Market Overview
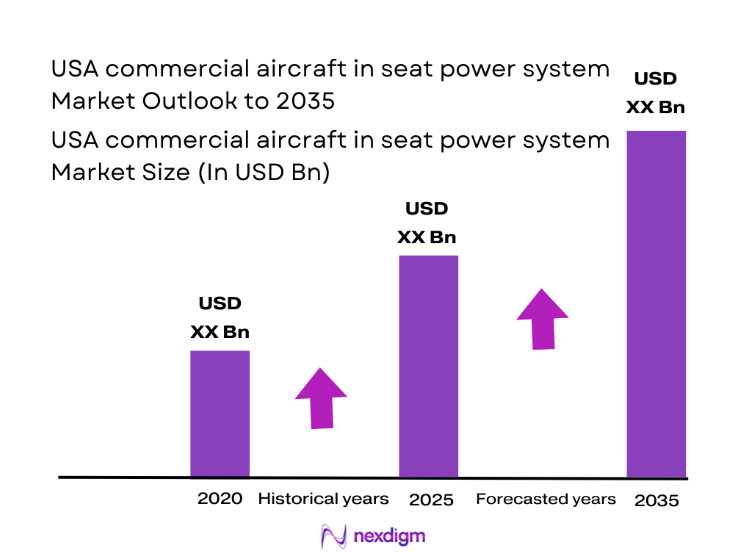
The USA commercial aircraft in seat power system market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained demand for certified onboard power solutions integrated within passenger seating. The market is shaped by fleet modernization cycles, mandatory compliance with aviation safety standards, and increasing device charging requirements across cabin classes. Investment in lightweight power electronics and modular seat architectures supports adoption, while maintenance and retrofit activities reinforce recurring demand through certified replacement components and service agreements across commercial aviation operators.
Demand concentration is strongest across major airline hubs and maintenance clusters, supported by dense route networks, high aircraft utilization, and mature MRO ecosystems. Regions with large narrowbody fleets benefit from faster retrofit cycles, while hubs hosting major seat integration facilities show stronger supplier presence. Policy environments emphasizing safety certification, electrical load management, and cabin safety compliance shape adoption patterns, alongside airport infrastructure that supports rapid aircraft turnaround and standardized cabin maintenance workflows.

Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
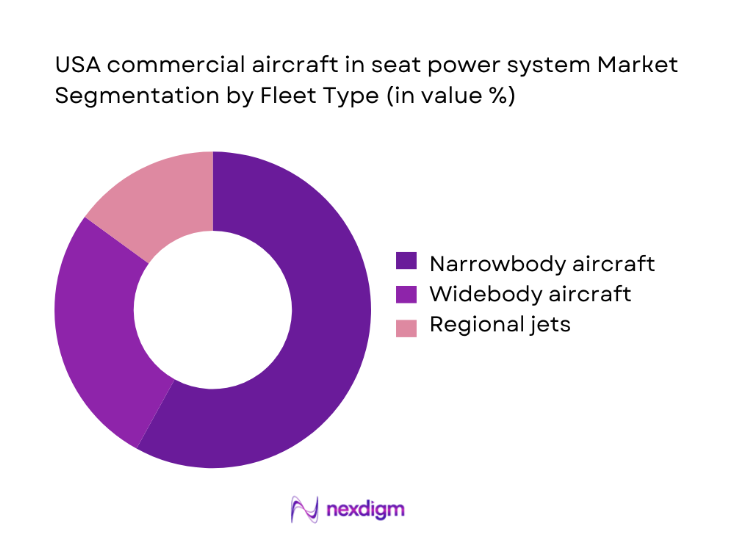
Narrowbody aircraft dominate adoption due to higher utilization rates on domestic routes, frequent cabin refresh cycles, and standardized seat architectures enabling faster power system retrofits. High-density single-aisle fleets operate multiple daily rotations, increasing wear on power outlets and accelerating replacement demand. Retrofit programs are prioritized on these fleets to align with device charging expectations and operational reliability requirements. Widebody aircraft contribute through premium cabin upgrades and long-haul utilization needs, while regional jets show selective adoption linked to weight and power budget constraints. Fleet harmonization strategies further reinforce standardized power modules across narrowbody platforms to streamline maintenance and certification workflows.
By Technology Architecture
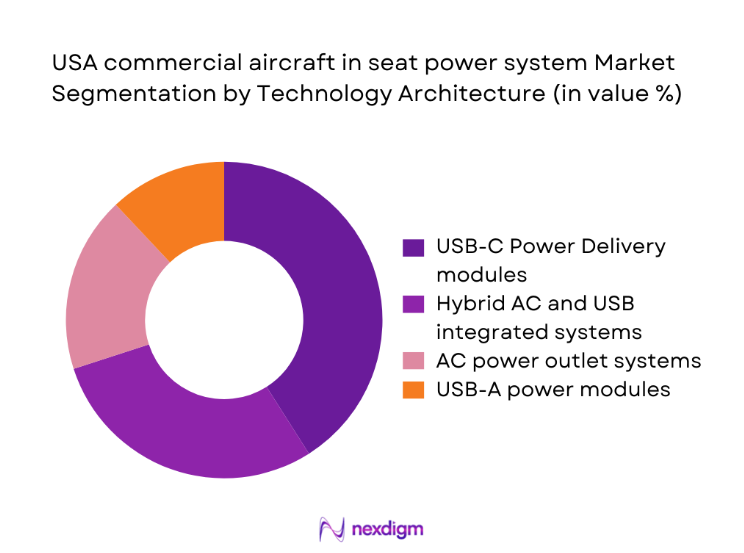
USB-C Power Delivery systems lead technology adoption as airlines prioritize higher wattage charging for modern devices and simplify cabin power management. Hybrid AC and USB configurations remain relevant in premium cabins where legacy device compatibility is required. AC outlets persist in selected long-haul configurations but face gradual rationalization due to weight and maintenance complexity. USB-A modules continue to serve backward compatibility needs during phased retrofits. Technology standardization across seat platforms reduces certification overhead and enables modular replacement strategies, while smart power management architectures support load balancing across cabin zones and improve reliability under peak charging demand.
Competitive Landscape
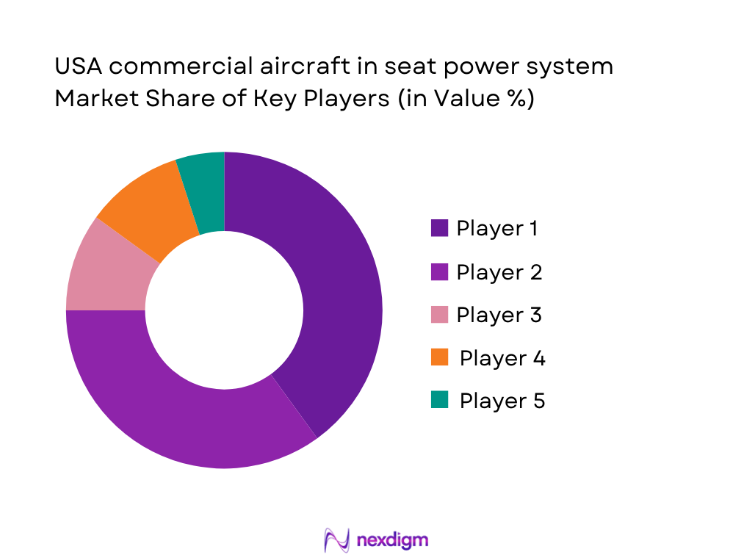
The competitive landscape is characterized by specialized aviation power system integrators and seat system partners focused on certification readiness, linefit integration, and aftermarket support. Competitive differentiation centers on power density performance, certification track record, and the ability to support fleet-wide retrofit programs with reliable logistics and service capabilities.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Astronics Corporation | 1968 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Safran Seats | 2018 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Collins Aerospace | 2018 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Panasonic Avionics Corporation | 1979 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Diehl Aviation | 2006 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA commercial aircraft in seat power system Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising passenger expectation for personal device charging on domestic flights
Passenger device dependence intensified across domestic air travel, with Transportation Security Administration checkpoint volumes exceeding 760000000 in 2024 and 780000000 in 2025, increasing dwell time and in-flight device usage. Federal Aviation Administration data recorded 7800 commercial aircraft in active U.S. service during 2024, with average daily utilization surpassing 10 flight hours per aircraft. U.S. smartphone shipments exceeded 160000000 units in 2024, with tablet shipments at 50000000 units, driving charging demand onboard. Department of Transportation on-time performance reporting highlights longer gate dwell times in 2024, reinforcing passenger reliance on seat power during delays. Airlines prioritize cabin power availability to maintain satisfaction amid congestion and operational volatility.
Fleet modernization and cabin retrofit programs across U.S. carriers
The Federal Aviation Administration certified 4200 supplemental type certificates during 2024 and 2025 for cabin modifications, indicating sustained retrofit momentum. Boeing delivered 528 narrowbody aircraft to U.S. operators in 2024, while Airbus deliveries to U.S. carriers reached 310 units in 2025, expanding the installed base requiring linefit power integration. The U.S. Department of Transportation reported average fleet age declining from 14.6 years in 2023 to 13.9 years in 2025 among major carriers, reflecting accelerated renewal. Major maintenance events averaged every 6 years for narrowbody cabins, triggering power system replacements aligned with seat refresh cycles. Certification throughput and delivery volumes jointly reinforce near-term installation demand.
Challenges
Stringent FAA certification and STC approval timelines
Federal Aviation Administration engineering review cycles averaged 180 days for electrical system modifications in 2024, extending to 210 days in 2025 due to staffing constraints. The number of FAA Designated Engineering Representatives active in avionics programs declined to 1320 in 2024 from 1460 in 2022, slowing throughput. Cabin power installations require compliance with FAR 25 electrical load, flammability, and smoke emission tests, each requiring laboratory cycles exceeding 30 days per iteration. The FAA reported 9800 certification backlog items in 2024 across cabin systems. These constraints elongate airline retrofit schedules, disrupt induction planning at MRO facilities, and increase downtime during peak travel seasons, affecting fleet availability and operational planning.
Weight and power budget constraints in single-aisle aircraft
Average single-aisle aircraft electrical generation capacity is constrained by auxiliary power unit limits of 90 kVA, with cabin systems competing against galley loads, IFE, and connectivity. FAA advisory circulars require load margin buffers of 10 percent, limiting incremental power allocation to seats. In 2024, U.S. carriers reported average cabin density of 176 seats per narrowbody, amplifying cumulative power draw per flight segment. Engineering assessments indicate incremental wiring adds 120 kilograms per aircraft, impacting fuel burn. The Environmental Protection Agency aircraft emissions reporting framework in 2025 heightened scrutiny on weight additions. These constraints necessitate careful power budgeting and lightweight component adoption, complicating retrofit scope and approval timelines.
Opportunities
Linefit installations on new narrowbody deliveries
Boeing and Airbus narrowbody deliveries to U.S. operators totaled 838 units across 2024 and 2025, creating linefit opportunities where power systems are integrated during manufacturing. Linefit reduces aircraft downtime by avoiding post-delivery modifications, with installation labor hours reduced by 40 per aircraft compared to retrofit benchmarks. FAA conformity inspections are completed during production, shortening entry-into-service timelines by 14 days. U.S. airline fleet plans filed with the Department of Transportation indicate sustained narrowbody induction through 2025, aligning with cabin standardization strategies. Coordinated production integration improves configuration control, reduces wiring rework, and supports faster certification acceptance for standardized power architectures across multiple aircraft types.
Standardization of USB-C PD across cabin classes
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology recognized USB-C PD interoperability frameworks in 2024, supporting harmonized power delivery up to 240 watts across devices. Consumer Electronics Association shipment data shows over 120000000 USB-C devices sold domestically in 2025, accelerating compatibility benefits. Standardization reduces the number of power SKUs per aircraft from 4 to 2, cutting spares complexity. Maintenance task cards decline by 18 per aircraft due to simplified diagnostics. FAA electrical conformity tests benefit from reduced variance in load profiles, improving approval predictability. Airlines adopting single-standard architectures improve training efficiency for technicians and enhance reliability by minimizing connector heterogeneity across cabin zones.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to advance through sustained fleet induction and recurring retrofit cycles, with increasing standardization of power architectures across cabins. Regulatory alignment around electrical safety and load management will shape product design priorities. Integration with cabin connectivity platforms will accelerate as airlines pursue harmonized digital cabin strategies through the forecast period.
Major Players
- Astronics Corporation
- Safran Seats
- Collins Aerospace
- Panasonic Avionics Corporation
- Diehl Aviation
- Thales Group
- RECARO Aircraft Seating
- Jamco Corporation
- Burrana
- Lufthansa Technik
- Amphenol PCD
- Mid-Continent Instrument
- KID-Systeme
- B/E Aerospace
- Zodiac Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airline fleet planning departments
- Aircraft interior integration teams at OEMs
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul providers
- Cabin systems certification specialists
- Supply chain and procurement leaders at airlines
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names including Federal Aviation Administration and Department of Transportation
- Airport operations authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Variables were defined around aircraft fleet composition, cabin density, electrical load constraints, certification pathways, and maintenance cycles specific to in-seat power systems. Data points included delivery pipelines, retrofit cadences, and certification backlogs across domestic operations.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
The market construct aligned fleet induction, retrofit events, and certification throughput with installation pathways across linefit and aftermarket programs. Interdependencies among power architecture, wiring weight, and maintenance intervals were modeled to reflect operational constraints.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on adoption pathways and technology standardization were validated through structured consultations with airline engineering leaders, certification specialists, and MRO program managers involved in cabin modifications and compliance workflows.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into a cohesive framework linking regulatory readiness, operational constraints, and technology evolution. Insights were stress-tested against institutional indicators and reconciled across fleet operations, certification processes, and maintenance practices.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope for in-seat power systems across U.S. commercial aircraft fleets, Aircraft class and power architecture taxonomy aligned to linefit and retrofit programs, Bottom-up market sizing using aircraft deliveries retrofits and seat-shipset penetration rates, Revenue attribution by shipset pricing STC upgrade contracts and aftermarket spares)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage patterns across cabin classes
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising passenger expectation for personal device charging on domestic flights
Fleet modernization and cabin retrofit programs across U.S. carriers
Adoption of USB-C Power Delivery for higher wattage devices
Growth in BYOD usage reducing reliance on embedded IFE screens
Increased aircraft utilization rates on narrowbody fleets
Regulatory push for certified low-smoke low-heat power electronics - Challenges
Stringent FAA certification and STC approval timelines
Weight and power budget constraints in single-aisle aircraft
Supply chain volatility in power electronics and connectors
Integration complexity with legacy seat and IFE platforms
Airline capex cyclicality and retrofit deferrals
Thermal management and reliability issues under high device loads - Opportunities
Linefit installations on new narrowbody deliveries
Standardization of USB-C PD across cabin classes
Retrofit demand driven by cabin densification programs
Aftermarket spares and maintenance contracts with U.S. carriers
Partnerships with seat OEMs for integrated power solutions
Upgrades aligned with next-generation cabin connectivity rollouts - Trends
Shift from AC outlets to high-wattage USB-C PD ports
Modular power units enabling faster seat reconfiguration
Integration of power health monitoring into cabin systems
Lightweight power electronics and smart load management
Convergence of seat power and connectivity platforms
Increased use of certified off-the-shelf power modules - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrowbody aircraft
Widebody aircraft
Regional jets
Business class configured sub-fleets within commercial aircraft - By Application (in Value %)
Passenger device charging
IFE system power delivery
Crew power outlets
Seat-back embedded electronics - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
AC power outlet systems
USB-A power modules
USB-C Power Delivery modules
Hybrid AC and USB integrated systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Passenger airlines
Charter and ACMI operators
Low-cost carriers
Premium full-service carriers - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Hardwired seat power systems
Seat power integrated with IFE networks
Seat power integrated with cabin connectivity management systems - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast U.S.
Midwest U.S.
South U.S.
West U.S.
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (product wattage range certification coverage airline program penetration seat OEM partnerships pricing flexibility aftermarket support STC portfolio U.S. carrier references)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Astronics Corporation
KID-Systeme GmbH
Diehl Aviation
Safran Seats
Thales Group
Collins Aerospace
Panasonic Avionics Corporation
Burrana
RECARO Aircraft Seating
Zodiac Aerospace
Mid-Continent Instrument Co.
Amphenol PCD
Lufthansa Technik
JAMCO Corporation
B/E Aerospace
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


