Market Overview
The USA Automotive Relays Market is valued at USD ~ million, supported by rising electrical content per vehicle and the continued build-out of power distribution and control circuits across body electronics, powertrain controls, safety modules, and charging-related systems. Demand is also tied to underlying vehicle activity: U.S. motor vehicle sales increased from ~ units to ~ units, expanding the installed base that consumes relays both in OEM fitment and replacement cycles. In parallel, new electric car registrations reached ~ million, reinforcing high-voltage and battery-related relay demand in electrified platforms.
The market is shaped heavily by U.S. automotive manufacturing and engineering hubs such as Detroit–Michigan (OEM/Tier-1 engineering, validation, sourcing), the Midwest manufacturing corridor (automotive electronics and power distribution production), and the U.S. South (fast-growing assembly and supplier footprint). The U.S. also anchors demand through its large vehicle parc and replacement ecosystem, while Japan and Germany remain influential as relay technology and platform architecture leaders through global suppliers embedded in U.S. OEM and Tier-1 programs. On the demand side, the operating environment remains closely connected to U.S. vehicle manufacturing momentum, where motor-vehicle production activity moved from ~ to ~ on an indexed basis, impacting component pull-through.
Market Segmentation
By Relay Type
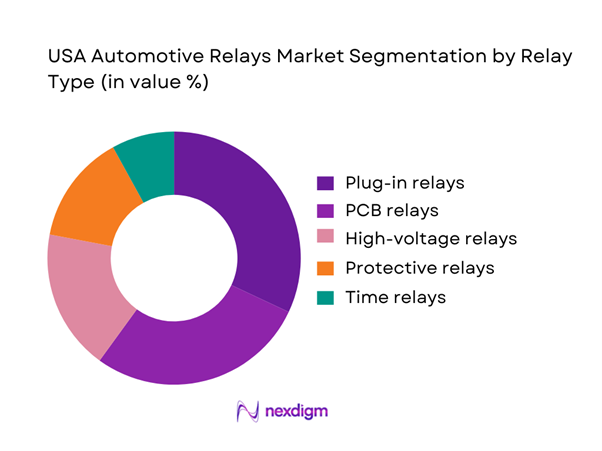
The USA Automotive Relays Market is segmented by relay type into plug-in relays, PCB relays, high-voltage relays, protective relays, and time relays. Recently, plug-in relays hold a dominant market share under relay type segmentation because they remain the workhorse architecture in fuse/relay boxes and serviceable power distribution layouts, especially across mass-market ICE and hybrid platforms where design reuse and field replacement are priorities. Plug-in formats are preferred in many circuits due to mechanical robustness, standardized footprints, and maintenance accessibility—important for fleets and high-mileage vehicles where relay replacement is a practical repair. In addition, plug-in relays align well with high-volume sourcing strategies: OEMs and Tier-1s can qualify families of relays across multiple platforms, reducing complexity in validation and supply continuity. Their dominance is reinforced by broad application coverage across lighting, HVAC blowers, wipers, fuel systems, and auxiliary loads, where cost-performance balance is critical.
By Load Type
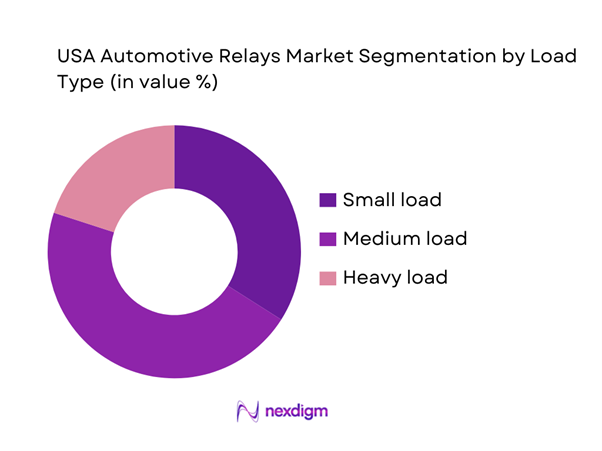
The USA Automotive Relays Market is segmented by load type into small load, medium load, and heavy load categories. Medium load relays dominate because they map to the highest-density set of real-world switching needs in modern vehicles—circuits that are neither tiny signal switching nor extreme high-current power, but the “middle layer” powering body electronics and comfort functions. These include HVAC actuators and blowers, lighting subsystems, pump and motor controls, heated features, and multiple body control loads coordinated by ECUs and power distribution modules. Medium load relays also benefit from being “platform-stable”: OEMs can carry the same relay specifications across several trims and model families, while Tier-1s bundle them into integrated junction boxes and power distribution units. As vehicles add more features (safety, comfort, connectivity), medium-load switching points grow faster than purely mechanical loads, sustaining demand and keeping this segment structurally ahead of small-load and heavy-load categories.
Competitive Landscape
The USA Automotive Relays Market shows moderate-to-high consolidation, with a set of global electro-mechanical and automotive electronics suppliers repeatedly winning design-in positions through OEM qualification depth, reliability track record, and breadth across relay families (PCB, plug-in, and high-voltage). Market leadership is strengthened by the ability to support platform-level supply, provide validated components that meet automotive-grade quality systems, and serve both OEM programs and the replacement channel through established distribution networks. Key supplier lists commonly include TE Connectivity, Bosch, Denso, Panasonic, Omron, Fujitsu, Mitsuba, and HELLA among others.
| Company | Est. Year | Headquarters | Relay Portfolio Focus | HV Relay Readiness | OEM/Tier-1 Design-in Strength | Manufacturing / Supply Footprint Signal | Automotive Quality Systems Signal | Aftermarket / Distribution Signal |
| TE Connectivity | 2007 | Switzerland / U.S. ops | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Robert Bosch | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Denso | 1949 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Panasonic | 1918 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Omron | 1933 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Automotive Relays Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Vehicle Electrification Depth
Electrification is expanding the number of high-duty electrical loads that still rely on switching and protection hardware, keeping relay demand structurally tied to EV/HEV build and the supporting charging ecosystem. U.S. plug-in electric vehicle sales reached over ~ units in the latest full-year tally, and the U.S. also recorded ~ plug-in vehicles sold in a single month (with ~ BEVs and ~ PHEVs) alongside ~ total light-duty vehicle sales in that month—an indicator of how quickly electrified variants are being added into mainstream production mixes that use more relays across power distribution, thermal management, and body electronics. On the infrastructure side, the U.S. added roughly ~ public charging points in one year, while public charging ports are heavily weighted toward Level-2 hardware and include high-power DC fast charging equipment rated up to ~ kW, reinforcing the need for robust switching architectures across vehicles and charging systems that interact with them. From a macro demand-capacity lens, the U.S. economy is operating at very large scale with GDP of about USD ~ (current US$), supporting continued vehicle production activity, fleet turnover, and capex in electrification supply chains that cascade into relay content per vehicle.
Circuit Proliferation Across Vehicle Platforms
Relay demand rises with the sheer number of switched circuits (comfort, convenience, thermal, lighting, wipers, pumps, fans, actuators, body controllers, and increasingly electrified auxiliaries) multiplied across the active vehicle parc and annual miles driven—because usage cycles and duty events are ultimately created by how many vehicles are on-road and how intensely they are used. The U.S. vehicle base remains enormous, with ~ registered vehicles in the latest published year, up from ~ the year prior, which expands the installed base that consumes relays not only in new production but also in service/aftermarket replacement (especially for high-cycle applications like cooling fans, blower motors, fuel/aux pumps, and lighting circuits). Utilization is also high and rising, with total vehicle miles traveled of ~ million miles in the latest full year, compared with ~ million miles in 2023 and ~ million miles before that—more miles means more switching events, higher thermal exposure underhood, and more vibration duty across relay housings and terminals. These “base load” fundamentals matter because relays sit at the intersection of circuit count × vehicle count × duty cycles, so even when platform consolidation occurs, the operating intensity of the parc sustains relay consumption through both OEM and replacement channels. Macro conditions remain supportive of large-scale mobility, with U.S. GDP at roughly USD ~ (current US$), a scale that underpins freight movement, commuter mobility, and service demand—all of which map directly into the mileage and usage cycles that stress relay contacts and coils.
Challenges
Relay Derating Under High Thermal Loads
Thermal stress is a structural engineering constraint in the U.S. market because many relays operate in under-hood or near-power-electronics zones (fans, pumps, compressors, heaters, DC/DC paths) where ambient and radiant temperatures can push contact resistance upward and accelerate coil aging—forcing derating, larger packages, or relocation that impacts harness design and BOM complexity. The U.S. climate burden is not theoretical, with ~ weather and climate disasters in a single year with damages exceeding USD ~ each, and the combined cost of these events at USD ~—a proxy for the severity and frequency of extreme heat, storms, flooding, and other stressors that translate into harsher operating and corrosion environments for vehicle electrical systems. Those extremes feed directly into higher under-hood thermal soak, higher humidity and condensation cycles, and greater salt/water intrusion risk—each of which can drive relay derating decisions, sealing requirements, and material upgrades. At the fleet-use level, ~ million miles of travel in 2024 means these thermal and environmental stressors are being applied across trillions of miles, not niche use cases. Macro conditions also matter because thermal mitigation must be absorbed across a vast production footprint supported by a very large U.S. economy (GDP roughly USD ~ current US$), while OEMs simultaneously demand stable supply and minimal redesign cycles—creating a squeeze where derating constraints become a recurring engineering-commercial conflict point for relay suppliers.
Contact Wear and Lifecycle Fatigue
Relay wear-out is fundamentally a physics-of-use problem: contact erosion, micro-welding, spring fatigue, and coil insulation aging all scale with switching cycles, load transients, vibration, and contamination—conditions that are amplified in the U.S. because the vehicle parc is huge and utilization is intense. Data shows ~ registered vehicles and total travel of ~ million miles in 2024—together implying an enormous national “switching-event factory” where relays are repeatedly cycling across lighting, HVAC blowers, radiator fans, pumps, and accessory loads. Lifecycle stress is compounded by extreme weather and debris exposure, with ~ billion-dollar disaster events in one year costing USD ~, correlating with more flooding, severe storms, and environmental contamination risks that accelerate corrosion at terminals and increase resistance heating at contact points. Safety stakes translate these physics into hard business pressure, with annual fatality totals of ~, ~, and ~ keeping reliability and fault tolerance in the spotlight, meaning relay-related intermittent faults face lower tolerance in validation and field performance. In addition, the commercial vehicle and pickup-heavy U.S. duty cycle often involves higher accessory loads, which increases switching stress and raises the importance of robust contact materials and sealing strategies. Macro capacity signals (GDP at about USD ~) support high mobility demand, but they also mean that even low failure rates can translate into large absolute recall and warranty populations.
Opportunities
High-Voltage Relay Demand from EV Platforms
High-voltage architectures increase the need for reliable isolation and switching in traction battery systems, pre-charge circuits, power distribution units, thermal systems, and fast-charging interfaces—creating a pathway for relay value growth driven by today’s EV build volumes and charging deployment. Reporting indicates over ~ plug-in vehicles sold in the latest full year, and continued high monthly volume, including ~ plug-in vehicles sold in a single month alongside ~ total light-duty vehicle sales—evidence that electrified platforms are being produced at scale, which increases the installed base of HV battery packs and power electronics that require isolation components. Charging infrastructure growth reinforces this opportunity, with about ~ public charging points added in a year and DC fast charging systems reaching up to ~ kW, intensifying the electrical stress environment that can increase the importance of robust contactor and relay solutions. Additionally, the U.S. driving duty cycle is enormous, with ~ million miles traveled in 2024, so EV platforms are accumulating real-world electrical switching and thermal cycles quickly. The macro backdrop (GDP about USD ~ current US$) supports continued fleet turnover and infrastructure capex, creating room for relay suppliers specializing in HV performance, arc suppression, thermal robustness, and automotive-grade qualification.
Smart Relay and Diagnostics Integration
Smart relays with built-in sensing, load diagnostics, current and temperature monitoring, and communication to body or power domain controllers are an opportunity because they directly address U.S. OEM pain points: field reliability, faster fault isolation, and reduced “no trouble found” service cycles as vehicles become more software-defined and electrified. The scale of U.S. operations makes diagnostic efficiency valuable, with ~ registered vehicles and ~ million miles traveled annually, meaning even small improvements in fault detection and isolation can impact large absolute volumes of service events and warranty decisions. Recall dynamics reinforce the pull for better electronics observability, with large recall counts and very large associated vehicle populations across recent years, and remedy-availability timelines measured in ~ days—highlighting how quickly issues must be identified, contained, and remedied once detected. Smart relays can support earlier detection of overcurrent, overheating, or intermittent contact behavior before it cascades into a safety event or broad campaign. Environmental harshness further strengthens the case, with ~ billion-dollar disaster events costing USD ~ in one year, reflecting more extreme operating conditions that can provoke electrical faults where embedded diagnostics improve reliability and serviceability. The macro backdrop (GDP about USD ~ current US$) supports continued investment in electronic architectures and feature content, positioning smart relays as a pathway to differentiate on uptime, functional safety support, and service intelligence in the U.S. automotive relays market.
Future Outlook
Over the next five to six years, the USA Automotive Relays Market is expected to expand steadily as vehicles add more electronic loads, denser power distribution architectures, and higher safety and diagnostics expectations. Electrification will continue to reshape mix demand—supporting high-voltage relay requirements in battery and charging circuits—while mainstream platforms sustain volume needs for plug-in and PCB relays across body and comfort applications. At the same time, OEMs and Tier-1s will push suppliers toward miniaturization, thermal robustness, lifecycle switching durability, and supply assurance, raising the bar for qualification and manufacturing resilience.
Major Players
- TE Connectivity
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Robert Bosch
- Denso
- HELLA
- Omron
- Panasonic
- Fujitsu
- Mitsuba
- Continental
- Aptiv
- Valeo
- Eaton
- Littelfuse
Key Target Audience
- OEM Procurement & Sourcing Heads
- Tier-1 Power Distribution / Junction Box Product Heads
- Tier-2 Relay Manufacturers’ Strategy and Sales Heads
- EV Platform & High-Voltage Architecture Leads
- Aftermarket Parts Distributors and Category Heads
- Fleet Maintenance & Reliability Procurement Heads
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We begin by mapping the U.S. relay ecosystem across OEMs, Tier-1 module suppliers, relay manufacturers, and distribution layers. Desk research is used to define the key demand variables such as relay-per-vehicle intensity, electrification-driven circuits, and replacement rates. This step establishes the segmentation framework and scope boundaries for consistent sizing.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical patterns in vehicle production and sales, electrification indicators, and component adoption are compiled to form the demand baseline. We align relay consumption to major application clusters and validate the mix across relay types and load classes. The output is a structured sizing model supported by triangulation across multiple datasets.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Key assumptions are validated through expert interviews with stakeholders across relay suppliers, Tier-1 electrical distribution teams, and aftermarket participants. These interactions refine pricing bands, qualification timelines, and program concentration realities. Expert inputs are used to stress-test the bottom-up and top-down reconciliation.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Finally, we synthesize learnings into a decision-ready narrative and competitive view, ensuring that segment shares, supplier positioning, and future outlook are coherent and benchmarkable. Cross-checks are conducted to confirm internal consistency across sizing, segmentation, and competitive mapping. The final report is delivered with structured exhibits and market-ready conclusions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Automotive Electrical Architecture Scope, Relay Classification Framework, Abbreviations, Demand-Side Sizing Logic, Supply-Side Capacity Mapping, OEM–Tier-1 Validation Approach, Primary Expert Interviews, Data Triangulation Model, Study Limitations and Analyst Caveats)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution of Automotive Switching Architectures
- Transition from Conventional Relays to Smart and Solid-State Relays
- Automotive Electrical Load Growth and Relay Relevance
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Vehicle Electrification Depth
Circuit Proliferation Across Vehicle Platforms
Safety and ADAS Content Expansion - Challenges
Relay Derating Under High Thermal Loads
Contact Wear and Lifecycle Fatigue
Cost Pressure from OEM Sourcing Programs - Opportunities
High-Voltage Relay Demand from EV Platforms
Smart Relay and Diagnostics Integration
Zonal Electrical Architecture Transition - Trends
Solid-State Relay Migration
Relay Miniaturization and Packaging Density Increase
Integration with Power Distribution Modules - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Relay ASP, 2019–2024
- By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Electromechanical Relays
Solid-State Relays
High-Voltage DC Relays
Latching Relays
Smart and PCB-Integrated Relays - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
12V Relays
24V Relays
48V Relays
High-Voltage Relays for EV Systems - By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Vehicles
Light Commercial Vehicles
Medium and Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Electric Vehicles
Off-Highway and Specialty Vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Powertrain and Engine Management
Body Control Modules
Safety and ADAS Systems
HVAC and Comfort Systems
Battery Management and Charging Circuits - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
OEM Direct Supply
Tier-1 System Integrators
Aftermarket Distribution
- Market Share of Major Players by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Product Portfolio Breadth, Voltage Range Coverage, Switching Cycle Durability, Thermal Resistance Capability, EV Relay Readiness, OEM Qualification Depth, Manufacturing Footprint in North America, Pricing Positioning)
- SWOT Benchmarking of Key Market Participants
- Pricing Analysis by Relay Type and Sales Channel
- Detailed Company Profiles
TE Connectivity
Panasonic Automotive Systems
Omron Corporation
Bosch
Denso Corporation
Aptiv
Littelfuse
Eaton
HELLA
Fujitsu Components
Song Chuan Precision
Mitsuba Corporation
Yazaki Corporation
NEC Tokin
Siemens Mobility Components
- OEM and Tier-1 Relay Demand Mapping
- Purchasing Criteria and Qualification Requirements
- Design-In Versus Design-Out Risk Analysis
- Cost and Performance Trade-Off Assessment
- Decision-Making and Approval Hierarchy
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Relay ASP, 2025–2030


