Market Overview
The USA commercial aircraft aerostructures market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting a mature industrial base with deeply embedded tiered supply networks, advanced materials adoption, and long-cycle manufacturing programs. The market is anchored by extensive risk-sharing partnerships, high tooling intensity, and certification-driven production planning. Capital intensity remains elevated across composite layup, precision machining, and automated assembly, reinforcing barriers to entry. Contractual lock-ins and long program lifecycles shape demand visibility and supplier capacity planning.
The market is concentrated across aerospace manufacturing corridors with dense clusters of OEM final assembly lines, Tier-1 integrators, and specialized composite fabrication centers. Proximity to major commercial aviation hubs supports rapid engineering iteration and logistics efficiency. Deep-rooted supplier ecosystems, skilled labor pools, and test infrastructure reinforce regional advantages. State-level industrial policies, workforce development programs, and certification frameworks further anchor production activity, while established MRO networks sustain aftermarket demand and structural modification activity.
Market Segmentation
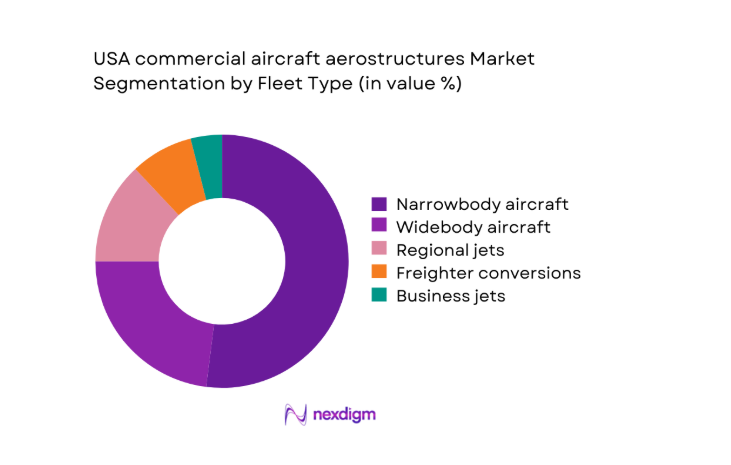
By Fleet Type
Narrowbody aircraft dominate aerostructure demand due to sustained production cadence, high shipset volumes, and dense domestic deployment across short and medium-haul networks. Structural content per aircraft remains optimized for weight reduction and manufacturability, favoring composite-intensive wings and fuselage sections. Widebody programs contribute significant unit complexity but face more volatile order cycles. Regional jets sustain steady structural replacement and modification demand, while freighter conversions expand structural reinforcement requirements. Business jet aerostructures add premium material specifications and shorter lead-time production runs, reinforcing diversified manufacturing workflows.
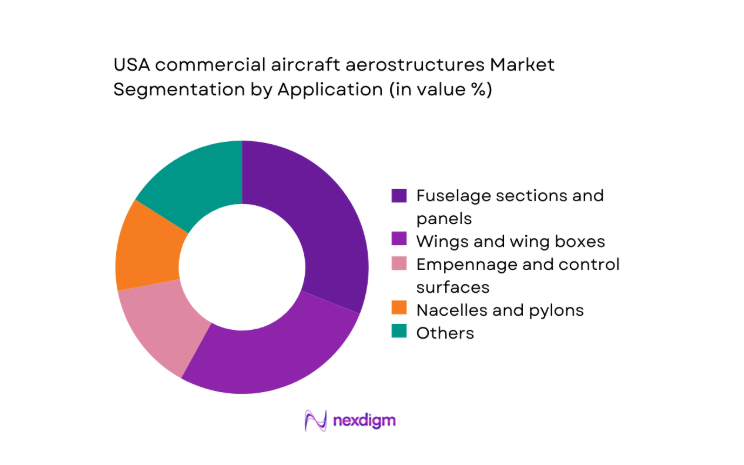
By Application
Fuselage sections and panels account for the largest structural content due to extensive surface area, pressurization requirements, and composite penetration. Wings and wing boxes follow, driven by aerodynamic load paths and high-performance material adoption. Empennage and control surfaces require precision manufacturing and recurring inspection-driven replacements. Nacelles and pylons benefit from propulsion integration complexity, while doors and access panels contribute steady aftermarket demand. Floor structures and load-bearing interior frames grow with cabin reconfiguration cycles, sustaining recurring fabrication and repair workflows across certified MRO facilities.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by long-term supply agreements, risk-sharing partnerships, and deep integration with OEM production systems. Capability differentiation is driven by composite process maturity, automation depth, certification track record, and capacity to absorb production rate variability across major aircraft programs.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Spirit AeroSystems | 2005 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Triumph Group | 1993 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Collins Aerospace | 2018 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GKN Aerospace | 1984 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo Aerostructure | 1912 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA commercial aircraft aerostructures Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Ramp-up of narrowbody production rates in the US supply chain
Narrowbody output acceleration is supported by production line expansions across multiple final assembly sites during 2024 and 2025, with monthly build rates moving from 38 to 52 units. FAA certification throughput increased by 11 in 2024 compared to 2023, enabling higher conformity inspections. Domestic supplier lead times shortened from 26 weeks to 19 weeks through 2025 due to automation adoption across 14 composite layup cells. Freight movements through major aerospace corridors increased by 420000 tons in 2024, supporting logistics reliability. Workforce additions of 8200 technicians in 2025 stabilized multi-shift operations across 6 manufacturing clusters nationwide.
Rising composite adoption for weight reduction and lifecycle cost
Composite content expanded across wings and fuselage sections, with thermoset and thermoplastic penetration rising from 41 in 2023 to 47 in 2025 across new shipsets. Autoclave capacity increased by 9 systems in 2024, while out-of-autoclave lines added 18 automated tape-laying heads by 2025. FAA approvals for composite repair schemes rose by 23 in 2024, accelerating aftermarket adoption. Scrap rates declined from 7 to 4 through process controls introduced across 12 facilities. Structural health monitoring pilots expanded to 260 aircraft in 2025, reinforcing composite lifecycle management practices nationwide.
Challenges
Supply chain disruptions for aerospace-grade aluminum and carbon fiber
Aerospace-grade aluminum billet lead times extended from 12 weeks in 2023 to 21 weeks in 2024 due to smelter maintenance cycles and logistics constraints. Carbon fiber precursor availability declined by 18 in 2024 following energy disruptions affecting 3 major production nodes. Port congestion added 9 days to inbound material transit in 2024 across two primary gateways. Inventory coverage fell from 74 days in 2023 to 53 days in 2025 for several Tier-2 suppliers. Qualification backlogs delayed 27 alternative material approvals in 2024, constraining substitution strategies and production continuity across 5 high-rate programs.
Skilled labor shortages in composite layup
Certified composite technicians declined by 6 in 2024 across key manufacturing regions, despite 14 training programs launched by state agencies. Attrition rates reached 17 in 2025 among experienced machinists due to retirements and cross-industry mobility. Training cycle duration averages 11 months for advanced layup certification, constraining ramp speed. Overtime utilization exceeded 22 hours per worker per month in 2024 across 9 plants, elevating fatigue risks. Rework incidence increased by 31 incidents in 2025 linked to novice errors, pressuring throughput and compliance across certified production lines.
Opportunities
Next-generation thermoplastic composites for high-rate production
Thermoplastic composite lines demonstrated cycle times of 6 minutes per part in 2024 pilot cells, compared to 38 minutes for thermoset curing. Welded joint adoption reduced fastener counts by 140 per shipset in 2025 across test programs. FAA conformity pathways issued 5 material process approvals in 2024, enabling broader certification pipelines. Energy consumption per cured panel declined by 24 in 2025 across two production cells. Recyclability trials recovered 62 kg of usable material per batch in 2024, aligning with industrial sustainability targets and supporting high-rate manufacturing scalability nationwide.
Automation and robotics in aerostructure fabrication
Robotic drilling and fastening cells increased from 47 in 2023 to 68 in 2025 across major Tier-1 sites, reducing takt time by 19 per station. Vision-guided inspection systems processed 1.6 million fastener points in 2024 with defect detection improvements of 14. Autonomous material handling reduced internal transit steps by 220 per shift in 2025. Programming cycle times for new parts dropped from 21 days to 9 days through digital twins deployed across 7 facilities. Injury incidents decreased by 33 in 2024, improving workforce safety and operational continuity.
Future Outlook
The market trajectory through 2035 reflects sustained production normalization, deeper composite penetration, and expanding automation across structural fabrication. Certification pathways and workforce development will shape ramp sustainability, while thermoplastic processes and digital manufacturing deepen productivity. Regional manufacturing hubs are expected to consolidate specialized capabilities, reinforcing domestic supply resilience.
Major Players
- Spirit AeroSystems
- Triumph Group
- Collins Aerospace
- GKN Aerospace
- Leonardo Aerostrutture
- Safran Nacelles
- Senior Aerospace
- Hexcel
- Toray Advanced Composites
- Barnes Aerospace
- Woodward
- Jamco America
- Kaman Aerospace
- PCC Structurals
- AAR Corp
Key Target Audience
- Commercial aircraft OEM procurement teams
- Tier-1 aerostructure integrators
- Tier-2 and Tier-3 component manufacturers
- Airlines and cargo fleet operators
- Aircraft lessors and asset managers
- MRO and modification centers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names: Federal Aviation Administration, Department of Transportation
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core variables include aircraft program build rates, shipset structural content, material mix, certification pathways, and domestic manufacturing capacity. Supply chain localization, automation penetration, and workforce availability were mapped to define market scope and boundaries.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Program-level production schedules, fleet utilization patterns, and structural replacement cycles were analyzed to construct demand logic. Material adoption curves and process maturity were integrated to assess technology-driven shifts across fabrication workflows.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through structured consultations with engineering leaders, quality managers, and production planners. Feedback loops refined capacity constraints, certification timelines, and operational bottlenecks affecting near-term execution.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized across supply, demand, technology, and regulatory dimensions. Cross-validation ensured internal consistency, while scenario framing captured sensitivity to production cadence, workforce dynamics, and process innovation trajectories.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and program-level aerostructure scope across US commercial fleets, Fleet and platform-based taxonomy for fuselage sections wings empennage nacelles and interiors structures, Bottom-up market sizing from shipset content per aircraft program with production rate normalization, Revenue attribution by contract value content per shipset and long-term supply agreements)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Aircraft production and replacement cycles
- Ecosystem structure
- Tiered supply chain and risk-sharing partnerships
- Certification and regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Commercial fleet renewal driven by fuel efficiency mandates
Ramp-up of narrowbody production rates in the US supply chain
Rising composite adoption for weight reduction and lifecycle cost
Expansion of freighter conversions and cargo aircraft demand
OEM localization of aerostructure manufacturing for supply resilience
Government incentives for domestic aerospace manufacturing - Challenges
Supply chain disruptions for aerospace-grade aluminum and carbon fiber
Skilled labor shortages in composite layup and precision machining
High capital intensity for tooling autoclaves and automation
Certification lead times for new materials and processes
Pricing pressure from OEMs under long-term contracts
Program rate volatility and order deferrals - Opportunities
Next-generation thermoplastic composites for high-rate production
Automation and robotics in aerostructure fabrication
Digital twins and predictive maintenance for structural components
Retrofit and modification demand for aging US fleets
Nearshoring and supplier consolidation by Tier-1s
Sustainable materials and recyclable composites development - Trends
Increased risk-sharing partnerships between OEMs and Tier-1s
Shift toward out-of-autoclave composite processes
Lightweighting through topology optimization and AM brackets
Longer-term supply agreements with performance-based incentives
Vertical integration by Tier-1 aerostructure suppliers
Greater use of digital thread across design-to-production - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft
Widebody aircraft
Regional jets
Business jets (commercial operations)
Freighter conversions - By Application (in Value %)
Fuselage sections and panels
Wings and wing boxes
Empennage and control surfaces
Nacelles and pylons
Doors and access panels
Floor structures and interiors load-bearing frames - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Aluminum alloy aerostructures
Titanium-intensive structures
Carbon fiber reinforced polymer structures
Hybrid metal-composite structures
Thermoplastic composite structures
Additively manufactured structural components - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Commercial passenger airlines
Cargo and logistics operators
Aircraft OEMs final assembly lines
Leasing companies fleet operators
Aftermarket MRO and modification centers - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Integrated structural health monitoring embedded
Digitally tracked components with RFID/serialization
Smart fasteners and sensor-enabled joints
Traditional non-connected structures - By Region (in Value %)
Pacific Northwest aerospace corridor
Southern aerospace manufacturing belt
Midwest manufacturing clusters
Southwest aerospace hubs
Northeast engineering and MRO hubs
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (manufacturing footprint and US localization, shipset content per aircraft program, composite vs metallic capabilities, automation and digital manufacturing maturity, long-term OEM contract coverage, cost competitiveness and yield rates, certification track record with FAA, aftermarket repair and modification capabilities)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Spirit AeroSystems
Boeing Aerostructures
Triumph Group
Collins Aerospace
GKN Aerospace
Leonardo Aerostrutture
Korea Aerospace Industries
Meggitt
Senior Aerospace
Hexcel
Toray Advanced Composites
Jamco America
Safran Nacelles USA
Barnes Aerospace
Woodward
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


