Market Overview
The USA commercial aircraft carbon brake market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting mature adoption across major airline fleets and sustained replacement demand within maintenance cycles. The ecosystem is shaped by long equipment lifecycles, stringent airworthiness requirements, and the operational need to manage high-energy landing events. Lifecycle service models, rotable exchange programs, and refurbishment pathways anchor recurring demand, while fleet modernization programs continue to reinforce baseline requirements for advanced braking solutions.
Activity is concentrated around aviation hubs such as Dallas–Fort Worth, Atlanta, Chicago, Seattle, and Phoenix, where fleet density, maintenance capacity, and technical talent pools are strongest. Proximity to major airline operations, FAA oversight infrastructure, and certified repair stations supports faster turnaround cycles and quality assurance. Regions with dense narrowbody operations show higher replacement intensity, while cargo hubs benefit from high-utilization freighter operations. Policy emphasis on safety compliance and domestic MRO capacity further concentrates demand within established aviation corridors.
Market Segmentation
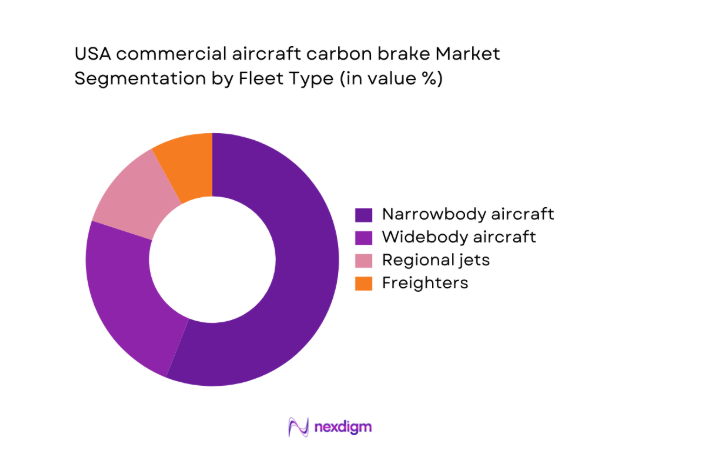
By Fleet Type
Narrowbody aircraft dominate demand due to higher utilization rates, shorter turnaround times, and dense domestic route networks that generate frequent landing cycles. These fleets operate multiple daily sectors, accelerating wear profiles and replacement intervals. Widebody fleets contribute steady but lower-frequency demand, driven by longer-haul operations with fewer cycles. Regional jets add incremental volume through high-frequency short-haul routes, while freighters exhibit elevated utilization intensity linked to overnight cargo schedules and hub-and-spoke logistics. Fleet age distribution also influences refurbishment intensity, with mid-life aircraft undergoing structured brake exchange programs aligned with scheduled heavy checks and predictive maintenance adoption.
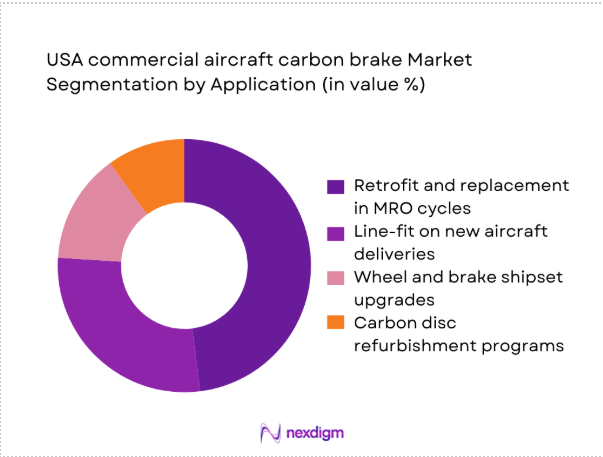
By Application
Retrofit and replacement within MRO cycles dominate demand, reflecting continuous wear management and safety-critical replacement schedules embedded in airline maintenance planning. Line-fit installations on new deliveries provide stable baseline volumes aligned to fleet renewal programs. Wheel and brake shipset upgrades are adopted selectively to improve energy absorption performance and thermal management on high-utilization routes. Carbon disc refurbishment programs expand lifecycle value by extending usable life across multiple shop visits, reducing downtime and inventory exposure for operators. The balance between exchange pools and in-house maintenance capabilities shapes application mix across network carriers and cargo operators.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a small set of technologically advanced suppliers aligned with OEM qualification pathways and extensive aftermarket service networks. Differentiation is driven by lifecycle performance, service responsiveness, and integration with airline maintenance planning systems.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Safran Landing Systems | 1925 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| RTX Collins Aerospace | 2018 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Honeywell Aerospace | 1906 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Meggitt Aircraft Braking Systems | 1857 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Liebherr-Aerospace | 1949 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA commercial aircraft carbon brake Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising US commercial fleet utilization and post-pandemic traffic recovery
Domestic passenger throughput across large hub airports recorded 2024 movements above 2019 levels, supported by runway slot utilization increases in Atlanta, Dallas–Fort Worth, and Chicago. Aircraft daily cycles for narrowbody fleets reached 5 to 7 sectors on high-frequency corridors, accelerating brake wear rates. FAA data shows 2025 active commercial aircraft registrations exceeding 7,600, while scheduled departure counts expanded across 42 primary airports. Jet fuel consumption volumes in 2024 rebounded to 2018 benchmarks, indicating sustained flight activity. These operational indicators elevate landing cycle accumulation, intensifying replacement cadence and refurbishment throughput across certified maintenance facilities nationwide.
Shift toward lightweight carbon brakes to improve fuel efficiency
Fleet modernization programs emphasize weight reduction to improve range and payload efficiency on dense domestic routes. New narrowbody variants delivered in 2024 incorporated advanced braking configurations aligned with composite-intensive airframes. US airline fleet planners referenced payload optimization on 1,000 to 2,000 kilometer sectors to improve utilization economics amid constrained airport turnaround windows. FAA certification approvals in 2025 covered multiple brake configuration upgrades integrated with wheel assemblies. Airline operational data shows average turnaround targets reduced to 35 minutes on high-frequency routes, incentivizing lighter components to support thermal management and faster cooling cycles, reinforcing adoption of carbon brake architectures.
Challenges
High upfront cost of carbon brake shipsets versus steel alternatives
Capital budgeting for component upgrades competes with airframe heavy checks, avionics retrofits, and engine shop visits. Airline maintenance planning in 2024 prioritized engine performance restoration cycles occurring every 20,000 to 25,000 flight hours, constraining allocation toward braking upgrades. Procurement committees compare lifecycle performance against immediate cash exposure during fleet-wide refresh programs. Financing constraints intensified in 2025 as interest rate environments tightened, extending approval timelines for non-mandatory upgrades. Inventory carrying levels for rotables were capped across several hubs, limiting buffer stocks. These conditions slow adoption despite operational benefits, particularly among cost-sensitive operators on short-haul networks.
Supply chain constraints for carbon-carbon composite materials
Composite precursor availability faced disruptions in 2024 due to capacity reallocation toward defense and space programs. Production lead times for high-temperature carbon-carbon components extended beyond 20 weeks at several facilities, affecting maintenance scheduling. Freight capacity volatility across transcontinental logistics corridors delayed inbound shipments to MRO hubs in Texas and Arizona. FAA repair station audits in 2025 emphasized traceability documentation, adding compliance processing time to inbound materials. Skilled technician availability for composite handling remained constrained, with training throughput limited by certification requirements. These bottlenecks elevated turnaround uncertainty, challenging airlines to maintain on-time fleet availability during peak travel periods.
Opportunities
Aftermarket growth from rising brake refurbishment and exchange programs
MRO throughput at major hubs increased in 2024 as deferred maintenance from earlier disruptions normalized. Certified repair stations expanded bay capacity by 12 to 18 lines in Phoenix and Dallas–Fort Worth to manage rising wheel and brake shop visits. Fleet age distribution shows 2025 mid-life narrowbody cohorts exceeding 3,000 aircraft, aligning with refurbishment cycles at heavy check intervals. FAA approvals for additional rotable exchange pools improved asset circulation efficiency. Airline reliability targets mandate dispatch availability above 99.5 across core domestic networks, elevating demand for rapid exchange programs to minimize aircraft-on-ground events and optimize maintenance planning across hub operations.
Adoption of predictive maintenance to optimize brake life cycles
Airline engineering departments expanded condition-based maintenance programs in 2024 using sensor-enabled wear tracking integrated into maintenance software platforms. Dispatch reliability metrics across large hubs target less than 2 unscheduled removals per 1,000 cycles, driving analytics deployment. FAA guidance on data-driven maintenance documentation supported broader adoption in 2025, standardizing reporting practices. Fleet telemetry coverage across narrowbody aircraft exceeded 80 of active tails in leading carriers, enabling earlier intervention scheduling. These indicators support lifecycle optimization, reducing unscheduled events and improving utilization planning, creating pathways for service models aligned to predictive maintenance frameworks across domestic fleets.
Future Outlook
Through 2035, fleet renewal, domestic traffic normalization, and maintenance digitization will shape demand patterns across hubs. Regulatory emphasis on safety compliance and MRO capacity expansion will reinforce structured replacement cycles. Integration of predictive maintenance with lifecycle service models is expected to improve asset utilization and operational resilience.
Major Players
- Safran Landing Systems
- RTX Collins Aerospace
- Honeywell Aerospace
- Meggitt Aircraft Braking Systems
- Liebherr-Aerospace
- Parker Aerospace
- Moog Inc.
- Crane Aerospace & Electronics
- AAR Corp.
- StandardAero
- Delta TechOps
- Lufthansa Technik
- HEICO Corporation
- GA Telesis
- Barnes Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Commercial passenger airlines
- Cargo airline operators
- Aircraft leasing companies
- Certified MRO providers
- Airport authorities and operators
- FAA and US Department of Transportation agencies
- State aviation regulatory bodies
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study mapped aircraft fleet composition, landing cycle intensity, maintenance intervals, and certification pathways relevant to braking systems. Regulatory requirements, repair station capabilities, and lifecycle service models were identified as core variables shaping demand and adoption dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Operational indicators across hub airports, fleet utilization patterns, and maintenance throughput were synthesized to construct demand scenarios. Segmentation logic aligned fleet types with application pathways and service models embedded in airline maintenance planning.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through structured discussions with airline maintenance leaders, FAA-certified repair station managers, and fleet planning teams to test assumptions on utilization, refurbishment cycles, and technology adoption constraints.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated into an integrated market narrative linking operational drivers, constraints, and opportunity pathways. Outputs were structured to inform strategic planning, investment prioritization, and service model development.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and aircraft brake system scope alignment for US commercial fleets, segmentation taxonomy by fleet class and brake technology architectures, bottom-up sizing using OEM deliveries and MRO replacement cycles, revenue attribution across line-fit and retrofit contracts, primary interviews with airline maintenance heads and brake system engineers, triangulation with FAA fleet data and MRO teardown analysis, assumptions on carbon-carbon disc life cycles and landing cycle utilization)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Aircraft braking system usage and maintenance pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and aftermarket channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising US commercial fleet utilization and post-pandemic traffic recovery
Shift toward lightweight carbon brakes to improve fuel efficiency
Higher landing cycle intensity in narrowbody fleets driving replacement demand
OEM preference for carbon brakes in new-generation aircraft programs
Expansion of domestic MRO capacity and wheel-and-brake service programs
Fleet modernization by US carriers toward next-gen narrowbody platforms - Challenges
High upfront cost of carbon brake shipsets versus steel alternatives
Supply chain constraints for carbon-carbon composite materials
Long qualification cycles and FAA certification requirements
Volatility in aircraft delivery schedules impacting line-fit demand
Dependence on OEM-approved repair stations for refurbishment
Exposure to airline capex cycles and fleet grounding risks - Opportunities
Aftermarket growth from rising brake refurbishment and exchange programs
Adoption of predictive maintenance to optimize brake life cycles
Retrofit demand for older fleets transitioning to carbon brakes
Long-term service agreements with US major carriers and LCCs
Localization of MRO capabilities to reduce turnaround time
Partnerships with lessors to standardize brake configurations - Trends
Increasing penetration of carbon brakes on narrowbody platforms
Growth of power-by-the-hour and rotable exchange programs
Integration of brake wear sensors with airline MRO software
Standardization of brake shipsets across mixed fleets
Rising use of analytics to extend disc life and optimize cycles
Supplier consolidation and long-term OEM sourcing agreements - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft
Widebody aircraft
Regional jets
Freighters - By Application (in Value %)
Line-fit on new aircraft deliveries
Retrofit and replacement in MRO cycles
Wheel and brake shipset upgrades
Carbon disc refurbishment programs - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Carbon-carbon brake discs
Hybrid carbon brake assemblies
Lightweight heat sink integrated brakes
High-energy absorption brake packs - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Passenger airlines
Cargo airlines
Aircraft leasing companies
Charter and ACMI operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Conventional brake wear monitoring
Sensor-enabled brake health monitoring
Predictive maintenance enabled brake systems
Digitally integrated wheel and brake systems - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (product portfolio breadth, installed base across US fleets, OEM line-fit approvals, MRO network coverage, brake life-cycle performance, pricing competitiveness, turnaround time for exchanges, digital monitoring capabilities)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Safran Landing Systems
RTX Collins Aerospace
Honeywell Aerospace
Meggitt Aircraft Braking Systems
Liebherr-Aerospace
Parker Aerospace
Moog Inc.
Crane Aerospace & Electronics
AAR Corp.
StandardAero
Delta TechOps
Lufthansa Technik
HEICO Corporation
GA Telesis
Barnes Aerospace
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


