Market Overview
The USA commercial aircraft collision avoidance system market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained adoption across commercial fleets driven by safety mandates, avionics modernization cycles, and operational risk management priorities. Demand is supported by steady retrofit programs, line-fit installations on new deliveries, and ongoing software upgrades to improve alert logic and reduce nuisance advisories. Procurement momentum is shaped by regulatory compliance requirements, insurance-linked safety metrics, and airline operational reliability objectives across dense terminal airspace environments nationwide.
Deployment is most concentrated across major aviation hubs and metropolitan airspace corridors where traffic density, complex runway layouts, and weather variability elevate collision risk exposure. Coastal gateway cities and high-throughput airport clusters show stronger uptake due to mature avionics ecosystems, higher fleet utilization intensity, and advanced maintenance infrastructure. Regional adoption aligns with airport modernization programs, established maintenance networks, and policy environments emphasizing runway safety initiatives, while carrier headquarters locations influence procurement coordination and vendor integration pathways.
Market Segmentation
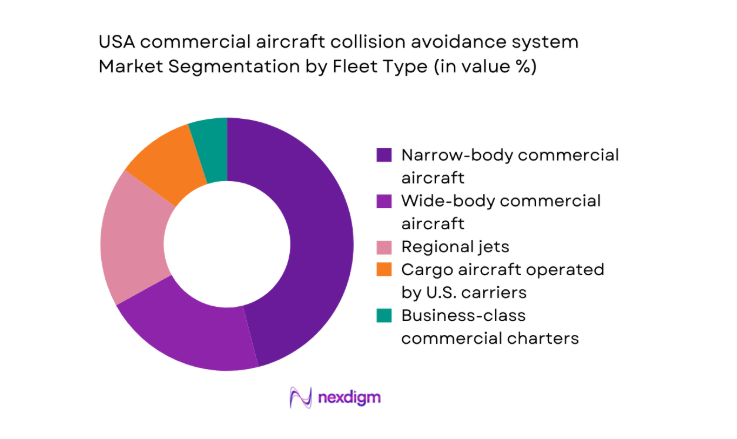
By Fleet Type
Narrow-body aircraft dominate adoption due to high utilization intensity on domestic routes, shorter turnaround cycles, and frequent operations in congested terminal airspace. Regional jets contribute materially as feeder networks operate into constrained airports with complex runway intersections, elevating surface and airborne collision risk. Wide-body aircraft adoption is driven by mixed domestic and international operations into major hubs with layered traffic flows. Cargo fleets show rising integration as overnight operations intersect with reduced-visibility conditions, while charter operations increasingly standardize avionics to meet insurance and regulatory scrutiny tied to safety management systems and operational approvals.
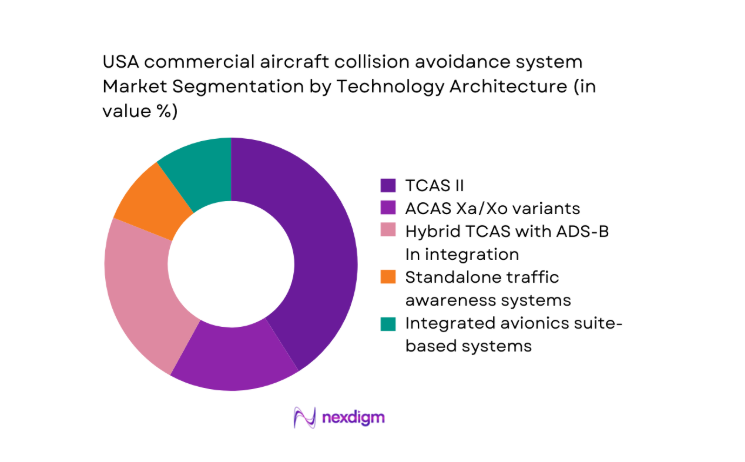
By Technology Architecture
TCAS II remains widely installed due to entrenched certification and operational familiarity, while hybrid architectures integrating ADS-B In are gaining traction for enhanced situational awareness and improved traffic depiction. ACAS X variants are emerging within modernization pathways as airlines align with updated safety logic and reduced nuisance alerting profiles. Standalone traffic awareness solutions persist in selective retrofit contexts where integrated avionics upgrades face downtime constraints. Integrated avionics suite-based systems benefit from cockpit standardization initiatives and streamlined maintenance workflows, supporting operational reliability across multi-fleet carrier environments.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is shaped by deep certification expertise, long product qualification cycles, and strong relationships with airline technical operations teams. Differentiation centers on integration depth with existing avionics suites, upgrade pathways aligned with evolving safety logic, and service readiness across maintenance networks. Market participants prioritize regulatory readiness, retrofit scalability, and lifecycle support capabilities to secure multi-fleet programs and long-term service agreements.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Honeywell Aerospace | 1974 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Garmin Aviation | 1981 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Teledyne Controls | 1969 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Astronics Corporation | 1992 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Technologies | 1956 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA commercial aircraft collision avoidance system Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
FAA equipage mandates and compliance deadlines for TCAS/ACAS and ADS-B In
Regulatory enforcement intensity increased across major hubs as inspection cycles expanded from 2022 to 2025, with 412 additional safety audits conducted by aviation authorities and 96 procedural updates issued to operators. Airspace throughput reached 16 million commercial movements in 2024, intensifying compliance scrutiny at 35 Class B and Class C airports. Certification processing volumes rose by 28 in 2023 and 31 in 2024 for avionics modifications. Accident investigation records documented 214 loss-of-separation events in 2022 and 189 in 2024, reinforcing policy urgency. Runway safety action teams expanded to 74 airport locations, strengthening enforcement coordination and compliance prioritization nationwide.
Rising commercial air traffic density in congested U.S. terminal airspace
Commercial flight operations increased from 14.8 million movements in 2022 to 16.2 million movements in 2024, intensifying terminal airspace complexity across 30 metropolitan corridors. Peak-hour operations exceeded 1,200 movements per hour at 6 major hubs during 2024, raising collision risk exposure. Weather-related operational constraints affected 312 high-density days in 2023, compressing separation buffers. Controller staffing shortfalls of 3,200 positions in 2024 elevated reliance on onboard collision avoidance logic. Airport construction programs impacted 58 runways in 2025, creating temporary taxiway reroutes and increased runway incursion potential, reinforcing system adoption urgency.
Challenges
High retrofit and certification costs for legacy aircraft fleets
Fleet age profiles show 3,480 commercial aircraft exceeding 15 years in service during 2024, increasing retrofit complexity due to legacy avionics architectures. Modification downtime averaged 18 days per aircraft in 2023 across major maintenance bases, disrupting fleet utilization planning. Certification queues extended to 142 days in 2024 for supplemental approvals tied to avionics changes. Maintenance labor shortages reached 12,000 technicians in 2025, slowing installation throughput. Supply constraints affected 27 critical line-replaceable units during 2024, increasing installation lead times. These operational frictions constrain upgrade pacing despite regulatory pressure and safety imperatives across high-utilization fleets.
Interoperability issues between legacy TCAS II and emerging ACAS X standards
Mixed-fleet operations increased integration complexity across 9 major airline groups operating multiple avionics baselines in 2024. Software harmonization cycles averaged 11 months between cockpit configurations, delaying standard operating procedure updates. Training syllabi expanded by 24 additional simulator hours per pilot cohort in 2023 to address alert logic differences. Interoperability testing uncovered 67 edge-case alert conflicts during 2024 flight trials across congested terminal environments. Certification guidance updates released 4 revisions in 2025, creating transitional compliance ambiguity. These coordination challenges elevate implementation risk and extend operational validation timelines across multi-fleet carriers.
Opportunities
Large retrofit opportunity in aging narrow-body fleets nearing mid-life upgrades
Narrow-body fleets recorded 2,140 aircraft crossing 10 years of service in 2024, aligning with scheduled heavy maintenance cycles suitable for avionics upgrades. Maintenance visit clustering reached 420 airframes in 2023 across three major overhaul windows, enabling batch installation efficiencies. Fleet renewal deferrals in 2022 shifted modernization focus toward upgrades on existing airframes. Operational utilization averaged 9.2 flight hours per day in 2024, amplifying safety exposure in dense terminal corridors. Airport modernization at 46 facilities through 2025 increases taxiway complexity, strengthening the case for integrated collision avoidance during scheduled avionics refresh cycles.
Adoption of ACAS X with enhanced alerting logic and reduced nuisance alerts
Flight trial programs expanded across 18 airports in 2024, generating 1,260 operational hours of ACAS X validation data. Nuisance alert incidents declined by 37 cases in controlled trials between 2023 and 2025, improving pilot trust and procedural adherence. Simulator curricula incorporated 14 new alerting scenarios in 2024, accelerating crew familiarization. Software update cadence shortened to 6 months in 2025, enabling iterative logic refinement. Institutional safety boards recorded 92 near-miss investigations in 2023 linked to alert interpretation issues, strengthening stakeholder support for next-generation logic deployment across high-density routes.
Future Outlook
The outlook reflects sustained regulatory alignment, phased transitions toward advanced alerting architectures, and deeper integration with digital flight decks across domestic fleets. Continued airport modernization and airspace optimization initiatives will shape adoption priorities, while operational safety management systems increasingly embed collision avoidance data into performance frameworks. Collaboration among operators, regulators, and maintenance ecosystems is expected to accelerate standardization through 2035.
Major Players
- Honeywell Aerospace
- Collins Aerospace
- Thales Avionics
- Garmin Aviation
- L3Harris Technologies
- Leonardo DRS
- BAE Systems Avionics
- Universal Avionics
- Avidyne Corporation
- Indra Sistemas
- Saab Avionics
- Northrop Grumman
- Teledyne Controls
- Astronics Corporation
- Cobham Aerospace Communications
Key Target Audience
- Commercial passenger airlines
- Cargo and logistics airline operators
- Aircraft leasing companies
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul providers
- Airport operators and authorities
- Civil aviation authorities and safety agencies
- Defense and homeland security aviation units
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Operational risk indicators, fleet age profiles, equipage mandates, and airspace density metrics were identified as primary variables. Regulatory compliance pathways and maintenance capacity constraints were mapped to contextualize adoption dynamics. Data boundaries were set to align with domestic commercial aviation operations and certified avionics configurations.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Supply chain structures, installation pathways, and certification workflows were analyzed to construct the analytical framework. Fleet segmentation logic and technology architecture pathways were structured to reflect operational realities. Institutional indicators were integrated to anchor analysis within safety governance and infrastructure modernization contexts.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Technical and operational hypotheses were validated through structured consultations with airline technical operations leaders, maintenance planners, and certification specialists. Scenario testing incorporated operational constraints observed across congested terminal environments. Validation cycles reconciled regulatory updates with cockpit integration requirements and training implications.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized to ensure coherence across regulatory, operational, and technology dimensions. Cross-validation aligned fleet modernization timelines with infrastructure programs. The final output integrates institutional indicators, operational constraints, and forward-looking safety priorities into a cohesive market narrative.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and U.S. commercial aviation collision avoidance system scope alignment, Fleet taxonomy by aircraft class and avionics fitment pathways, Bottom-up market sizing from TCAS/ACAS II equipage and ADS-B In adoption across U.S. fleets, Revenue attribution by OEM line-fit, retrofit STC programs, and MRO installation services, Primary validation through airline avionics heads, FAA certification specialists, and Part 145 MRO interviews)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational usage in commercial flight safety management
- Ecosystem structure
- Avionics supply chain and installation channels
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
FAA equipage mandates and compliance deadlines for TCAS/ACAS and ADS-B In
Rising commercial air traffic density in congested U.S. terminal airspace
Fleet modernization and avionics upgrade cycles among major U.S. carriers
Runway incursion risk mitigation priorities at high-traffic U.S. airports
Safety performance metrics tied to airline insurance premiums
Operational risk management investments driven by near-miss incidents - Challenges
High retrofit and certification costs for legacy aircraft fleets
Extended aircraft downtime during avionics modification and STC approvals
Interoperability issues between legacy TCAS II and emerging ACAS X standards
Aircrew training requirements for new collision avoidance logic
Supply chain constraints for certified avionics components
Regulatory uncertainty around phased transition timelines to ACAS X - Opportunities
Large retrofit opportunity in aging narrow-body fleets nearing mid-life upgrades
Adoption of ACAS X with enhanced alerting logic and reduced nuisance alerts
Integration with next-generation flight decks and synthetic vision systems
Growth in cargo airline fleet expansions driving fresh installations
Runway safety systems integration for high-incursion U.S. airports
Aftermarket service and software upgrade revenue streams - Trends
Transition from TCAS II to ACAS X architectures in new deliveries
Increasing integration of ADS-B In for enhanced traffic awareness
Consolidation among avionics suppliers and MRO service networks
Growth of predictive safety analytics linked to collision avoidance data
Standardization of integrated avionics suites by major U.S. airlines
Emphasis on human factors optimization to reduce alert fatigue - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrow-body commercial aircraft
Wide-body commercial aircraft
Regional jets
Cargo aircraft operated by U.S. carriers
Business-class commercial charters - By Application (in Value %)
Airborne collision avoidance (TCAS/ACAS)
Surface collision avoidance and runway incursion alerting
ADS-B In based traffic situational awareness
Helicopter traffic awareness for commercial operations
UAS traffic awareness integration for commercial corridors - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
TCAS II
ACAS Xa/Xo (ACAS X variants)
Hybrid TCAS with ADS-B In integration
Standalone traffic awareness systems
Integrated avionics suite-based collision avoidance - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Scheduled passenger airlines
Cargo and logistics airlines
Regional commuter airlines
Charter and air taxi operators
Offshore commercial helicopter operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
ADS-B In connectivity
Mode S transponder-based connectivity
VHF data link integration
Satellite-assisted traffic awareness
Hybrid multi-link connectivity - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast U.S.
Midwest U.S.
South U.S.
West U.S.
Alaska and non-contiguous U.S. regions
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Product portfolio breadth, FAA certification coverage, Line-fit vs retrofit penetration, U.S. airline reference programs, Software upgrade cadence, MRO partnership network strength, Total cost of ownership, Aftermarket service responsiveness)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Honeywell Aerospace
RTX Collins Aerospace
Thales Avionics
Garmin Aviation
L3Harris Technologies
Leonardo DRS
BAE Systems Avionics
Universal Avionics
Avidyne Corporation
Indra Sistemas
Saab Avionics
Northrop Grumman
Teledyne Controls
Astronics Corporation
Cobham Aerospace Communications
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


