Market Overview
The USA Commercial Aircraft Aftermarket Outlook to 2035 market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained demand for maintenance, repair, and overhaul services across commercial fleets. Ongoing fleet utilization patterns, component replacement cycles, and compliance-driven maintenance events underpin steady aftermarket activity. Parts availability, repair turnaround time, and service network coverage continue to shape procurement decisions. Contractual service models and long-term maintenance agreements influence operator preferences, while technical documentation access and certification frameworks affect competitive positioning across the service ecosystem.
Activity is concentrated around major aviation hubs such as Dallas–Fort Worth, Atlanta, Miami, Chicago, Los Angeles, and Seattle, supported by dense airline operations, engine and component repair clusters, and established logistics infrastructure. These regions benefit from mature hangar capacity, proximity to aircraft fleets, skilled technician pools, and regulatory familiarity. Policy environments that prioritize safety compliance and domestic repair station certification reinforce localized service ecosystems, while cargo corridors and coastal gateways concentrate heavy maintenance and parts distribution activities.
Market Segmentation
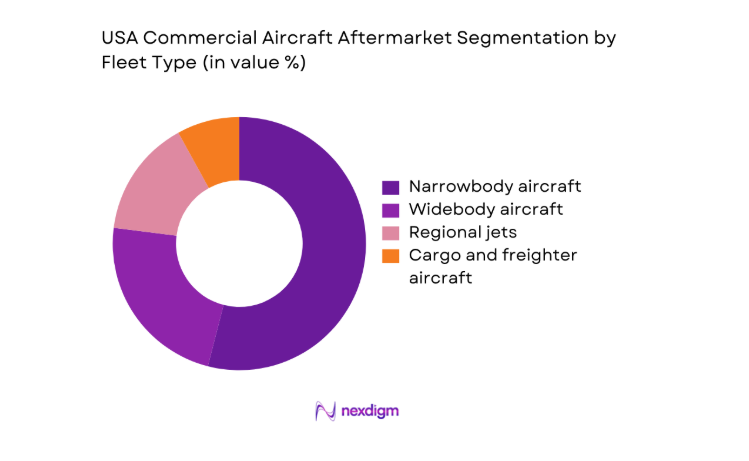
By Fleet Type
Narrowbody aircraft dominate aftermarket demand due to high-frequency short-haul operations, dense domestic route networks, and elevated flight cycle accumulation. These aircraft experience accelerated wear on landing gear, brakes, and avionics, increasing line maintenance and component exchange volumes. Widebody aircraft generate concentrated heavy maintenance demand linked to structural checks and engine shop visits, while regional jets contribute steady base-load activity through commuter networks. Freighter fleets intensify structural modification and cargo handling system maintenance, supported by strong logistics utilization across hub-and-spoke cargo routes and integrated express networks.
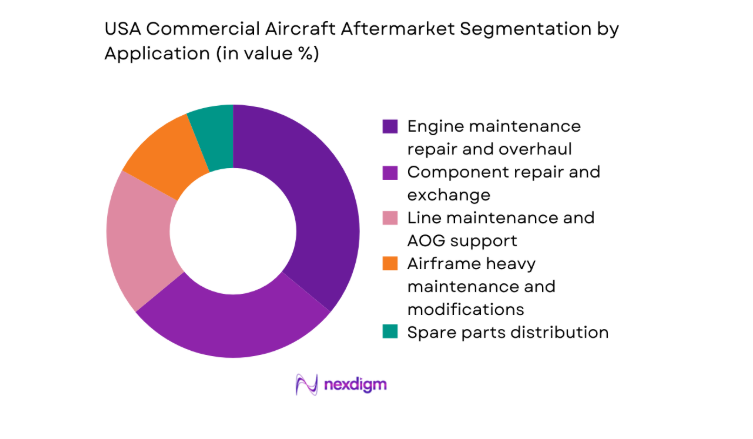
By Application
Engine maintenance repair and overhaul represents the most complex and resource-intensive application, driven by life-limited part cycles, performance restoration events, and compliance with airworthiness directives. Component repair and exchange sustains recurring demand due to high-failure-rate rotables across avionics, hydraulics, and environmental control systems. Line maintenance supports daily operational continuity through scheduled checks and AOG response, while airframe heavy maintenance concentrates on structural inspections and cabin modifications. Spare parts distribution underpins the ecosystem through inventory pooling, logistics coordination, and turnaround time optimization across operator networks.
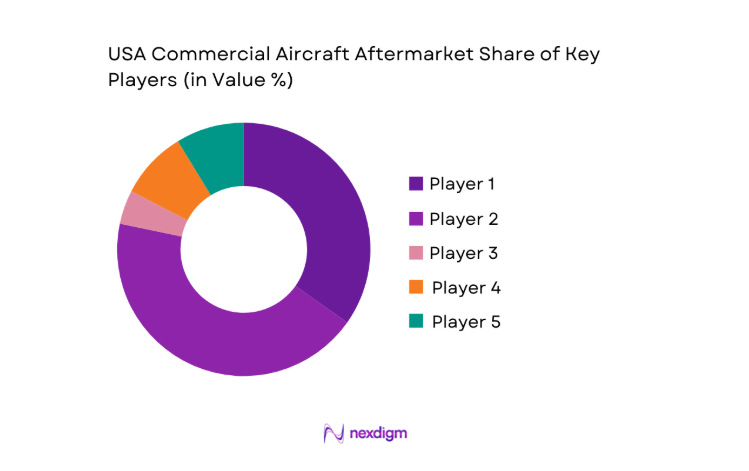
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape reflects a mix of airline-affiliated maintenance organizations, independent service providers, and OEM-aligned support entities. Competition is shaped by certification breadth, turnaround reliability, digital maintenance integration, and depth of component capabilities, with regional proximity to fleet hubs influencing service adoption.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Boeing Global Services | 2017 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GE Aerospace | 1917 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| RTX Pratt & Whitney | 1925 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lufthansa Technik | 1954 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AAR Corp. | 1951 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Commercial Aircraft Aftermarket Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of narrowbody fleets driven by domestic route growth
Domestic air travel volumes in the United States recovered to 860 million passenger boardings during 2024, supported by 19 major hub airports handling more than 30 million passengers each. Fleet planners added 412 narrowbody aircraft into active service across 2024 and 2025, increasing average daily flight cycles per aircraft to 5.6 on high-density routes. FAA traffic operations reached 45 million movements in 2024, intensifying brake, tire, and avionics replacement frequencies. Higher utilization rates elevate scheduled maintenance events, driving demand for line maintenance capacity, component exchange pools, and rapid turnaround support across domestic networks.
Rising average fleet age increasing heavy maintenance events
The average age of active commercial aircraft in the United States reached 13.2 years in 2025, compared with 11.8 years in 2022, increasing the frequency of structural inspections and corrosion mitigation tasks. FAA records show 18,400 heavy maintenance checks conducted across large transport category aircraft during 2024, reflecting elevated D-check and C-check volumes. Deferred retirements added 286 older airframes into continued service during 2024 and 2025, expanding demand for landing gear overhauls, wiring inspections, and cabin system refurbishments. Aging fleets require deeper maintenance packages, extending shop visit durations and raising component shop workloads nationwide.
Challenges
Skilled labor shortages in licensed A&P mechanics
The United States recorded 21,400 active airframe and powerplant technicians entering retirement eligibility by 2025, while training pipelines produced 12,600 newly certified technicians across 2024 and 2025. FAA-approved maintenance schools reported 9,300 graduates in 2024, insufficient to offset attrition across major hubs. Technician vacancy rates exceeded 14 across large maintenance bases in 2025, increasing overtime hours and maintenance backlogs. Workforce shortages lengthen turnaround times for heavy checks, constrain hangar throughput, and elevate compliance risks during peak demand periods. Competition for licensed personnel intensifies recruitment costs and delays service capacity expansions.
Supply chain disruptions for rotables and life-limited parts
Component lead times for selected rotables extended from 42 days in 2022 to 78 days in 2025 due to constrained machining capacity and material bottlenecks. FAA Parts Manufacturer Approval processing averaged 146 days in 2024, delaying alternate sourcing approvals. Inventory backorders affected 6,800 aircraft-on-ground incidents recorded by large carriers in 2024, up from 4,900 in 2022. Logistics congestion at five major cargo gateways added 3 to 5 days to inbound part delivery windows. Prolonged supply variability complicates maintenance scheduling, increases AOG exposure, and strains exchange pool availability across fleets.
Opportunities
Expansion of engine MRO capacity for LEAP and GTF platforms
The active installed base of next-generation narrowbody engines exceeded 6,400 units across U.S.-operated fleets by 2025, with shop visit intervals tightening after 3,200 flight cycles for early production batches. FAA certification of 11 additional engine test cells during 2024 expanded domestic throughput potential. Hangar expansions added 24 dedicated engine bays across three major maintenance clusters in 2025. Increased shop visit frequency and parts replacement cycles create sustained demand for engine disassembly, module repair, and performance restoration services, enabling capacity investments to capture rising maintenance volumes within domestic networks.
Aftermarket demand for used serviceable material
Aircraft retirements and part-out events supplied 1,120 airframes into dismantling channels across 2024 and 2025, increasing availability of serviceable components for legacy platforms. Component reuse cycles shortened average procurement lead times by 19 days in 2024 for avionics and hydraulic units. Regulatory acceptance of traceable used serviceable material supported 27 additional repair station approvals in 2025, expanding certified distribution networks. Operators increased pooling participation across 14 major hubs, reducing AOG exposure. Expanded part-out throughput and traceability systems create opportunities to stabilize supply for aging fleets under cost containment pressures.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to experience sustained operational intensity through 2030 and beyond, driven by high utilization of narrowbody fleets and prolonged service lives of in-service aircraft. Digital maintenance integration and predictive analytics adoption will continue to reshape maintenance planning. Domestic capacity expansions across engine and component shops are likely to rebalance turnaround timelines. Regulatory oversight will remain stringent, reinforcing compliance-driven service demand. Strategic partnerships across airlines and service providers are set to deepen ecosystem coordination.
Major Players
- Boeing Global Services
- GE Aerospace
- RTX Pratt & Whitney
- Lufthansa Technik
- AAR Corp.
- StandardAero
- Delta TechOps
- United Airlines Tech Ops
- American Airlines Tech Ops
- HAECO Americas
- STS Aviation Group
- Sabreliner Aviation
- FEAM Aero
- Air France Industries KLM Engineering & Maintenance
- Barnes Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Commercial passenger airlines
- Cargo and logistics operators
- Aircraft leasing companies
- Independent maintenance, repair, and overhaul providers
- Parts distributors and inventory pooling organizations
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Federal Aviation Administration and U.S. Department of Transportation
- State-level aviation authorities and airport commissions
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Fleet utilization intensity, maintenance interval thresholds, regulatory compliance cycles, and component failure patterns were mapped across domestic commercial operations. Variables reflected aircraft age profiles, route density, and shop visit frequencies across major hubs.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Operational indicators, maintenance event counts, and capacity availability were synthesized to construct service demand profiles. Application-level workflows were structured across engine, airframe, line maintenance, and component repair domains.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights were validated through structured discussions with airline maintenance leadership, certified repair station managers, and regulatory compliance officers. Assumptions on utilization recovery and capacity constraints were stress-tested against operational benchmarks.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were reconciled through cross-validation of operational indicators and service workflows. Scenario narratives were developed to reflect utilization normalization, capacity expansion pathways, and regulatory enforcement trajectories.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope boundaries for U.S. commercial aircraft MRO and parts aftermarket, Fleet and component-level taxonomy across airframe engine component and line maintenance segments, Bottom-up market sizing using fleet utilization flight cycles and maintenance event frequencies, Revenue attribution through parts consumption rates labor hours and MRO contract values)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and maintenance pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and distribution channels
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of narrowbody fleets driven by domestic route growth
Rising average fleet age increasing heavy maintenance events
Growth in cargo operations and freighter conversions
FAA safety and compliance mandates increasing inspection cycles
Higher utilization rates post-pandemic normalization
Long-term service agreements by OEMs and MRO providers - Challenges
Skilled labor shortages in licensed A&P mechanics
Supply chain disruptions for rotables and life-limited parts
OEM parts pricing pressure and proprietary data access limits
Aircraft-on-ground events due to parts availability constraints
Capacity bottlenecks at U.S. MRO facilities
Regulatory certification timelines for new repair capabilities - Opportunities
Expansion of engine MRO capacity for LEAP and GTF platforms
Aftermarket demand for used serviceable material
Digital MRO platforms for predictive maintenance adoption
Growth in freighter conversion and P2F modification programs
Localization of component repair capabilities within the U.S.
Additive manufacturing for low-volume and legacy parts - Trends
Shift toward power-by-the-hour and integrated MRO contracts
Increasing use of aircraft health monitoring and analytics
Rising demand for used serviceable material in cost-sensitive fleets
Strategic partnerships between airlines and independent MROs
Investments in automation and robotics in hangar operations
Consolidation among independent MRO providers - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft
Widebody aircraft
Regional jets
Cargo and freighter aircraft - By Application (in Value %)
Engine maintenance repair and overhaul
Airframe heavy maintenance and modifications
Line maintenance and AOG support
Component repair and exchange
Spare parts distribution - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Traditional scheduled maintenance programs
Power-by-the-hour and performance-based logistics
Predictive maintenance and digital MRO platforms
Additive manufacturing for spare parts
Condition-based monitoring systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Passenger airlines
Cargo and logistics operators
Aircraft lessors
Charter and ACMI operators
Government and public service operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Connected aircraft health monitoring systems
Non-connected maintenance operations
Real-time telematics and AHM platforms
Ground-based maintenance IT systems - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (fleet coverage, engine platform capability, FAA repair station certifications, turnaround time performance, geographic footprint in the U.S., pricing models and contract structures, digital MRO platform maturity, parts availability and exchange pool depth)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Boeing Global Services
GE Aerospace
RTX Pratt & Whitney
Lufthansa Technik
AAR Corp.
StandardAero
Delta TechOps
United Airlines Tech Ops
American Airlines Tech Ops
HAECO Americas
STS Aviation Group
Sabreliner Aviation
FEAM Aero
Air France Industries KLM Engineering & Maintenance
Barnes Aerospace
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


