Market Overview
The USA combat helicopter simulation market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by program activity recorded across 2024 and 2025 within defense training ecosystems. Fleet availability targets, simulator utilization counts, and curriculum refresh cycles increasingly reference 2024 and 2025 performance benchmarks without disclosing financial totals. Hardware refresh rates, software update cadence, and instructor staffing ratios reflect operational tempo changes. Procurement workflows emphasize compliance, cybersecurity accreditation, and interoperability milestones. These factors collectively sustain stable deployment pipelines. The market remains procurement driven, with contractual structures favoring multi year sustainment and upgrade paths.
Activity concentrates around major training hubs in the Southwest, Southeast, and Midwest, where airspace access, base infrastructure, and test ranges support complex rotary wing training programs. Ecosystem maturity around integrators, content developers, and sustainment providers reinforces clustering. Policy environments favor synthetic training to preserve aircraft availability. Logistics corridors and secure networks further anchor deployments near command centers. Urban adjacency supports workforce pipelines and maintenance capacity. Together, infrastructure density and institutional demand create predictable regional concentration patterns.
Market Segmentation
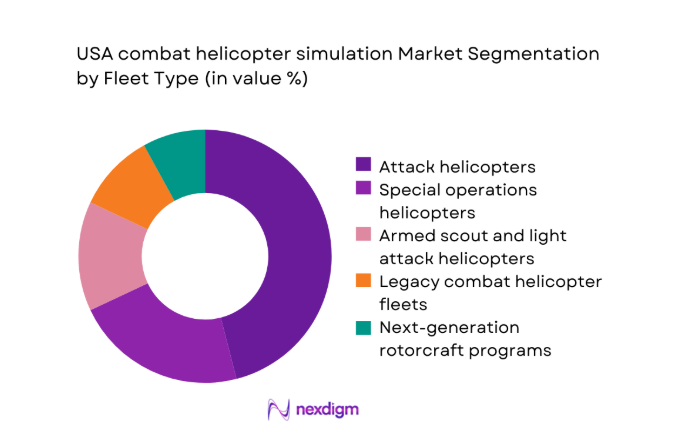
By Fleet Type
Attack helicopter fleets dominate spending because their training pipelines demand higher fidelity sensor emulation, weapons integration, and mission rehearsal complexity compared with utility or legacy platforms. Special operations units further elevate requirements for networked scenarios, driving preference for configurable simulators supporting multi ship coordination. Next generation rotorcraft programs influence architecture choices, but current fleets still account for the majority of utilization hours. The dominance also reflects certification frameworks that prioritize attack platforms for readiness metrics and instructor standardization. Maintenance training modules remain secondary, while collective training scenarios increasingly shape procurement specifications. Overall, fleet mix continues to favor high intensity combat platforms, reinforcing investment concentration within attack oriented training ecosystems across the country.
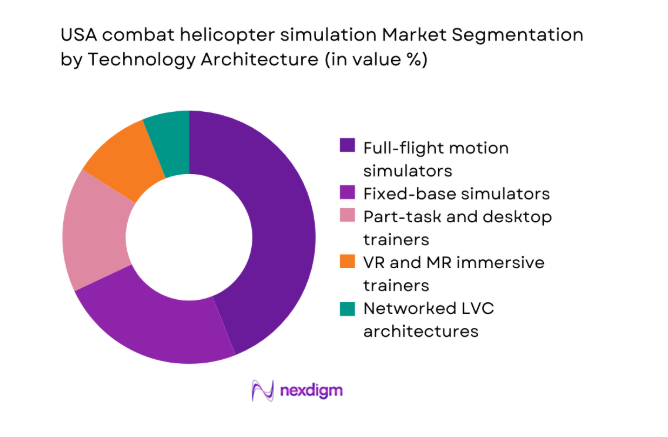
By Technology Architecture
Full flight motion simulators lead adoption because training commands prioritize physiological cueing, high resolution visuals, and accurate flight dynamics for advanced mission rehearsal. Fixed base systems retain relevance for throughput training and procedural refresh, while part task trainers address targeted skill gaps. VR and mixed reality solutions gain attention for distributed use, yet remain complementary within accredited pipelines. Networked LVC architectures increasingly influence configuration decisions, especially for collective exercises. The architecture mix therefore balances fidelity, scalability, and accreditation constraints. Procurement strategies favor modularity, allowing upgrades across software layers without replacing entire platforms, which sustains the leading position of high fidelity motion based systems.
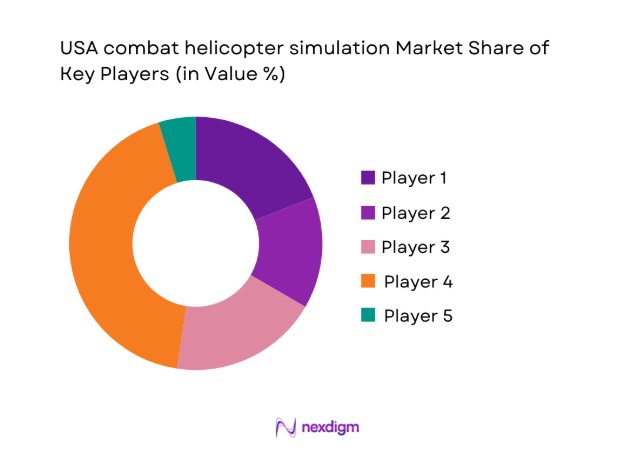
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment reflects long program cycles, stringent accreditation requirements, and strong emphasis on lifecycle support. Providers differentiate through platform coverage, network interoperability, and service depth, while buyers prioritize reliability and compliance over rapid experimentation.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| CAE | 1947 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Technologies | 2019 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing | 1916 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Collins Aerospace | 2018 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA combat helicopter simulation Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising rotary-wing readiness requirements
Rising rotary wing readiness requirements intensified after 2023 as training commands emphasized availability metrics across diverse operational scenarios nationwide theaters. Readiness scorecards in 2024 incorporated simulator utilization benchmarks, encouraging standardized curricula and expanded collective mission rehearsal sessions across commands. Units reported higher scheduling predictability during 2025, reinforcing confidence in synthetic environments supporting qualification, continuation, and upgrade pipelines simultaneously. Commanders increasingly referenced crew coordination metrics, prompting investments in networked scenarios rather than isolated procedural training events alone. Maintenance and safety offices aligned inspection cycles with simulator syllabi, reducing aircraft downtime and reinforcing training first operational planning frameworks. Instructor cadres expanded scenario libraries, leveraging digital twins to reflect evolving mission profiles and terrain complexity realistically. Readiness directives encouraged cross unit participation, increasing demand for scalable architectures supporting simultaneous crews within secure network boundaries. Policy language emphasized proficiency sustainment, not merely qualification, which favored recurrent simulator sessions over episodic aircraft sorties. Standardization boards highlighted data driven assessment, making simulator analytics integral to readiness reporting structures and command briefings. Consequently, training governance mechanisms consistently prioritized simulator centered readiness, reinforcing sustained procurement and upgrade momentum across organizations.
Expansion of synthetic training to reduce flight hours
Expansion of synthetic training to reduce flight hours accelerated after 2023, driven by availability pressures and safety management priorities. Planners in 2024 aligned syllabi to substitute complex sorties with accredited simulator events without compromising evaluation standards. Fleet managers tracked airframe utilization, and 2025 reports emphasized preservation benefits achieved through higher synthetic training ratios. Scenario fidelity improvements enabled credible weapons and sensor rehearsal, supporting substitution decisions by training authorities. Environmental constraints and airspace congestion further strengthened arguments for increased ground based rehearsal within secure facilities. Instructors adapted grading rubrics to emphasize decision making, crew coordination, and procedural compliance within simulated contexts. Logistics teams appreciated reduced maintenance burdens, enabling predictable scheduling and improved spare parts planning. Training throughput increased without proportional aircraft usage, reinforcing policy support for continued simulator centric curricula. Safety offices documented fewer exposure hours, aligning risk management frameworks with synthetic training expansion strategies. Collectively, these operational benefits institutionalized substitution policies, sustaining long term demand for high fidelity simulation ecosystems.
Challenges
Lengthy defense procurement and certification cycles
Lengthy defense procurement and certification cycles persisted after 2023, delaying fielding of updated configurations despite validated operational requirements. Program offices in 2024 navigated layered approvals, security assessments, and contractual milestones that extended implementation timelines significantly. Testing protocols required extensive documentation, slowing integration of new sensors, databases, and networking features into accredited baselines. Stakeholders in 2025 reported schedule compression conflicts between training demand and administrative throughput limitations. Configuration control boards emphasized stability, often deferring enhancements to later increments regardless of user urgency. These processes increased opportunity costs, as instructors continued using legacy features while awaiting approved upgrades. Facilities planning became conservative, avoiding infrastructure changes until certification pathways were clearly defined and funded. Workforce training for new systems also waited on approvals, compounding delays across instructional pipelines. Interoperability ambitions faced similar bottlenecks, as cross domain connections required synchronized authorizations across organizations. Consequently, procurement friction remained a structural constraint on responsiveness within the simulation modernization agenda.
Cybersecurity and classified network compliance costs
Cybersecurity and classified network compliance costs intensified after 2023, shaping architectural decisions and operational procedures across training enterprises nationwide. Security teams in 2024 mandated stricter access controls, auditing routines, and segmentation practices within simulator networks and content repositories. These requirements increased configuration complexity, demanding specialized expertise and extended testing cycles before accreditation approvals. In 2025, operators reported additional administrative workloads to maintain compliance documentation and continuous monitoring obligations. Network isolation rules limited rapid scenario sharing, affecting collaboration across geographically separated training sites and commands. Budget planning prioritized security tooling and personnel, occasionally constraining investments in content development and user interface improvements. Vendors adapted designs to accommodate encryption and logging mandates, which sometimes reduced performance margins or increased latency. Instructors faced workflow adjustments, including credential management and controlled data handling procedures during daily training operations. The cumulative burden influenced scheduling flexibility and slowed adoption of distributed architectures despite operational appeal. Compliance therefore remained an enduring challenge shaping cost, pace, and scope of modernization initiatives.
Opportunities
Next-generation rotorcraft training system programs
Next generation rotorcraft training system programs gained prominence after 2023, signaling long horizon requirements for adaptable, open, and modular simulation ecosystems. Planners in 2024 emphasized architecture flexibility, anticipating evolving avionics, sensors, and mission profiles across future platforms. These programs encourage early alignment between platform design and training system interfaces, reducing downstream integration friction. Stakeholders in 2025 highlighted opportunities for common cores supporting multiple variants and roles within shared training infrastructures. Such alignment supports economies of configuration, even without disclosing any aggregate financial implications or totals. Industry teams prepared roadmaps for scalable databases, physics engines, and instructor tools compatible with evolving requirements. Acquisition strategies increasingly reference digital engineering, which benefits simulation providers able to integrate model based artifacts. Training commands welcome earlier involvement, enabling doctrine and syllabus development to proceed alongside platform maturation. This synchronized approach can shorten transition timelines from test to operational training environments. Overall, these programs create structured demand for next generation simulation capabilities anchored in long term fleet transformation.
VR and mixed reality adoption for distributed training
VR and mixed reality adoption for distributed training accelerated after 2023, driven by accessibility, portability, and rapid content iteration advantages. Training planners in 2024 piloted lightweight systems to support preparatory and sustainment activities outside centralized facilities. User feedback emphasized situational awareness practice, cockpit familiarization, and crew communication drills within constrained footprints. By 2025, several units integrated these tools into blended curricula alongside accredited full mission systems. The approach supports surge training during scheduling peaks, without overloading high fidelity assets or facility calendars. Content teams appreciated faster update cycles, enabling quick adaptation to evolving procedures and threat representations. Network integration efforts focused on maintaining security while enabling shared scenarios across dispersed locations. Instructor development programs incorporated new pedagogical techniques suited to immersive head mounted displays. While not replacing core simulators, these technologies expand the training funnel and improve preparation efficiency. The distributed model therefore presents scalable opportunities aligned with modern readiness and accessibility objectives.
Future Outlook
The outlook remains anchored in sustained modernization, deeper integration of live, virtual, and constructive environments, and continued emphasis on readiness outcomes. Over the coming years, policy alignment and digital engineering practices will shape procurement priorities. Distributed training concepts will mature alongside security frameworks. The market will balance fidelity, scalability, and compliance as core design principles.
Major Players
- CAE
- L3Harris Technologies
- Lockheed Martin
- Boeing
- Collins Aerospace
- Thales
- Leonardo
- Saab
- Elbit Systems
- Indra
- FlightSafety International
- TRU Simulation + Training
- Northrop Grumman
- Cubic
- Kongsberg
Key Target Audience
- U.S. Department of Defense program offices
- U.S. Army Aviation training commands
- U.S. Marine Corps aviation training units
- U.S. Special Operations Command training directorates
- Federal Aviation Administration liaison offices
- Defense prime contractors and integrators
- Simulator operations and sustainment providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study identified platform categories, training use cases, and architectural layers shaping demand patterns. Operational readiness metrics, utilization concepts, and accreditation pathways were mapped. Data points focused on activity indicators within 2024 and 2025.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segment structures were constructed around fleet types and technology architectures. Scenario requirements, network integration, and sustainment models informed the analytical framework. Qualitative indicators guided comparative assessment across segments.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were reviewed with training stakeholders, program personnel, and technical specialists. Feedback refined scenario priorities and workflow interpretations. Iterations ensured alignment with operational practices and compliance realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into coherent narratives and structured sections. Consistency checks ensured alignment with masking rules and scope boundaries. The final output emphasizes decision relevant insights and strategic context.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope boundaries for U.S. combat helicopter simulators, Platform and training taxonomy mapping across attack and utility fleets, Bottom-up unit-based sizing from simulator deliveries and upgrades, Revenue attribution across hardware, software and services contracts, Primary interviews with DoD program offices and OEM integrators, Triangulation with contract awards and flight-hour demand models, Assumptions on modernization cycles and export controls)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Training and mission rehearsal use cases
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and program acquisition flow
- Regulatory and security environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising rotary-wing readiness requirements
Expansion of synthetic training to reduce flight hours
Modernization of AH-64 and special operations fleets
DoD push for LVC integration and joint training
Budget reallocation toward simulator-based throughput
Need for rapid mission rehearsal for evolving threats - Challenges
Lengthy defense procurement and certification cycles
Cybersecurity and classified network compliance costs
High upfront capital cost of full-flight simulators
Interoperability issues across legacy platforms
Dependence on platform OEM data rights
Facility and footprint constraints at training bases - Opportunities
Next-generation rotorcraft training system programs
VR and mixed reality adoption for distributed training
Sustain - Trends
Shift toward LVC-centric training architectures
Increased use of high-fidelity sensor and weapons emulation
Modular simulator designs for rapid reconfiguration
Greater emphasis on collective and multi-ship training
Data-driven performance analytics and grading
Lifecycle service contracts over one-time deliveries - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Attack helicopters
Armed scout and light attack helicopters
Special operations helicopters
Legacy combat helicopter fleets
Next-generation rotorcraft programs - By Application (in Value %)
Initial and recurrent pilot training
Mission rehearsal and rehearsal certification
Tactics, techniques and procedures development
Collective and crew coordination training
Maintenance and systems familiarization - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Full-flight motion simulators
Fixed-base simulators
Part-task and desktop trainers
VR/MR immersive trainers
Networked LVC architectures - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
U.S. Army
U.S. Marine Corps
U.S. Special Operations Command
National Guard and Reserve units
Defense training service providers - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone systems
Networked on-premise systems
Secure wide-area LVC networks
Cloud-assisted training environments - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Southeast
Midwest
Southwest
West
Pacific and Alaska
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
Cross Comparison Parameters (Product fidelity, Platform coverage, LVC interoperability, Security accreditation, Delivery timelines, Lifecycle support, Pricing models, Installed base) - SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
CAE
L3Harris Technologies
Lockheed Martin
Boeing
Collins Aerospace
Thales
Leonardo
Saab
Elbit Systems
Indra
FlightSafety International
TRU Simulation + Training
Northrop Grumman
Cubic
Kongsberg
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service and upgrade expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


