Market Overview
The USA electric seat adjustment systems market is valued at USD ~ billion, underpinned by strong domestic new-vehicle throughput and continued up-trimming of comfort features in high-volume nameplates. In the prior year, overall demand conditions were supported by ~ U.S. light-vehicle sales, which rose to ~ in the latest year, sustaining steady OEM production schedules and seat content ordering. Electrification of seating functions (multi-way adjustment, lumbar, memory, and multi-row availability) continues to expand the addressable motor/ECU content per vehicle.
Within the USA, demand and supply concentration is anchored around Detroit/SE Michigan (OEM engineering, tier-1 purchasing, validation labs), with manufacturing density across the Midwest and South where assembly plants and supplier parks drive just-in-time seat module logistics. The step-up from ~ to ~ U.S. light-vehicle sales reinforced production-led dominance of these clusters, while Mexico and Canada remain critical cross-border sourcing/assembly partners for seat structures, trim, motors, and electronics due to integrated North American automotive supply chains and synchronized platform sourcing.
Market Segmentation
By Vehicle Category
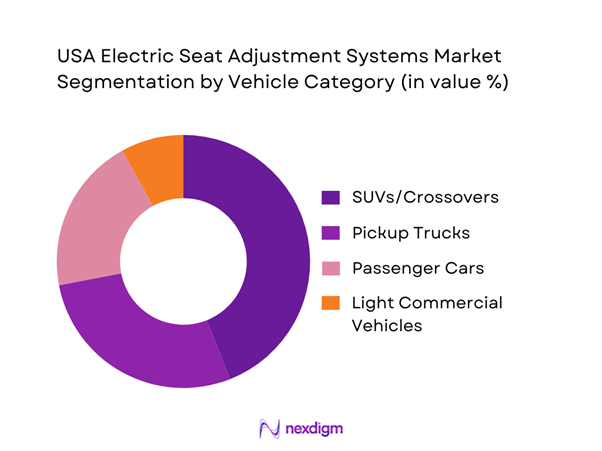
The USA electric seat adjustment systems market is segmented by vehicle category into passenger cars, SUVs/crossovers, pickup trucks, and light commercial vehicles. Recently, SUVs/crossovers hold a dominant share because they sit at the center of the U.S. demand mix and are increasingly positioned with higher trim bundles where multi-way powered seating and driver memory are standard or heavily optioned. OEMs also use seating personalization (lumbar, memory profiles, power recline/height) as a high-perceived-value feature to differentiate mid- and high-range SUV trims. Additionally, three-row SUVs expand the scope for second-row power functions, lifting motor/actuation content per vehicle versus conventional sedans.
By Adjustment Function Type
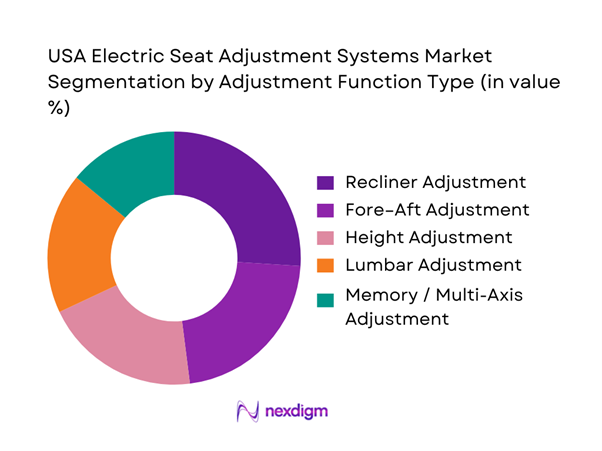
The USA electric seat adjustment systems market is segmented by adjustment function type into fore–aft, height, recliner, lumbar, and memory/multi-axis systems. Recently, recliner adjustment dominates because it is foundational to powered comfort in both mainstream and premium front-row seats and is frequently bundled with multi-way seat packages across high-volume vehicles. Recliner mechanisms also face stringent durability expectations under real-world cycles (seatback loading, repeated adjustments, occupant weight variance), which tends to favor established designs and validated actuator architectures at scale. As OEMs expand feature bundling, recliner actuation commonly serves as the “core powered function” that pulls along incremental add-ons such as lumbar and memory modules.
Competitive Landscape
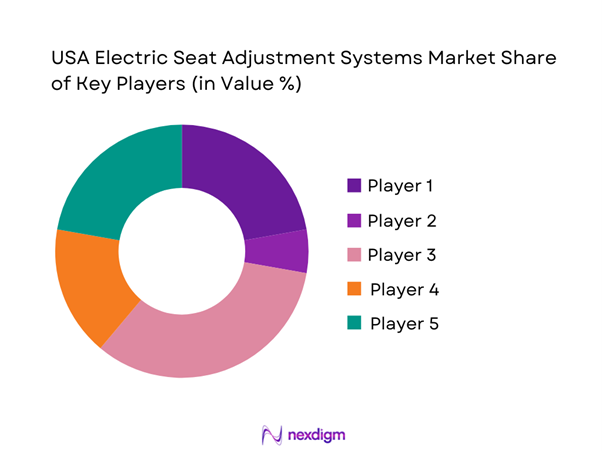
The USA electric seat adjustment systems market is led by a concentrated set of global seat integrators and motion/actuation specialists that are deeply embedded in OEM vehicle programs. This consolidation reflects the importance of validated safety, durability, NVH performance, and program execution at automotive scale, where switching costs are high and supplier selection is closely tied to platform timelines, manufacturing footprint, and module integration capability.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Core role in seat adjustment systems | Strength in integrated seat modules | Actuation & motor capability | Electronics/ECU integration depth | U.S. manufacturing footprint posture | Typical OEM customer proximity |
| Lear Corporation | 1917 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Adient | 2016 | Ireland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Magna Seating | 1957 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| FORVIA (Faurecia Seating) | 1997 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Brose | 1908 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Electric Seat Adjustment Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Premium Seat Content Penetration
Premium trims in the U.S. keep pulling electric seat adjustment content “up the stack” because higher disposable income supports option-heavy purchases and longer feature lists per vehicle. The U.S. economy produced USD ~ trillion in output, and GDP per capita reached USD ~, indicating a large addressable base that can absorb feature-content upgrades beyond the base seat frame. In the vehicle market that feeds this content, total vehicle sales were running at ~ units (SAAR) in Nov (with auto sales ~ (SAAR) and light truck sales ~ (SAAR)), sustaining OEM scale for higher-content seat programs. Premium-seat penetration is also reinforced by the U.S. product mix shifting toward higher-margin trims in crossovers and SUVs, where multi-way power adjustment, lumbar, and memory functions are increasingly packaged together, raising the electric actuation “count” per seat system rather than only adding incremental features.
Multi-Motor Seat Architecture Adoption
Seat systems are increasingly built around multiple small motors (fore-aft track, height, tilt, recline, lumbar, bolster, headrest, and sometimes powered cushion extension), and the U.S. scale encourages this “distributed motor” architecture because OEMs can amortize validation across high build volumes. Macroeconomically, GDP per capita rose from USD ~ to USD ~ and then USD ~, supporting demand for comfort features that go beyond basic ~-way power adjustment into ~-way/~ and memory-enabled configurations. On the production side, U.S. new-vehicle demand is large enough that total light vehicle sales (SAAR) repeatedly sit in the mid-teens in millions, which helps suppliers industrialize multi-motor seat platforms with common ECUs, shared harness architectures, and modular motor/gearbox families. The shift toward multi-motor designs also reflects the need for finer ergonomics to reduce fatigue in long-distance driving, especially in large vehicles where seating position variability is wider.
Challenges
System Cost Escalation
As seat systems add motors, sensors, memory logic, and safety-related diagnostics, the bill of materials grows and integration becomes more complex—even when OEMs try to modularize platforms. While you asked not to cite pricing/costing, the macro constraint is still visible: the U.S. market must absorb increasingly feature-dense vehicles at scale, and scale can be volatile because sales volumes swing with financing conditions and consumer confidence. The industry must therefore manage content growth within a demand environment measured in tens of millions of units (SAAR) (e.g., ~ total vehicle sales (SAAR) in a recent month), meaning any complexity-induced yield loss or rework quickly becomes operationally material. At the same time, the U.S. economy’s size (USD ~ trillion GDP) supports premiumization, but OEMs still face portfolio tension: expanding electric seat content beyond premium trims can stress standardization plans and supplier capacity if too many variants proliferate. The challenge is not only component count, but also software integration (memory logic, anti-pinch behaviors, network communication) that adds validation steps per platform.
Weight and Power Consumption Constraints
Seat systems compete for mass and electrical power budget, particularly as vehicles integrate more electronics (ADAS sensors, displays, powered closures, and high-wattage comfort features). Even without discussing future standards, the present constraint is that OEMs must manage incremental loads in vehicles sold at very high scale—light truck sales ~ (SAAR) in a recent month—where seat frames are larger and motors may need higher torque. For EVs and hybrids, accessory loads also matter because they draw from the same electrical system supporting propulsion and thermal management, increasing the need for efficient motor control, low-standby-power ECUs, and smarter sleep/wake strategies. Macro context: U.S. GDP per capita at USD ~ supports demand for powered convenience features, but it also pressures engineering teams to deliver those features without undermining vehicle efficiency targets and customer expectations. This pushes suppliers toward improved motor efficiency, optimized gear ratios, and lightweight seat structures—while still meeting durability requirements for heavier vehicles and a wide occupant range.
Opportunities
Rear-Seat Electrification Expansion
Rear-seat electrification is an opportunity because U.S. vehicle mix is heavily skewed to larger vehicles where rear-seat comfort matters (three-row SUVs, premium pickups, and family crossovers). The demand foundation is visible in the sales mix: light truck sales ~ (SAAR) versus auto sales ~ (SAAR) in a recent month, indicating the platform categories where rear-seat feature content is most relevant dominate U.S. volumes. Rear-seat electrification is also supported by the broader electrification ecosystem: EV infrastructure data cites ~ Level ~ and ~ DC fast charging ports, and EV/PHEV registrations of ~ and ~ respectively—evidence that more vehicles on the road are designed around larger electrical architectures that can support additional powered comfort loads and smarter power management. With GDP per capita at USD ~, OEMs have room to position rear-seat power functions as premium comfort differentiators (captain’s chairs, powered recline/slide), especially in high-trim family vehicles and chauffeur-style use cases.
Memory Seat Penetration in Mid-Segment Vehicles
Memory seats moving into mid-segment trims is a volume opportunity because it converts a “premium-only” electronic module into a high-run-rate interior ECU feature, often bundled with mirrors and steering column memory. The U.S. consumer base can support this migration: GDP per capita climbed from USD ~ to USD ~, and the vehicle market continues to operate at very large build volumes (e.g., ~ total vehicle sales (SAAR) in a recent month), meaning even modest packaging expansion creates multi-million-unit electronics demand. The EV transition also reinforces memory use cases because quieter cabins elevate perceived refinement, and broader EV adoption infrastructure helps normalize higher-tech interiors; charging port counts of ~ Level ~ and ~ DC fast reflect the ecosystem’s maturity that correlates with electronics-heavy vehicles in the parc. For suppliers, the growth lever is standardizing memory ECUs, reducing harness complexity with zonal architectures, and ensuring robust position sensing (Hall/encoder) that maintains recall accuracy over long duty cycles without drift.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the USA electric seat adjustment systems market is expected to expand steadily as OEMs continue pushing higher comfort content into core trims and as seating becomes a more visible “experience” differentiator in EVs and premium ICE platforms. Increased personalization (memory profiles, multi-axis adjustment), wider adoption in second-row seating, and deeper electronics integration will lift content per vehicle. At the same time, suppliers will compete on lightweighting, NVH refinement, and module-level integration that reduces OEM complexity.
Major Players
- Lear Corporation
- Adient
- Magna Seating
- FORVIA
- Toyota Boshoku
- TS Tech
- Brose Fahrzeugteile
- Bosch Mobility
- Denso
- Valeo
- Johnson Electric
- Mitsuba Corporation
- Nidec Corporation
- Continental Automotive
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEM Procurement & Supplier Management Teams
- Automotive OEM Seating/Interior Engineering & Platform Architecture Teams
- Tier-1 Seating System Integrators and Module Assemblers
- Actuator Motors, Gearbox, and Mechatronics Component Manufacturers
- Automotive Semiconductor/ECU and Body Electronics Suppliers
- Aftermarket Distributors and Service Networks
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We begin by mapping the complete seating ecosystem in the USA, including OEM assembly footprints, tier-1 seat integrators, and actuation/electronics suppliers. Desk research is used to define system boundaries (motor, mechanism, ECU, switch interfaces) and the variables that drive content per vehicle. The goal is to establish consistent market definitions and unit economics logic.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical demand indicators using vehicle sales/production direction, platform mix, and trim-level seat content patterns. A bottom-up build is developed using seat-row fitment logic, adjustment function penetration, and typical motor/ECU content per seat. This produces value and volume views aligned to OEM ordering behaviors.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses are validated through structured interviews (including CATI-style expert calls) with stakeholders across seating design, program management, supplier sales, and operations. These discussions validate platform-level adoption patterns, supplier allocation by OEM programs, and the commercial structure of seat actuation sourcing.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are triangulated across demand-side program signals and supply-side capability/footprint realities. We refine segment shares, competitive positioning, and procurement decision drivers (quality, NVH, durability, electronics integration) to finalize market sizing, segmentation logic, and strategic insights for decision-makers.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definition and Boundary Mapping, System Architecture Assumptions, Seat Content Mapping by Vehicle Class, OEM–Tier-1 Revenue Attribution Logic, Installed Base vs Shipment Assessment, Primary Interview Coverage by OEM/Tier-1/Integrator, Demand-Side Validation, Supply-Side Validation, Data Triangulation Framework, Assumptions and Limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Technology Evolution of Electric Seat Adjustment Systems
- Seat System Content Progression in US Vehicles
- OEM Seat Architecture Strategy Overview
- Value Chain and Supply Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Premium Seat Content Penetration
Multi-Motor Seat Architecture Adoption
EV Interior Differentiation
Pickup Truck Feature Upscaling
Consumer Comfort Expectations - Challenges
System Cost Escalation
Weight and Power Consumption Constraints
Motor Noise and Durability Issues
Semiconductor Dependence
Warranty Failure Sensitivity - Opportunities
Rear-Seat Electrification Expansion
Memory Seat Penetration in Mid-Segment Vehicles
Smart Seat Integration
Software-Defined Seating - Trends
Multi-Axis Motion Seats
Seat-ADAS Integration
Lightweight Motor Technologies
Modular Seat Platforms - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Motor Count per Vehicle, 2019–2024
- By Application (in Value %)
Fore-Aft Adjustment
Height Adjustment
Recliner Adjustment
Lumbar Adjustment
Multi-Axis Memory Adjustment - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Front Row Seats
Second Row Seats
Third Row Seats - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles
Hybrid Vehicles
Battery Electric Vehicles - By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
SUVs and Crossovers
Pickup Trucks
Light Commercial Vehicles - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone Motor-Driven Systems
ECU-Integrated Seat Control Systems
Networked Seat Systems (CAN/LIN) - By Region (in Value %)
Midwest
South
West
Northeast
- Market Share of Major Players by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (OEM Program Penetration, Motors per Seat Capability, Multi-Axis Adjustment Capability, ECU Integration Depth, Noise/Vibration Performance, Weight Optimization, Platform Scalability, US Manufacturing Footprint)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Content Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lear Corporation
Adient plc
Magna Seating
Faurecia (FORVIA Seating)
Toyota Boshoku
TS Tech
Brose Fahrzeugteile
Bosch Mobility Solutions
Denso Corporation
Valeo Seating Systems
Johnson Electric
Mitsuba Corporation
Nidec Corporation
Continental Automotive
Hyundai Transys
- OEM Demand and Seat Content Strategy
- Vehicle Program Level Adoption Patterns
- Platform-Level Cost Sensitivity
- Feature Bundling and Trim Strategy
- OEM Decision-Making and Supplier Selection Criteria
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Motor Content, 2025–2030


