Market Overview
The USA Commercial Aircraft Disassembly market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting the steady pipeline of aircraft entering end-of-life processing and component recovery. Asset owners increasingly prioritize teardown over long-term storage as airframe condition deteriorates, while sustainability mandates elevate recycling and used serviceable material circulation. The ecosystem integrates teardown facilities, parts certification workflows, and logistics networks to recover high-value components and compliant materials, with operational economics shaped by regulatory compliance, traceability requirements, and environmental handling standards.
Operational activity concentrates around storage corridors and maintenance clusters across the Southwest, West Coast, and Southeast, where dry climate conditions support aircraft parking and induction. Regional airports with long runways and available apron space anchor disassembly throughput, supported by proximity to MRO capabilities, logistics hubs, and aerospace supply chains. Policy alignment with environmental compliance and FAA oversight reinforces clustering near certified repair stations, while workforce availability and transport connectivity shape site selection and throughput reliability.
Market Segmentation
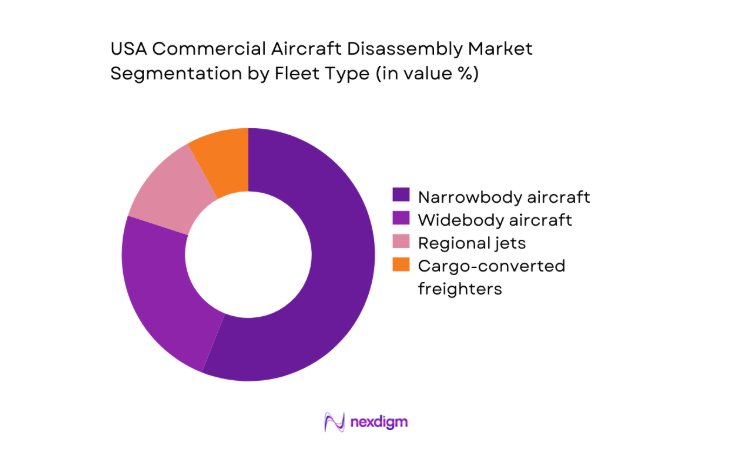
By Fleet Type
Narrowbody aircraft dominate disassembly throughput due to accelerated retirements driven by fleet renewal programs and capacity right-sizing. Operators prioritize narrowbody teardowns because component interchangeability across high-utilization platforms improves resale velocity for engines, avionics, and rotable parts. The installed base of single-aisle fleets across domestic routes increases feedstock consistency, while standardized maintenance records streamline certification workflows. Widebody teardowns follow cyclical international capacity shifts, whereas regional jets contribute opportunistic volumes tied to route rationalization. Cargo-converted freighters extend airframe life, delaying teardown timing but elevating parts harvesting value when conversions reach secondary retirement cycles.
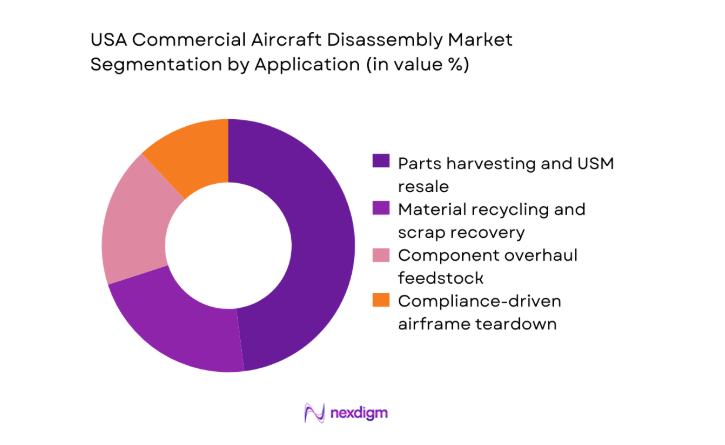
By Application
Parts harvesting and USM resale lead application demand as operators seek alternatives to OEM lead times and supply constraints. Component recovery feeds MRO channels with certified rotables, reducing aircraft-on-ground risks and stabilizing maintenance cycles. Material recycling remains secondary but expands with sustainability commitments and landfill diversion policies. Compliance-driven airframe teardown supports records closure for asset managers and lessors, while component overhaul feedstock links disassembly with downstream repair ecosystems. Digital traceability and documentation increasingly influence application choice, as buyers prioritize provenance and conformity records to accelerate induction into service channels across domestic fleets.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment features vertically integrated teardown operators aligned with MRO networks and parts trading platforms. Differentiation centers on throughput capacity, certification rigor, digital traceability, and logistics integration with storage hubs and repair stations.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| AAR Corp | 1951 | Illinois, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GA Telesis | 2001 | Florida, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AerSale | 2008 | Florida, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| STS Aviation Group | 1984 | Florida, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| StandardAero | 1911 | Arizona, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Commercial Aircraft Disassembly Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising retirements of aging narrowbody and widebody fleets
Airline fleet renewal accelerated as 2024 saw 412 commercial aircraft withdrawn from active US operations, up from 358 in 2023, driven by reliability concerns and maintenance intensity. FAA registry records indicate 1,964 aircraft exceeded 20 years of service in 2025, increasing teardown eligibility. Storage inventories at desert facilities averaged 1,127 units across 2024–2025, sustaining induction pipelines. MRO labor hours per heavy check reached 7,400 in 2024, reinforcing retire-or-teardown decisions. Environmental compliance audits increased 38 inspections in 2025, pushing asset managers toward certified disassembly pathways aligned with records closure requirements.
Growing demand for used serviceable materials to offset OEM lead times
Parts supply constraints intensified as 2024 average OEM lead times extended to 196 days for avionics LRUs and 284 days for select engine accessories. Aircraft-on-ground events across US carriers reached 1,642 occurrences in 2025, elevating reliance on USM channels. FAA 8130 certification throughput at repair stations increased to 2,418 approvals in 2024, indicating stronger acceptance of harvested components. Warehouse turns for rotable pools improved from 3.1 in 2023 to 3.8 in 2025, validating faster circulation. Logistics dwell time at hubs declined 22 hours in 2024, supporting quicker redeployment cycles.
Challenges
Regulatory compliance and environmental permitting complexities
Disassembly operations face multi-layer compliance across FAA records retention, EPA hazardous material handling, and state permitting regimes. In 2024, 76 environmental permits were processed for teardown facilities across key states, with median approval timelines of 143 days. Compliance audits documented 219 findings in 2025 related to fluids management, composite disposal, and traceability documentation. Hazardous waste manifests averaged 4.2 per aircraft in 2024, increasing administrative burden. Workforce certification renewals required 1,386 technician endorsements in 2025, adding operational friction. These institutional requirements extend induction timelines and constrain throughput predictability.
Certification and traceability requirements for harvested components
Component release to service depends on documentation completeness and conformity verification. In 2023, 18 percent of harvested parts were quarantined pending records reconciliation, declining to 12 percent in 2025 after digitalization investments. FAA conformity checks averaged 3 inspections per teardown induction in 2024. Repair station backlogs reached 29 days in 2025 for non-routine findings tied to life-limited parts documentation. Serialized component reconciliation required 11 verification steps per engine module in 2024. These procedural demands elevate cycle times and inventory dwell, tightening working capital efficiency across teardown-to-MRO pathways.
Opportunities
Capacity expansion of US-based teardown facilities
Storage site congestion rose as average apron occupancy reached 87 in 2024 across desert corridors, indicating unmet induction capacity. State infrastructure grants supported 14 runway-adjacent apron expansions in 2025, improving access for widebody ferry flights. Skilled labor pipelines expanded through 26 vocational programs in 2024 aligned with airframe dismantling competencies. Equipment utilization at existing teardown lines averaged 0.71 in 2023 and 0.79 in 2025, signaling room for throughput gains. Regulatory processing time for facility amendments fell 21 days in 2025, improving time-to-operate for capacity additions aligned with sustained retirements.
Digital marketplaces for USM pricing transparency
Platform adoption accelerated as 63 percent of US-based MROs integrated digital procurement workflows in 2024, up from 49 in 2023. API connections between teardown inventories and repair station ERP systems reached 118 integrations in 2025, reducing manual reconciliation. Transaction confirmation times fell from 9 days in 2023 to 4 days in 2025. Traceability data fields expanded to 42 attributes per component in 2024, improving buyer confidence. Institutional digitization initiatives across logistics corridors supported 27 warehouse management system upgrades in 2025, enabling scalable marketplace participation.
Future Outlook
Through 2035, retirement cycles and sustainability mandates will keep disassembly activity structurally relevant. Regional clustering around storage hubs and MRO corridors will deepen, while digital traceability becomes standard practice. Policy alignment and environmental compliance will shape facility investments, and integrated teardown-to-MRO networks will define competitive advantage.
Major Players
- AAR Corp
- GA Telesis
- Vallair
- AerSale
- Tarmac Aerosave
- AFI KLM E&M
- Chromalloy
- StandardAero
- STS Aviation Group
- Triumph Group
- VSE Corporation
- CAVU Aerospace
- eCube Solutions
- ATS Technic
- Jet Yard
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airlines and fleet operators
- Aircraft leasing and asset management firms
- MRO service providers and repair stations
- Parts distributors and aftermarket traders
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names including the Federal Aviation Administration and Environmental Protection Agency
- Airport authorities and storage facility operators
- Logistics and aerospace supply chain integrators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Scope boundaries defined teardown eligibility, fleet age cohorts, and certification pathways across US jurisdictions. Variables captured induction rates, parts categories, compliance workflows, and logistics constraints. Regulatory frameworks and environmental handling protocols informed process mapping and data taxonomy.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Bottom-up modeling aligned storage inventories with facility throughput and certification capacity. Induction pipelines were mapped to MRO demand cycles and parts categories. Process flows incorporated documentation checkpoints, hazardous handling, and logistics dwell considerations.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Operational assumptions were validated through structured consultations with teardown operators, repair station managers, and logistics coordinators. Iterations refined bottleneck estimates, certification cycle impacts, and workforce capacity constraints under prevailing regulatory regimes.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized across regulatory, operational, and ecosystem dimensions to construct coherent market narratives. Cross-validation reconciled process flows with institutional indicators, ensuring consistency of assumptions and practical relevance for strategic planning.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and teardown boundaries for end-of-life commercial aircraft in the US, fleet age cohort taxonomy and aircraft program segmentation, bottom-up facility throughput modeling using tear-down capacity and induction rates, parts harvest value attribution by component class and USM resale channels, primary interviews with MROs lessors asset managers and teardown operators)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Environmental and sustainability considerations
- Growth Drivers
Rising retirements of aging narrowbody and widebody fleets
Growing demand for used serviceable materials to offset OEM lead times
High parts pricing and supply chain disruptions in new spares
Expansion of cargo conversion programs increasing feedstock demand
Sustainability mandates driving higher recycling and part reuse
Increased lessor-led asset lifecycle optimization - Challenges
Regulatory compliance and environmental permitting complexities
Volatility in teardown yields linked to aircraft condition
Certification and traceability requirements for harvested components
Labor shortages and specialized skill requirements
Fluctuations in scrap metal and composite recycling economics
Dependence on airline retirement timing and storage availability - Opportunities
Capacity expansion of US-based teardown facilities
Digital marketplaces for USM pricing transparency
Advanced composite recycling and material recovery technologies
Strategic partnerships with lessors and cargo conversion firms
Long-term teardown contracts with major airlines
Value recovery from next-generation aircraft retirements - Trends
Consolidation among teardown and USM distributors
Increased use of digital twins and part traceability tools
Rising focus on ESG reporting for aircraft end-of-life
Vertical integration with MRO and parts trading platforms
Shift toward regional disassembly hubs near storage sites
Standardization of teardown processes and documentation - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft
Widebody aircraft
Regional jets
Cargo-converted freighters - By Application (in Value %)
Parts harvesting and USM resale
Material recycling and scrap recovery
Component overhaul feedstock
Airframe teardown for compliance and records - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Manual teardown operations
Semi-automated disassembly lines
Digital asset tracking and part certification systems
Advanced material separation technologies - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Commercial airlines
Aircraft lessors and asset managers
MRO service providers
Parts distributors and traders - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone facility operations
Digitally connected inventory and marketplace platforms
Integrated MRO and teardown networks - By Region (in Value %)
West Coast
Southwest
Midwest
Southeast
Northeast
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (facility capacity and induction rate, breadth of USM portfolio, regulatory certifications and FAA compliance, digital inventory and traceability capabilities, geographic footprint across US storage hubs, turnaround time and throughput efficiency, recycling and ESG performance metrics, strategic partnerships with airlines and lessors)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
AAR Corp
GA Telesis
Vallair
AerSale
Tarmac Aerosave
AFI KLM E&M
Chromalloy
StandardAero
STS Aviation Group
Triumph Group
VSE Corporation
CAVU Aerospace
eCube Solutions
ATS Technic
Jet Yard
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


