Market Overview
The USA OTA market is underpinned by the expanding installed base of connected vehicles and the rising average software value per vehicle. Vehicle platforms now host over ~ million lines of code, driving continuous update requirements. OEMs increasingly rely on OTA to reduce recall costs, which exceeded USD ~ billion annually across the US automotive industry. OTA also enables post-sale feature upgrades, shifting revenue models toward software-driven margins.
The market is dominated by automotive innovation hubs including California, Michigan, Texas, and Arizona. California leads due to EV density, autonomous testing zones, and software talent concentration. Michigan remains critical due to OEM headquarters and Tier-1 engineering centers, while Texas and Arizona host growing vehicle software, cloud infrastructure, and testing ecosystems.
Market Segmentation
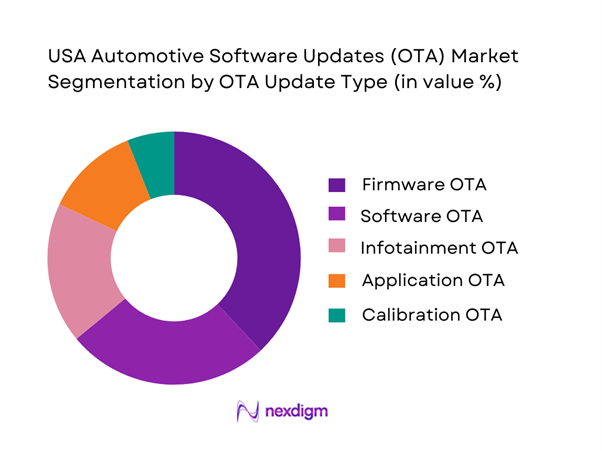
By OTA Update Type
Firmware OTA dominates due to its critical role in safety, powertrain control, and ADAS reliability. As vehicles integrate more electronic control units, firmware updates ensure compliance and performance consistency, especially in EV platforms where battery and motor software are continuously optimized.
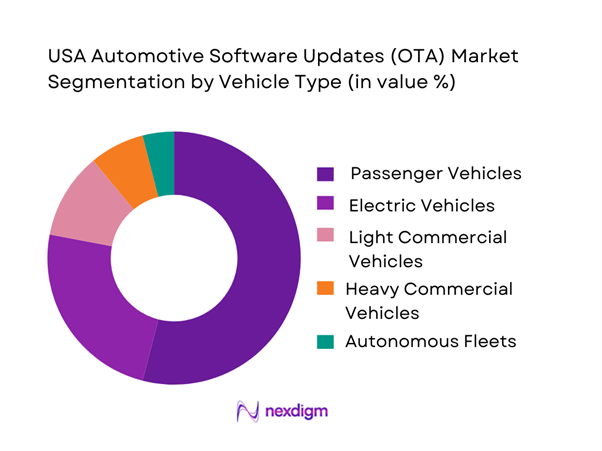
By Vehicle Type
Passenger vehicles dominate OTA adoption due to sheer vehicle parc size and consumer demand for infotainment, safety, and performance updates. EVs show the fastest uptake as software defines driving range, charging behavior, and autonomous readiness.
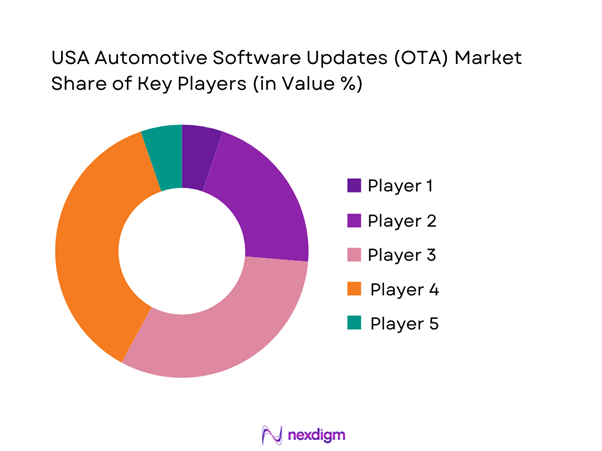
Competitive Landscape
The USA OTA market is moderately consolidated, dominated by a mix of Tier-1 suppliers, cloud hyperscalers, and OEM-developed software stacks. Strategic partnerships between OEMs and cloud providers define deployment scalability and cybersecurity resilience.
| Company | Established | HQ | OTA Coverage | OEM Integrations | Cloud Dependency | Cybersecurity Certs | Monetization Enablement | Update Scale |
| Bosch | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Continental | 1871 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Harman | 1980 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Blackberry QNX | 1984 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbiquity | 1999 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Automotive Software Updates (OTA) Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Software-Defined Vehicle Transition
U.S. vehicle software is increasingly being treated as a regulated “safety performance layer,” not just an infotainment add-on—visible in the recall system itself. In one year, ~ recalled vehicles were remedied through over-the-air updates, showing OTA is already being used as a safety remedy at multi-million-vehicle scale. At the same time, the U.S. light-duty parc is enormous—~ light-duty vehicles are in operation—so once OEMs migrate platforms to centralized compute and unified software stacks, each incremental OTA capability can be leveraged across a very large installed base. The macro backdrop supports this software transition because the U.S. economy generates the scale of R&D and engineering spend required for multi-year software platform programs: U.S. GDP is USD ~ billion and GDP per capita is USD ~. Consumer-price inflation is ~, which matters because when hardware BOM inflation is not spiking, OEMs have more room to shift value creation into software features and post-sale digital lifecycle management rather than repeated hardware redesigns. Finally, scale of addressable vehicles is reinforced by overall registrations: the U.S. has ~ total motor vehicles registered, meaning OTA strategy is not a niche EV-only topic—it is a fleetwide lifecycle capability across passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, and mixed-use light fleets.
EV Software Content Expansion
EVs structurally increase software surface area, which expands what can be updated post-sale. The U.S. EV parc is now measured in millions: the U.S. has ~ electric light-duty vehicles in operation, including ~ BEVs and ~ PHEVs. This matters for OTA because EV customer experience is tightly coupled to software, so OEMs use OTA to correct performance issues, optimize controls, and deploy feature upgrades without physical service events. The software-as-safety dimension also shows up in recall patterns: EV-specific component recalls were ~ recalls affecting ~ vehicles in 2024 shown, indicating that EV programs are generating recall activity that can sometimes be mitigated faster when software remedies are feasible. The macro indicators still underpin investment capacity and consumer affordability for tech-heavy vehicles: U.S. population is ~, which supports large-scale vehicle demand; GDP per capita is USD ~, which supports higher adoption of digitally featured trims; and inflation is ~, which influences consumer financing conditions and OEM input costs. Crucially, because ~ light-duty vehicles exist in the parc, even a partial shift of high-software EV learnings into mainstream ICE and hybrid platforms expands the OTA addressable market operationally.
Challenges
Functional Safety Validation
OTA introduces a validation problem: every update must be proven safe not only in the lab but across a heterogeneous on-road fleet and real-world operating states. The U.S. fleet’s size and usage intensity compound this: ~ vehicles are registered, and annual travel totals ~ million vehicle-miles, meaning the number of state combinations is massive. This is not theoretical—recall reporting is fundamentally tied to safety defect determinations and FMVSS conformance, and the recall ecosystem at scale creates ongoing pressure for rapid, correct fixes rather than iterative trial-and-error. EV platform complexity adds another layer: the U.S. has ~ electric light-duty vehicles, and EV- specific component recalls alone show ~ recalls affecting ~ vehicles in 2024 shown, meaning safety-relevant defects can exist in electrified architectures that rely heavily on software controls. Functional safety validation for OTA therefore becomes a gating constraint on speed, requiring rigorous regression testing, staged rollouts, health monitoring, and robust fail-safe and rollback behaviors. The macro environment explains why OEMs are expected to carry that burden: the U.S. economy is USD ~ billion with GDP per capita USD ~, enabling regulators, consumers, and insurers to demand high safety assurance standards.
OTA Failure Liability
OTA failures are not just customer experience issues; in the U.S. they can become safety events that trigger investigations, consumer advisories, and recall obligations. Recalls with severe advisories such as do-not-drive or park-outside-away-from-structures can scale rapidly, with multi-year volumes reaching ~ vehicles in one year shown, illustrating how quickly safety communications can expand when risk is elevated. OTA increases the need for update governance because a faulty update can propagate across many vehicles quickly; conversely, the same propagation speed can be beneficial when the fix is correct, highlighting the importance of liability controls such as staged deployment, canary cohorts, rollback, cryptographic signing, and auditability. Operationally, recall rules impose strict notification expectations, requiring manufacturers to notify owners of a final remedy within ~ days of filing a recall report. If an OTA update fails and the fix requires physical intervention, OEMs can be forced into complex remedy logistics under tight timelines. The macro context reinforces why litigation and compliance intensity is high: U.S. GDP is USD ~ billion, population is ~, and GDP per capita is USD ~, creating a large consumer base and a high-value mobility ecosystem where safety lapses can have wide-scale social and regulatory impact.
Opportunities
Feature Monetization via OTA
The opportunity is that OTA has already proven it can deliver safety-critical changes at scale, which is the same operational foundation needed for rapid feature deployment such as ADAS enhancements, charging optimizations, interface improvements, and energy management modes. The strongest proof point is current execution: ~ recalled vehicles were remedied via OTA updates, confirming that remote delivery pipelines exist in-market and can reach millions of vehicles. The installed base that can potentially receive new software value is also measurable and growing in the most software-intensive segment: ~ electric light-duty vehicles are in operation, including ~ BEVs, which tend to be sold with higher digital feature density and higher connected-service usage. Meanwhile, the broader market opportunity is anchored in scale: ~ light-duty vehicles exist in the U.S., so as more platforms become OTA-capable, feature deployment can extend beyond EVs into mainstream ICE and hybrid vehicles and commercial light fleets. Macroeconomic capacity supports monetization models built on software value: GDP per capita is USD ~, GDP is USD ~ billion, and inflation is ~, indicating an economy where consumers and fleets can evaluate ongoing digital value propositions and OEMs can invest in product management, cloud operations, and secure release engineering.
Subscription-Based Software Unlocks
Subscription-based software unlocks depend on two present-day realities: a sufficiently large connected and OTA-capable base and governance systems that can manage continuous releases safely and compliantly. On capability, the U.S. already demonstrates OTA at scale via safety remedies, with ~ recalled vehicles remedied through OTA updates, indicating the existence of remote authentication, deployment tooling, and in-vehicle update clients that can be repurposed for feature unlock workflows. On addressable base, the U.S. has ~ electric light-duty vehicles and ~ total light-duty vehicles; as OTA-capable architectures spread, subscription models can expand from EV-heavy early adopters to broader trims and fleet configurations. Regulatory and operational discipline is reinforced by recall rules requiring manufacturers to notify owners of a final remedy within ~ days of filing a recall report, pushing OEMs to build robust release processes, telemetry, and rollback capability that are also prerequisites for subscription reliability. The macro base—U.S. GDP USD ~ billion, population ~, and inflation ~—supports the scale economics for subscription operations while making reliability and compliance non-negotiable due to high consumer expectations and safety scrutiny.
Future Outlook
The market will increasingly shift toward centralized compute platforms, subscription-based OTA feature unlocks, and AI-driven update orchestration. OTA will become a foundational pillar of vehicle lifecycle management rather than a support function, enabling OEMs to maintain software relevance across vehicle lifespans exceeding a decade.
Major Players
- Bosch
- Continental
- Harman
- Aptiv
- Visteon
- Blackberry QNX
- Wind River
- Airbiquity
- HERE Technologies
- Google Automotive Services
- Amazon Web Services Automotive
- Microsoft Automotive Cloud
- Tesla
- Ford
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEM Strategy Teams
- Tier-1 Automotive Software Suppliers
- EV Platform Manufacturers
- Fleet Operators and Mobility Providers
- Cloud and Edge Infrastructure Providers
- Cybersecurity Solution Providers
- Investment and Venture Capital Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Mapping OTA stakeholders, vehicle parc, software architectures, and regulatory forces through secondary and proprietary databases.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical OTA penetration, ECU software density, and revenue attribution modeling across vehicle categories.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
CATI interviews with OEM engineers, Tier-1 suppliers, and cloud architects.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Cross-validation using OEM disclosures, cloud usage metrics, and regulatory filings.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, OTA Software Taxonomy, Abbreviations, Bottom-Up and Top-Down Market Sizing Logic, Vehicle Parc and Software Installed-Base Mapping, ECU-Level Revenue Attribution Logic, Primary Interviews with OEMs, Tier-1s, Cloud Vendors, Regulatory Bodies, Limitations and Data Validation Framework)
- Definition and Scope
- OTA Software Evolution in US Automotive Ecosystem
- Timeline of OTA Adoption Across OEMs
- Automotive Software Business Cycle
- OTA Software Value Chain and Stakeholder Mapping
- Growth Drivers
Software-Defined Vehicle Transition
EV Software Content Expansion
Cybersecurity Patch Mandates
Connected Vehicle Parc Growth
Recall Cost Avoidance Economics - Challenges
Functional Safety Validation
OTA Failure Liability
Vehicle Homologation Constraints
Cybersecurity Attack Surface Expansion
Legacy Vehicle Compatibility - Opportunities
Feature Monetization via OTA
Subscription-Based Software Unlocks
Fleet OTA Management Platforms
AI-Driven Update Optimization - Trends
Zonal Architecture Adoption
Continuous Deployment Models
Secure Boot and Encrypted OTA Chains - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- Installed Base of OTA-Enabled Vehicles, 2019–2024
- OTA Transaction Volume, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Vehicles
Light Commercial Vehicles
Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Electric Vehicles
Autonomous Test Fleets - By Application (in Value %)
Firmware Updates
Core Vehicle Software Updates
Infotainment and HMI Updates
ADAS and Safety Software Updates
Powertrain and Energy Management Updates - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Distributed ECU Architecture
Domain Controller Architecture
Zonal Architecture
Centralized Vehicle Compute Architecture - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Embedded Telematics
Tethered Connectivity
Hybrid Connectivity - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Personal Mobility
Commercial Logistics
Shared Mobility and Ride-Hailing
Public Transportation Fleets
Industrial and Utility Fleets
- Market Share Assessment by OTA Software Revenue
- Cross Comparison Parameters (OEM integrations, OTA deployment scale, ECU coverage depth, cybersecurity certifications, rollback reliability, cloud dependency, update frequency capability, software monetization enablement)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- OTA Pricing and Licensing Models
- Detailed Company Profiles
Bosch
Continental
Harman
Aptiv
Visteon
Blackberry QNX
Wind River
Airbiquity
HERE Technologies
Google Automotive Services
Amazon Web Services Automotive
Microsoft Automotive Cloud
Tesla
Ford
General Motors
- Vehicle Owner Acceptance
- Fleet Operator OTA Readiness
- OEM Software Monetization Strategy
- Update Consent Models
- Downtime Sensitivity
- By Value, 2025–2030
- Installed Base of OTA-Enabled Vehicles, 2025–2030
- OTA Transaction Volume, 2025–2030


