Market Overview
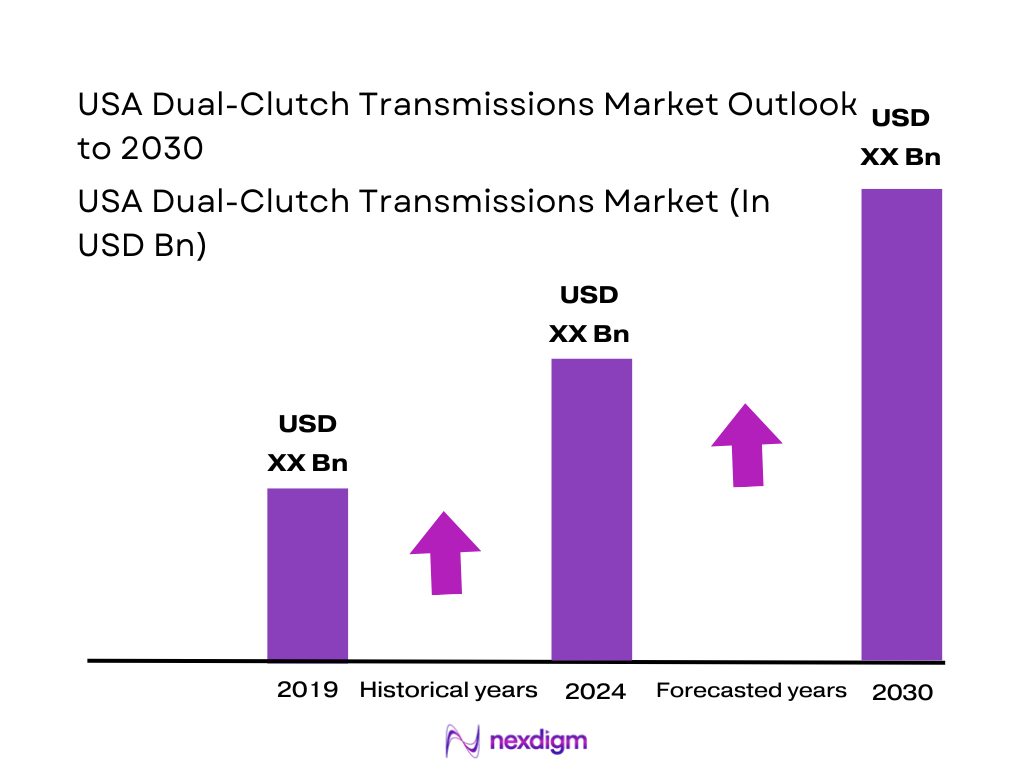
The USA dual-clutch transmissions market sits inside a globally expanding DCT landscape, where the overall DCT market moved from USD ~ billion (prior year) to USD ~ billion (latest year), driven by OEM demand for faster shift performance, tighter fuel-economy / emissions compliance pathways, and the continued migration from manual to automated architectures in performance and “sport” trims. In the U.S., the DCT market is on track to reach USD ~ billion by the end of its forecast window, reflecting sustained platform-level adoption across passenger cars and performance-oriented nameplates.
From a production-and-integration standpoint, U.S. DCT demand concentrates around major automotive hubs where powertrain engineering, calibration, and supplier localization are strongest—Detroit–Ann Arbor (Michigan) for OEM engineering and Tier-1 integration, Ohio/Indiana/Kentucky corridors for drivetrain manufacturing ecosystems, and the Southeast where multiple OEM plants and suppliers cluster around high-volume assembly footprints. These regions dominate because DCT success depends on tight mechatronics integration (TCU, actuators, sensors), fast validation loops, and launch support at assembly plants—capabilities that are densest in these U.S. automotive belts.
Market Segmentation
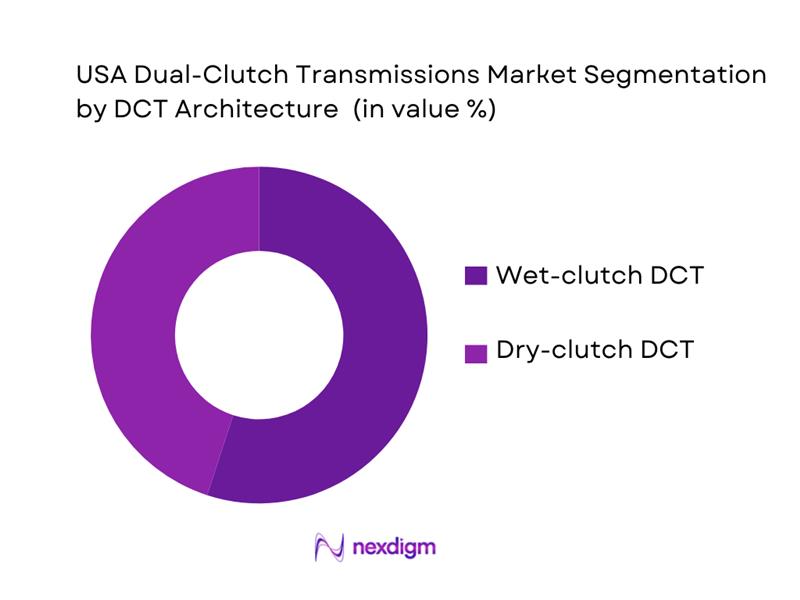
By DCT Architecture
USA DCT demand is segmented by architecture into wet-clutch DCT and dry-clutch DCT. Wet-clutch systems typically dominate where higher torque handling, thermal robustness, and repeated launch events matter (performance cars, higher-output turbo applications, towing/grade duty cycles). In practice, wet DCTs are favored in U.S. applications that prioritize shift speed under load and durability under heat—especially where calibration targets aggressive launch feel and repeatable track/spirited driving. Industry summaries commonly cite wet-clutch as the leading architecture in the DCT category, reflecting the U.S. tilt toward higher-displacement/higher-torque nameplates and “sport” trims.
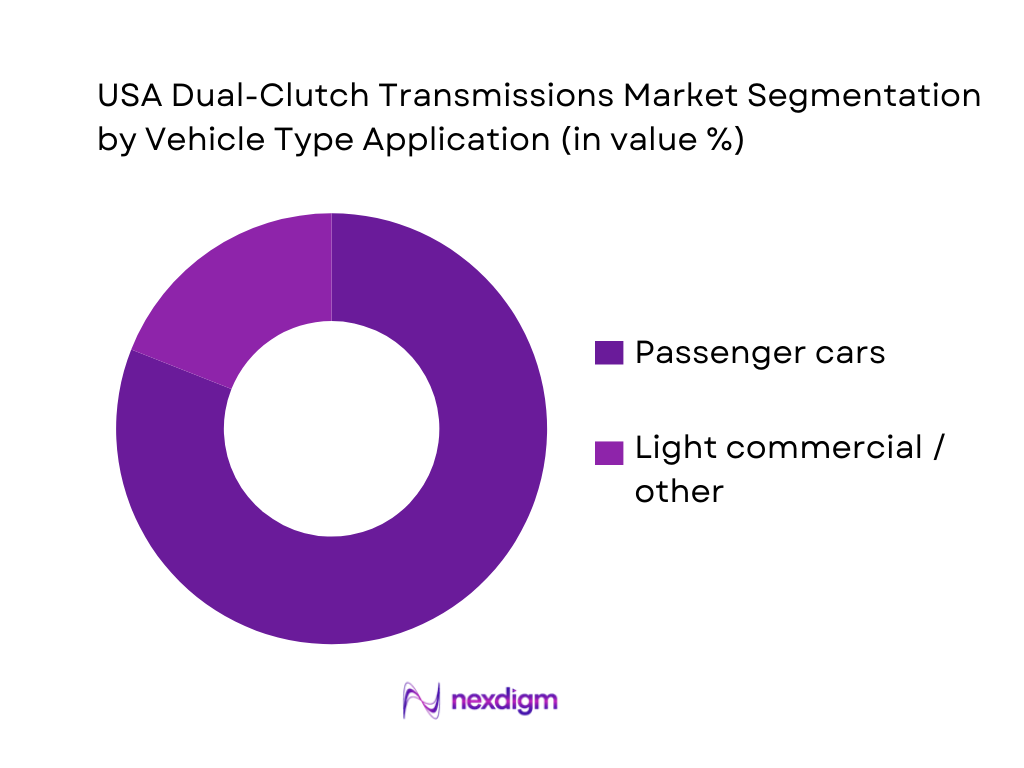
By Vehicle Type Application
USA DCT demand is segmented by vehicle type into passenger cars and light commercial / specialty applications. Passenger cars dominate because DCT value is easiest to monetize where customers pay for shift quality, acceleration feel, and sporty driving character. Also, DCT adoption aligns with performance-oriented subsegments where OEMs use DCT as a differentiator versus conventional automatics. Market reporting typically shows passenger cars as the primary demand pool for DCT systems.
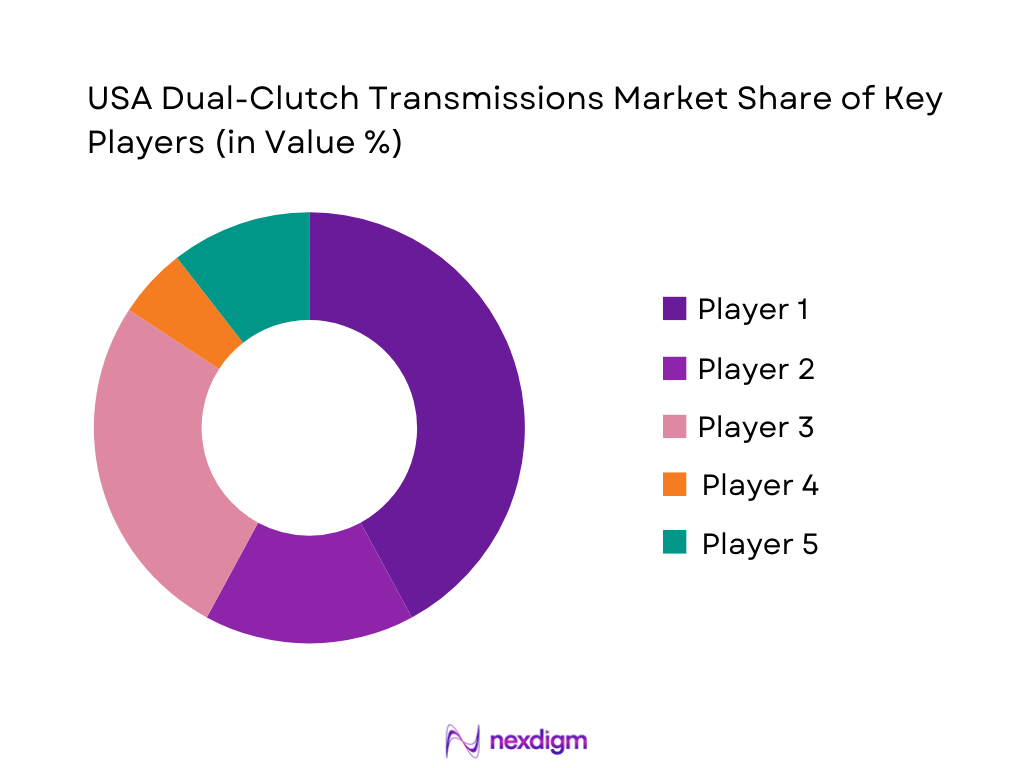
Competitive Landscape
The USA dual-clutch transmissions market is shaped by a concentrated set of transmission and driveline specialists (Tier-1 / Tier-2) plus a smaller number of performance transmission manufacturers. Competition centers on torque capacity + thermal robustness, shift-feel calibration IP, mechatronics reliability, and packaging for hybridized powertrains (P2/P3, DHT variants)—with OEM platform awards typically locking supplier positions for long cycles.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | USA Presence / Footprint | DCT Portfolio Focus | Typical DCT Type | Electrification Fit (HEV / PHEV) | Mechatronics / Controls Capability | Key GTM Model |
| BorgWarner | 1880 | Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Magna (GETRAG heritage) | 1957 | Aurora, Ontario, Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ZF | 1915 | Friedrichshafen, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Schaeffler (LuK) | 1946 | Herzogenaurach, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tremec | 1964 | Querétaro, Mexico (global HQ) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Dual-Clutch Transmissions Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Fleet uptime needs
U.S. fleet operations are being pushed harder on utilization, and that amplifies the value of fast, repeatable shift quality and reduced driveline shock—exactly where well-calibrated DCTs can protect uptime in high-duty cycles. National road activity is high and sustained: cumulative U.S. travel reached ~ billion vehicle-miles (VMT) with an increase of ~ billion vehicle-miles versus the prior year, keeping freight, service vans, and mixed-use fleets on tighter maintenance windows and higher daily run rates. At the same time, the macro backdrop supports sustained vehicle use: U.S. nominal GDP expanded from ~ billion to ~ billion and then ~ billion dollars, which correlates with higher goods movement, field-service activity, and “time-is-money” fleet scheduling pressure. In that operating context, DCT advantages become a fleet KPI tool—especially where fleets standardize driver behavior and route profiles and can realize the reliability upside of consistent shift logic. The demand signal is not “enthusiast-only”; it is increasingly operational: higher annual road use and economic throughput raise the penalty of unplanned downtime, making transmission architectures that can be tuned for repeatability, thermal control, and automated protection strategies more strategically relevant to U.S. OEM and Tier-1 roadmaps that serve commercial/utility-adjacent trims.
Performance trims
The U.S. market continues to reward “performance-per-dollar” trim walks—higher output, faster response, and sport calibrations—where DCTs are a natural fit because they can deliver rapid gear changes and strong launch behavior without requiring large-displacement engines. EPA’s latest trends show how mainstream performance has moved up the curve: average new-vehicle horsepower reached ~ hp in the latest finalized model-year dataset, and the same report shows real-world fleet metrics like ~ grams CO₂ per mile and 27.1 mpg (industry record) that OEMs must balance against performance targets. That combination—higher power expectations while still pushing efficiency metrics—creates space for transmission solutions that can hold engines closer to optimal operating zones and use aggressive yet precise shift scheduling. DCTs, when paired with modern control strategies, enable tighter gear spacing, reduced shift lag, and “always-on” torque management. The macro demand context remains supportive: a larger economy sustains discretionary spend on higher-trim vehicles, and higher national driving activity means consumers experience drivability differences daily— making responsiveness, smoothness, and perceived “tech” content more salient. In short, U.S. performance trims aren’t only niche halo cars; rising mainstream output metrics plus compliance pressure push OEMs toward sophisticated powertrain packages where DCTs can be positioned as a measurable differentiator in acceleration feel and efficiency tradeoffs without citing market sizing.
Challenges
Field quality exposure
DCT programs face outsized “field quality exposure” because customer experience is immediate, and small calibration or component variances can cascade into high complaint intensity and service burden. The U.S. market environment amplifies that risk: the latest annual safety recall reporting year logged ~ recalls with an affected population of ~ vehicles and equipment, demonstrating how quickly quality issues can scale nationally once a defect pattern is identified. High usage adds stress-test pressure—U.S. drivers logged ~ billion vehicle-miles cumulatively across the year—meaning driveline systems see massive real-world cycles across mixed climates and stop-start congestion that can surface edge-case behavior in clutch control and thermal management. Macro conditions also matter because they sustain utilization: nominal GDP rose from ~ to ~ billion dollars, supporting continued freight and consumer activity that keeps vehicles on the road. For DCTs specifically, this combination means validation must be “U.S.-duty-cycle ready”: hot-weather thermal strategies, traffic creep calibration, hill-hold robustness, and contamination tolerance. If those controls are immature, the field can turn into a durability lab—creating elevated warranty risk, service campaign pressure, and reputational damage. The U.S. market’s scale and recall visibility make “getting it right” non-negotiable: the same features that make DCTs attractive (software-defined shifting, high performance) also increase the attack surface for field issues when calibration, supplier variation, or diagnostics are not mature.
Recall sensitivity
Recall sensitivity is structurally high in the U.S. because defect disclosure is public, remedy execution is tracked, and media/consumer awareness can quickly attach a narrative to a specific technology. The numbers show the environment OEMs operate in: ~ recalls were recorded in the annual recall reporting year, affecting ~ vehicles and equipment—a scale that makes every driveline defect potentially national. For DCTs, this is particularly challenging because failures can present as drivability symptoms long before a catastrophic event, and those symptoms can still trigger large campaigns if they are tied to safety, stall risk, or loss of motive power. High road use raises exposure: total travel reached ~ billion vehicle-miles, expanding the number of “events” where edge-case calibration or component weakness can appear. The macro setting sustains vehicle activity and replacement cycles, with nominal GDP at ~ billion dollars and prior-year GDP at ~ billion dollars, reinforcing that the U.S. remains a high-throughput auto market where recall narratives can influence broad buyer segments quickly. In practice, this recall sensitivity forces DCT suppliers and OEMs to over-invest in fault detection, limp-home logic, and diagnostic transparency, because the downside isn’t only warranty cost—it is technology trust. Once a DCT architecture is associated with high-profile campaigns, it can depress take-rates across multiple platforms, even if later designs are improved.
Opportunities
Hybrid-compatible DCTs
The biggest near-term opportunity for DCTs in the U.S. is to align with electrification pathways where drivability and efficiency must improve without sacrificing performance—creating room for hybrid-compatible DCT architectures that integrate electric assist with multi-gear control. The current adoption signal is visible in official EV tracking: cumulative U.S. plug-in electric vehicle sales reached ~ units by the end of July in the latest reporting year-to-date snapshot, versus ~ units at the same point one year prior—evidence of a larger electrified parc entering daily use and reshaping OEM product planning. The same source reports ~ plug-in EVs sold in a single month and total light-duty sales of ~ units for that month, underscoring the scale at which powertrain architectures are being selected and validated. This matters for DCTs because hybridization often increases low-end torque and transient demands; a DCT that is designed around hybrid torque blending, clutch thermal management, and smooth low-speed behavior can offer both performance and efficiency benefits in U.S. driving. Macro tailwinds remain supportive—nominal GDP is ~ billion dollars—so OEMs have incentive to differentiate electrified trims (including performance hybrids) with more engaging drivetrains. The opportunity, therefore, is not “future stats”; it’s today’s electrified sales scale and OEM portfolio momentum creating immediate design slots where hybrid-ready DCTs can win platforms.
Modular AWD pairings
A second opportunity is modular “DCT + AWD” pairings that let OEMs scale performance and all-weather capability across crossovers and higher-trim packages while controlling efficiency metrics through smart calibration. EPA’s trends show that U.S. manufacturers are balancing higher capability with efficiency pressure: the latest finalized model-year dataset reports ~ grams CO₂ per mile and 27.1 mpg real-world fuel economy (record), alongside higher mainstream output. That mix creates design tension: buyers want capability and performance, but OEMs must keep fleet metrics moving in the right direction. Modular AWD systems, when integrated tightly with a DCT control stack (torque coordination, shift scheduling, clutch protection), can deliver consistent traction and sporty feel without relying on oversized engines, especially when paired with turbo engines or electrified assist. High national driving usage— ~ billion vehicle-miles in cumulative travel—means AWD-equipped vehicles are used across diverse weather and road conditions, making “capability as a daily feature” more valuable in customer decision-making. With nominal GDP at ~ billion dollars, the U.S. continues to support higher-trim demand where AWD packages are common, giving OEMs a commercial reason to engineer modular driveline families that can be deployed across multiple platforms. The opportunity is therefore present-tense: today’s capability/performance expectations plus compliance metrics push OEMs toward tightly integrated modular drivetrains where DCTs can be positioned as a premium, scalable module.
Future Outlook
Over the next several years, the USA dual-clutch transmissions market is expected to evolve along two parallel tracks: performance-and-premium adoption where shift speed and driver feel remain key purchase triggers, and electrified powertrain re-architecture, where DCT-like layouts are adapted into hybridized drive units and efficiency-focused packaging. Supplier differentiation will increasingly hinge on thermal management, software robustness, and platform launch execution, as OEMs demand faster validation cycles and fewer quality escapes.
Major Players
- BorgWarner
- Magna Powertrain
- ZF
- Schaeffler
- Tremec
- Valeo
- Eaton
- Aisin
- Jatco
- Hyundai Transys
- Ricardo
- Punch Powertrain
- Exedy
- GKN Automotive
Key Target Audience
- OEM Powertrain & Vehicle Platform Strategy Teams
- Tier-1 Powertrain Procurement & Supplier Development Leaders
- Transmission & Driveline Component Manufacturers
- Automotive Software / Controls Suppliers
- Aftermarket & Remanufacturing Networks
- Fleet Operators & Mobility Providers
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We build a U.S.-specific ecosystem map covering OEMs, Tier suppliers, calibration partners, and service channels. Desk research consolidates platform-level transmission fitment, drivetrain plant footprints, and supplier capability signals. The goal is to define the variables that move adoption: torque class, thermal limits, software maturity, and electrification architecture fit.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical adoption using platform/trim-level mapping, transmission-option penetration, and supplier shipment logic. This is supported by triangulating production footprints, platform cycles, and supplier program announcements. We also classify demand by architecture and vehicle-type use case to align with how DCT value is monetized in the U.S.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate hypotheses through CATIs with OEM engineers, Tier-1 program managers, and aftermarket specialists. Interviews focus on launch constraints, warranty/quality learnings, calibration complexity, and sourcing risks. These inputs refine assumptions on adoption momentum, platform continuity, and the role of hybridization.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize top-down (platform awards, OEM roadmap signals) with bottom-up (supplier program footprints, component shipments) to finalize the dataset. Findings are cross-checked for consistency across architecture, vehicle type, and powertrain pathways. The output is structured for decision-makers (strategy, sourcing, product, and investment teams).
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definition & scope, transmission taxonomy, OEM program tracking approach, primary interviews, validation & triangulation, assumptions, limitations, sensitivity checks, glossary/abbreviations)
- Definition, scope & boundary conditions
- Where DCTs sit in the USA powertrain mix
- DCT operating model & technology primer
- Adoption lifecycle in the USA
- DCT use-case clusters
- Growth drivers
fleet uptime needs
performance trims
calibration gains
OEM platform strategy - Challenges
field quality exposure
recall sensitivity
dealer service complexity
customer perception - Opportunities
hybrid-compatible DCTs
modular AWD pairings
software monetization via drive modes - Trends
shift-by-wire
OTA calibration updates
integrated e-axle substitution pathways
module standardization - Regulatory & compliance landscape
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Stakeholder ecosystem
- Scenario framework
- By value, 2019-2024
- By volume, 2019-2024
- Installed base of DCT-equipped vehicles, 2019-2024
- OEM-fitment vs replacement demand, 2019-2024
- Average realization by configuration, 2019-2024
- By clutch architecture (in Value %)
wet DCT
dry DCT
hybridized multi-mode variants
- By actuation & mechatronics (in Value %)
electro-hydraulic
electro-mechanical
integrated mechatronic module types
- By speed count / gearset family (in Value %)
6-speed
7-speed
8-speed
9-speed+
- By torque class (in Value %)
sub-200 Nm
200–350 Nm
350–500 Nm
500 Nm+
- By vehicle category (in Value %)
passenger car
CUV/SUV
light trucks
niche/performance
- By powertrain pairing (in Value %)
ICE
mild hybrid
HEV/PHEV
dedicated hybrid drive DCTs
- By driveline layout (in Value %)
FWD
RWD
AWD
torque-vectoring compatibility
- By channel (in Value %)
OEM factory fitment
remanufactured
aftermarket modules/parts
- Competitive intensity map (Tier-1 vs OEM-captive; performance vs mass-market focus)
- Cross Comparison Parameters (DCT architecture coverage, Torque band & duty-cycle certification, Mechatronics integration level, Calibration & shift-quality toolchain, Thermal management robustness, Software governance readiness, Localization & supply resilience, Field quality performance)
- Strategic initiatives & recent developments
- Competitive SWOT snapshots
- Pricing & cost structure approach
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
BorgWarner
Magna Powertrain
ZF Friedrichshafen
Aisin
JATCO
Hyundai Transys
Schaeffler
Valeo
Tremec
Volkswagen Group
Porsche
Mercedes-Benz / Mercedes-AMG
Ford
Nissan
- OEM sourcing & nomination logic
- Dealer/service readiness & cost-to-serve
- Fleet/operator lens where applicable
- Customer experience expectations
- Warranty, recall and brand-risk implications
- By value, 2025-2030
- By volume, 2025-2030
- Installed base of DCT-equipped vehicles, 2025-2030
- OEM-fitment vs replacement demand, 2025-2030
- Average realization by configuration, 2025-2030


