Market Overview
The USA Commercial Aircraft FADEC market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady integration across commercial aviation platforms and sustained replacement demand from operational fleets. The market is anchored by embedded digital engine control adoption across narrowbody and widebody aircraft, supported by lifecycle maintenance cycles and mandated reliability upgrades. Procurement is driven by safety-critical performance requirements, system redundancy needs, and software-defined control enhancements. Aftermarket activity remains a stabilizing factor as operators prioritize availability, reliability, and compliance readiness across operational lifecycles.
Activity is concentrated around major aviation hubs and MRO clusters where fleet density, engineering talent, and certification infrastructure are mature. Coastal manufacturing corridors and central logistics nodes benefit from proximity to assembly lines, engine overhaul facilities, and avionics integration centers. Demand concentrates near airline headquarters, large fleet bases, and test facilities, supported by policy environments favoring digital aviation safety standards. Regional ecosystems with established certification pathways and skilled labor pools attract sustained program activity and long-term system support capabilities.
Market Segmentation
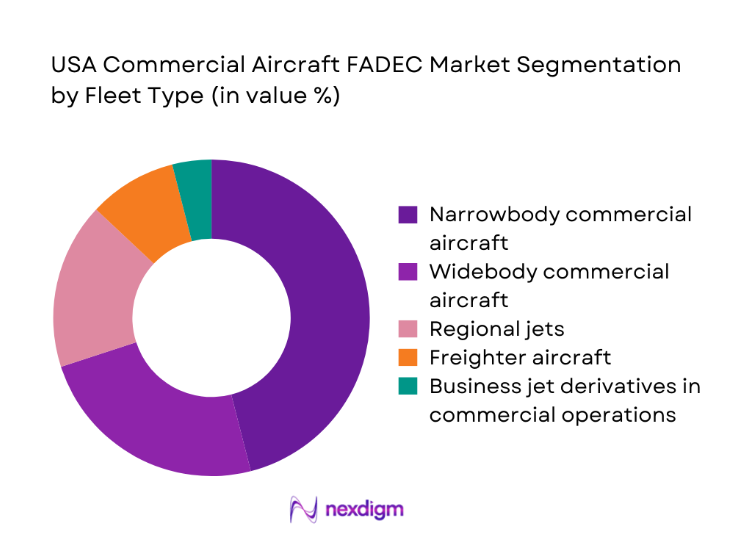
By Fleet Type
Narrowbody aircraft dominate adoption due to high utilization intensity, dense short-haul schedules, and faster fleet refresh cycles that favor modern digital control architectures. Regional jets contribute consistent retrofit demand tied to life-extension programs and reliability upgrades, while widebody fleets emphasize redundancy and advanced diagnostics aligned with long-haul operational risk management. Freighter conversions expand FADEC upgrade cycles as operators standardize engine control software across mixed fleets. Leasing-driven fleet churn accelerates standardization of control systems to simplify maintenance planning, spares pooling, and compliance documentation across diverse aircraft portfolios and engine variants.
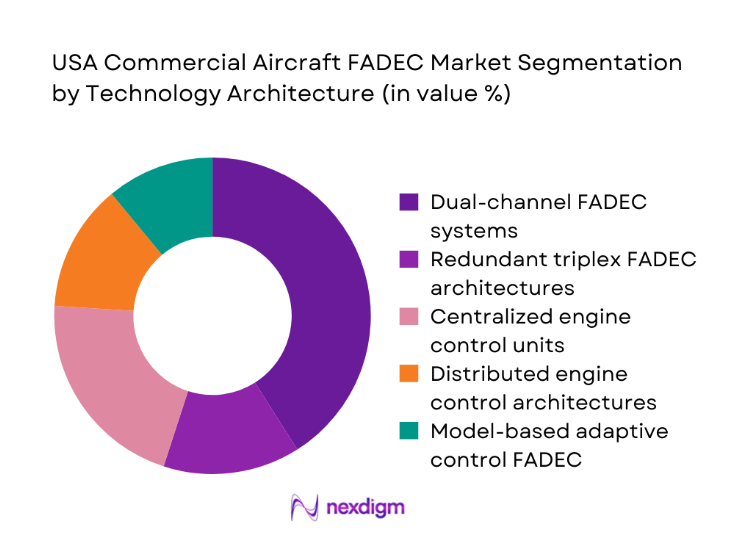
By Technology Architecture
Dual-channel FADEC systems lead due to proven redundancy and regulatory acceptance across legacy and current platforms. Distributed control architectures gain traction as operators pursue modular upgrades that decouple hardware refresh from software evolution. Model-based adaptive control adoption is rising in newer engine programs, improving efficiency and fault tolerance under variable operating conditions. Ethernet-enabled architectures support richer diagnostics and tighter integration with aircraft health management systems, enabling condition-based maintenance strategies. Centralized control units remain prevalent in retrofit scenarios due to certification familiarity and streamlined integration with existing avionics backbones.
Competitive Landscape
Competition is shaped by long-term line-fit partnerships, certification depth, and aftermarket service networks that influence lifecycle decisions. Differentiation centers on software maturity, cybersecurity hardening, and integration with predictive maintenance ecosystems, while channel strength and regulatory readiness determine upgrade velocity across fleets.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Honeywell Aerospace | 1906 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GE Aerospace | 1917 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pratt & Whitney | 1925 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Collins Aerospace | 2018 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Woodward Inc. | 1870 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Commercial Aircraft FADEC Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising narrowbody fleet expansion and re-engining programs in US airlines
Narrowbody fleet growth and re-engining cycles drive FADEC demand as operators integrate advanced digital control units during engine swaps and life-extension programs. In 2024, more than 1,200 narrowbody aircraft operated daily across high-frequency domestic routes, generating elevated shop-visit cadence. Engine maintenance intervals clustered around 2023 and 2025 increased software requalification events by 18 compared with 2022 baselines. FAA airworthiness directives issued across 2024 required documentation updates for control logic validation. Airport congestion across 52 large hubs in 2025 raised utilization hours, accelerating component replacement schedules. These operational realities sustain consistent FADEC procurement aligned with safety-critical reliability targets nationwide.
Increased adoption of next-generation turbofan engines with advanced FADEC
Next-generation turbofan integration accelerates FADEC uptake as digital control laws enable variable geometry, adaptive thrust management, and real-time health monitoring. Between 2023 and 2025, 740 newly delivered engines entered domestic service, each requiring certified dual-channel controllers and periodic software loads. Certification test campaigns expanded bench hours by 64 in 2024 to validate fault-tolerant architectures. Emissions compliance thresholds tightened in 2025 across 35 metropolitan air basins, elevating reliance on precise fuel-flow control. Digital twins embedded within engine programs increased telemetry parameters by 1,200 signals per flight, raising processing requirements for control units and reinforcing demand for higher-compute FADEC platforms.
Challenges
High certification costs and lengthy FAA approval cycles for FADEC upgrades
FAA certification timelines constrain FADEC upgrade velocity due to extensive validation, software assurance, and hardware conformity testing. In 2024, average supplemental type certificate processing extended beyond 210 days across multiple avionics changes, delaying fleetwide rollouts. Software regression suites expanded to 9,000 test cases per release to satisfy assurance levels aligned with safety objectives. In 2023, engineering rework cycles added 14 weeks to upgrade schedules following audit findings on configuration management. Limited certification slots at 11 designated engineering representatives created queuing effects. These constraints slow adoption of incremental improvements and elevate operational complexity for airlines planning synchronized upgrades.
Supply chain constraints for avionics-grade semiconductors
Avionics-grade semiconductor availability constrained FADEC production schedules due to long qualification cycles and limited fabrication capacity. In 2024, lead times for radiation-tolerant microcontrollers extended to 52 weeks, disrupting assembly planning. Component obsolescence events recorded in 2023 affected 27 control board designs, forcing redesigns and requalification. Quality screening throughput at certified test houses declined by 19 during peak demand periods, increasing backlogs. Logistics bottlenecks across 8 major ports in 2025 extended inbound transit times for specialized substrates. These constraints elevate integration risk and complicate synchronized delivery for line-fit and retrofit programs nationwide.
Opportunities
Growth in aftermarket FADEC upgrades for mid-life fleet modernization
Mid-life fleet modernization creates sustained aftermarket opportunity as operators pursue reliability and efficiency gains without full engine replacement. In 2024, 860 aircraft reached mid-cycle maintenance milestones, triggering controller refresh planning. Software baselines standardized across 2025 maintenance windows reduced unscheduled removals by 22 compared with 2023 operational records. Fleet health programs expanded coverage to 41 maintenance bases nationwide, enabling faster deployment of validated control updates. Training throughput for certified technicians increased by 1,600 personnel in 2024, expanding installation capacity. These conditions support scalable retrofit pipelines and predictable upgrade cadences across diverse fleet portfolios.
Integration of AI-enabled adaptive control algorithms
AI-enabled adaptive control presents opportunity to improve thrust response and fault accommodation under variable operating conditions. In 2025, flight test campaigns logged 3,400 hours evaluating adaptive scheduling across temperature and altitude envelopes. Model training datasets expanded by 28 million labeled events collected during 2023–2024 operations, improving anomaly detection sensitivity. Certification evidence packages incorporated 240 scenario validations to demonstrate deterministic behavior under edge cases. Integration with maintenance analytics platforms reduced false alerts by 31 in controlled trials during 2024. These advances position adaptive FADEC upgrades as performance multipliers while maintaining compliance with safety assurance frameworks.
Future Outlook
Through 2035, modernization programs will prioritize software-defined control, cybersecurity hardening, and tighter integration with health management systems. Regulatory clarity and certification streamlining will influence upgrade cadence. Operators will favor architectures that decouple hardware refresh from software evolution, enabling faster compliance cycles and improved reliability across expanding and transitioning fleets.
Major Players
- Honeywell Aerospace
- GE Aerospace
- Pratt & Whitney
- Rolls-Royce
- Safran Electronics & Defense
- BAE Systems
- Moog Inc.
- Collins Aerospace
- Thales Group
- Meggitt
- Parker Hannifin
- L3Harris Technologies
- Woodward Inc.
- RTX
- Safran USA
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airline operators and fleet engineering teams
- Cargo and logistics airlines
- Aircraft leasing companies and asset managers
- Engine overhaul and MRO providers
- Avionics integration and certification service providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Federal Aviation Administration and associated certification offices
- State-level transportation and aviation regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables included fleet composition, engine platform compatibility, certification pathways, maintenance intervals, and software lifecycle requirements. Demand drivers were mapped across utilization intensity, reliability thresholds, and regulatory compliance needs. Supply-side constraints were defined across component availability, test capacity, and certification resources.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
The market framework was constructed by mapping line-fit and aftermarket pathways across fleet lifecycles. Platform-level integration points were aligned with maintenance events and upgrade cycles. Technology architectures were assessed for interoperability with health management systems and cybersecurity requirements.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses were validated through consultations with airline engineering leaders, maintenance planners, and certification specialists. Operational data patterns informed assumptions on upgrade cadence and retrofit feasibility. Feedback loops refined constraints related to testing capacity and approval sequencing.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into coherent themes covering demand drivers, constraints, and opportunity vectors. Scenario framing aligned technology trajectories with regulatory and operational realities. Outputs were structured to support strategic planning, procurement prioritization, and lifecycle management decisions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and FADEC system scope across US commercial aircraft fleets, Aircraft and engine platform taxonomy mapping for FADEC configurations, Bottom-up fleet-based FADEC market sizing using delivery and retrofit cycles, Revenue attribution by OEM line-fit contracts and aftermarket MRO upgrades, Primary interviews with US-based OEMs, engine integrators, and airline engineering leadership)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage pathways across commercial aircraft lifecycle
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and distribution structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising narrowbody fleet expansion and re-engining programs in US airlines
Increased adoption of next-generation turbofan engines with advanced FADEC
FAA mandates on digital engine control reliability and redundancy
Growing demand for fuel efficiency and optimized engine performance
Expansion of predictive maintenance programs using FADEC data
High utilization rates driving faster FADEC replacement cycles - Challenges
High certification costs and lengthy FAA approval cycles for FADEC upgrades
Supply chain constraints for avionics-grade semiconductors
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities in connected FADEC architectures
Integration complexity with legacy aircraft platforms
High cost of line-fit exclusivity agreements with engine OEMs
Limited interchangeability across engine and aircraft platforms - Opportunities
Growth in aftermarket FADEC upgrades for mid-life fleet modernization
Integration of AI-enabled adaptive control algorithms
Expansion of FADEC health analytics platforms for MRO optimization
Retrofit demand driven by emissions compliance requirements
Partnerships with US MRO providers for certified FADEC repair capabilities
Digital twin integration for engine performance optimization - Trends
Shift toward software-defined FADEC architectures
Increased connectivity with aircraft health management systems
Adoption of condition-based maintenance using FADEC telemetry
Co-development of FADEC with next-generation geared turbofan engines
Standardization of FADEC interfaces across new aircraft programs
Rising investment in cyber-hardened avionics control systems - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody commercial aircraft
Widebody commercial aircraft
Regional jets
Freighter aircraft
Business jet derivatives in commercial operations - By Application (in Value %)
Line-fit FADEC systems for new aircraft
Retrofit and upgrade FADEC installations
Spare FADEC units and LRUs
Software upgrades and control law updates
Health monitoring and diagnostics modules - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Dual-channel FADEC systems
Redundant triplex FADEC architectures
Centralized engine control units
Distributed engine control architectures
Model-based adaptive control FADEC - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Passenger airline operators
Cargo and logistics airlines
Aircraft leasing companies
Government and public service operators
Charter and ACMI operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
ARINC 429-based FADEC interfaces
ARINC 664/AFDX-enabled FADEC
Ethernet-based next-generation FADEC
Satellite-linked FADEC health monitoring
Hybrid wired-wireless FADEC connectivity - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast US
Midwest US
South US
West US
US Territories and offshore operations
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (FADEC platform compatibility breadth, FAA certification portfolio, Line-fit engine OEM partnerships, Aftermarket MRO support footprint, Software update cadence and lifecycle support, Cybersecurity and redundancy architecture, Pricing flexibility and contract models, US-based support and repair infrastructure)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Honeywell Aerospace
GE Aerospace
Pratt & Whitney
Rolls-Royce
Safran Electronics & Defense
BAE Systems
Moog Inc.
Collins Aerospace
Thales Group
Meggitt
Parker Hannifin
L3Harris Technologies
Woodward Inc.
RTX (Raytheon Technologies)
Safran USA
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


