Market Overview
The US space mining and robots market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting early-stage commercialization across robotic prospecting, surface mobility, and in-situ resource utilization systems. Demand is shaped by mission-readiness requirements, qualification cycles, and platform integration with launch and surface operations. Capital intensity remains high due to extreme-environment engineering, redundancy standards, and verification regimes. The market is characterized by long development timelines, iterative mission demonstrations, and tight coupling with orbital logistics and surface power architectures.
Activity concentrates around launch corridors, cislunar mission operations hubs, and advanced robotics manufacturing clusters. Infrastructure density near coastal launch sites and test ranges supports integration and qualification workflows. Demand clusters where mission planning, autonomy software, and space systems engineering talent co-locate with deep-space communications assets. Ecosystem maturity is reinforced by policy alignment with lunar exploration programs, permitting pathways for mission licensing, and coordinated safety frameworks governing in-space operations, spectrum access, and planetary protection.
Market Segmentation
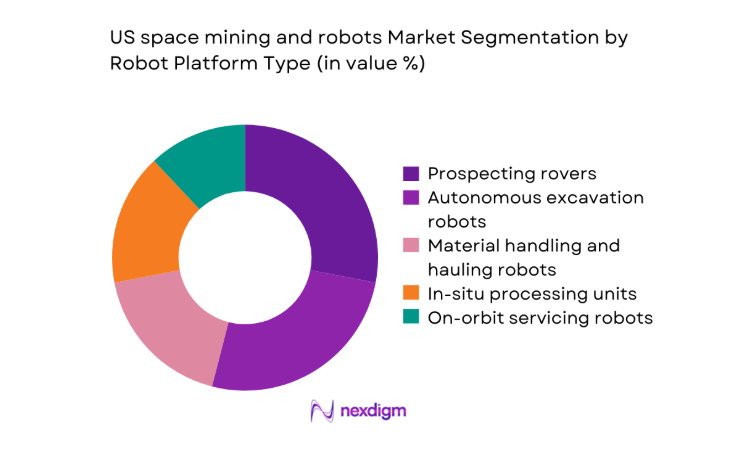
By Robot Platform Type
Autonomous prospecting rovers and excavation robots dominate due to mission-critical roles in terrain mapping, regolith handling, and payload delivery under constrained power and thermal envelopes. Material handling units and in-situ processing systems gain traction where surface operations extend beyond single sorties into multi-mission campaigns. On-orbit servicing robots complement surface platforms by enabling assembly, inspection, and transfer tasks that reduce mission risk and increase utilization of deployed assets. Platform modularity supports rapid reconfiguration across prospecting, extraction, and logistics functions, while software-defined autonomy allows capability upgrades without hardware refits, improving lifecycle efficiency and mission adaptability across heterogeneous environments.
By Deployment Environment
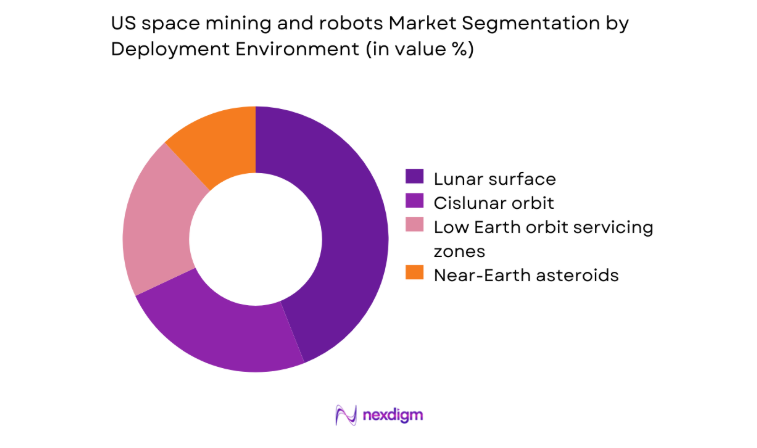
Lunar surface deployments lead adoption because of mission cadence, surface-accessibility, and established communications relays. Cislunar orbit operations support assembly and logistics, creating demand for dexterous robotic systems with rendezvous and docking capabilities. Near-Earth asteroid missions remain selective, driven by technology readiness thresholds and navigation complexity. Low Earth orbit zones emphasize servicing and inspection use cases that derisk deeper-space operations through incremental validation. Environmental constraints such as radiation exposure, abrasive regolith, and thermal cycling shape platform selection, driving ruggedization, redundancy, and autonomy upgrades that favor deployment environments with predictable mission windows and established support infrastructure.
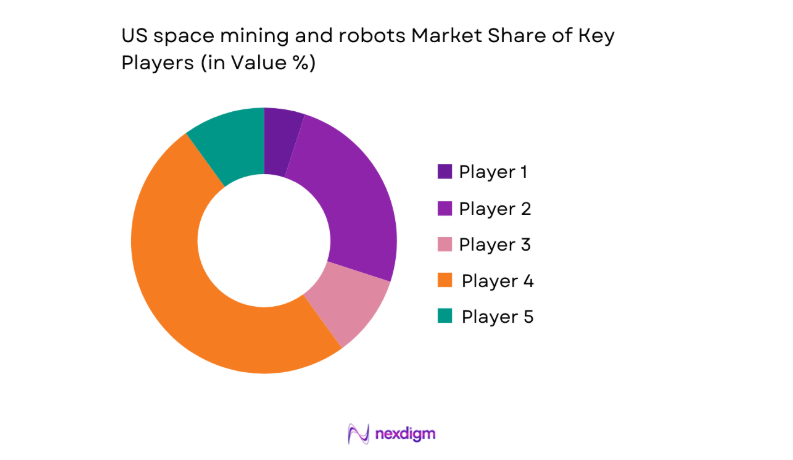
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment features vertically integrated system developers alongside specialized autonomy, robotics hardware, and mission-operations providers. Partnerships across launch integration, surface power, and communications enable differentiated mission performance. Competitive positioning hinges on technology readiness, mission heritage, and regulatory preparedness, while commercial models increasingly emphasize modular platforms and service-based delivery to shorten procurement cycles and de-risk deployment.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Astrobotic Technology | 2007 | Pittsburgh, PA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Intuitive Machines | 2013 | Houston, TX | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Honeybee Robotics | 1983 | Pasadena, CA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Maxar Technologies | 1957 | Westminster, CO | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Redwire Space | 2020 | Jacksonville, FL | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
US space mining and robots Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising US investment in lunar and cislunar infrastructure
Federal appropriations supported 2024 mission allocations exceeding ~across exploration, surface systems, and cislunar logistics, with 2025 programmatic increases aligned to sustained lunar presence. Launch cadence expanded to 9 deep-space missions in 2024 and 11 planned for 2025, increasing demand for surface robotics integration and operations support. Regulatory approvals processed through licensing offices rose by 17 cases in 2024, accelerating mission readiness. Expansion of deep-space communications added 6 relay upgrades during 2023–2024, improving operational uptime. These institutional commitments anchor long-horizon deployment pipelines, reducing uncertainty for robotics suppliers and integrators.
Demand for in-situ resource utilization to reduce launch mass
ISRU demonstrations advanced from laboratory validation to surface analog trials, with 14 field tests conducted during 2023–2025 across desert and polar simulants. Propellant production prototypes achieved continuous operation exceeding 72 hours in 2024 test campaigns, validating thermal and power management. Payload mass constraints remain binding, with launch performance envelopes limiting single-mission delivered mass to 3,500 kilograms for typical lunar transfer profiles in 2025. Mission architectures targeting refueling nodes logged 4 integrated system rehearsals in 2024. These constraints incentivize robotic extraction and processing to localize consumables, directly expanding demand for autonomous excavation and beneficiation systems.
Challenges
High technology development and qualification costs
Qualification cycles require environmental testing across vacuum, radiation, and thermal extremes, with 18 standardized test protocols mandated across 2023–2025 for flight readiness. Component-level failure rates observed in thermal vacuum chambers averaged 2 failures per 100 cycles in 2024, extending redesign timelines. Radiation hardening thresholds increased by 30 krad requirements for surface electronics in 2025 mission profiles. Reliability assurance necessitates redundant actuation channels, adding 4 additional subsystems per mobility platform. Integration with power and comms stacks requires 5 interface certifications before flight acceptance. These cumulative requirements slow iteration velocity and constrain deployment schedules for new robotic platforms.
Uncertain commercial viability and ROI timelines
Commercial mission backlogs reached 7 contracted payloads awaiting surface windows during 2024–2025, reflecting scheduling bottlenecks and financing gaps. Insurance underwriting for deep-space robotics added 2 new risk exclusions in 2024, complicating coverage structures. Demonstration-to-commercial transition timelines extend beyond 36 months for surface extraction workflows validated in 2023. Contract milestones depend on 3 sequential mission successes before multi-mission commitments activate. Institutional procurement cycles average 18 months, delaying scale deployment. These factors elongate payback horizons, tempering near-term adoption despite validated technical performance and increasing institutional interest.
Opportunities
Public–private partnerships for lunar ISRU demonstrations
Co-funded demonstration frameworks expanded to 6 collaborative mission slots in 2024–2025, enabling shared risk across surface robotics, power, and comms stacks. Test campaigns increased field readiness through 9 integrated rehearsals in analog sites during 2024. Data-sharing agreements unlocked access to 4 mission telemetry repositories, accelerating algorithm tuning for autonomy and navigation. Contract vehicles now permit milestone-based releases after 2 successful surface operations, improving cashflow predictability for suppliers. Standardized payload interfaces adopted across 5 mission profiles reduce integration friction. These structures lower barriers for emerging robotics platforms to achieve flight heritage and scale deployment pathways.
Integration of robotics with in-space manufacturing
Additive manufacturing payloads completed 8 microgravity fabrication trials in 2023–2024, validating feedstock handling and quality control. Surface manufacturing pilots demonstrated continuous tool-path operation exceeding 48 hours in 2025 analog trials. Robotics-manufacturing integration enables localized part replacement, reducing resupply dependencies constrained by launch windows capped at 12 viable lunar transfer periods annually. Autonomous inspection systems logged 1,200 defect detections across 2024 trials, improving maintenance outcomes. Standard tool changers adopted across 3 platform families enable cross-compatibility. These capabilities create new service models around on-site fabrication, spares logistics, and adaptive mission reconfiguration for sustained surface operations.
Future Outlook
The market is set to mature as sustained lunar operations transition from demonstration to repeatable mission architectures. Policy continuity and mission cadence will deepen ecosystem readiness, while autonomy and modular platforms compress deployment cycles. Integration with surface power and in-space manufacturing will broaden use cases, supporting durable operational footprints through the late decade.
Major Players
- Astrobotic Technology
- Intuitive Machines
- Moon Express
- ispace U.S.
- OffWorld
- Honeybee Robotics
- Maxar Technologies
- Northrop Grumman
- Lockheed Martin
- Blue Origin
- SpaceX
- Redwire Space
- Sierra Space
- Axiom Space
- Made In Space
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capital firms
- NASA
- Federal Aviation Administration Office of Commercial Space Transportation
- Federal Communications Commission
- US Department of Defense
- Commercial lunar mission operators
- Satellite operators and in-orbit service providers
- Space systems integrators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Program milestones, mission cadence, autonomy maturity, power architectures, and surface-operability constraints are scoped to define demand drivers and adoption thresholds. Regulatory pathways and licensing workflows are mapped to deployment feasibility. Supply-side capability variables capture platform modularity, interface standards, and qualification readiness.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Mission pipelines, launch manifests, and infrastructure readiness are synthesized to construct adoption pathways. Technology readiness levels are aligned to operational use cases. Value-chain linkages across robotics hardware, autonomy software, power, and comms are integrated to reflect system-level dependencies.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Operational assumptions are stress-tested against mission analog data and regulatory requirements. Engineering feasibility is validated through field-test outcomes and integration benchmarks. Institutional procurement dynamics are examined to refine deployment timelines and partnership structures.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are consolidated into scenario-based outlooks linking policy continuity, mission cadence, and platform maturity. Cross-segment implications are harmonized to ensure internal consistency. Outputs are structured to inform strategic planning, partnerships, and deployment sequencing.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and mission-phase boundaries, Primary interviews with space mining startups and robotics integrators, Expert consultations with NASA and DoD space systems officials)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and launch-to-orbit channel structure
- Growth Drivers
Rising US investment in lunar and cislunar infrastructure
Demand for in-situ resource utilization to reduce launch mass
Growth of commercial lunar missions and CLPS programs - Challenges
High technology development and qualification costs
Uncertain commercial viability and ROI timelines
Harsh lunar and asteroid operating environments - Opportunities
Public–private partnerships for lunar ISRU demonstrations
Integration of robotics with in-space manufacturing
Long-term contracts for propellant production and supply - Trends
Shift toward modular and reconfigurable robotic systems
Increased use of AI-driven autonomy and edge computing - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Unit Economics, 2020–2025
- By Robot Platform Type (in Value %)
Prospecting rovers
Autonomous excavation robots
Material handling and hauling robots
In-situ processing and beneficiation units
On-orbit servicing and assembly robots - By Mission Phase (in Value %)
Prospecting and surveying
Sample collection and return
Pilot-scale extraction
Resource processing and storage
On-orbit transfer and utilization - By Resource Target (in Value %)
Water ice
Rare earth elements and platinum group metals
Regolith for construction and shielding
Volatiles for propellant production
Silicates for manufacturing feedstock - By Deployment Environment (in Value %)
Lunar surface
Near-Earth asteroids
Cislunar orbit and Lagrange points
Low Earth orbit in-orbit servicing zones - By Autonomy Level (in Value %)
Teleoperated systems
Supervised autonomy
Fully autonomous robotic systems
- Market share of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology readiness level, Autonomy and AI maturity, Mission heritage and flight validation, ISRU process integration capability, Robotics payload mass efficiency, Power and thermal management capability, Partnerships with launch providers, Compliance with US regulatory frameworks)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Astrobotic Technology
Intuitive Machines
Moon Express
ispace U.S.
OffWorld
Honeybee Robotics
Maxar Technologies
Northrop Grumman
Lockheed Martin
Blue Origin
SpaceX
Redwire Space
Sierra Space
Axiom Space
Made In Space
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Unit Economics, 2026–2035