Market Overview
The USA automotive welding equipment market is valued at USD ~ billion in 2023 and USD ~ billion in 2024, as tracked through a U.S.-specific industrial equipment market sizing series. Market expansion is driven by sustained vehicle production volumes, increasing automation intensity in body-in-white and chassis assembly, growing electric vehicle manufacturing investments, and OEM focus on defect reduction and cycle-time optimization. Welding equipment demand is also supported by retooling of legacy production lines, higher adoption of robotic arc and resistance spot welding systems, and integration of digital weld monitoring and quality control technologies across Tier 1 and Tier 2 supplier facilities.
Within the USA, demand concentration is highest in automotive manufacturing hubs such as the Midwest manufacturing belt (Michigan, Ohio, Indiana), the Southern auto corridor (Tennessee, Alabama, Kentucky, Georgia), and parts of Texas and California. These regions dominate due to dense clusters of OEM assembly plants, Tier 1 module suppliers, welding automation integrators, and established industrial supply chains. The presence of skilled manufacturing labor, logistics infrastructure, and long-term automotive capital investment further reinforces regional dominance in welding equipment procurement and installed base expansion.
Market Segmentation
By Welding Technology
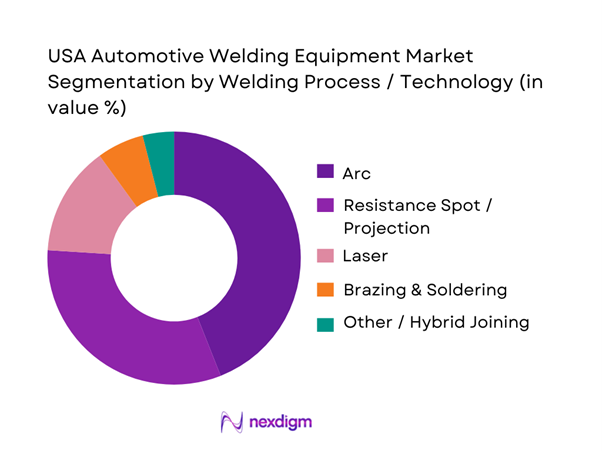
The USA Automotive Welding Equipment market is segmented into arc welding, resistance welding, laser welding, brazing & soldering, and hybrid joining technologies. Arc welding holds the dominant share because MIG/MAG and TIG processes are extensively used across chassis, structural components, and sub-assemblies requiring flexibility and high deposition rates. Arc welding systems are cost-effective, compatible with robotic automation, and well-established in automotive manufacturing standards, making them the preferred choice for both OEMs and Tier suppliers. Resistance spot welding remains critical for body-in-white applications, while laser welding adoption is increasing for precision joints and lightweight materials, particularly in electric vehicle platforms.
By Automation Level
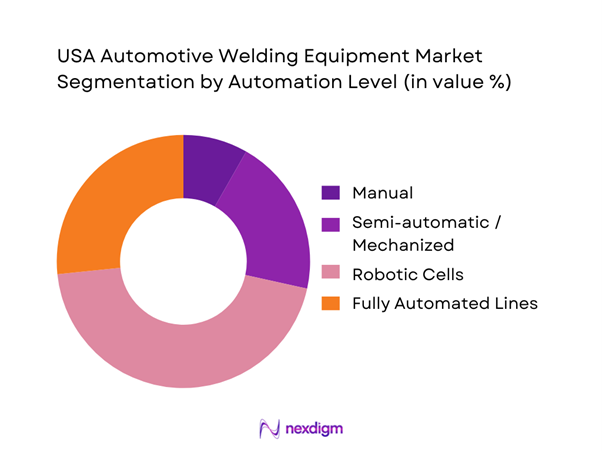
The USA Automotive Welding Equipment market is segmented into manual welding, semi-automatic welding, robotic welding cells, and fully automated production lines. Robotic welding systems dominate due to their ability to deliver consistent weld quality, reduce dependency on skilled manual labor, and meet high-throughput requirements of automotive assembly plants. OEMs increasingly invest in robotic cells integrated with vision systems, real-time monitoring, and safety enclosures to improve first-pass yield and minimize rework. Fully automated lines are primarily deployed in high-volume body shops, while manual and semi-automatic systems remain relevant for low-volume, repair, and specialized fabrication applications.
Competitive Landscape
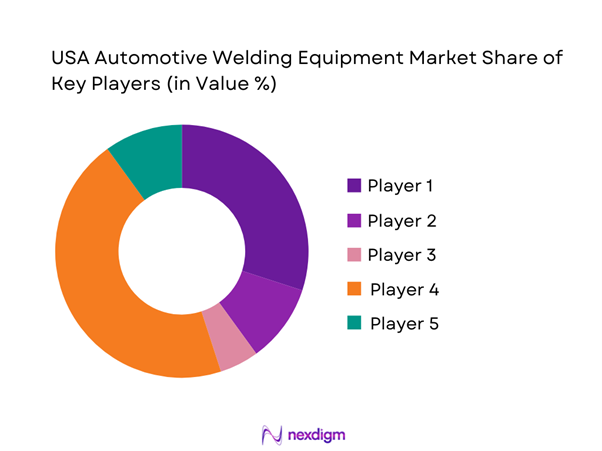
The USA automotive welding equipment market is moderately consolidated, with global welding equipment manufacturers, robotics companies, and automation integrators competing alongside strong domestic suppliers. Competitive differentiation is driven by technology breadth, automotive OEM qualification depth, automation integration capability, aftersales service coverage, and digital weld quality solutions. Suppliers with strong relationships with automotive OEMs and Tier suppliers benefit from long-term framework agreements and multi-plant deployment opportunities.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Core Automotive Welding Strength | Process Breadth | Automation/Robot Packaging | Digital Connectivity/Traceability | North America Service Footprint | Typical Automotive Use-Cases |
| Lincoln Electric | 1895 | Cleveland, Ohio, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Miller Electric (ITW) | 1929 | Appleton, Wisconsin, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ESAB | 1904 | Gothenburg, Sweden (NA ops in USA) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Fronius International | 1945 | Pettenbach, Austria (NA ops in USA) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Panasonic Welding Systems | 1918 | Osaka, Japan (NA ops) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Automotive Production Automation and Quality Demands
Rising vehicle production volumes combined with stricter quality standards are driving increased adoption of advanced welding equipment across U.S. automotive plants. Body-in-white manufacturing requires thousands of welds per vehicle, making consistency and repeatability critical. Welding automation enables OEMs to maintain tight dimensional tolerances, reduce defect rates, and comply with internal quality benchmarks. As automotive platforms diversify and production complexity increases, welding equipment becomes a foundational investment rather than a discretionary cost.
Electric Vehicle Manufacturing Expansion
Electric vehicle platforms require new welding approaches for battery trays, lightweight structures, aluminum components, and mixed-material assemblies. Automotive OEMs are investing heavily in retooling production lines to accommodate EV architectures, directly increasing demand for laser welding systems, advanced arc welding power sources, and precision resistance welding equipment. Welding equipment suppliers benefit from higher per-line investment intensity and technology upgrades associated with EV production programs.
Challenges
Skilled Workforce Constraints
Despite automation, welding operations still require skilled technicians for programming, maintenance, quality assurance, and troubleshooting. The U.S. manufacturing sector faces persistent shortages of skilled welding and automation professionals, which can slow adoption and increase operating risk. OEMs and suppliers must invest in training and support services, increasing the total cost of ownership for welding systems.
Capital Intensity and Line Downtime Risks
Automotive welding equipment, particularly robotic and laser systems, requires significant upfront capital expenditure. Installation and commissioning often coincide with production line shutdowns, creating operational risk. OEMs carefully evaluate supplier reliability, service responsiveness, and system uptime before committing to large-scale deployments, which can lengthen procurement cycles.
Opportunities
Advanced Welding for Lightweight Materials
The shift toward lightweight materials such as aluminum and advanced high-strength steel creates opportunities for suppliers offering specialized welding solutions. OEMs increasingly require equipment capable of handling thinner gauges, dissimilar material joining, and heat-sensitive components without compromising structural integrity.
Digital Welding and Quality Analytics
Integration of digital sensors, real-time weld monitoring, and data analytics represents a major growth opportunity. Predictive maintenance, closed-loop quality control, and traceability systems enhance value propositions for welding equipment vendors and align with OEM Industry 4.0 strategies.
Future Outlook
Over the next planning cycle, the USA Automotive Welding Equipment market is expected to grow steadily as OEMs expand automation density, modernize legacy production lines, and scale electric vehicle manufacturing. Investment momentum will be strongest in robotic arc welding, resistance spot welding upgrades, and laser welding systems aligned with lightweight vehicle architectures. Suppliers with strong service networks and digital capabilities are expected to gain competitive advantage.
Major Players
- Lincoln Electric
- Miller Electric (ITW)
- ESAB
- Fronius International
- Panasonic Welding Systems
- OTC DAIHEN
- Carl Cloos Schweisstechnik
- voestalpine Böhler Welding
- Kemppi
- Coherent
- ABB Robotics
- FANUC America
- KUKA
- Yaskawa Motoman
- ACRO Automation Systems
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEM manufacturing and body shop leadership
- Tier 1 automotive module suppliers
- Tier 2 and Tier 3 automotive component manufacturers
- Robotic welding automation integrators
- Industrial distributors and welding equipment dealers
- Automotive EV platform developers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies (OSHA, EPA)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We construct a U.S. automotive manufacturing ecosystem map covering OEMs, Tier suppliers, welding equipment manufacturers, robotics providers, and automation integrators. Market boundaries are defined around welding equipment used in automotive production and component manufacturing.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We analyze historical equipment shipments, installed base trends, automotive production capacity, and capex cycles. Demand is mapped across welding technologies, automation levels, and end-user categories.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions are validated through interviews with automotive manufacturing engineers, welding automation specialists, system integrators, and distributor networks.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Top-down market indicators are reconciled with bottom-up equipment adoption patterns to finalize sizing, segmentation, and competitive benchmarking.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Automotive Welding Value-Chain Boundary, Market Sizing Approach, Triangulation Logic, Primary Interview Mix by Stakeholder Type, Data Validation, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Evolution and Genesis
- Timeline of Major Automotive Manufacturing Milestones
- Automotive Production Cycle Touchpoints
- Equipment Supply Chain and Value Chain
- Typical Automotive Welding Workflows
- Growth Drivers
Automation in Automotive Manufacturing
Electric Vehicle Production Expansion
Quality and Compliance Requirements
Productivity and Labor Optimization - Challenges
Skilled Workforce Constraints
Capital Intensity and Downtime Risks
Technology Integration Complexity - Opportunities
Lightweight Material Welding
Digital and Smart Welding Solutions
Aftermarket and Service Expansion - Trends
Industry 4.0 Integration
Robotic and Collaborative Welding
Laser Welding Adoption - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Equipment Price, 2019–2024
- By Welding Technology (in Value %)
Arc
Resistance Spot / Projection
Laser
Brazing & Soldering
Other / Hybrid Joining - By Automation Level (in Value %)
Manual
Semi-Automatic / Mechanized
Robotic Cells
Fully Automated Lines - By Equipment Type (in Value %)
Power Sources
Wire Feeders / Torch Packages
Resistance Welding Systems
Laser Welding Systems
Positioners, Fixtures, Jigs & Clamps - By Application (in Value %)
Body-in-White
Chassis & Suspension Modules
Exhaust & Aftertreatment Assemblies
Battery Pack/Tray & EV Structural Parts
Seating, Interior Frames, Closures - By End User (in Value %)
Automotive OEM Assembly Plants
Tier-1 Module Suppliers
Tier-2/3 Component Fabricators
Contract Manufacturers / Metal Fabrication for Automotive - By Region (in Value %)
Midwest Manufacturing Belt
South / Southeast Auto Corridor
West
Northeast
- Market Share Assessment
Share by Welding Technology
Share by Automation Level - Cross Comparison Parameters (installed robotic welding base, OEM qualification coverage, automation integration capability, digital weld monitoring readiness, service footprint, product portfolio breadth, duty-cycle capability, safety and compliance features)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Packaging Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lincoln Electric
Miller Electric
ESAB
Fronius International
Panasonic Welding Systems
ABB Robotics
FANUC
KUKA
Yaskawa Motoman
OTC DAIHEN
Carl Cloos
Kemppi
voestalpine Böhler Welding
Coherent
ACRO Automation Systems
- Demand and Utilization Patterns
- Budget Ownership and Buying Centers
- Evaluation Criteria and Vendor Selection
- Needs, Desires, and Pain Point Analysis
- Decision-Making Process
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Equipment Price, 2025–2030


