Market Overview
The USA automotive PCB boards market is valued at USD ~ million, supported by the rising electronics content per vehicle across EV power electronics, ADAS compute, infotainment, and domain/zonal controllers. Demand is reinforced by the step-up in electrification volumes—~ new electric car registrations were recorded in the United States in the prior year—and by overall vehicle production/sales normalization, with US light-vehicle sales reaching ~ units versus ~ units in the prior year.
Demand concentration is highest in the Western United States, supported by EV/AV software-defined vehicle ecosystems, dense electronics design activity, and proximity to advanced manufacturing supply chains; this region is identified as the largest demand center for automotive PCBs. Beyond the West, Detroit–Ann Arbor (Michigan) anchors OEM engineering and Tier-1 program releases; Bay Area–Los Angeles (California) concentrates EV platforms, compute/AI, and connected-car stacks; Austin–Dallas (Texas) accelerates electronics manufacturing and semiconductor-linked capacity; and Ohio–Indiana corridors sustain Tier-~ manufacturing and vehicle assembly adjacency—together shaping PCB spec cycles and sourcing decisions.
Market Segmentation
By PCB Type
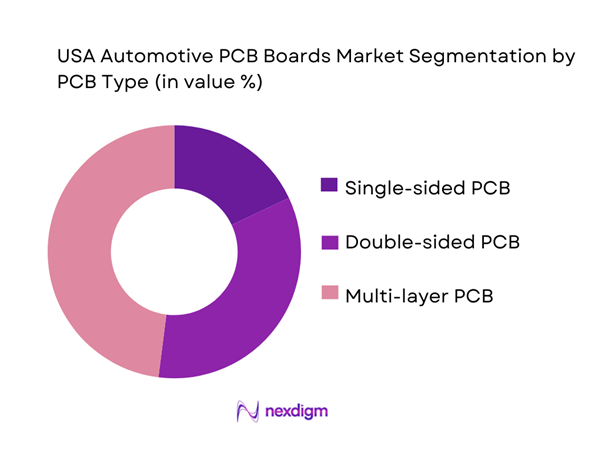
USA automotive PCB boards market is segmented by PCB type into single-sided PCB, double-sided PCB, and multi-layer PCB. Recently, multi-layer PCB holds the dominant market share due to the rapid migration toward consolidated ECUs, domain controllers, and high-pin-count processors used in ADAS perception stacks, zonal architectures, and EV powertrain control. Multi-layer builds (with higher layer counts, tighter impedance control, and advanced via structures) enable signal integrity for high-speed networking (e.g., automotive Ethernet), reduce harness complexity through integration, and improve functional density in space-constrained modules (camera/radar, gateway, BMS). As OEMs push compute centralization and functional safety, suppliers increasingly specify higher-reliability multilayer constructions with robust thermal performance and tighter process controls aligned with automotive qualification.
By Application
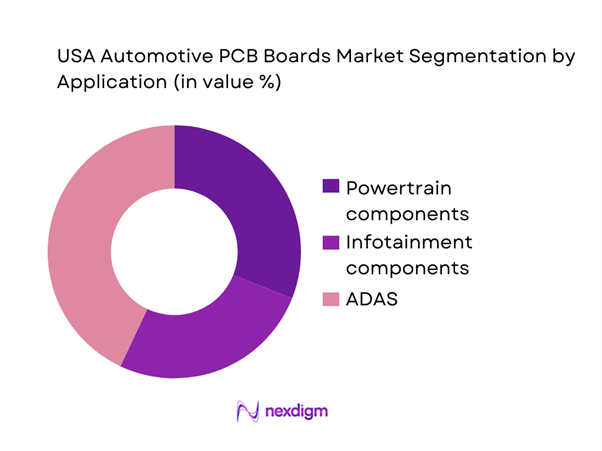
USA automotive PCB boards market is segmented by application into powertrain components, infotainment components, and ADAS. Recently, ADAS dominates market share as camera/radar/ultrasonic sensing, sensor fusion compute, and safety feature roadmaps increase the number and sophistication of electronic modules per vehicle. ADAS PCBs typically require higher layer counts, controlled impedance, and stringent reliability for high-speed data paths and real-time processing; they also pull demand for higher-grade materials and advanced assembly (fine pitch, BGAs). While powertrain PCBs scale with EV penetration (inverters, onboard chargers, DC-DC, BMS), ADAS sees broader fitment across ICE/HEV/BEV platforms, accelerating its volume base. Regulatory attention on safety performance and OEM differentiation further sustains ADAS electronics intensity.
Competitive Landscape
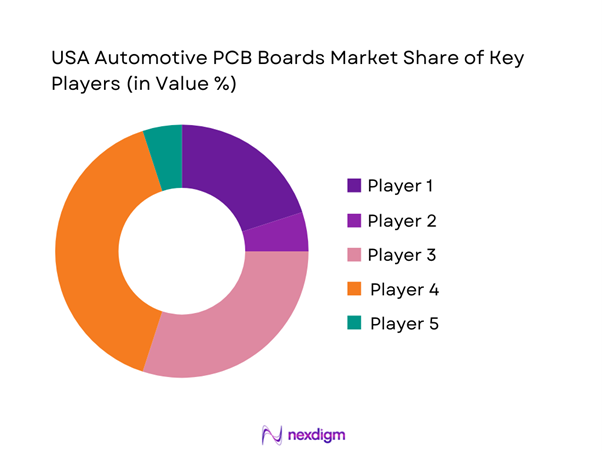
The USA automotive PCB boards market is characterized by a mix of specialty automotive PCB fabricators, US-based advanced PCB manufacturers, and global electronics groups serving automotive programs through qualified plants and EMS partnerships. Competition is shaped by qualification depth (IATF/PPAP), high-mix reliability manufacturing, multilayer capability, lead-time resilience, and the ability to co-design with Tier-1s on thermal, EMI/EMC, and functional-safety constraints.
| Company | Est. Year | Headquarters | Automotive-grade capability focus | Key PCB technology strength | Typical automotive programs served | Quality & compliance posture | US footprint / delivery model | Differentiation lever |
| TTM Technologies | 1998 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AdvancedPCB | 2005 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Benchmark Electronics | 1986 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Kyocera (incl. AVX ecosystem) | 1959 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Multek (Flex) | 1984 | USA (Flex HQ) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Automotive PCB Boards Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
ADAS ECU proliferation
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are pushing more electronic control units (ECUs) and more complex PCBs into US-built and US-sold vehicles—especially as OEMs scale camera/radar-based perception, sensor fusion, and centralized compute. In the US macro backdrop, the economy is large enough to sustain high electronics intensity in vehicles: GDP is USD ~ trillion and GDP per capita is USD ~, supporting continued demand for feature-rich vehicles and higher trim penetration. On the safety/regulatory side, NHTSA’s Standing General Order (SGO) requires manufacturers/operators to report crashes involving ADS and SAE Level-~ ADAS vehicles, creating a strong compliance and validation loop for ADAS deployments. A public-facing crash-data summary drawn from NHTSA’s ADS-equipped reporting ecosystem shows ~ “number of reported crashes” (as posted in the mid-year update), illustrating the expanding real-world operational footprint of ADS/ADAS-equipped fleets and consumer vehicles that rely on multi-board sensor/compute stacks. As ADAS expands, PCB BOM shifts toward higher layer-count, controlled impedance, HDI/fine-line routing for dense processors and high-speed interfaces, plus robust power integrity for ECU stability—raising domestic PCB content per vehicle even without quoting market value figures.
EV power electronics content expansion
Electrification increases PCB intensity in traction inverters, onboard chargers, DC-DC converters, battery management systems, thermal control, and high-voltage distribution—driving demand for heavy-copper, high-TG laminates, robust creepage/clearance designs, and higher reliability interconnects. The US economic base (GDP ~ trillion, GDP per capita ~) provides the scale for sustained vehicle turnover and technology adoption that pulls more power-electronics PCBs through domestic and North American supply chains. On the demand signal, the US DOE reported that annual new light-duty EV sales exceeded ~ units and cumulative new light-duty plug-in vehicle sales since ~ reached ~ units—evidence of a large installed base that increases service demand for EV electronics and accelerates OEM platform refresh cycles. For the more recent pulse, an EV market spotlight reports ~ EV sales in the US (light-duty) during the latest full-year tally it covers, reinforcing the reality that EV architectures are now mainstream in US showrooms; higher EV penetration directly translates into more power PCB area per vehicle versus ICE equivalents (more conversion stages, sensing, and protection). This is exactly the mix shift that raises automotive PCB complexity and qualification needs across US programs—especially for thermal cycling, vibration, and high-voltage isolation requirements.
Challenges
Long automotive qualification cycles
Automotive PCB programs in the US face long qualification and change-control cycles because boards must clear reliability, traceability, and validation gates (PPAP discipline, process capability, supplier audits), and because design changes ripple into safety, EMI/EMC, and thermal performance. In a large economy (GDP ~ trillion, GDP per capita ~), OEMs run many concurrent vehicle platforms, but each platform still requires deep validation and supplier process lock-down—stretching time-to-revenue for new PCB technologies (new laminates, via structures, embedded components). Federal safety oversight further reinforces this: NHTSA’s crash reporting and safety monitoring frameworks for automated/ADAS systems create additional scrutiny on electronics behavior, and manufacturers must manage compliance documentation and field performance signals before scaling. The result is that even when demand is strong, PCB suppliers often experience slower ramp rates and longer NPI cycles, tying up engineering resources and delaying volume stability. For business planning, this challenge manifests as (a) extended sample-to-SOP timelines, (b) higher cost of quality, (c) higher working capital in proto builds and pilot runs, and (d) a need for stronger program management to avoid late-stage redesigns. The macro environment supports investment, but it does not shorten qualification: automotive-grade boards remain among the most demanding “high consequence” electronics classes in the US manufacturing stack.
HDI yield loss and complex stackups
As US automotive PCBs move toward HDI (microvias, stacked/staggered via structures), dense BGAs, and mixed-signal + power co-design, yield management becomes a major constraint. Scrap and rework risks increase when drilling/laser via formation, via-fill, lamination registration, and fine-line etch windows tighten—especially across high layer-count stackups. The US economic scale (GDP ~ trillion, GDP per capita ~) supports sophisticated manufacturing, but it also raises expectations for near-zero defect rates in safety-critical electronics, which amplifies the cost of yield loss. A practical driver of HDI complexity is the electrification and ADAS compute trend evidenced by the US’s large and growing EV installed base (millions of plug-ins sold cumulatively) and the expanding operational footprint of ADAS/ADS vehicles in NHTSA’s monitoring environment—both of which imply more advanced compute and power modules. Complex stackups also interact with materials availability and process stability: tighter impedance targets and thermal requirements increase sensitivity to resin content, glass weave effects, and copper roughness—making consistent yields harder to maintain across batches. In this environment, US automotive PCB suppliers must invest in advanced AOI/AXI, tighter SPC, and supplier qualification for laminates and copper foils, while customers push for higher performance per board. The challenge is not demand; it is the manufacturability and repeatability of advanced automotive-grade HDI at scale without compromising reliability.
Opportunities
Domestic reshoring for high-reliability boards
A major opportunity for the US automotive PCB boards ecosystem is reshoring/nearshoring for high-reliability, safety-critical, and supply-assured boards—particularly those tied to EV power electronics, ADAS compute, and secure connectivity modules. The macro case is clear: the US operates at GDP ~ trillion and GDP per capita ~, supporting large capex cycles and supplier investment in advanced manufacturing. A current infrastructure signal that strengthens the business case for localized electronics production is the rapid build-out of national EV charging availability—because it reflects sustained electrification momentum and the scaling needs of EV platforms that use PCB-rich power and control systems. The US Joint Office of Energy and Transportation reported more than ~ public EV charging ports available nationwide, demonstrating tangible nationwide electrification infrastructure scale that correlates with ongoing OEM platform commitments and higher demand for automotive-grade electronics. Reshoring gains credibility when OEMs want shorter lead times, tighter engineering collaboration, and reduced policy/logistics risk—especially for boards where requalification is painful and field failures are expensive. Suppliers that can meet automotive traceability, deliver HDI capability, and pass rigorous audit requirements are positioned to capture higher-value programs as OEMs diversify away from single-region dependencies.
High-speed signal integrity PCB demand
As vehicles become rolling data centers—central compute, multi-camera perception, high-speed networking, secure gateways—signal integrity becomes a differentiator, expanding demand for controlled-impedance, low-loss materials, tighter via design, and robust EMC design practices. The US market’s macro strength (GDP ~ trillion; GDP per capita ~) supports both the consumer willingness to pay for advanced features and the industrial investment required to build low-loss PCB capability. A key enabler of these connected, OTA-driven, data-heavy vehicle systems is national digital infrastructure measured by federal reporting: the FCC’s Internet Access Services status report aggregates internet access connection data as of ~ in its latest reporting set, reinforcing that the US connectivity backbone is large and systematically tracked—creating the environment where connected vehicles and cloud-dependent features can scale. Pair that with the NTIA-documented gain of ~ internet users over a two-year window, and you have a concrete indicator of expanding digital participation that supports growth in connected services ecosystems—including vehicle-linked applications and fleet platforms. For PCB suppliers, the opportunity is to specialize: low-loss stackups, tighter impedance tolerances, better dielectric control, and advanced test/validation to meet automotive environmental constraints while carrying higher data rates. Providers that master these requirements can win “compute- and network-heavy” automotive modules that are structurally growing in content per vehicle.
Future Outlook
The USA automotive PCB boards market is expected to expand steadily, driven by (i) continued electrification of powertrains, (ii) ADAS feature proliferation and compute centralization, (iii) migration toward zonal architectures reducing harness complexity but increasing controller sophistication, and (iv) supply-chain localization efforts in critical electronics. Platform decisions made now—controller consolidation, sensor suite upgrades, and power electronics scaling—will meaningfully lift multilayer demand, thermal-management requirements, and automotive-grade qualification intensity across the PCB value chain.
Major Players
- TTM Technologies
- AdvancedPCB
- Multek
- Benchmark Electronics
- Kyocera Corporation
- Sumitomo Electric Industries
- Zentech Manufacturing
- Avery Dennison
- Jabil
- Sanmina
- Celestica
- Würth Elektronik
- Nippon Mektron
- Unimicron Technology
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEM electronics procurement & platform sourcing teams
- Tier-1 module makers strategic sourcing heads
- EV power electronics and battery system manufacturers procurement leads
- ADAS sensor and compute module manufacturers sourcing & engineering leadership
- Automotive EMS and contract manufacturers
- Automotive semiconductor and connectivity ecosystem companies
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We map the USA automotive PCB ecosystem across OEMs, Tier-~s, PCB fabricators, EMS partners, laminate/material suppliers, and test/inspection vendors. Desk research consolidates technology and demand variables such as layer-count mix, ADAS compute intensity, EV power electronics scaling, qualification standards, and localization trends.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We construct the market using historical demand signals (vehicle sales, EV registrations, electronics content trends) and convert module-level adoption into PCB value pools by application. Market totals are reconciled with credible published benchmarks for the USA automotive PCB market sizing and growth outlook.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate assumptions through structured expert interactions (CATI/online interviews) with PCB manufacturing leaders, Tier-~ sourcing managers, and automotive electronics program owners. Discussions focus on multilayer vs double-sided migration, lead-time dynamics, quality hurdles, and application-level demand shifts.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize primary inputs with secondary sources to finalize market sizing, competitive positioning, and segmentation logic. Outputs are cross-checked against program releases, technology roadmaps, and observed manufacturing/qualification constraints to ensure decision-grade conclusions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Scope Boundary: PCB Fabrication vs PCBA vs Box-Build, Market Sizing Approach, Bottom-Up Build Using Vehicle Electronics Content, Primary Interviews: OEM, Tier-1, EMS, Material Suppliers, Validation via Trade, Shipment and Capacity Signals, Limitations and Data Confidence Framework)
- Definition and Scope
- Overview Genesis
- Timeline of Major Players
- Business Cycle
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
ADAS ECU proliferation
EV power electronics content expansion
Vehicle connectivity and telematics scaling
Zonal and domain controller architectures
Functional safety and redundancy requirements - Challenges
Long automotive qualification cycles
HDI yield loss and complex stackups
Copper foil and laminate price volatility
Trade policy and sourcing exposure
Skilled labor and NPI constraints - Opportunities
Domestic reshoring for high-reliability boards
High-speed signal integrity PCB demand
Thermal management boards for EVs
Redundancy-focused safety electronics
Lifecycle and aftermarket PCB support - Trends
Automotive IPC addendum adoption
Shift toward rigid-flex architectures
Controlled impedance as standard design
Increased AXI and boundary scan usage
Digital traceability and serialization - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Price, 2019–2024
- By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Rigid
Flex
Rigid-Flex / Semi-Flex
HDI
Metal-Core / IMS
Ceramic / High-Temperature Substrates - By Application (in Value %)
ADAS & Sensor Fusion Modules
Powertrain & Engine/Transmission Control
Body Control, Lighting & Comfort Electronics
Infotainment, Telematics & Connectivity
Battery Management & Power Electronics - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Passenger Vehicles
Light Commercial Vehicles
Medium & Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Off-Highway / Specialty Vehicles
Electric Vehicles Platforms - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
1–2 Layer
4 Layer
6–10 Layer
12+ Layer
Heavy Copper / High-Current Designs - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Standard FR-4
High-Tg / Low-CTE FR-4
Polyimide
High-Frequency / Low-Loss Materials
Thermal Substrates - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
OEM Direct Sourcing
Tier-1 / Tier-2 Module Makers
EMS / ODM
Aftermarket Electronics
Defense and Industrial Automotive-Grade Demand
- Market Share Benchmarking
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Automotive Qualification Depth, HDI Capability, Rigid-Flex Manufacturing Maturity, Thermal Management Portfolio, Signal Integrity Engineering, Test and Inspection Stack, Supply Resilience, Traceability and Digital Thread)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Commercial Benchmarking
- Company Profiles
TTM Technologies
Summit Interconnect
AdvancedPCB
Sanmina
Jabil
Flex
Plexus
Benchmark Electronics
Celestica
Kimball Electronics
Creation Technologies
Sierra Circuits (ProtoExpress)
Rush PCB
Green Circuits
- Market Demand and Utilization
- Procurement and Supplier Qualification
- Specification Priorities by Application
- Failure Modes and Reliability Risks
- Decision-Making Process
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Price, 2025–2030