Market Overview
The USA automotive power tools market (professional cordless + pneumatic tools used in dealership bays, independent repair, collision, tire/undercar, and fleet MRO) is most consistently sized in public sources through the U.S. cordless power tools lens. In 2024, market value is USD ~ billion, with a clear demand pull from industrial end-users, including automotive service activities. A 2023 anchor for the service environment is the U.S. automotive aftermarket at USD ~ million, supporting recurring tool consumption through repair/maintenance workloads and shop productivity pressure.
The market is dominated by U.S. industrial and vehicle-service hubs rather than a single geography: the South leads cordless power tool demand due to its large workshop base and operating intensity, while Michigan/Ohio/Indiana remain critical for automotive and supplier ecosystems, and California/Texas/Florida contribute scale through vehicle parc, collision volumes, and high-throughput service chains. Vendor dominance is reinforced by dense pro-dealer networks, tool-truck routes, rapid fulfillment, and battery-platform lock-in that is easier to sustain in large metro corridors than in low-density rural markets.
Market Segmentation
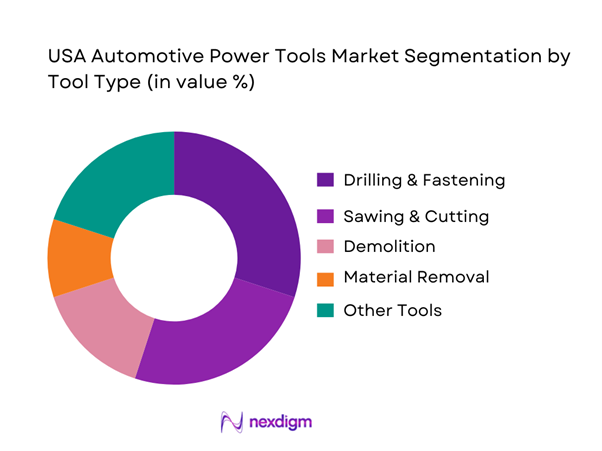
By Tool Type
The U.S. cordless power tools market is segmented into drilling & fastening, sawing & cutting, demolition, material removal, routing, and other tools. In automotive service, drilling & fastening dominates because it is directly tied to the highest-frequency operations across bays—wheel-off/wheel-on, suspension and brake work, underbody fasteners, and routine disassembly/reassembly. The segment is also structurally advantaged by battery-platform economics: shops standardize on a single ecosystem (batteries/chargers) and expand within that ecosystem first through impact wrenches, impact drivers, drills, and cordless ratchets. Compared with cutting or demolition tools, fastening tools deliver the clearest payback through reduced cycle time and reduced dependency on fixed air lines, while enabling mobile work anywhere in the shop. This is consistent with market findings that drilling/fastening is the largest product cluster in power tools demand.
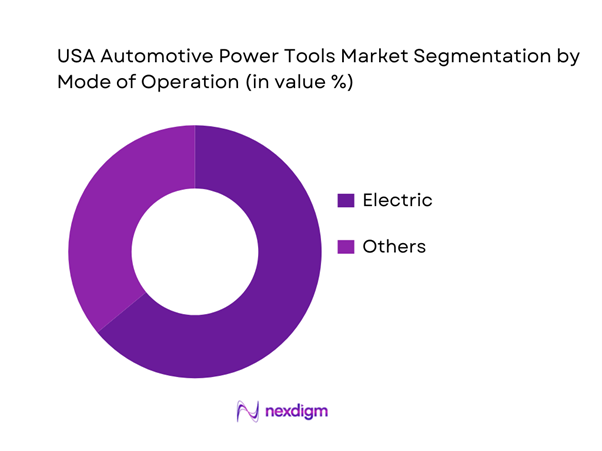
By Mode of Operation
The market is segmented into electric and non-electric (others). Electric tools dominate because the professional workflow increasingly rewards mobility, reduced hose-management, and simplified safety/compliance—especially in multi-bay environments where technicians move across lifts and shared equipment. Electric tools held ~ of the global power tools revenue mix in 2024 benchmark, with cordless growth inside electric accelerating faster than the overall market; this directionality is particularly relevant to automotive service where high-torque cordless platforms are replacing air tools for many fastening tasks. Pneumatic tools still hold a practical foothold in shops with sunk compressed-air infrastructure and in duty cycles that favor continuous runtime, while hydraulic/specialty solutions remain niche for ultra-high-torque or specialty applications. Overall, electrification plus battery ecosystem breadth remains the primary competitive lever in automotive tool purchasing decisions.
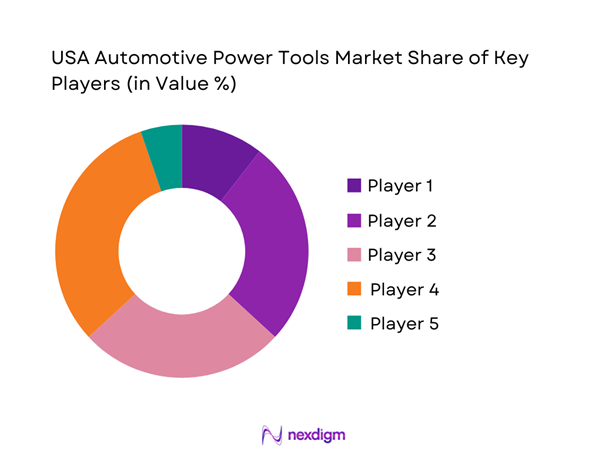
Competitive Landscape
The USA automotive power tools market is highly competitive, led by a small group of platform-scale manufacturers (battery ecosystems, broad catalogs, pro-channel coverage) alongside tool-truck brands and specialty players in pneumatic abrasives and finishing. Consolidation is most visible in battery-platform ecosystems and in route-to-market control (big-box + industrial distribution + e-commerce + tool-truck). Competitive advantage typically comes from torque/durability at the tool level, battery/charger platform lock-in, service turnaround and warranty handling, and availability of automotive-ready kits (tool + sockets/abrasives + storage).
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Core Automotive Use-Cases | Battery/Power Platform Strategy | Channel Strength | After-sales & Service Footprint | Differentiation Lever | Typical Buyer Fit |
| Stanley Black & Decker (DEWALT / Mac Tools) | 1843 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Techtronic Industries (Milwaukee Tool) | 1985 | Hong Kong | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Snap-on Incorporated | 1920 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Robert Bosch Tool (Bosch Professional) | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Makita | 1915 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Automotive Power Tools Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Cordless conversion rate acceleration
Cordless conversion in U.S. automotive bays is being pulled by a larger “work-per-day” vehicle base and rising economic throughput that rewards mobility and faster fastening/removal cycles. The U.S. economy’s scale supports steady professional tool replenishment: GDP is USD ~ trillion and GDP per capita is USD ~, which correlates with high vehicle utilization and dense service infrastructure in major metros. On the usage side, road-load remains structurally high—vehicle miles traveled are ~ million miles (monthly measure), which increases routine maintenance events and the number of repeat fastening operations where cordless impact wrenches/ratchets displace air tools. Workforce and service intensity reinforce the shift: automotive service technicians’ median annual wage is USD ~, making time-saving tooling (cordless, brushless, quick-change accessories) a direct productivity lever in many shops because labor hours are the scarce constraint rather than tool availability.
Service bay productivity pressure
Service-bay productivity pressure is tightly linked to national vehicle activity and the macro environment that sustains high car ownership and repair demand. The World Bank reports U.S. GDP growth at ~ and consumer inflation at ~ (annual), conditions that push operators to protect margins through throughput—more ROs per bay-day—rather than relying on price expansion. Vehicle utilization remains the strongest mechanical driver: monthly vehicle miles traveled reach ~ million miles, indicating a consistently heavy travel base that keeps maintenance intervals turning. High travel activity increases brake jobs, suspension jobs, tire rotations, and undercar repairs—tasks dominated by power fastening and abrasive prep. In parallel, labor availability makes speed non-negotiable: projections indicate about ~ openings per year for automotive service technicians and mechanics (replacement-driven), so shops focus on reducing “touch time” per job using faster torque delivery, fewer hose changes, and less tool staging—advantages that favor cordless platforms and standardized battery ecosystems.
Challenges
Tool downtime and reliability costs
Tool downtime is a direct operational tax in automotive service because a stalled impact, failed trigger, or charger downtime immediately slows throughput and forces labor substitution. The labor side is expensive and sensitive: technicians’ median annual wage is USD ~, so each avoidable idle hour is economically painful for both dealers and independents. The staffing environment also raises the penalty for downtime: expectations indicate about ~ openings per year for automotive service technicians and mechanics, meaning shops often operate near staffing constraints and cannot easily “absorb” productivity losses. High national driving activity amplifies the impact—vehicle miles traveled reach ~ million miles (monthly), keeping bays loaded and leaving less slack capacity to tolerate tool failures. When a primary fastening tool is down, technicians revert to slower alternatives (manual, shared tools, or pneumatic workarounds), which creates queueing at air drops, more repositioning, and more rework risk. This is why warranty turnaround time, spare tool availability, and local service coverage become decisive procurement filters for professional tool buyers.
Battery lifecycle economics
Battery lifecycle economics is challenging for U.S. automotive power tool buyers because battery performance and safety compliance sit inside a broader lithium battery risk environment and a tightening logistics/safety framework. Lithium battery incident tracking highlights safety relevance beyond consumer devices, underlining why storage, handling, and charging protocols matter for shops running multiple high-output packs daily. Lithium battery shipping compliance updates reinforce that regulated transport rules and documentation are operational requirements for distributors and service networks moving batteries/chargers at scale. On the macro side, inflation is ~ (annual), which pressures shops to optimize total cost of ownership: more disciplined charging practices, pack rotation, inventory control, and consolidation into fewer battery families to avoid stranded packs. In practice, buyers increasingly care about pack durability, warranty terms, and replacement availability—because any battery failure can reduce tool availability and increase downtime in peak workload weeks.
Opportunities
High-torque cordless displacement
High-torque cordless displacement (replacing pneumatic for many wheel-end and undercar fastening tasks) is a major growth opportunity because the U.S. automotive service environment is structurally large and time-sensitive, and because facilities have incentives to simplify tool infrastructure. Macro capacity supports continued pro tool investment: GDP is USD ~ trillion and GDP growth is ~, indicating sustained economic activity that keeps vehicle utilization and repair intensity high. On the demand side, travel volume stays heavy—vehicle miles traveled reach ~ million miles (monthly), keeping brake, suspension, tire and general repair cycles active, which are the highest-frequency use cases for high-torque impacts and cordless ratchets. On the labor side, median annual wage for technicians is USD ~ and for technicians in automobile dealers is USD ~, so cordless tools that reduce job cycle time and repositioning deliver an immediate productivity benefit. The opportunity for suppliers is to win “platform conversion” deals (tools + batteries + chargers + accessories) by proving torque consistency, thermal durability, and rapid service support in high-throughput bays.
Tool tracking and asset management
Tool tracking and asset management is an expanding opportunity in the U.S. automotive power tools market because the operating footprint is large, technician time is costly, and loss/misplacement creates hidden downtime. The scale of the service ecosystem supports adoption: private repair-and-maintenance establishments number ~ across consecutive quarters, which implies a vast base of shops, service chains, and maintenance locations where tools circulate across bays, shifts, and sites. National travel demand stays strong—vehicle miles traveled reach ~ million miles (monthly), which sustains repair volume and increases the value of minimizing “non-productive minutes” spent locating tools, batteries, and chargers. Macro conditions also support digitization: GDP per capita is USD ~, consistent with strong adoption capacity for software-enabled workflows (inventory control, standard operating procedures, and connected-tool ecosystems). Vendors that combine connected tools, battery fleet analytics, and distributor-managed programs can reduce shrinkage, improve utilization, and support multi-site standardization without adding headcount.
Future Outlook
Over the next five to six years, the USA automotive power tools market is expected to expand steadily as service bays prioritize throughput, technician efficiency, and tool mobility. The shift toward cordless electrification remains the central theme, driven by improving battery performance, broader platform ecosystems, and greater acceptance of high-torque cordless as a substitute for pneumatic in many fastening operations. Channel strategies will also evolve: offline remains critical for pro buyers, but online and direct programs are rising as shops seek faster replenishment and standardized kitting.
On the demand side, industrial usage remains the primary engine for cordless tool consumption, supported by repair and maintenance workloads and the need to reduce cycle time per job. Suppliers that combine platform breadth (tools + batteries + accessories), service turnaround, and pro-focused financing/kits are best positioned to win incremental share.
Major Players
- Techtronic Industries
- Stanley Black & Decker
- Snap-on Incorporated
- Makita U.S.A.
- Robert Bosch Tool Corporation
- Hilti
- Ingersoll Rand
- Chicago Pneumatic
- Matco Tools
- Mac Tools
- Apex Tool Group
- 3M
- Dynabrade
- Mirka
Key Target Audience
- Automotive dealership groups & service operations leadership
- Independent repair shop chains & franchise operators
- Collision repair MSOs and bodyshop networks
- Fleet maintenance operators
- Industrial/MRO distributors and authorized tool dealers
- Tool-truck/franchise distribution owners and regional operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We begin by mapping the automotive power tools ecosystem across manufacturers, tool-truck networks, industrial distributors, and end-user shop formats. Desk research is used to define the variables that move demand: bay throughput, duty cycle, battery platform adoption, accessory attach, warranty/service turnaround, and channel availability.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical indicators from published market datasets for the U.S. cordless power tools space and triangulate them with automotive service activity proxies (aftermarket environment, shop footprint, and industrial end-use signals). Segment frameworks are constructed around tool type, mode of operation, end-users, and channels.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are validated using structured expert consultations (CATI-style) with workshop owners, dealer service managers, distributor category managers, and brand service partners. These inputs refine assumptions about tool replacement cycles, platform standardization behavior, and price-band trade-offs.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We consolidate findings using a bottom-up view of tool families used per bay and verify with supplier/distributor feedback on mix shifts, service turnaround bottlenecks, and accessory pull-through. The result is a validated market narrative, segmentation logic, and competitive positioning suitable for investment and GTM decisions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Scope Boundaries, Sizing Logic, Triangulation Framework, Primary/Secondary Mix, Interview Universe, Data Cut Rules, Validation Checks, Limitations and Confidence Scoring)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Industry Timeline
- Supply Chain and Value Chain
- Demand Centers
- Growth Drivers
Cordless conversion rate acceleration
Service bay productivity pressure
Technician time economics
Fleet uptime requirements
Accessory pull-through and platform stickiness - Challenges
Tool downtime and reliability costs
Battery lifecycle economics
Counterfeit and gray-market imports
After-sales service capability gaps
Compressed-air inefficiencies - Opportunities
High-torque cordless displacement
Tool tracking and asset management
Kitting and managed tool programs
Collision-repair cordless penetration - Trends
Brushless motor adoption and electronics density
Compact high-torque tool design
Vibration and noise reduction
Dust extraction integration
Connected tool ecosystems - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Installed Base / Active Users, 2019–2024
- By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Cordless Electric
Corded Electric
Pneumatic
Hydraulic / Specialty Power Systems - By Application (in Value %)
Fastening and Removal
Cutting and Grinding
Surface Preparation
Finishing
Thermal and Specialty Applications - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Non-connected Tools
Battery Platform–Based Systems
Mixed-Fleet Interoperability Systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
OEM Dealership Workshops
Independent Repair Shops
Collision Repair and Bodyshops
Tire and Quick Lube Specialists
Fleet Maintenance Operations
Industrial and Auto-Adjacent MRO - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Market Share of Major Players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (battery ecosystem breadth, torque and RPM performance envelope, duty-cycle durability and thermal derate behavior, ergonomics vibration and noise profile, warranty terms and service turnaround time, distribution reach and fill-rate, accessory ecosystem depth and attach rate, connected features and enterprise readiness)
Competitive Positioning Matrix - Pricing Analysis Basis SKUs
- Go-to-Market and Route-to-Market Analysis
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Techtronic Industries (Milwaukee Tool)
Stanley Black & Decker (DEWALT)
Makita U.S.A.
Robert Bosch Tool Corporation
Snap-on Incorporated
Matco Tools
Mac Tools
Ingersoll Rand
Chicago Pneumatic
Apex Tool Group
3M
Dynabrade
Mirka
Festool
Metabo HPT
- Demand and Utilization Patterns
- Buyer Economics
- Workflow Fit and Adoption
- Compliance and Safety Requirements
- Purchasing Journey
- Pain Points and Unmet Needs
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025–2030
- By Installed Base / Active Users, 2025–2030


