Market Overview
The automotive MEMS sensor market generated USD ~ million in 2024 and is anchored by ADAS penetration, electrification, and safety-critical sensing content per vehicle. In 2024, an accessible regional benchmark shows North America at USD ~ billion, reflecting strong pull from TPMS/pressure sensing, inertial sensing for stability control, and growing sensor count in EV thermal/battery subsystems. For adjacent demand context, the broader U.S. automotive sensors market moved from USD ~ billion to USD ~ billion.
Within North America, the United States is the dominant consumption and design hub due to a large installed base of ADAS-enabled vehicles and fleets, deep OEM/Tier-1 engineering presence, and system-level validation infrastructure tied to functional safety and automotive qualification flows. Dominance is reinforced by Detroit–Michigan for OEM and Tier-1 integration, validation, and sourcing, California for ADAS and autonomous stacks, silicon design, and AI compute adjacency, and Texas for the semiconductor ecosystem, packaging and test, and automotive electronics supply chain. Globally, the U.S., Japan, Germany, and South Korea remain pivotal because they concentrate OEM platforms, Tier-1 modules, and automotive-grade sensor manufacturing scale.
Market Segmentation
By Sensor Type
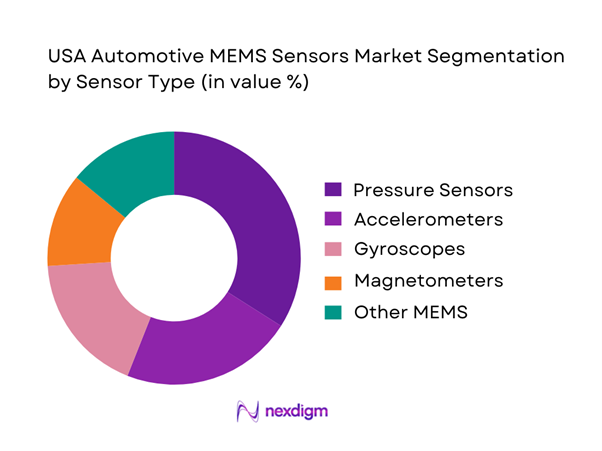
The USA Automotive MEMS Sensors Market is segmented by sensor type into pressure sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes, magnetometers, and microphones and ultrasonic MEMS. Pressure sensors dominate because they are structurally embedded across high-volume safety and control loops including TPMS, engine air management, transmission hydraulics, brake boosters, and HVAC and thermal management, creating repeatable content per vehicle across ICE, hybrid, and EV architectures. In addition, pressure sensing benefits from a mature qualification path, standardized packaging, and stable design-wins in Tier-1 ECUs. As EV and thermal management complexity increases, pressure points across coolant loops and heat-pump control add incremental sockets, supporting sustained leadership versus inertial sensing, which is more concentrated in specific dynamics and safety modules.
By Vehicle System Application
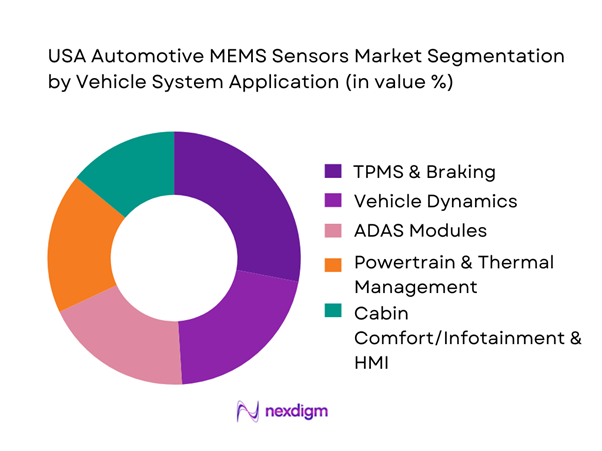
The market is segmented by application into TPMS and braking, vehicle dynamics including ESC, rollover, and IMU, ADAS sensing modules, powertrain and thermal management, and cabin comfort, infotainment, and HMI. TPMS and braking leads because it is both regulatory-anchored and fleet-critical, and it scales across nearly every passenger vehicle platform with consistent bill-of-material inclusion. In addition, brake system modernization including electronic brake control and stability integration relies on robust sensing for pressure and motion, sustaining recurring volumes even as vehicle propulsion shifts. ADAS grows rapidly, but it is more architecture-dependent, while TPMS and core braking remain broad-based and less optional. EV adoption also increases thermal management sensing, yet TPMS and braking remains the highest-volume always-on socket across the parc.
Competitive Landscape
The USA Automotive MEMS Sensors Market is moderately concentrated at the automotive-grade tier, where a small set of global sensor leaders and integrated device manufacturers secure most OEM and Tier-1 design wins due to qualification depth, multi-plant supply assurance, and packaged module co-development capability. Recent strategic activity reflects the importance of scale, automotive reliability, and long program lifecycles.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | Automotive-Grade Quality Stack | Core Automotive MEMS Portfolio | Packaging & Test Strength | OEM/Tier-1 Design-Win Depth | US/NA Supply & Support Footprint | Differentiation Signal |
| Bosch | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Infineon Technologies | 1999 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| STMicroelectronics | 1987 | Switzerland (operational) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Denso | 1949 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Analog Devices (ADI) | 1965 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Automotive MEMS Sensors Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Platform and Trim Content Mapping
Automotive MEMS sensor demand in the United States is directly driven by rising vehicle production complexity and increasing electronic content per vehicle across trims. The United States produced ~ motor vehicles, including passenger cars and light trucks. Light trucks and SUVs represented the majority of new vehicle registrations, categories that typically integrate higher counts of pressure, inertial, and motion MEMS sensors due to stability control, advanced braking, and body electronics. U.S. industrial production for motor vehicles and parts was reported at an index level of ~, reflecting sustained electronics integration across platforms. Additionally, the U.S. vehicle parc stood at over ~ registered vehicles, creating a massive installed base requiring MEMS-enabled systems such as TPMS, airbag sensors, and chassis controls. Higher trim proliferation within single vehicle platforms further increases sensor sockets, as premium trims embed additional electronic stability, ride control, and comfort sensing features compared to base variants.
ADAS and Autonomy Compute Centralization Impact
Centralization of compute architectures in U.S. vehicles significantly increases MEMS sensor utilization by intensifying data fusion requirements. More than ~ vehicles on U.S. roads are equipped with at least one advanced driver assistance feature such as electronic stability control, lane assistance, or collision warning. These systems rely on MEMS accelerometers, gyroscopes, and pressure sensors to provide real-time motion and inertial reference data to centralized ECUs. Road fatalities were reported at ~, reinforcing regulatory and OEM focus on ADAS expansion. Additionally, average vehicle age stood at ~ years, increasing the need for advanced sensing to compensate for mixed traffic environments where newer ADAS-equipped vehicles operate alongside older vehicles. Centralized compute platforms require higher sensor reliability and redundancy, further increasing MEMS integration density per vehicle without referencing pricing or unit economics.
Challenges
Wafer Manufacturing Footprint Constraints
Automotive MEMS sensor supply in the U.S. faces constraints due to limited domestic specialty wafer fabrication capacity. Silicon wafer imports exceeded USD ~ billion, indicating reliance on offshore manufacturing for critical semiconductor substrates. Legacy node fabs essential for MEMS operate at high utilization, restricting rapid capacity expansion. Automotive MEMS sensors require specialty processes such as deep reactive-ion etching and wafer bonding, which are less prevalent in advanced logic fabs. This mismatch between automotive demand and available fabrication infrastructure constrains supply continuity during demand spikes.
Specialty Materials and Equipment Dependencies
MEMS manufacturing depends on specialized materials and equipment with limited global suppliers. Concentrated import flows for semiconductor manufacturing equipment exceeded USD ~ billion, highlighting exposure to supply chain disruptions. Critical MEMS processes rely on precision etching tools, specialty gases, and bonding materials regulated under export control frameworks. Expanded oversight on semiconductor equipment trade has introduced compliance friction. Automotive MEMS suppliers must secure uninterrupted access to these inputs to meet OEM quality thresholds.
Opportunities
Domestic Supply Assurance and Localization
Domestic semiconductor localization initiatives present a structural opportunity for automotive MEMS sensors. Incentives allocated under semiconductor manufacturing programs totaled USD ~ billion, with automotive and legacy-node production explicitly highlighted. Supply chain reviews identify automotive sensors as critical components requiring domestic resilience. Increased localization reduces lead-time volatility and strengthens OEM sourcing confidence, benefiting MEMS suppliers aligned with U.S.-based manufacturing ecosystems.
High-Value IMU Opportunities
Advanced inertial measurement units represent a high-value expansion area supported by current vehicle dynamics. Police-reported crashes exceeded ~, reinforcing demand for stability and motion control technologies. IMUs support rollover detection, trailer sway control, and ADAS fusion layers. With over ~ vehicles operating in mixed traffic environments, enhanced inertial sensing improves safety outcomes. As ADAS compute consolidates, high-performance IMUs gain strategic importance without relying on pricing expansion.
Future Outlook
Over the next cycle, the USA Automotive MEMS Sensors Market is expected to expand on three structural vectors: higher sensor content per vehicle from ADAS and electrification, tighter safety and diagnostics expectations pushing redundant sensing and better signal integrity, and platform standardization that locks multi-year volumes once qualified. Industry outlooks for the automotive MEMS sensor space indicate strong forward momentum supported by ADAS, EV platforms, and regulatory-linked safety features.
Major Players
- Bosch
- Infineon Technologies
- STMicroelectronics
- Denso
- Analog Devices
- Texas Instruments
- NXP Semiconductors
- TDK InvenSense
- Murata Manufacturing
- Sensata Technologies
- TE Connectivity
- Honeywell
- onsemi
- Renesas Electronics
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEM Strategy and Advanced Engineering Teams
- Tier-1 Module Manufacturers covering chassis, braking, ADAS, and body electronics
- EV Powertrain and Thermal System Integrators
- Semiconductor and MEMS Sensor Product Management Leaders
- Automotive Aftermarket TPMS and Diagnostics Platform Companies
- Private Equity, Investments, and Venture Capitalist Firms focused on mobility, semiconductors, and deep technology
- Government and Regulatory Bodies including NHTSA, U.S. Department of Transportation, and U.S. Department of Energy
- Fleet Operators and Fleet Safety and Telematics Buyers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We map the full USA automotive MEMS ecosystem across OEMs, Tier-1s, sensor OEMs, fabs and OSATs, and channel partners, and define variables such as sensor sockets per vehicle, qualification cycles, and platform lifetimes. Desk research is paired with database triangulation to establish an evidence-led baseline for the market model.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We construct a bottom-up model using vehicle production and registrations, content per vehicle by system, and qualification grade differentiation. We cross-check the build with shipment signals and supplier disclosures where available to avoid single-source dependence.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate assumptions via interviews with Tier-1 sourcing leads, MEMS product managers, and automotive quality and validation experts. Interviews focus on design-win timing, platform carryover, dual-sourcing behavior, and failure-return learnings that shift supplier preference.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We finalize sizing and segmentation through triangulation across bottom-up socket modeling, supplier portfolio mapping, and program-level checks with integrators. Outputs are converted into decision-ready views including segment attractiveness, competitive positioning, and opportunity white spaces.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Engineering Framework, Top-Down Sizing Logic, Bottom-Up Program and Platform Mapping, Primary Interviews with OEMs, Tier-1s, Foundries and OSATs, Data Triangulation, Validation Checks, Limitations and Sensitivity Notes)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Adoption Timeline
- MEMS Role in Vehicle E/E Architectures
- Demand Stack Across USA Vehicle Parc
- Automotive MEMS Supply Chain and Value Chain
- Growth Drivers
Platform and Trim Content Mapping
ADAS and Autonomy Compute Centralization Impact
EV and Hybrid Thermal and Pressure Sensing Pull
Safety and Compliance-Driven Volumes
Fleet and Commercial Use Cases - Challenges
Wafer Manufacturing Footprint Constraints
Specialty Materials and Equipment Dependencies
OSAT and Test Capacity Bottlenecks
Quality Systems and Traceability Burden
Supply Risk and Continuity - Opportunities
Domestic Supply Assurance and Localization
High-Value IMU Opportunities
EV-Specific Sensing Adjacencies
Software-Defined Vehicle Enablement
Premium Reliability Niches - Trends
Centralized Compute and Sensor Fusion
Increased IMU Performance Density
Advanced Packaging and Miniaturization
Software-Centric Sensor Differentiation - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Unit Shipments, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Application (in Value %)
Accelerometers
Gyroscopes
Pressure Sensors
Microphones
Magnetometers - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Safety Restraints
Chassis and Stability
Powertrain and Thermal
ADAS and Autonomy
Cabin Experience - By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
Light Trucks and SUVs
Medium and Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Off-Highway and Work Trucks
Robotaxis and Autonomous Shuttles - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
ICE Vehicles
Hybrid Vehicles
Battery Electric Vehicles
Fuel Cell Vehicles
Mixed Fleets - By Region (in Value %)
OEM Direct
Tier-1 Integrated Modules
Aftermarket and Service
Fleet Retrofit
Industrial and Adjacent Pull-Through
- Competitive Intensity Map
Market Share Assessment Framework - Cross Comparison Parameters (AEC-Q100 grade breadth, ISO 26262 and ASIL safety collateral depth, IMU performance metrics including bias instability and drift, shock and vibration survivability specifications, package portfolio and warpage control capability, calibration and test automation throughput, supply assurance and dual sourcing capability, automotive design-win penetration)
- Strategic Moves
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Robert Bosch GmbH
Analog Devices, Inc.
STMicroelectronics N.V.
TDK InvenSense
Infineon Technologies AG
NXP Semiconductors N.V.
Texas Instruments Incorporated
Microchip Technology Inc.
onsemi
Sensata Technologies, Inc.
Honeywell International Inc.
TE Connectivity Ltd.
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
Panasonic Industry
Alps Alpine Co., Ltd.
- Buyer Stakeholder Map
- RFQ to SOP Cycle Anatomy
- Supplier Selection Criteria
- Switching Costs
- Common Failure Modes and Voice of Customer
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Unit Shipments, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025–2030


