiny and civil liability risks
Civil litigation related to use-of-force incidents resulted in 614 filed cases during 2024, intensifying scrutiny on device safety and training adequacy. Policy reviews across 23 cities mandated expanded reporting thresholds and post-incident medical evaluation protocols in 2023. In 2025, 41 municipal councils introduced moratorium clauses pending updated safety certifications, delaying procurement cycles. Independent oversight bodies in 12 jurisdictions required quarterly audits of non-lethal deployments, increasing administrative burden. Media amplification of adverse events elevated reputational risk for agencies, prompting conservative rollout schedules and prolonged pilot phases before fleetwide issuance across patrol units and custodial teams.
Inconsistent training standards across jurisdictions
Training requirements vary across 50 states, with 27 states lacking uniform certification hours for conducted electrical devices in 2024. During 2023, 186 agencies reported instructor shortages, constraining qualification throughput. Recertification intervals differed across 19 statewide frameworks, complicating mutual aid interoperability during multi-agency operations in 2025. Policy updates in 14 states introduced scenario-based assessments without harmonized scoring rubrics, creating deployment uncertainty. Variability in medical clearance protocols across 31 jurisdictions delayed device issuance to frontline officers, slowing adoption momentum and increasing compliance overhead for procurement teams coordinating cross-border operations.
Opportunities
Body-worn camera and CEW data integration solutions
Integrated evidence workflows expanded rapidly as 410000 body-worn cameras operated across agencies in 2025, creating demand for synchronized device telemetry and incident metadata. In 2024, 96 agencies piloted unified evidence management protocols linking activation logs with case management systems. Federal interoperability guidance issued in 2023 promoted standardized data schemas across 8 agencies, enabling cross-jurisdictional analytics. Prosecutorial offices in 37 districts requested automated evidence packaging to accelerate case processing timelines. These indicators support scalable platforms that connect non-lethal device data with digital evidence chains, improving transparency, compliance audits, and operational learning loops.
Non-lethal solutions for corrections and detention upgrades
Corrections modernization accelerated as 29 facility refresh programs were executed in 2024, prioritizing safer custodial control tools. Incident reporting reforms in 2023 required enhanced de-escalation tool availability across 312 detention centers. Occupational safety benchmarks in 2025 mandated expanded non-lethal coverage for shift teams, aligning procurement with workforce protection standards. State oversight bodies in 18 jurisdictions introduced compliance audits tied to injury reduction targets. These institutional shifts create sustained demand for durable, low-injury tools optimized for confined environments, supported by training modules tailored to custodial workflows and post-incident medical protocols.
Future Outlook
Policy-led reforms will continue to anchor non-lethal adoption across municipal, federal, and corrections environments through 2035. Standardized training, interoperability mandates, and evidence integration will shape procurement criteria. Federal frameworks and state-level compliance updates are likely to favor platforms with strong certification, serviceability, and data governance capabilities. Cross-agency coordination will expand multi-year purchasing agreements and accelerate modernization cycles.
Major Players
- Axon Enterprise
- Safariland Group
- PepperBall Technologies
- Byrna Technologies
- Mace Security International
- Combined Systems
- Federal Laboratories
- NonLethal Technologies
- Amtec Less-Lethal Systems
- CTS
- ASP
- Lamperd Less Lethal
- Condor Outdoor Products
- Defense Technology
- Veritas Tactical Solutions
Key Target Audience
- Municipal and state law enforcement procurement departments
- Federal law enforcement agencies including DOJ and DHS
- State departments of corrections and detention authorities
- Border security agencies including U.S. Customs and Border Protection
- Port authorities and transportation security agencies
- Public safety training academies and certification bodies
- Systems integrators serving public sector security deployments
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Operational use-of-force frameworks, device categories, training standards, certification pathways, and regulatory readiness were mapped across law enforcement, corrections, and border security contexts. Demand signals were derived from procurement frameworks, compliance mandates, and interoperability requirements. Channel structures and service models were delineated to capture lifecycle dependencies and deployment constraints.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Agency procurement programs, framework agreements, and modernization initiatives were synthesized to construct demand drivers and adoption pathways. Technology readiness, training throughput, and compliance burdens were evaluated to contextualize deployment velocity. Ecosystem mapping aligned vendors, distributors, trainers, and oversight bodies within operational workflows.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were stress-tested through structured consultations with procurement officials, training coordinators, and compliance officers. Scenario-based validation assessed policy impacts on adoption timelines and interoperability requirements. Institutional indicators were triangulated to refine assumptions on deployment scalability and service integration.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated into actionable narratives linking policy, training, technology, and service ecosystems. The synthesis prioritized practical decision levers for buyers and suppliers, ensuring consistency across segmentation, competitive positioning, and future outlook. Output formatting aligned with publication standards and decision-maker usability.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and use-of-force and non-lethal classification framework, Law enforcement and corrections procurement audits and contract tracking, DoD and DHS non-lethal capabilities program analysis, Vendor shipment disclosures and channel checks, Agency interviews and training doctrine reviews, Incident usage and outcomes data triangulation, State and municipal regulatory and liability case review)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and deployment pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and distribution channels
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising emphasis on de-escalation and use-of-force reform
Increased federal and state funding for less-lethal modernization
Urbanization and crowd-control requirements
Officer safety mandates and reduced lethal force incidents
Advancements in CEW reliability and data capture
Procurement standardization across agencies - Challenges
Public scrutiny and civil liability risks
Inconsistent training standards across jurisdictions
Regulatory variability at state and municipal levels
Supply chain constraints for specialized components
Technology misuse and safety controversies
Budget cyclicality in local governments - Opportunities
Body-worn camera and CEW data integration solutions
Non-lethal solutions for corrections and detention upgrades
Export-compliant variants for federal agencies
Training-as-a-service and certification platforms
Less-lethal options for border security and ports of entry
Lifecycle services and fleet refresh programs - Trends
Connected CEWs with evidence management platforms
Shift toward lower-injury kinetic projectiles
Procurement via multi-year framework agreements
Integration of non-lethal tools into standard issue kits
Expanded scenario-based training adoption - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Product Type (in Value %)
Conducted electrical weapons (CEWs/Tasers)
Impact munitions and batons
Chemical irritants and sprays
Acoustic and optical devices
Launchers and delivery platforms - By Technology and Output (in Value %)
Electrical neuromuscular incapacitation
Oleoresin capsicum and chemical agents
Kinetic impact projectiles
Directed energy and optical dazzlers
Acoustic hailing and deterrence - By End User (in Value %)
Municipal and state law enforcement
Federal law enforcement agencies
Corrections and detention facilities
Border security and homeland security
Private security and commercial users - By Distribution Channel (in Value %)
Direct government contracts
Authorized distributors and integrators
GSA schedules and framework agreements
OEM direct-to-agency programs
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Product breadth, Technology differentiation, Safety certifications and compliance, Pricing tiers and total cost of ownership, Contract coverage and government schedules, Training and certification offerings, Data and evidence management integration, After-sales service footprint)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Axon Enterprise
Combined Systems Inc.
Byrna Technologies
PepperBall Technologies
Safariland Group
NonLethal Technologies
Amtec Less-Lethal Systems
CTS (Combined Tactical Systems)
ASP, Inc.
Federal Laboratories
Mace Security International
Veritas Tactical Solutions
Condor Outdoor Products
Defense Technology (Safariland brand)
Lamperd Less Lethal
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


