Market Overview
The USA EV Power Electronics Market is valued at USD ~, spanning traction inverter power stages, onboard charger power stages, high-voltage DC-DC conversion, and the power semiconductor modules and controls that drive efficiency, range, and charging performance. Demand is structurally linked to EV production, higher onboard power requirements, and the shift toward wide-bandgap devices that raise value per vehicle through advanced packaging, thermal stacks, and functional safety design. The market’s strategic importance is amplified by localization pressure, supply assurance needs for critical power devices, and OEM platform strategies that increasingly treat power electronics as a performance differentiator rather than a commodity.
The USA EV Power Electronics market is concentrated in domestic EV manufacturing and engineering hubs where platform decisions, supplier awards, and validation infrastructure are densest, including the West and South regions with strong EV adoption, charging buildout, and expanding manufacturing footprints. Within the country, these regions dominate because they combine high demand pull, proximity to OEM and Tier-1 engineering sites, and faster deployment of charging ecosystems that push higher onboard power specifications. Globally, supply and technology influence is driven by leading power semiconductor and module ecosystems that shape SiC process maturity, packaging know-how, and reliability qualification practices, which the USA market depends on for performance roadmaps, capacity scaling, and equipment-led yield improvements.
Market Segmentation
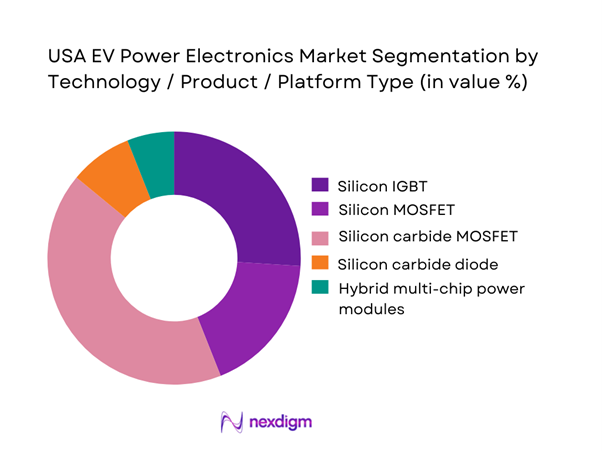
By Technology / Product / Platform Type
Wide-bandgap silicon carbide MOSFET solutions dominate the technology mix within the highest-value EV power electronics applications because they unlock the efficiency and thermal headroom required for high-power traction inverters and fast-charging oriented architectures. In the USA, OEMs prioritize improved highway efficiency, repeatable fast-charge performance, and power density that reduces mass and thermal system burden, which collectively push programs toward SiC in the drivetrain power stage. SiC-based designs also reduce switching and conduction losses, enabling smaller passive components and lower cooling demands at comparable output, which improves packaging flexibility and supports integrated e-axle strategies. The dominance is reinforced by supplier investments in domestic capacity, longer-term allocation agreements, and the need for robust automotive qualification that favors established wide-bandgap portfolios with mature reliability data and proven module packaging ecosystems.
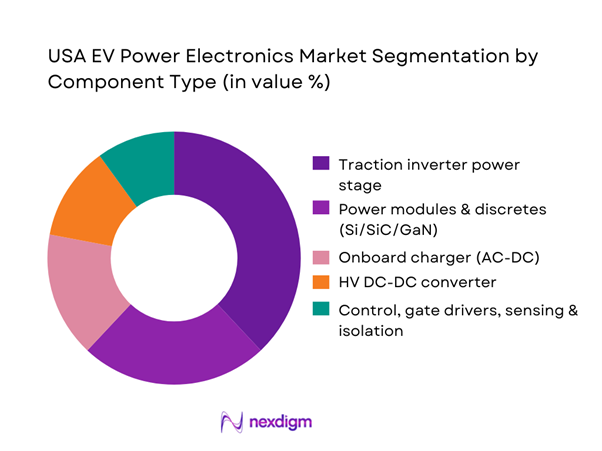
By Component Type
USA EV Power Electronics market is segmented by component type into traction inverter power stage, onboard charger (OBC), HV DC-DC converter, power modules & discretes (Si/SiC/GaN), and control/gate-driver & sensing/isolation. Traction inverter power stages hold the dominant share because every BEV and most PHEVs require high-power conversion at the drivetrain, and the U.S. mix is skewed toward higher-output vehicles (SUVs/pickups) that demand higher current handling, robust thermal management, and increasingly SiC devices for switching efficiency. As U.S. OEMs push fast-charge capability and better highway efficiency, inverter BOM value rises through higher-voltage components, advanced packaging, and tighter functional safety requirements—making the inverter the largest value pool inside vehicle-side power electronics.
Competitive Landscape
The USA EV Power Electronics market is dominated by a few major players, including Infineon Technologies and global or regional brands like onsemi, STMicroelectronics, and Texas Instruments. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | USA Manufacturing / Footprint | Power Electronics Focus | WBG (SiC/GaN) Strength | Automotive Qualification | Key Go-to-Market Route | Typical EV Touchpoints |
| Infineon Technologies | 1999 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ON Semiconductor | 1999 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Wolfspeed | 1987 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Texas Instruments | 1930 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| STMicroelectronics | 1987 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA EV Power Electronics Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
EV production ramp and model proliferation
The USA EV Power Electronics market expands as OEMs broaden EV lineups and increase production, which lifts demand for traction inverter and charger power stages and pulls through higher volumes of power modules, passives, and control ICs. As platforms proliferate, suppliers benefit from repeated design reuse and standardized inverter families that accelerate qualification, while OEMs push for performance differentiation through tighter efficiency targets and higher sustained power. The outcome is a structural rise in power electronics content per vehicle, deeper sourcing engagements, and more multi-year supply agreements that reward scale, automotive-grade reliability, and design-in support. This accelerates consolidation around suppliers able to deliver validated platforms with predictable lead times, robust quality systems, and scalable manufacturing footprints.
Wide-bandgap adoption for efficiency and range
Wide-bandgap adoption increases demand for advanced devices and packaging because SiC-based power stages enable lower losses, higher switching frequencies, and improved thermal operation, which collectively increase vehicle range and reduce charging and propulsion energy waste. In the USA, OEMs pursue this to deliver improved real-world efficiency without compromising acceleration or sustained performance, while also enabling smaller and lighter power electronics packaging that supports integrated drive modules. The impact is an upgrade cycle from silicon-heavy architectures to SiC-rich designs, raising value per inverter and increasing requirements for module packaging sophistication, gate driver robustness, and insulation integrity. The outcome is stronger pricing power for qualified SiC portfolios and a premium for suppliers with mature reliability data and stable capacity.
Challenges
Automotive qualification lead times and validation burden
Qualification complexity remains a binding constraint because EV power electronics must pass rigorous electrical, thermal, and mechanical validation across wide operating envelopes, and failures can translate into high warranty exposure and costly recalls. In the USA, OEM and Tier-1 programs require extensive DV and PV cycles, end-of-line test coverage, and functional safety documentation, which slows the onboarding of new materials, new packaging, and new suppliers. The impact is longer time-to-revenue for entrants and slower technology diffusion when qualification evidence is incomplete. The outcome is a market that favors incumbents with established automotive-grade process controls, deep failure-analysis capability, and long-term support commitments that reduce program risk for OEMs.
Thermal reliability and power-cycling durability
Thermal reliability is a core challenge because high switching currents and frequent load transients create power-cycling stress that can degrade interconnects, solder layers, and packaging over time, especially under aggressive duty cycles. In the USA, customer expectations for consistent performance across climates and use cases increases the demand for robust thermal stack design, including cold-plate integration, advanced interconnect methods, and carefully selected interface materials. The impact is higher engineering and validation cost and a need for tight supplier control over packaging variability and materials traceability. The outcome is continued investment in advanced packaging, reliability modeling, and test protocols that can prove lifetime durability without sacrificing power density.
Opportunities
Integrated e-axle and inverter consolidation
Integration offers a major opportunity because combining the inverter with motor and gearbox into an integrated drive unit reduces harness complexity, improves packaging efficiency, and can lower system cost through shared cooling and consolidated housings. In the USA, OEMs target integration to improve manufacturability and reduce assembly steps, while also enabling quicker platform scaling through common drive-unit families. The impact is a shift in value capture toward suppliers that can deliver integrated power electronics with validated thermal and EMI performance inside compact enclosures. The outcome is new partnership structures between OEMs, Tier-1s, and semiconductor providers to co-optimize devices, packaging, and control software for integrated modules.
Bidirectional charging and vehicle-to-everything readiness
Bidirectional capability creates opportunity because vehicle-side power electronics can evolve from one-way conversion toward energy services, enabling vehicle-to-home and vehicle-to-grid functionality that increases the strategic role of onboard chargers and power conversion control. In the USA, this is attractive for resilience use cases, grid services, and fleet energy optimization, which drive requirements for higher power OBC architectures, improved isolation and safety controls, and reliable power stage operation in both directions. The impact is an upgrade cycle for charger power stages and control stacks and a new layer of certification, test, and warranty considerations. The outcome is differentiation for suppliers with bidirectional-ready reference architectures, robust protection, and validation toolchains that reduce integration time.
Future Outlook
The USA EV Power Electronics market will be shaped by a continued shift toward higher efficiency architectures, deeper integration of propulsion power stages, and stronger domestic supply-chain emphasis for critical power devices and modules. Competitive advantage will increasingly depend on validated wide-bandgap roadmaps, packaging and thermal innovation, and the ability to provide stable multi-year supply assurance while meeting stringent automotive-grade qualification and functional safety expectations. OEMs and Tier-1s will prioritize platform scalability, reduced complexity, and software-enabled diagnostics, pushing suppliers toward more integrated, standardized power electronics building blocks that can be reused across multiple vehicle lines and duty cycles.
Major Players
- Infineon Technologies
- Onsemi
- Wolfspeed
- STMicroelectronics
- Texas Instruments
- Analog Devices
- Microchip Technology
- NXP Semiconductors
- Renesas Electronics
- Bosch
- Continental
- BorgWarner
- Dana Incorporated
- ZF
- SEMIKRON Danfoss
Key Target Audience
- EV OEM procurement and powertrain engineering teams
- Tier-1 inverter, e-axle, and charging system integrators
- Power semiconductor and module manufacturers
- Charging equipment manufacturers focused on vehicle-side power stages
- Fleet operators and electrification program owners
- Aftermarket service networks for power electronics replacement and remanufacturing
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This step builds a full ecosystem map of the USA EV Power Electronics market, covering OEMs, Tier-1s, semiconductor vendors, module packagers, and key validation stakeholders. We define critical variables that drive market value, including device technology selection, voltage architecture, power density targets, thermal stack choices, and qualification requirements. The outcome is a taxonomy that aligns product definitions with real procurement and engineering decision points.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We construct the market by mapping demand to EV platform requirements and the resulting content per vehicle for inverter, OBC, DC-DC, and supporting control and protection stacks. Historical dynamics are analyzed through program ramp patterns, design win cycles, and supplier capacity planning realities. The model is cross-checked for scope consistency across devices, modules, and system-level power stages to ensure coherent revenue attribution.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses around device mix, integration trajectories, and reliability constraints are validated through structured expert interactions with stakeholders across the USA EV power electronics value chain. These consultations test assumptions on qualification lead times, thermal and EMI constraints, and commercial contracting structures. Insights are used to refine segment logic and ensure that conclusions match how OEMs and Tier-1s actually deploy and source power electronics.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize findings into an integrated narrative covering market structure, segmentation, competition, and strategic implications, ensuring internal consistency across sizing logic and segment definitions. The report is finalized through quality checks for taxonomy accuracy, duplication elimination, and adherence to client-deliverable tone. Final outputs emphasize decision-relevant insights tied to sourcing, engineering, and investment priorities in the USA EV Power Electronics market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Inclusions/Exclusions, Abbreviations, Topic-Specific Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Revenue Attribution Logic Across Use Cases or Care Settings, Primary Interview Program Design, Data Triangulation and Validation, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- EV Power Electronics Usage and Value-Chain Mapping
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- USA EV Manufacturing and Powertrain Delivery Architecture
- Growth Drivers
EV production ramp and model proliferation
Shift toward higher-voltage architectures
Wide-bandgap adoption for efficiency and range
Fast-charging expectations and higher onboard power
Domestic manufacturing incentives and localization pull
Thermal and power-density engineering breakthroughs - Challenges
SiC wafer and device supply tightness cycles
Automotive qualification lead times and validation burden
Thermal reliability and power-cycling durability
EMI and functional safety compliance complexity
Cost volatility across substrates, packaging, and passives
Workforce constraints in power electronics engineering - Opportunities
Integrated e-axle and inverter consolidation
Bidirectional charging and vehicle-to-everything readiness
Advanced packaging and double-sided cooling modules
Domestic module assembly and localized supply assurance
Software-defined power control and diagnostics
Power electronics for commercial and fleet electrification - Trends
Higher switching frequency and smaller passive footprints
Transition from discrete to highly integrated modules
Increased use of advanced interconnect and sintering
Co-packaged sensing and protection
Standardized inverter platforms across vehicle lines
Greater design reuse through reference platforms - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Installed Base, 2019–2024
- By Segment Type 1 (in Value %)
Traction inverter power stage
On-board charger power stage
HV DC-DC converter
Power module and discrete devices
Gate drivers and isolation
Sensing and protection - By Segment Type 2 (in Value %)
Passenger battery electric vehicles
Passenger plug-in hybrid electric vehicles
Light commercial electric vehicles
Medium-duty electric vehicles
Heavy-duty electric vehicles
Off-highway and specialty electric vehicles - By Technology / Product / Platform Type (in Value %)
Silicon IGBT
Silicon MOSFET
Silicon carbide MOSFET
Silicon carbide diode
Gallium nitride power devices
Hybrid multi-chip power modules - By Deployment / Delivery / Distribution Model (in Value %)
Direct OEM sourcing
Tier-1 integration supply
Contract manufacturing / EMS
Authorized distribution channel
Aftermarket service and remanufacturing - By End-Use Industry / Customer Type (in Value %)
OEM powertrain engineering organizations
Tier-1 power electronics integrators
Fleet operators and commercial mobility
Charging equipment manufacturers
Aftermarket service networks
Government and public fleet programs - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Competition ecosystem overview
- Cross Comparison Parameters (SiC portfolio depth, inverter power density, switching efficiency under load, thermal architecture maturity, 400V and 800V platform coverage, functional safety readiness, automotive qualification breadth, North America manufacturing footprint, supply assurance and allocation strength, design-in toolchain and reference design support)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and commercial model benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Infineon Technologies
onsemi
Wolfspeed
STMicroelectronics
Texas Instruments
Analog Devices
Microchip Technology
NXP Semiconductors
Renesas Electronics
Bosch
Continental
BorgWarner
Dana Incorporated
ZF
SEMIKRON Danfoss
- Buyer personas and decision-making units
- Procurement and contracting workflows
- KPIs used for evaluation
- Pain points and adoption barriers
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Installed Base, 2025–2030


