Market Overview
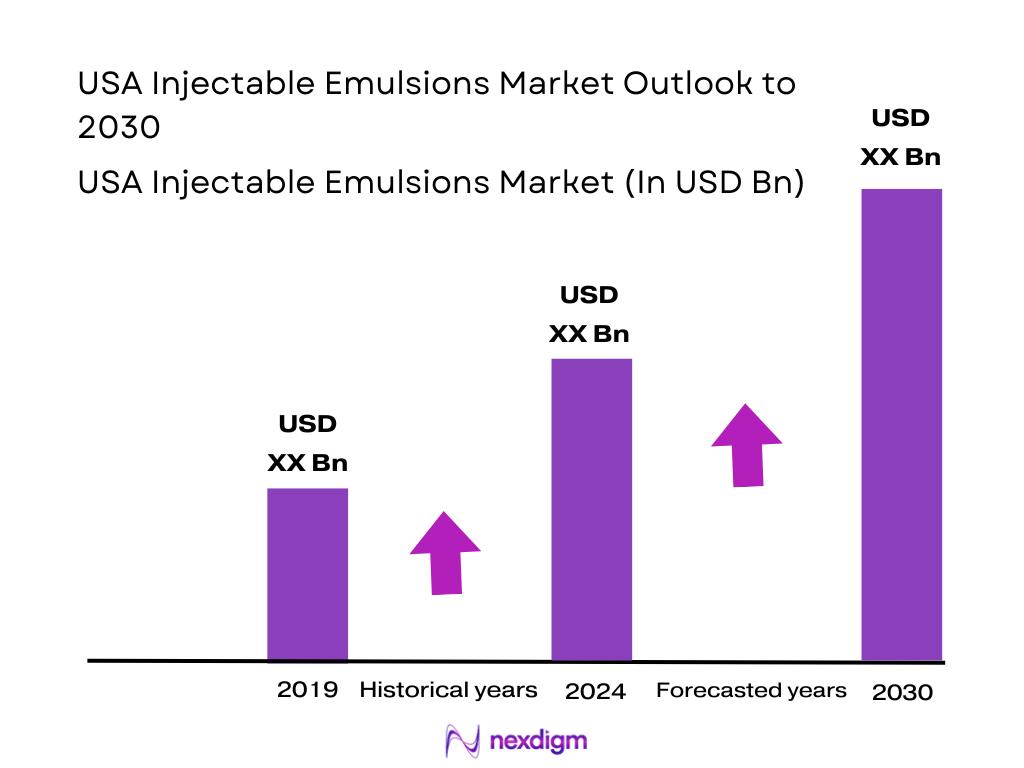
The USA Injectable Emulsions Market sits at the intersection of parenteral nutrition (PN), intravenous anesthesia and drug delivery. Global lipid injectable emulsions are valued at about USD ~ billion in revenue, with North America the largest regional contributor. Within parenteral nutrition, the United States alone generates roughly USD ~ billion in PN revenue and accounts for more than one-third of global spend, reflecting high healthcare utilization, intensive-care burden and hospital expenditures of around USD 1.5 trillion within overall national health spending of USD ~ trillion. Based on these benchmarks and U.S. share of PN and lipid emulsions, the USA Injectable Emulsions Market is reasonably approximated at around USD 1.3 billion in 2024, with a forecast growth trajectory of about 5.5–6.0% annually through 2030.
The USA Injectable Emulsions Market is highly concentrated in large, tertiary hospitals and academic medical centers, which sit at the core of the country’s 6,000-plus hospital network and roughly 34 million annual admissions. Utilization is most intense in critical-care units, oncology centers and large children’s hospitals that manage complex malnutrition, short-bowel syndrome, neonatal intensive care and major surgery.
Market Segmentation
By Clinical Application
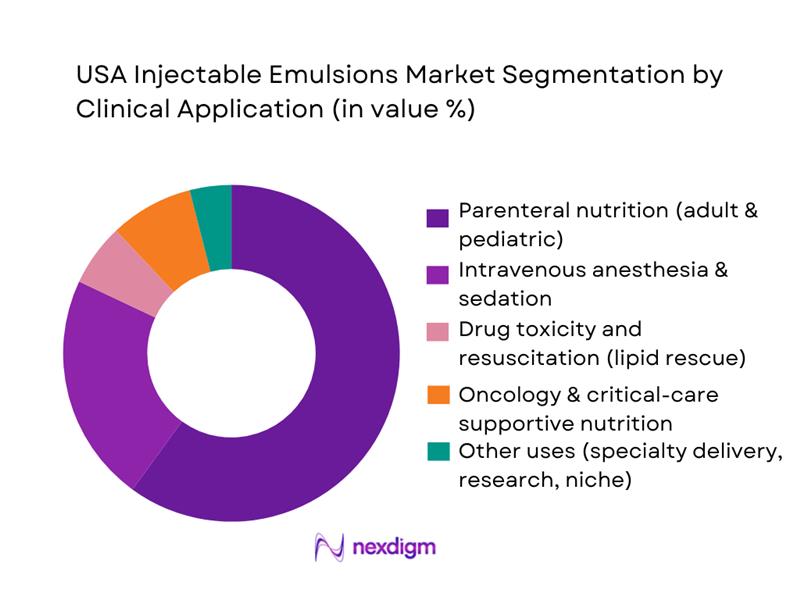
The USA Injectable Emulsions Market is segmented by clinical application into parenteral nutrition, intravenous anesthesia and sedation, drug toxicity and resuscitation, oncology and critical-care supportive nutrition, and other uses. Parenteral nutrition dominates this segmentation because emulsions are an indispensable calorie and essential fatty-acid source for patients unable to use their gastrointestinal tract. U.S. data indicate roughly 34,000 hospitalized patients receive PN annually, while separate analyses estimate around 40,000 patients on home PN at any given time, underscoring structurally high parenteral demand. These patients typically require multi-day to multi-month lipid infusions, far exceeding the exposure associated with single-procedure anesthesia or episodic lipid rescue. High ICU occupancy and the growing burden of complex chronic disease further reinforce PN’s share of injectable emulsion volumes in U.S. hospitals.
By Lipid Formulation Type
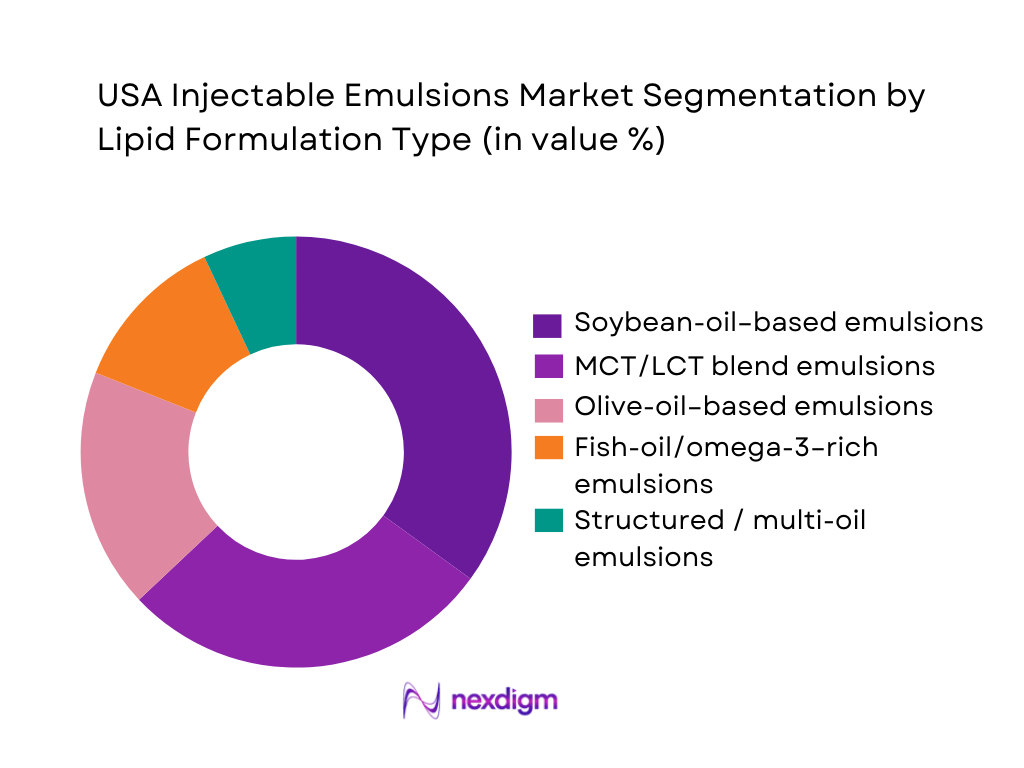
The USA Injectable Emulsions Market is segmented by lipid formulation into soybean-oil–based emulsions, MCT/LCT blends, olive-oil–based emulsions, fish-oil/omega-3–rich emulsions, and structured multi-oil mixtures. Soybean-oil–based products retain a large installed base and currently dominate share because legacy brands such as Intralipid have been used for decades in U.S. PN programs, with well-understood safety profiles and established purchasing contracts. Many hospitals standardize formularies around these conventional emulsions and rely on bulk pharmacy packaging for three-in-one admixtures, reinforcing volume. While newer mixed-oil products like SMOFlipid and olive-oil–based Clinolipid are gaining traction, their uptake is concentrated in academic centers and high-acuity ICUs, which still represent a smaller fraction of national PN volume compared with widespread use of traditional soybean-based emulsions.
Competitive Landscape
The USA Injectable Emulsions Market is relatively concentrated and characterized by a handful of global infusion and injectable nutrition specialists. Companies such as Fresenius Kabi, Baxter, B. Braun, Pfizer (through Hospira) and Otsuka anchor the lipid-emulsion and PN ecosystem, often offering complete systems that bundle emulsions, amino acids, dextrose and multi-chamber bags. Brand-level differentiation centers on lipid source (soybean vs multi-oil), stability and admixture compatibility, pediatric labeling, and support services like PN compounding, dose-calculation tools and clinical education. U.S. buyers—especially IDNs and group purchasing organizations—typically negotiate multi-year contracts, making formulary access and supply security critical competitive levers alongside price.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters (Global / US) | Key Injectable Emulsion Brands (USA) | Primary Clinical Focus in USA | US PN / Emulsion Manufacturing or Fill-Finish Presence | Distribution Footprint (Hospitals & Home Infusion) | Strategic Focus in Emulsions (USA-Specific) | Recent US Regulatory / Product Milestones |
| Fresenius Kabi | 1912 | Bad Homburg, Germany / Lake Zurich, IL | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Baxter International | 1931 | Deerfield, IL, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| B. Braun Medical | 1839 | Melsungen, Germany / Bethlehem, PA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pfizer (Hospira) | 1849 | New York, NY, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Otsuka Pharmaceutical | 1964 | Tokyo, Japan / Rockville, MD | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
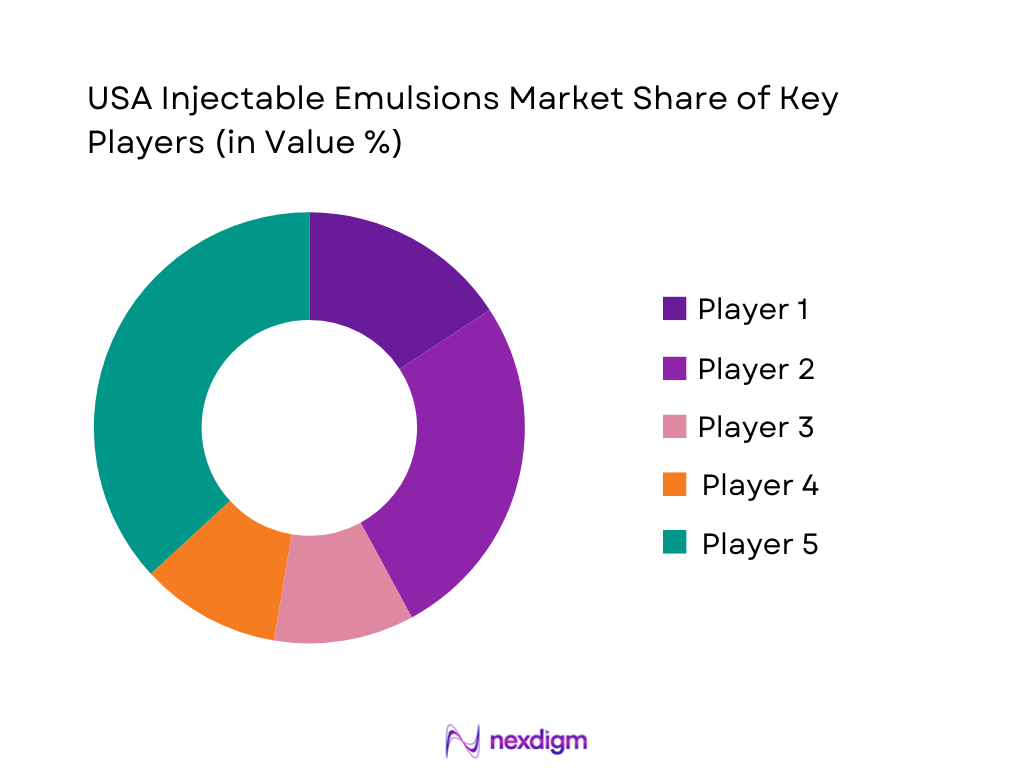
USA Injectable Emulsions Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
ICU, NICU and OR procedure volume growth
Rising critical-care and surgical intensity directly drives demand for lipid injectable emulsions and PN admixtures. The U.S. has about 35,601 NICU beds across 1,424 hospitals, reflecting substantial neonatal critical-care capacity that increasingly relies on PN and lipid emulsions for preterm and complex infants. Around 9.8% of all infants were admitted to a NICU, based on recent birth-certificate data covering roughly 3.6 million births, underscoring high utilization of intensive care. Ambulatory surgery is also expanding: national estimates show about 12.4 million ambulatory surgery encounters in hospital-owned facilities in a recent year, alongside 51.4 million inpatient surgical procedures across hospitals, keeping OR PN and propofol-based lipid emulsions central to peri-operative nutrition and anesthesia workflows.
Rising PN penetration
A growing burden of chronic and complex disease underpins higher use of PN and injectable emulsions. Recent estimates indicate about 129 million U.S. adults live with at least one chronic condition, and nearly 50 million people are aged 65 or older, a cohort with higher rates of cancer, intestinal failure, and surgical complications that often require PN. National health spending reached about 4.8 trillion U.S. dollars, or roughly 14,423 dollars per person, with 93% of the population insured, supporting access to high-cost therapies such as PN. Within this context, professional societies and clinical guidelines describe tens of thousands of patients on long-term home parenteral nutrition and continued growth in hospital PN use, reinforcing steady demand for lipid emulsions across inpatient and home-care settings.
Market Challenges
Sterile injectable capacity constraints
Injectable emulsions compete for capacity within a constrained U.S. sterile manufacturing base. Between January and July of a recent year, federal assessments documented more than 100 active drug shortages, with a large share involving sterile injectables vital to hospitals and oncology centers. Over 292 new molecular entities approved in a five-year period added further load, with nearly half requiring refrigeration or freezing, increasing pressure on cleanroom, lyophilization, and fill-finish capacity. At the same time, U.S. healthcare spending of ~ trillion U.S. dollars and high insured rates sustain demand for biologics, anti-infectives, and PN, leaving limited flexibility when factories experience quality deviations or capacity outages. For injectable emulsions, any plant shutdown or quality event can rapidly propagate into PN supply constraints at hospital and home-infusion level.
Drug shortage episodes
Persistent drug-shortage cycles in the U.S. disproportionately affect sterile injectables, including PN components and lipid emulsions. Professional monitoring reports have recorded more than 300 active drug shortages at several points in recent years, the highest levels seen in over a decade, with many incidents involving critical care, oncology, and anti-infective injectables. Federal drug-shortage lists similarly show over 100 ongoing shortages, often concentrated in generic sterile injectables produced by a small number of global manufacturers. These disruptions intersect with a hospital sector that manages around 674,000 staffed beds and millions of surgical cases annually, magnifying the operational impact when a single PN component or lipid emulsion is constrained. Hospitals must frequently implement therapeutic substitutions and rationing strategies, creating clinical and procurement challenges specific to injectable emulsions.
Opportunities
Upgrading from legacy soybean-only emulsions to 4th-generation mixed-oil products
Current U.S. disease and spending patterns create a compelling base for wider conversion to advanced injectable emulsions. With national health expenditures at about 4.8 trillion U.S. dollars and per-capita spending above 14,000 U.S. dollars, payers are increasingly focused on interventions that reduce complications and length of stay. Chronic disease affects roughly 129 million adults, and obesity is at or above 40% in most states, contributing to high rates of intestinal failure, pancreatitis, and complex surgical recovery where PN is often required. Pediatric and neonatal acuity is also significant, with nearly 10% of infants admitted to NICUs and 35,601 NICU beds nationwide. Clinical studies highlight that malnutrition and PN-related complications in ICUs and PICUs can add tens of thousands of dollars per case. These pressures underpin strong clinical and economic rationale for upgrading from older soybean-only emulsions to mixed-oil and fish-oil–containing products that may support better liver profiles, immune modulation, and outcomes in high-risk PN populations.
Future Outlook
Over the next six years, the USA Injectable Emulsions Market is expected to grow steadily as hospitals, home-infusion providers and specialty centers manage rising chronic-disease burden and more nutritionally at-risk patients. Global lipid injectable emulsion studies project mid-single-digit annual growth, and the broader parenteral nutrition market is forecast to expand at roughly 6% annually through the end of the decade, with North America remaining the largest revenue base. In the U.S., this translates into an anticipated injectable-emulsion CAGR of about 5.5–6.0% over 2024–2030, supported by higher ICU acuity, aging demographics, and increased reliance on PN in surgical oncology, advanced GI disorders and neonatal intensive care.
Major Players
- Fresenius Kabi
- Baxter International Inc.
- B. Braun Melsungen AG / B. Braun Medical Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- Abbott Laboratories
- Grifols, S.A.
- Kelun Pharmaceutical Group
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
- Macopharma
- Biocodex
- Smiths Medical
- Heron Therapeutics
- The Medicines Company / Novartis
- AstraZeneca
Key Target Audience
- Injectable emulsion manufacturers and parenteral nutrition solution blenders
- Hospital pharmacy departments and medication-use evaluation committees
- Integrated delivery networks and large multi-hospital health systems
- Home infusion and alternate-site infusion therapy providers
- Group purchasing organizations and pharmaceutical wholesalers
- Health insurance companies and pharmacy benefit managers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involved constructing an ecosystem map for the USA Injectable Emulsions Market, spanning lipid-emulsion manufacturers, PN compounders, hospitals, home-infusion providers, regulators and guideline-setting bodies. Extensive desk research drew on secondary and proprietary databases, clinical guidelines and regulatory documents to capture market structure, clinical indications, product classes and utilization patterns. This step enabled the identification of critical variables such as PN penetration, ICU and oncology caseloads, product mix by lipid source, and the financial scale of related PN and lipid-emulsion categories.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In the second phase, we compiled historical data for global lipid injectable emulsions, regional PN markets and U.S. healthcare expenditure, aligning them with hospital-admission and chronic-disease statistics. Using a bottom-up approach, we triangulated U.S. injectable-emulsion demand from PN volumes, anesthesia procedure counts and published lipid-emulsion market values. Where U.S.-specific injectable-emulsion values were not explicitly reported, proportional allocation based on North American share and PN revenue was applied, while carefully preserving the definitions of each underlying data series.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses on segment dominance, lipid-formulation mix and growth drivers were validated against clinical-practice literature, ASPEN safety recommendations and FDA product labels for key emulsions such as Intralipid, SMOFlipid and Clinolipid. Insights from published surveys on PN utilization, malnutrition prevalence and home-infusion trends were used as proxies for expert commentary, highlighting real-world constraints like reimbursement gaps, PN access issues and compounding capacity. This process helped refine assumptions around application-level shares and adoption curves for newer lipid formulations.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Finally, we synthesized quantitative estimates with qualitative insights from competitive-landscape analyses, company disclosures and market-research summaries covering lipid injectables and pharmaceutical emulsions. Segmental market shares by application and lipid type were constructed as internally consistent analyst estimates anchored to published global and regional revenue figures, while acknowledging data gaps where direct U.S. injectable-emulsion values are not disclosed. The resulting USA Injectable Emulsions Market report integrates these triangulated datasets into a coherent narrative on market size, structure, competition and forward-looking dynamics tailored for business and investment decision-makers.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope specific to injectable emulsions only, product inclusion–exclusion criteria for lipid injectable emulsions and emulsion-formulated drugs, data triangulation using hospital purchasing, charge-master and distributor sell-out, validation with ASPEN/ASHP clinical practice inputs, bottom-up SKU-level volume build-up by care setting, top-down calibration with parenteral nutrition and anesthesia spend, price realization and contract discount assumptions, limitations around non-reported home infusion volumes)
- Definition, Scope & Product Classification
- Market Genesis & Evolution Path
- Stakeholder Ecosystem Mapping
- Supply Chain & Value Chain Analysis
- Lifecycle, Business Cycle & Demand Seasonality
- Growth Drivers
ICU, NICU and OR procedure volume growth
Rising PN penetration
Expansion of home PN programs
Preference for ready-to-use emulsions and multi-chamber PN bags
Clinical adoption of fish-oil and mixed-oil emulsions - Market Challenges
Sterile injectable capacity constraints
Drug shortage episodes
Complex cold-chain and storage requirements
Risk of emulsion instability and particulate contamination
PN-associated complications - Opportunities
Upgrading from legacy soybean-only emulsions to 4th-generation mixed-oil product Expanding home and alternate-site PN
Penetrating mid-size and community hospitals with standardized PN protocols
Lifecycle management and line extensions
CMO/CDMO partnership opportunities - Trends
Shift toward fish-oil–containing emulsions and advanced lipid profiles
Growth of standardized PN order sets and closed-loop EMR integration
Increased use of multi-chamber PN bags over pharmacy-compounded PN
Digitization of PN and sedation dosing tools - Regulatory, Quality & Safety Framework
Technology, Formulation & Packaging Innovations - Stakeholder Ecosystem & Decision-Making
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Risk Assessment & Scenario Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Standardized Volume, 2019-2024
- By Therapeutic Class, 2019-2024
- By Clinical Indication (in Value %)
Parenteral nutrition–acute inpatient PN
Parenteral nutrition–home and chronic PN
Peri-operative and ICU anesthesia/sedation
Oncology and critical-care supportive emulsions
Other emerging emulsion-based therapies) - By Lipid/Emulsion Composition (in Value %)
Soybean-only emulsions
MCT–soybean blends
Mixed-oil emulsions including olive oil
Fish-oil–based emulsions
Structured and advanced-generation emulsions - By Concentration & Strength (in Value %)
10% lipid injectable emulsions
20% lipid injectable emulsions
Higher-concentration specialty emulsions
Standard vs high-osmolarity PN admixtures
Propofol - By Patient Age Group (in Value %)
Preterm and term neonates
Pediatric patients
Adults in general care and ICU
Geriatric and long-term care PN
Sedation populations - By Care Setting (in Value %)
Academic medical centers and tertiary hospitals
Community and regional hospitals
Dedicated children’s hospitals and NICU centers
ambulatory surgery centers and procedure suites
home infusion and long-term care providers - By Distribution & Contracting Channel (in Value %)
Wholesaler distribution
Direct-to-hospital contracts
IDN and GPO-negotiated contracts
Specialty distributors and home infusion pharmacies
Federal and government supply channels - By Manufacturing & Sourcing Model (in Value %)
Domestic captive sterile injectable plants
US-based CDMO supply
Imported finished-dose emulsions
Hybrid sourcing models with dual supply strategies
- Market Share Snapshot by Value and Standardized Volume
- Market Share by Key Segments
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Portfolio breadth in PN and injectable lipid emulsions, depth of anesthesia and critical-care emulsion portfolio, sterile injectable manufacturing footprint and US plant capacity, track record on FDA quality observations and recall history, formulary and GPO contract coverage across IDNs, support services for PN teams and anesthesia departments including tools and training, strength in home infusion and alternate-site PN supply, pipeline and lifecycle-management strategy in advanced lipid and emulsion technologies)
- Competitive Strategy & Positioning Analysis
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing, Contracting & Discounting Landscape
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Fresenius Kabi USA LLC
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Braun Medical Inc.
Pfizer Inc.
Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
Viatris Inc.
Sandoz Inc.
Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Accord Healthcare Inc.
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Inc. (US Injectables)
Grifols USA LLC
American Regent, Inc.
Pacira BioSciences, Inc.
- Acute Care Hospitals & Academic Medical Centers
- Community Hospitals & Regional Systems
- Children’s Hospitals & Neonatal Centers
- Ambulatory Surgery Centers & Procedural Suites
- Home Infusion, LTAC & Rehabilitation Settings
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Standardized Volume, 2025-2030
- By Therapeutic Class, 2025-2030