Market Overview
The USA commercial aircraft engines market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained demand for propulsion systems across narrowbody, widebody, and regional aircraft fleets, supported by ongoing fleet renewal and maintenance cycles. The market encompasses original equipment deliveries, aftermarket maintenance, repair, and overhaul services, and component replacements across in-service fleets. Value creation is driven by technology upgrades, reliability improvements, and lifecycle service agreements that support operators’ uptime and operational continuity.
Activity is concentrated around major aviation hubs and industrial clusters with dense airline operations, MRO capacity, and advanced manufacturing ecosystems. Coastal gateway cities host high-utilization fleets and heavy maintenance facilities, while interior aerospace corridors support component production, testing, and engineering services. Demand concentration aligns with strong airport infrastructure, skilled labor availability, and proximity to regulatory and certification bodies. Policy environments emphasizing safety compliance, emissions performance, and domestic manufacturing resilience further shape regional investment priorities and supply chain localization.
Market Segmentation
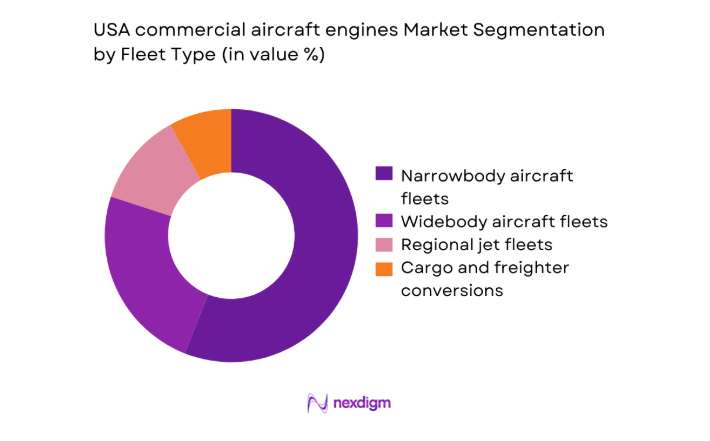
By Fleet Type
Narrowbody aircraft fleets dominate engine demand due to dense domestic route networks, high aircraft utilization, and accelerated fleet renewal cycles. Operators prioritize fuel efficiency and time-on-wing reliability to sustain high daily flight cycles, elevating aftermarket activity for quick-turn maintenance. Regional jet fleets maintain stable demand through hub-and-spoke connectivity, while widebody fleets concentrate demand around transcontinental and international gateways. Cargo and freighter conversions contribute countercyclical engine utilization patterns tied to e-commerce logistics peaks. Fleet composition decisions increasingly reflect maintenance infrastructure availability, spare engine pooling access, and service network coverage to minimize aircraft-on-ground events and sustain operational resilience.
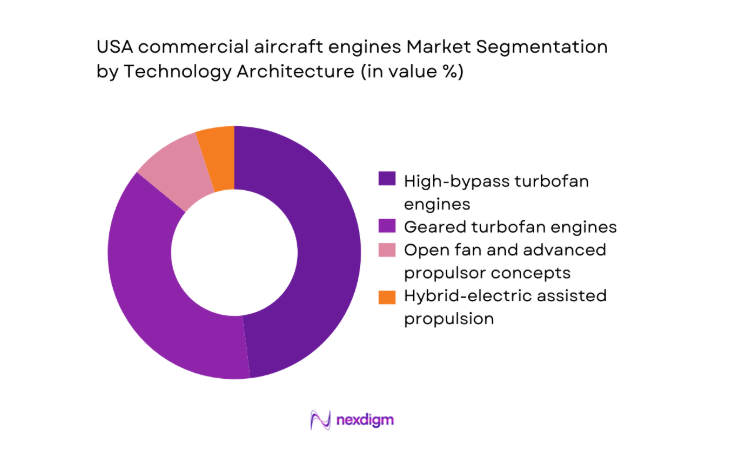
By Technology Architecture
High-bypass turbofan engines remain prevalent across established fleets, supported by mature maintenance ecosystems and broad parts availability. Geared turbofan architectures expand within narrowbody programs due to efficiency and noise performance benefits, increasing demand for specialized tooling and shop capabilities. Open fan and advanced propulsor concepts are emerging within demonstrator programs, shaping future maintenance competencies and supplier qualification pathways. Hybrid-electric assisted propulsion initiatives influence subsystem integration and thermal management requirements, prompting investments in diagnostics and digital twins. Technology choices are guided by certification readiness, reliability performance in high-cycle operations, and compatibility with sustainable fuel pathways.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment features vertically integrated engine programs alongside extensive aftermarket service ecosystems. Positioning is shaped by program participation across narrowbody and widebody platforms, domestic MRO footprints, digital health monitoring maturity, and regulatory readiness for next-generation propulsion architectures.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| GE Aerospace | 1892 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pratt & Whitney | 1925 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| CFM International | 1974 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rolls-Royce | 1906 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MTU Aero Engines | 1934 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA commercial aircraft engines Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Fleet renewal driven by fuel efficiency mandates
Airlines increased narrowbody deliveries to 912 units in 2024 and 874 units in 2025, driven by stricter emissions benchmarks under federal aviation standards and airport noise compliance thresholds. Average daily utilization across domestic short haul routes reached 7.8 cycles per aircraft in 2024, elevating engine on-wing requirements. Engine shop visit intervals compressed from 5.6 years in 2022 to 4.9 years in 2025 due to higher cycle intensity. Federal test programs expanded to 14 facilities in 2024 to validate low-emissions combustor performance. These indicators collectively reinforce propulsion upgrade demand anchored in regulatory compliance and operational efficiency mandates nationwide.
Surge in narrowbody deliveries for domestic route expansion
Domestic route additions increased by 312 city pairs in 2024 and 286 in 2025, supported by runway capacity expansions at 9 primary hubs and terminal throughput upgrades across 23 airports. Narrowbody utilization rose to 11.2 hours per day in 2025 from 10.4 in 2022, intensifying engine cycle accumulation. Dispatch reliability benchmarks tightened to 99.7 in 2024, pushing operators toward higher spare engine ratios of 0.14 in 2025 versus 0.11 in 2022. FAA airworthiness directives related to high-cycle fatigue prompted 27 compliance programs in 2024, reinforcing propulsion system demand aligned with network growth.
Challenges
Supply chain disruptions for castings forgings and semiconductors
Backlogs for precision castings extended to 38 weeks in 2024 from 21 weeks in 2022, constraining module availability for shop visits. Semiconductor lead times for FADEC components averaged 26 weeks in 2025, delaying line maintenance closures. Domestic forging capacity utilization reached 92 in 2024, limiting surge production during peak maintenance seasons. Quality escape incidents recorded 147 events in 2023 across certified suppliers, triggering additional inspections and rework cycles. Logistics dwell times at ports averaged 9 days in 2024, complicating just-in-time flows. These constraints elevate turnaround variability and pressure engine availability across high-cycle fleets.
Geared turbofan durability and premature shop visit issues
Premature removals rose to 3.4 events per 1,000 cycles in 2024 compared with 1.9 in 2022, driven by powder metal contamination findings and bearing wear. Inspection intervals shortened from 2,400 cycles in 2022 to 1,600 cycles in 2025 under revised airworthiness guidance. Engine change rates at major hubs increased to 1.6 per aircraft annually in 2025, elevating spare engine pooling requirements. Component scrap rates reached 7.2 in 2024 within affected modules. Additional non-destructive testing capacity expanded by 18 facilities in 2025, yet throughput remains constrained during peak maintenance windows nationwide.
Opportunities
Aftermarket services expansion through long-term service agreements
Contracted maintenance coverage expanded to 64 percent of domestic fleets in 2024 from 51 in 2022, reflecting operator preference for predictable uptime management. Engine health monitoring adoption reached 78 percent of active narrowbody fleets in 2025, enabling predictive interventions that reduced unscheduled removals by 214 incidents year over year. Shop visit planning accuracy improved with digital twins validated across 19 facilities in 2024. Turnaround time reductions of 6 days were recorded in 2025 across certified shops using advanced borescope analytics. Institutional safety targets set at 0.2 in-flight shutdowns per 100,000 hours incentivize service agreements.
Engine leasing and power-by-the-hour adoption by airlines
Spare engine leasing utilization increased to 0.18 per aircraft in 2024 from 0.12 in 2022, supporting higher dispatch reliability across high-cycle networks. Power-by-the-hour enrollment expanded to 43 percent of narrowbody fleets in 2025, stabilizing maintenance planning under variable utilization. Average contract tenors extended to 7 years in 2024, improving lifecycle alignment with fleet renewal schedules. Fleet technical reliability programs standardized 22 performance indicators across 2025 service contracts, enhancing accountability. Institutional financing frameworks for aviation assets approved 31 new leasing structures in 2024, lowering barriers for capacity access during peak maintenance demand.
Future Outlook
The market outlook to 2035 reflects sustained fleet renewal cycles, deeper digitalization of maintenance workflows, and broader certification of next-generation propulsion architectures. Policy emphasis on emissions performance and domestic manufacturing resilience will shape supplier investments and MRO capacity planning. Airlines are expected to deepen long-term service partnerships and expand predictive maintenance adoption. Technology maturation will influence time-on-wing reliability and lifecycle management strategies across high-utilization domestic networks.
Major Players
- GE Aerospace
- Pratt & Whitney
- CFM International
- Rolls-Royce
- Safran Aircraft Engines
- MTU Aero Engines
- RTX Corporation
- StandardAero
- AAR Corp
- Delta TechOps
- Lufthansa Technik
- SR Technics
- IAE International Aero Engines
- Triumph Group
- Barnes Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airlines and fleet operators
- Aircraft leasing companies
- Engine MRO providers and service networks
- Aerospace component manufacturers
- Airports and aviation infrastructure authorities
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Federal Aviation Administration and Department of Transportation
- State aviation authorities and regulatory agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core variables include fleet mix, engine architecture adoption, utilization intensity, maintenance cycles, regulatory compliance requirements, and MRO capacity distribution across domestic hubs. Data points are structured to reflect operational drivers and technology readiness within commercial propulsion ecosystems.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
The framework integrates fleet delivery schedules, utilization patterns, shop visit cycles, and regulatory directives to construct demand pathways across original equipment and aftermarket services. Cross-validation aligns operational indicators with infrastructure capacity and certification readiness.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions are tested through structured consultations with airline technical leadership, maintenance planners, certification specialists, and supply chain operations managers. Feedback loops refine cycle assumptions, capacity constraints, and adoption timelines.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are synthesized into scenario-based narratives linking policy direction, operational constraints, and technology maturation. Outputs prioritize decision relevance for fleet planning, capacity investments, and service network optimization.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for USA commercial aircraft propulsion platforms, Aircraft class and engine architecture taxonomy mapping across narrowbody widebody and regional fleets, Bottom-up market sizing using OEM delivery schedules airline fleet plans and engine shop visit data, Revenue attribution across OE engine sales spare parts and MRO service contracts)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and maintenance pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Fleet renewal driven by fuel efficiency mandates
Surge in narrowbody deliveries for domestic route expansion
Rising engine MRO demand from aging in-service fleets
Air cargo growth supporting freighter engine demand
OEM backlog fulfillment accelerating engine shipments
Sustainable aviation fuel compatibility driving engine upgrades - Challenges
Supply chain disruptions for castings forgings and semiconductors
Geared turbofan durability and premature shop visit issues
Skilled labor shortages in engine MRO facilities
Regulatory certification timelines for new engine architectures
Aftermarket parts shortages and long turnaround times
Capital intensity of next-generation engine programs - Opportunities
Aftermarket services expansion through long-term service agreements
Engine leasing and power-by-the-hour adoption by airlines
Retrofit programs for fuel efficiency and emissions compliance
Digital MRO analytics for predictive maintenance optimization
Partnerships with SAF producers for engine compatibility validation
Development of open fan demonstrators for future narrowbody fleets - Trends
Shift toward geared turbofan penetration in narrowbody fleets
Increased engine health monitoring and predictive maintenance adoption
Vertical integration between OEMs and MRO networks
Localization of critical component manufacturing in the USA
Lifecycle service bundling with aircraft acquisition
Rising investment in hybrid-electric propulsion R&D - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft fleets
Widebody aircraft fleets
Regional jet fleets
Cargo and freighter conversions - By Application (in Value %)
Passenger transport
Air cargo and logistics
Charter and ACMI operations
Government-supported commercial services - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
High-bypass turbofan engines
Geared turbofan engines
Open fan and advanced propulsor concepts
Hybrid-electric assisted propulsion - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Scheduled passenger airlines
Low-cost carriers
Air cargo operators
Aircraft leasing companies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
FADEC-enabled digital engine control
Health monitoring and prognostics connectivity
Airline-OEM digital twins integration
Secure data links with MRO platforms - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (engine thrust class coverage, platform program participation, OE versus aftermarket revenue mix, MRO network footprint in the USA, time-on-wing performance metrics, total cost of ownership for airlines, SAF compatibility readiness, digital health monitoring maturity)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
GE Aerospace
Pratt & Whitney
CFM International
Rolls-Royce
Safran Aircraft Engines
MTU Aero Engines
RTX Corporation
Boeing Global Services
StandardAero
AAR Corp
Delta TechOps
Lufthansa Technik
SR Technics
IAE International Aero Engines
Triumph Group
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


