Market Overview
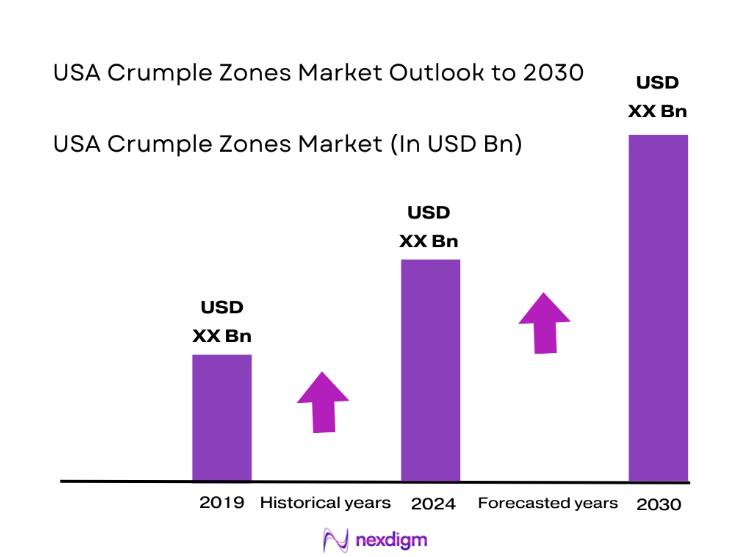
The USA Crumple Zones Market is valued at USD ~, reflecting its position as a structurally critical segment of the automotive safety ecosystem. Demand is fundamentally driven by regulatory enforcement of crashworthiness standards, OEM commitments to five-star safety ratings, and the growing complexity of vehicle architectures that require advanced energy-absorption systems. Crumple zones have evolved from basic deformation structures into engineered safety modules that integrate materials science, digital crash simulation, and modular manufacturing. Their role is no longer limited to passive protection but extends to enabling safer electrification, optimizing body-in-white design, and reducing total accident severity costs across the automotive value chain.
Within the country, dominance is concentrated in automotive manufacturing corridors such as the Midwest and the Southern production belt, where the density of OEM assembly plants and Tier-one suppliers accelerates innovation and large-scale deployment of advanced crash structures. These regions benefit from proximity to testing facilities, materials research centers, and skilled engineering talent. At the technology and supply level, the market is strongly influenced by global safety-engineering ecosystems that shape design standards, simulation tools, and advanced materials, even though production and integration remain domestically anchored. This combination of regional manufacturing strength and global technology leadership reinforces the USA’s central role in shaping next-generation crumple zone systems.
Market Segmentation
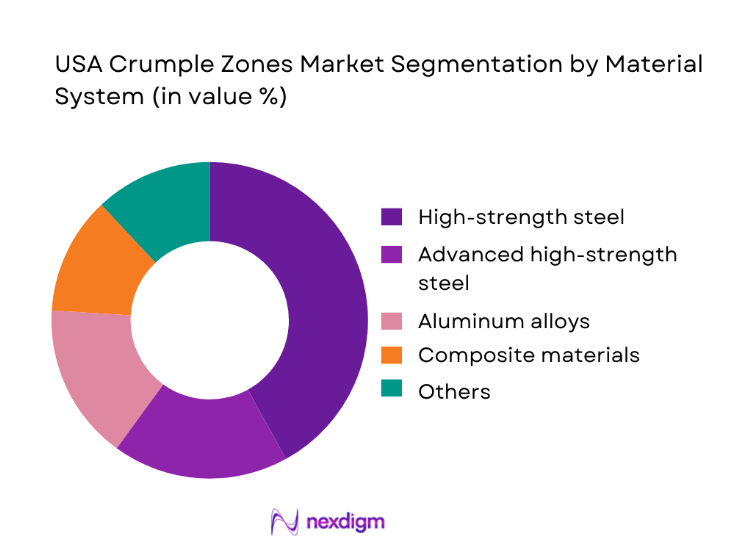
By Material System
The USA Crumple Zones Market is segmented by material system into high-strength steel, advanced high-strength steel, aluminum alloys, composite materials, magnesium alloys, and hybrid multi-material structures. High-strength steel continues to dominate this segmentation because it delivers the most reliable balance between controlled deformation, cost efficiency, and large-scale manufacturability. OEMs prioritize predictable crash behavior that aligns with regulatory test protocols, and steel-based structures offer unmatched consistency in energy absorption across varied impact scenarios. In addition, the established tooling ecosystem for stamped steel enables faster platform rollouts and easier localization, which is critical in high-volume passenger vehicle production. While aluminum and composites gain relevance in lightweighting strategies, their higher joining complexity and cost barriers limit universal adoption. As a result, high-strength steel remains the backbone of crumple zone engineering, especially for mainstream vehicle platforms where safety compliance and production economics are equally decisive.
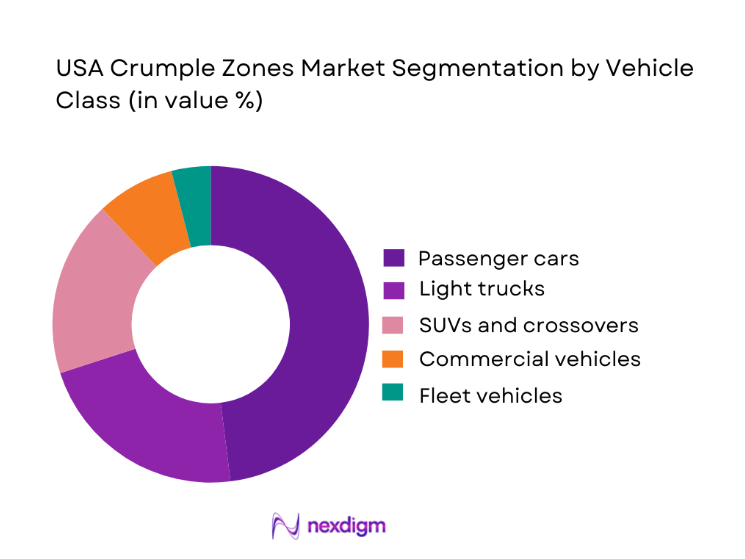
By Vehicle Class
The market is segmented into passenger cars, light trucks, SUVs and crossovers, commercial vehicles, and fleet vehicles. Passenger cars lead this segmentation due to their sheer production volumes and the intense influence of consumer safety ratings on purchase behavior. Manufacturers consistently prioritize advanced crash structures in passenger vehicles to achieve top-tier safety scores, which directly translate into brand trust and market competitiveness. In addition, urban driving patterns and higher accident exposure rates further justify OEM investment in refined crumple zone designs for this segment. While SUVs and light trucks continue to expand in popularity, passenger cars remain the primary testing ground for new safety architectures, adaptive deformation strategies, and cost-optimized materials. This first-mover advantage ensures that innovations in crumple zone technology typically debut in passenger vehicles before scaling across other classes, reinforcing their dominant share in the overall market.
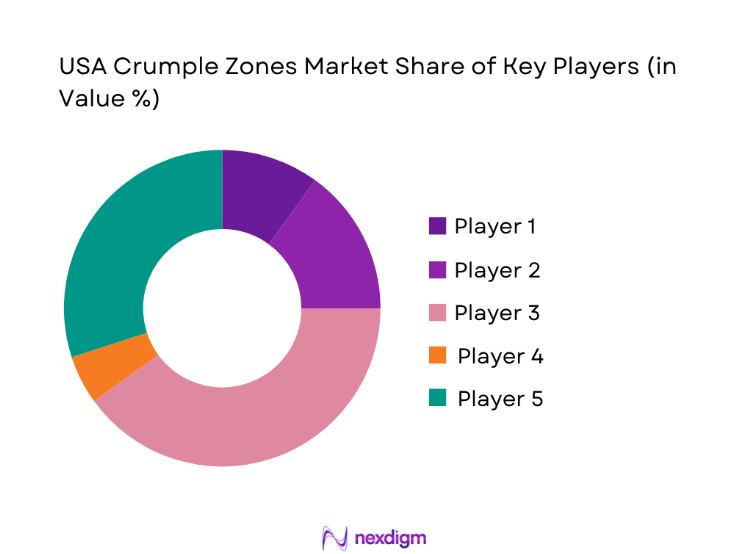
Competitive Landscape
The USA Crumple Zones Market market is dominated by a few major players, including Magna International and global or regional brands like ZF Friedrichshafen, Autoliv, and Hyundai Mobis. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Est. Year | Headquarters | Core Technology Focus | Material Expertise | OEM Partnerships | EV Integration Capability | Crash Test Validation Wins | R&D Investment Level |
| Magna International | 1957 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ZF Friedrichshafen | 1915 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lear Corporation | 1917 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hyundai Mobis | 1977 | South Korea | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Autoliv | 1953 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Crumple Zones Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Regulatory escalation in crash safety standards
Escalating safety regulations across the automotive sector have transformed crumple zones from optional design features into mandatory engineering priorities. Stricter frontal, side-impact, and rollover protection requirements compel OEMs to invest heavily in advanced energy-absorbing structures. This regulatory pressure directly drives demand for sophisticated material systems, modular crash components, and validated deformation behavior. As safety benchmarks rise, manufacturers compete to exceed minimum compliance, positioning superior crash performance as a brand differentiator. The result is a virtuous cycle where regulation stimulates innovation, innovation increases product value, and higher value reinforces market expansion across vehicle categories.
Electrification-driven structural redesign
The rapid shift toward electrified vehicles is fundamentally reshaping vehicle architecture, placing crumple zones at the center of battery protection strategies. Unlike conventional powertrains, electric platforms require crash structures that not only absorb kinetic energy but also shield high-voltage systems from intrusion and thermal risk. This has elevated the strategic importance of front, side, and underbody deformation zones. As OEMs redesign platforms around battery packs, crumple zone systems are becoming more complex, more integrated, and more valuable. This structural transformation drives sustained investment and accelerates the adoption of next-generation crash management technologies.
Challenges
Multi-material joining complexity
The growing use of mixed materials in crumple zone design introduces major engineering and manufacturing challenges. Joining steel with aluminum or composites requires advanced bonding, welding, and fastening techniques that increase production complexity and quality risk. These processes demand higher capital investment and specialized expertise, often extending development timelines. For many OEMs, this complexity slows the pace of innovation and raises the total cost of ownership for new safety architectures. As a result, the market faces a constant tension between performance optimization and manufacturability, which shapes strategic material choices.
High tooling and validation costs
Crumple zone systems require extensive physical and virtual testing to meet safety certification standards. Each design iteration involves costly tooling changes, crash simulations, and real-world impact testing. These high validation costs disproportionately affect smaller suppliers and new entrants, reinforcing market concentration among established players. For OEMs, the financial burden of repeated safety validation can delay platform launches and limit experimentation with novel materials or designs. This economic pressure constrains the speed of technological diffusion despite strong long-term demand fundamentals.
Opportunities
Adaptive and smart crumple zone development
The integration of sensors and intelligent control systems into crash structures presents a transformative opportunity for the market. Adaptive crumple zones that respond dynamically to impact conditions can significantly enhance occupant protection while optimizing structural efficiency. This evolution aligns with the broader shift toward software-defined vehicles, where safety becomes an active system rather than a purely passive feature. Suppliers that master this convergence of mechanics and electronics will gain strong competitive positioning in future vehicle platforms.
Lightweighting for EV range optimization
As vehicle electrification accelerates, weight reduction becomes a strategic imperative to extend driving range and improve energy efficiency. Crumple zones are increasingly targeted for lightweighting through advanced alloys and composites that maintain crash performance while reducing mass. This creates a powerful opportunity for material innovators and system integrators who can deliver validated safety outcomes with lower structural weight. The ability to balance crash protection and efficiency will define next-generation competitive advantage in the market.
Future Outlook
The USA Crumple Zones Market is positioned for structurally sustained growth as safety regulation, electrification, and digital engineering converge to redefine crash management systems. Over the coming years, the market will move beyond traditional deformation structures toward intelligent, modular, and sustainability-aligned safety architectures. Companies that invest in adaptive technologies, multi-material expertise, and simulation-driven design will shape the next phase of competitive leadership, while OEMs increasingly view crumple zones as strategic enablers of brand value, regulatory compliance, and long-term vehicle platform resilience.
Major Players
- Magna International
- ZF Friedrichshafen
- Autoliv
- Hyundai Mobis
- Lear Corporation
- Continental Automotive
- Robert Bosch Mobility
- Denso Corporation
- Aisin Corporation
- Benteler Automotive
- Martinrea International
- Valeo
- Faurecia Forvia
- Toyota Boshoku
- Gestamp
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEM safety engineering divisions
- Tier-one body-in-white and crash system suppliers
- Electric vehicle platform development teams
- Fleet and mobility service operators
- Automotive component procurement leaders
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies (NHTSA, IIHS)
- Automotive insurance and risk assessment organizations
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with mapping the complete crumple zone ecosystem, covering OEMs, suppliers, material innovators, and regulatory authorities. Secondary intelligence sources and proprietary automotive databases are used to define the core demand, supply, and technology variables shaping the market.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical production data, safety compliance trends, and supplier revenue streams are analyzed to construct the market framework. This phase establishes correlations between vehicle output, regulatory intensity, and crash system adoption patterns.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Preliminary findings are validated through structured consultations with safety engineers, procurement leaders, and materials specialists. These discussions refine assumptions related to technology adoption, cost structures, and future demand drivers.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All quantitative and qualitative insights are synthesized into a unified market model. Cross-validation ensures consistency between top-down regulatory impact assessment and bottom-up supplier revenue analysis, resulting in a robust final report.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, terminology and abbreviations, crumple zone design and materials taxonomy, market sizing logic by vehicle production and system content value, revenue attribution across components materials and integration services, primary interview program with OEMs Tier 1s safety engineers and materials suppliers, data triangulation and validation approach, assumptions limitations and data gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution of Crash Energy Management Systems
- Safety Regulation Impact on Crumple Zone Adoption and Standardization
- Vehicle Architecture Mapping and Front Rear Crumple Strategy Trends
- Value Chain Structure Across OEMs Tier 1 Body in White and Materials Suppliers
- Growth Drivers
Stringent safety regulations and NCAP requirement escalation
OEM focus on improved crash test ratings and occupant protection
Increasing adoption of lightweighting strategies with crash performance retention
Shift toward integrated safety module strategies
Rising consumer awareness of safety ratings and insurance incentives - Challenges
Cost weight and manufacturability trade offs in lightweight solutions
Complexity of material joining and mixed material interfaces
High tooling and validation costs for new platforms
Crashworthiness performance variability across vehicle segments
Aftermarket retrofit limitations and safety compliance concerns - Opportunities
Modular crash box and energy absorber solutions for rapid platform derivatives
Advanced composite adoption for dual benefit of weight and energy absorption
Localized crumple zone design centers for US OEM programs
Digital simulation and CAE optimization services for crash energy management
Partnership programs between material innovators and Tier 1 integrators - Trends
Increased use of mixed materials and aluminum intensive structures
Growth in composite and engineered polymer energy absorbers
Simulation led design workflows for optimization of energy paths
Integration of crash sensors and structural health monitoring
Standardization of energy management architectures across EV and ICE platforms - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By System Content Value per Vehicle, 2019–2024
- By OEM vs Aftermarket Revenue Split, 2019–2024
- By Segment Mix and ASP Waterfall, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger cars
SUVs and crossovers
Light trucks and pickup vehicles
Heavy duty vehicles and vocational platforms
Electric and hybrid vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Front crumple zones
Rear crumple zones
Side impact energy management
Corner and integrated safety modules
Pedestrian protection energy absorbers - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
High strength steel based designs
Aluminum and mixed metal energy absorbers
Advanced composites and hybrid structures
Foam filled and sacrificial insert systems
Crash box and modular energy tube solutions - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
OEM platform nomination and direct integration
Tier 1 module supply and assembly
Sub tier component and material supply
Aftermarket replacement and retrofit channels
Contract manufacturing and conversion programs - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Light vehicle OEMs
Commercial vehicle OEMs
Tier 1 body structure module suppliers
Aftermarket collision repair and body shops
Material suppliers and converters - By Region (in Value %)
Midwest automotive manufacturing belt
Southeast production corridor
Texas and South Central heavy vehicle hubs
West Coast EV and advanced vehicle production region
Northeast engineering and OEM clusters
- Competitive ecosystem structure across OEM nominated body structure specialists and materials innovators
- Positioning driven by crash performance validation manufacturing scalability and cost effectiveness
- Partnership models between OEMs Tier 1s and materials technology providers
- Cross Comparison Parameters (energy absorption per impact speed, specific energy absorption efficiency, material density and mass penalty, manufacturability and joining complexity, crash simulation correlation and test validation, integration readiness with platform architecture, warranty and quality performance, cost competitiveness)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and commercial model benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Magna International
Gestamp
Benteler
Dura Automotive Systems
Tower International
Dongfeng Structural Components
Shiloh Industries
AK Steel / Cleveland Cliffs
Novelis
SGL Carbon
Rockwest Composites
Hexagon Metrology
Plasan Advanced Composites
Faurecia
- OEM chassis body engineering priorities and specification drivers
- Tier 1 module integration evaluation criteria
- Aftermarket body shop demand and part replacement cycles
- Fleet safety policy impact on collision resistance expectations
- Total cost of ownership drivers across weight materials and serviceability
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By System Content Value per Vehicle, 2025–2030
- By OEM vs Aftermarket Revenue Split, 2025–2030
- By Segment Mix and ASP Waterfall, 2025–2030


