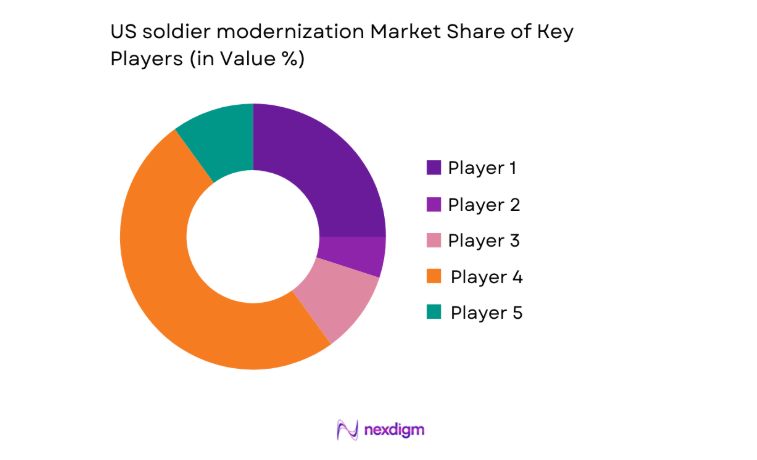
Market Overview
The US soldier modernization market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained investment across lethality, protection, networking, and human performance capabilities. Funding prioritization emphasizes modular upgrades, open-architecture integration, and lifecycle sustainment across deployed units. Budget allocations remain oriented toward capability refresh cycles, rapid prototyping pathways, and fielding at scale. Portfolio emphasis spans individual weapons, protective systems, soldier-borne electronics, and tactical communications, with recurring refresh driven by evolving operational requirements and interoperability mandates.
Demand concentration is anchored in regions with dense defense infrastructure, testing ranges, and program management hubs, including the National Capital Region, Texas, California, and Arizona. These locations benefit from mature defense industrial ecosystems, proximity to training installations, and access to integration facilities. Policy environments supporting rapid acquisition authorities and experimentation corridors accelerate adoption. Co-location of primes, subsystem suppliers, and integration labs strengthens collaboration, while logistics corridors and sustainment depots reinforce deployment readiness and lifecycle support.
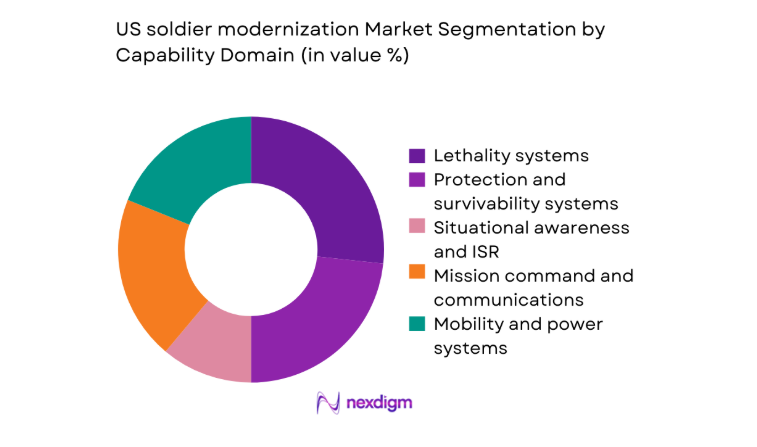
Market Segmentation
By Capability Domain
Spending concentration is highest in lethality and situational awareness, driven by squad-level overmatch priorities and networked operations requirements. Protection and survivability benefit from materials science advances that reduce load while maintaining ballistic thresholds, improving soldier endurance and mission duration. Mission command and communications remain critical to joint interoperability and edge decision-making, reinforcing investments in secure radios and soldier networking kits. Mobility and power systems gain traction as electrification increases power density needs for wearables and sensors. Human performance and training technologies are expanding through immersive simulation and physiological monitoring, improving readiness and reducing injury risk during high-tempo operations.
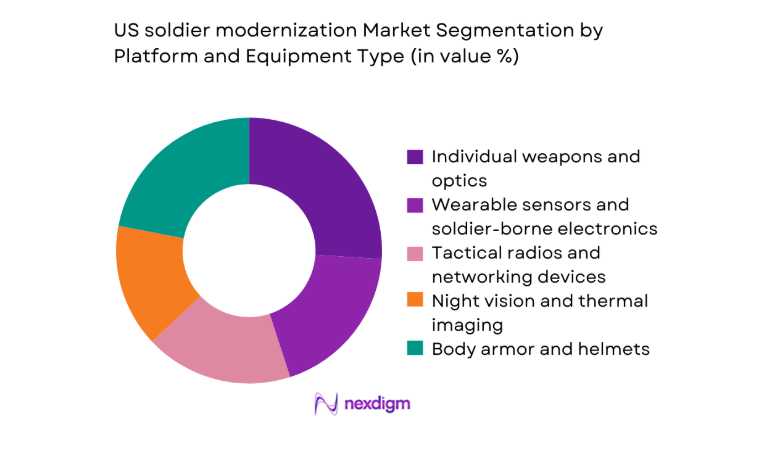
By Platform and Equipment Type
Individual weapons and optics dominate allocations due to multi-year replacement cycles and modular upgrade programs. Wearable sensors and soldier-borne electronics show strong uptake as networked operations require persistent sensing and data fusion at the edge. Tactical radios and networking devices remain foundational for joint force interoperability, sustaining refresh cycles aligned to waveform and security upgrades. Night vision and thermal imaging continue modernization driven by sensor miniaturization and fusion capabilities. Body armor and helmets benefit from incremental materials improvements, while power sources and energy management expand as device density increases across the soldier system.
Competitive Landscape
Competition is shaped by platform integration depth, compliance with defense acquisition standards, and the ability to deliver modular, interoperable subsystems at program scale. Differentiation centers on systems engineering maturity, secure networking expertise, sustainment capacity, and readiness to support rapid prototyping and fielding cycles across multiple soldier capability domains.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | Bethesda, MD | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon Technologies | 2020 | Arlington, VA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Technologies | 2019 | Melbourne, FL | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | London, UK | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| General Dynamics Mission Systems | 1952 | Fairfax, VA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
US soldier modernization Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising peer and near-peer threat environment
Heightened strategic competition increased training tempo across major combat training centers, with 2024 rotations exceeding 250 events and 2025 schedules sustaining similar cadence. Forward deployments expanded across 12 rotational brigades, reinforcing requirements for resilient soldier networks and protection systems. Defense planning documents emphasized contested electromagnetic spectrum operations across 4 theaters, elevating demand for secure radios and sensor fusion. Procurement actions accelerated under rapid acquisition authorities enacted in 2023, with 38 prototypes transitioning to limited fielding in 2024. Interoperability mandates across 5 service components increased integration requirements, sustaining modernization momentum across lethality, protection, and situational awareness portfolios.
DoD priority on overmatch at the squad level
Capability roadmaps prioritized squad overmatch with standardized kits deployed across 27 brigades during 2024 and expanded to 31 brigades in 2025. Training pipelines increased throughput at 9 modernization integration facilities, enabling accelerated fielding cycles. Operational assessments across 3 combatant commands validated networked fires coordination improvements during 2024 exercises. Soldier system integration events increased by 41 demonstrations in 2025, reinforcing iterative upgrades. Doctrine updates released in 2024 emphasized decentralized decision-making supported by edge analytics. These institutional shifts align funding and acquisition pathways to sustain rapid refresh of soldier-borne sensors, communications, and protective equipment.
Challenges
Complex and lengthy DoD acquisition cycles
Program baselines experienced milestone delays across 6 major soldier programs during 2024, extending integration timelines by 14 months on average. Contract award lead times expanded due to compliance reviews across 9 statutory checkpoints. Test and evaluation throughput was constrained by capacity limits at 4 integration ranges, creating scheduling backlogs. Security accreditation cycles added 11 procedural gates for networked devices in 2025, slowing fielding. Interoperability certification across 5 waveform standards further elongated timelines. These institutional frictions impede rapid iteration and complicate synchronization of hardware, firmware, and secure communications upgrades across soldier systems.
Integration challenges across legacy and new systems
Legacy soldier kits deployed across 18 brigades require backward compatibility with new radios, optics, and power systems. Interface mismatches across 7 proprietary protocols created field integration issues during 2024 exercises. Software version fragmentation across 22 device variants increased configuration complexity. Power budgets across wearable stacks exceeded thresholds in 2025 field trials, reducing endurance during 72-hour operations. Data assurance policies required harmonization across 3 classification tiers, complicating sensor fusion at the edge. These constraints elevate integration risk, increase test cycles, and delay operational acceptance across networked soldier architectures.
Opportunities
Expansion of AI-enabled situational awareness
Edge analytics deployments expanded across 16 pilot units in 2024, improving target identification latency by 9 operational minutes during exercises. Sensor fusion architectures integrated feeds from 5 wearable modalities and 3 unmanned sources in 2025, enabling richer situational pictures. Training pipelines certified 420 operators on AI-assisted mission planning tools, increasing adoption readiness. Doctrine updates across 2 service components formalized edge decision support. Secure compute modules certified across 4 security tiers expanded deployability in contested environments. These indicators demonstrate institutional readiness and technical feasibility to scale AI-enabled situational awareness across soldier modernization portfolios.
Advanced materials for lighter protection systems
Materials test programs evaluated 28 composite formulations in 2024, achieving weight reductions while meeting ballistic thresholds across 3 threat classes. Production readiness assessments in 2025 validated manufacturing consistency across 5 pilot lines. Field trials across 7 brigades demonstrated endurance gains during 96-hour operations. Supply chain localization across 4 domestic materials clusters improved reliability and qualification cycles. Certification pathways streamlined testing across 6 accredited labs. Institutional endorsement through updated equipment standards in 2024 signals readiness to accelerate adoption of lighter protection systems without compromising survivability requirements.
Future Outlook
The modernization trajectory will continue emphasizing modular, interoperable soldier systems aligned to evolving operational doctrines. Over the coming years, integration of edge analytics, secure networking, and lighter protection materials will deepen. Rapid prototyping pathways and iterative fielding will compress deployment cycles. Interoperability mandates will standardize interfaces across soldier-borne devices, supporting scalable upgrades. Sustained alignment between acquisition authorities and operational feedback loops will shape portfolio priorities through the outlook period.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Raytheon Technologies
- L3Harris Technologies
- BAE Systems
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- Northrop Grumman
- Thales Defense & Security
- Elbit Systems of America
- Oshkosh Defense
- Viasat
- Garmin
- Gentex Corporation
- 3M
- FLIR Systems
- Safariland
Key Target Audience
- Program Executive Office Soldier
- U.S. Army Contracting Command
- Defense Logistics Agency
- Department of Defense Chief Digital and AI Office
- Combatant Command operational planners
- Systems integrators and prime contractors
- Tier-1 and Tier-2 defense subsystem suppliers
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core variables included capability domains, platform categories, technology layers, contracting vehicles, and lifecycle phases. Operational requirements and interoperability mandates were mapped to soldier-borne subsystems. Data capture focused on acquisition pathways, certification stages, and sustainment cycles. Institutional constraints shaping deployment cadence were cataloged.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Capability portfolios were structured across lethality, protection, networking, power, and human performance layers. Platform interactions were mapped to integration workflows and certification gates. Deployment pathways were aligned with acquisition authorities and test pipelines. Scenario framing incorporated operational theaters and doctrine updates.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were stress-tested with acquisition practitioners, program managers, and integration leads. Field deployment feedback informed integration feasibility and adoption barriers. Policy alignment was reviewed against acquisition reforms and interoperability mandates. Technical readiness levels were validated through program milestones and certification pathways.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated into a coherent framework linking capability needs to deployment pathways. Cross-domain interactions were synthesized to reflect system-of-systems dependencies. Findings were refined for clarity, consistency, and policy relevance. The final output emphasizes actionable implications for planning and procurement stakeholders.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and capability domains mapping, Primary interviews with DoD program offices and PEO Soldier, Vendor briefings and solution validation workshops)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and operational deployment pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Defense acquisition and supply chain structure
- Growth Drivers
Rising peer and near-peer threat environment
DoD priority on overmatch at the squad level
Increased funding for lethality and protection programs - Challenges
Complex and lengthy DoD acquisition cycles
Integration challenges across legacy and new systems
Weight, power, and ergonomics constraints for soldiers - Opportunities
Expansion of AI-enabled situational awareness
Advanced materials for lighter protection systems
Modular open systems architectures adoption - Trends
Networked soldier systems and edge computing
Augmented reality for training and combat operations - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Unit Economics, 2020–2025
- By Capability Domain (in Value %)
Lethality systems
Protection and survivability systems
Situational awareness and ISR
Mobility and power systems
Mission command and communications
Human performance and training technologies - By Platform and Equipment Type (in Value %)
Individual weapons and optics
Body armor and helmets
Wearable sensors and soldier-borne electronics
Tactical radios and networking devices
Night vision and thermal imaging
Power sources and energy management - By Technology Layer (in Value %)
Hardware systems
Embedded software and firmware
AI-enabled analytics and decision support
Secure communications and networking
Power management and battery technologies - By Procurement Program (in Value %)
Next Generation Squad Weapon programs
Integrated Visual Augmentation System programs
Nett Warrior and soldier network programs
Personal protective equipment programs
Tactical communication modernization programs - By Contracting Vehicle (in Value %)
Direct DoD procurement contracts
IDIQ and multi-award contracts
OTA and prototyping agreements
- Market share of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (product portfolio breadth, technology maturity level, contract win rate, interoperability compliance, cost competitiveness, manufacturing scale, cybersecurity certifications, sustainment capability)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
Raytheon Technologies
L3Harris Technologies
BAE Systems
General Dynamics Mission Systems
Elbit Systems of America
Northrop Grumman
Thales Defense & Security
Oshkosh Defense
FLIR Systems
Safariland
Viasat
Garmin
Gentex Corporation
3M
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Unit Economics, 2026–2035