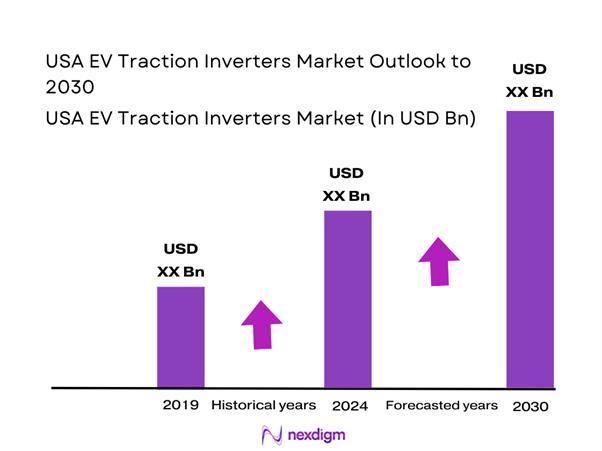
Market Overview
The USA Automotive Hand Tools Market is valued at USD ~, reflecting its structural role within the automotive service, maintenance, and repair ecosystem. Demand is fundamentally driven by the size and aging profile of the national vehicle parc, the continuous requirement for routine maintenance, and the sustained relevance of mechanical fastening, cutting, and measuring tasks even as vehicles become more electronically complex. Revenue generation is closely linked to workshop density, fleet utilization intensity, and the recurring replacement cycle of professional-grade tools, which positions automotive hand tools as a stable, non-discretionary segment within the broader automotive aftermarket.
Within the country, demand concentration is strongest in the Midwest and South, where high vehicle ownership, logistics activity, and dense networks of independent workshops and fleet maintenance hubs exist. The Midwest benefits from proximity to automotive manufacturing, technical labor pools, and long-established service ecosystems, while the South is supported by fast-growing vehicle populations and fleet operations. On the supply and technology side, global tool design standards and metallurgy expertise from industrialized economies strongly influence USA market offerings, reinforcing premium positioning, durability expectations, and professional-grade compliance norms.
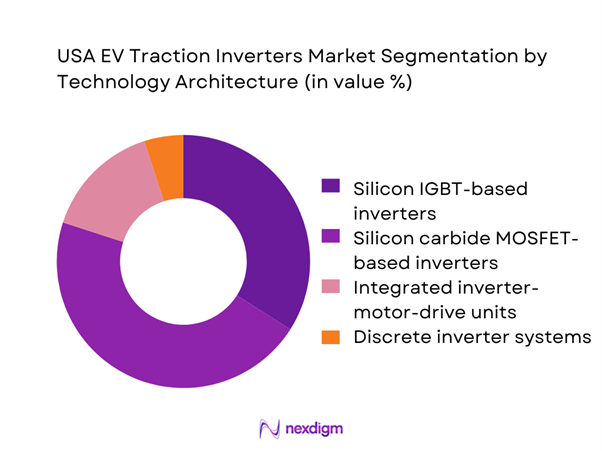
Market Segmentation
By Tool Category
The USA automotive hand tools market is segmented by tool category into wrenches and spanners, sockets and ratchets, screwdrivers, pliers and cutters, hammers and striking tools, and torque tools. Among these, sockets and ratchets dominate the market due to their universal applicability across passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, and fleet maintenance operations. Modern automotive service workflows rely heavily on socket-based fastening because of speed, compatibility with torque control requirements, and adaptability across engine, chassis, and body applications. Workshops typically invest in complete socket systems rather than individual tools, driving higher average spend per buyer. Additionally, the recurring wear of ratcheting mechanisms and sockets in high-frequency service environments leads to predictable replacement demand, reinforcing the dominance of this sub-segment across professional and semi-professional users.
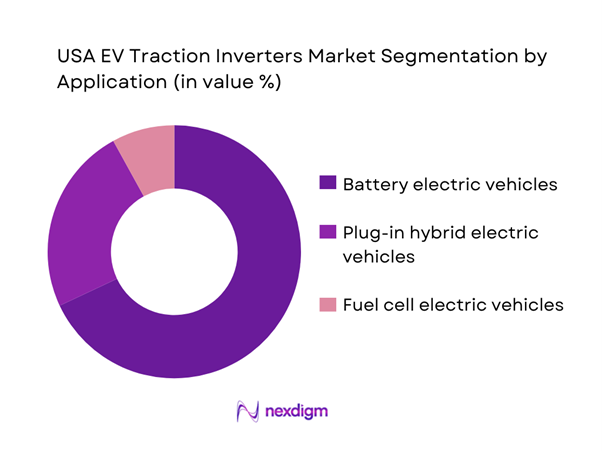
By End-Use Application
The market is segmented into passenger vehicle repair, commercial vehicle repair, dealership service centers, independent workshops, and DIY/consumer use. Independent workshops hold the dominant position due to their numerical strength, broad service scope, and continuous procurement of hand tools across multiple price tiers. Unlike dealerships, which often standardize tool purchases centrally, independent workshops make frequent replacement and incremental purchases based on immediate operational needs. They also service mixed vehicle brands and ages, requiring broader tool compatibility and larger inventories. Furthermore, independent operators are more likely to adopt both premium and mid-range tools depending on task criticality, which expands overall market value captured from this segment.
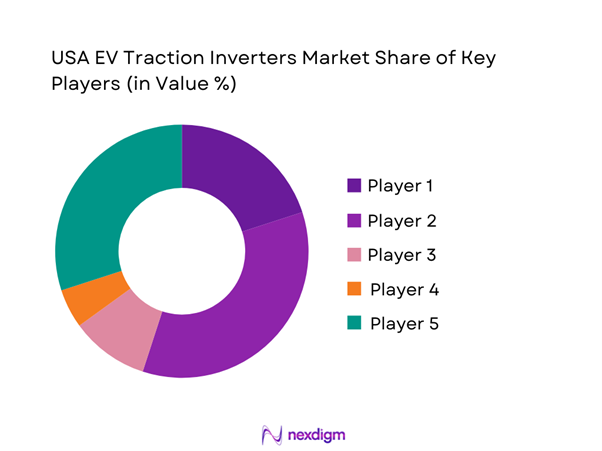
Competitive Landscape
The USA Automotive Hand Tools market is dominated by a few major players, including Snap-on and global or regional brands like Stanley Black & Decker, Apex Tool Group, and Mac Tools. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | USA Manufacturing / Footprint | Power Electronics Focus | WBG (SiC/GaN) Strength | Automotive Qualification | Key Go-to-Market Route | Typical EV Touchpoints |
| Infineon Technologies | 1999 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ON Semiconductor | 1999 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Wolfspeed | 1987 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Texas Instruments | 1930 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| STMicroelectronics | 1987 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Automotive Hand Tools Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Vehicle Parc Expansion and Aging Fleet
The steady expansion of the national vehicle parc, combined with the rising average age of vehicles in operation, directly intensifies maintenance and repair activity across the automotive ecosystem. As vehicles remain in service for longer durations, the frequency of mechanical wear-related failures increases across braking systems, suspension components, steering assemblies, drivetrain elements, and chassis parts. These repair activities are fundamentally labor-intensive and rely heavily on manual intervention, reinforcing sustained demand for automotive hand tools. Aging vehicles often fall outside OEM warranty coverage, shifting repair work toward independent workshops and fleet maintenance facilities, where tool utilization rates are high and replacement cycles are shorter. This dynamic results in consistent, repeat demand for durable hand tools, including sockets, wrenches, pliers, pullers, and striking tools, forming a structurally resilient demand base for the market.
Rising Complexity of Vehicle Systems
While modern vehicles incorporate advanced electronics and software layers, mechanical complexity has not diminished and, in many cases, has increased. The use of lightweight alloys, composite materials, modular assemblies, and compact engine bay layouts requires higher precision during installation and servicing. Fastening tolerances have tightened, and improper torque application can lead to component failure, safety risks, or warranty disputes. As a result, technicians increasingly depend on calibrated hand tools such as torque wrenches, specialty fasteners, and precision-adjustment tools. Additionally, ergonomic considerations have become more critical as repair tasks grow more intricate and time-consuming. This shift elevates demand for professional-grade hand tools with superior metallurgy, accurate tolerances, and fatigue-reducing designs, strengthening the position of established brands and increasing value per tool purchase.
Challenges
Price Sensitivity and Margin Pressure
Automotive hand tool purchasing decisions are highly sensitive to price, particularly among small and mid-sized independent workshops operating under tight cash-flow constraints. These buyers frequently compare premium-branded tools against lower-cost alternatives that appear functionally similar at the point of purchase. As a result, replacement cycles for high-quality tools may be extended, and workshops often adopt mixed-brand toolkits to optimize costs. This behavior compresses margins for premium manufacturers and forces continuous justification of higher pricing through durability claims, warranty coverage, and after-sales service. At the same time, distributors face pressure to offer discounts, bundled pricing, or extended credit terms. The combination of cost-conscious buyers and intense brand competition creates sustained margin pressure across the value chain.
Proliferation of Low-Cost Imports
The growing availability of low-cost imported automotive hand tools has significantly altered competitive dynamics within the market. These products, often distributed through online platforms and informal retail channels, appeal strongly to price-sensitive customers and first-time workshop setups. However, inconsistent material quality, limited durability, and lack of certification can lead to premature tool failure and safety risks. Despite these limitations, aggressive pricing places downward pressure on average selling prices and weakens brand differentiation. Established manufacturers must invest more heavily in branding, quality assurance, and customer education to defend their market position. Managing reputation risk while competing against visually similar but lower-quality products remains an ongoing challenge, particularly in e-commerce-driven purchasing environments where direct product evaluation is limited.
Opportunities
Premium and Professional-Grade Tools
As automotive repair tasks demand higher precision, consistency, and reliability, professional technicians are increasingly recognizing the long-term value of premium hand tools. Errors caused by tool slippage, incorrect torque application, or poor ergonomics can result in rework, component damage, or safety incidents, all of which carry high indirect costs. This awareness is driving stronger acceptance of professional-grade tools designed for durability, precision machining, and extended daily use. Manufacturers that emphasize rigorous testing standards, ergonomic certification, corrosion resistance, and lifetime warranty programs are well positioned to capture loyalty among high-usage professional buyers. This segment offers opportunities for higher margins, brand stickiness, and repeat purchases driven by tool standardization across workshop operations.
EV-Compatible and Insulated Tools
The growing penetration of electrified vehicles introduces a distinct opportunity within the automotive hand tools market. Servicing electric and hybrid vehicles requires insulated tools designed to safely handle high-voltage components, battery systems, and power electronics. Workshops expanding their service capabilities must invest in certified insulated hand tools, torque tools, and EV-specific service kits to comply with safety protocols. This transition creates demand for specialized products that are not easily substituted by generic tools, allowing suppliers to differentiate through compliance standards, training support, and bundled EV tool solutions. Manufacturers that proactively develop and certify EV-compatible tool ranges can establish early leadership in this emerging service segment and benefit from long-term adoption as electrification accelerates.
Future Outlook
The USA automotive hand tools market is expected to remain structurally resilient, supported by sustained vehicle usage, the coexistence of internal combustion and electric vehicles, and the indispensable role of manual tools in repair workflows. Competitive advantage will increasingly hinge on product quality, brand trust, distribution efficiency, and alignment with evolving service requirements rather than volume expansion alone.
Major Players
- Snap-on
- Stanley Black & Decker
- Apex Tool Group
- Mac Tools
- Matco Tools
- Proto Industrial
- Klein Tools
- Irwin Tools
- Craftsman
- Channellock
- SK Tools
- GearWrench
- Milwaukee Tool
- Cornwell Tools
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEM service networks
- Independent automotive repair workshop owners
- Fleet maintenance and logistics operators
- Automotive dealership groups
- Automotive component manufacturing plants
- Tool distributors and industrial suppliers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins by mapping the automotive service and repair ecosystem and defining the scope of hand tools used across professional and consumer settings. Key demand, pricing, and replacement variables are identified through structured desk research.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical usage patterns, distribution flows, and end-user procurement behaviors are analyzed to construct a bottom-up view of market value and tool category contribution.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings are validated through expert discussions with distributors, workshop operators, and product specialists to confirm assumptions around demand drivers and buyer behavior.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All inputs are synthesized through triangulation to produce a consistent, validated market model aligned with industry realities.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Inclusions/Exclusions, Abbreviations, Topic-Specific Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Revenue Attribution Logic Across Use Cases or Care Settings, Primary Interview Program Design, Data Triangulation and Validation, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Automotive Service and Repair Value-Chain Mapping
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- USA Automotive Service and Distribution Architecture
- Growth Drivers
Vehicle Parc Expansion and Aging Fleet
Rising Complexity of Vehicle Systems
Growth of Independent Repair Workshops
Expansion of Fleet and Logistics Operations
DIY Culture and Consumer Tool Ownership
Aftermarket Service Standardization - Challenges
Price Sensitivity and Margin Pressure
Proliferation of Low-Cost Imports
Tool Counterfeiting and Quality Variance
Skilled Labor Shortages in Repair Ecosystem
Inventory and SKU Management Complexity - Opportunities
Premium and Professional-Grade Tools
Ergonomic and Safety-Optimized Designs
EV-Compatible and Insulated Tools
Private Label Expansion by Distributors
Digital and Direct-to-Workshop Sales - Trends
Shift Toward Torque-Accuracy Tools
Rising Demand for Insulated Hand Tools
E-commerce Penetration in B2B Sales
Modular Tool Kits and Custom Sets
Brand Consolidation and M&A Activity - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- Installed Base / Active Usage Metric, 2019–2024
- Service / Revenue Mix, 2019–2024
- By Tool Category (in Value %)
Wrenches and Spanners
Sockets and Ratchets
Screwdrivers
Pliers and Cutters
Hammers and Striking Tools
Torque Tools - By End-Use Application (in Value %)
Passenger Vehicle Repair
Commercial Vehicle Repair
Dealership Service Centers
Independent Workshops
DIY / Consumer Use - By Tool Function Type (in Value %)
Fastening Tools
Striking Tools
Cutting Tools
Measuring and Precision Tools
Holding and Clamping Tools - By Distribution Model (in Value %)
Direct OEM / Dealer Supply
Specialty Automotive Tool Retailers
Industrial Distributors
E-commerce Platforms - By End-Use Customer Type (in Value %)
OEM and Authorized Dealerships
Independent Repair Workshops
Fleet Maintenance Operators
Automotive Component Manufacturers
Individual Consumers - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Competition ecosystem overview
- Cross Comparison Parameters (tool durability, torque accuracy, material grade, ergonomic compliance, SKU breadth, price positioning, distribution reach, warranty terms)
- SWOT analysis of major players
Pricing and commercial model benchmarking - Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Snap-on
Stanley Black & Decker
Apex Tool Group
Mac Tools
Matco Tools
Proto Industrial
Klein Tools
Irwin Tools
Craftsman
Channellock
SK Tools
GearWrench
Milwaukee Tool
Cornwell Tools
Lisle Corporation
- Buyer personas and decision-making units
- Procurement and contracting workflows
- KPIs used for evaluation
- Pain points and adoption barriers
- By Value, 2025–2030
- Installed Base / Active Usage Metric, 2025–2030
- Service / Revenue Mix, 2025–2030


