Market Overview
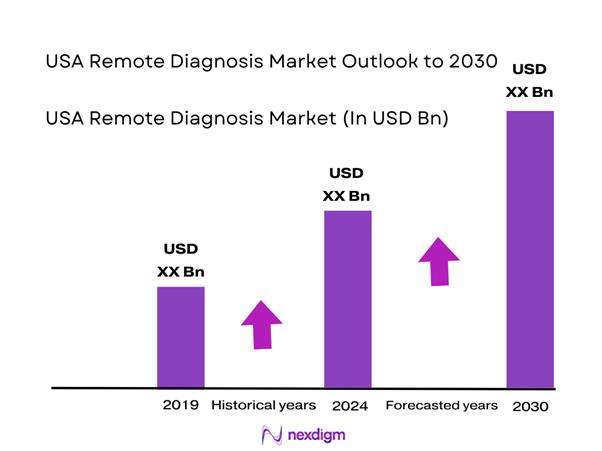
The USA Remote Diagnosis market is valued at USD ~ billion, reflecting its role as a core enabler of digital healthcare delivery across hospital, ambulatory, and home settings. The market supports early detection, clinical decision support, and continuous monitoring by extending diagnostic capabilities beyond physical care sites. Demand is structurally linked to chronic disease prevalence, clinician capacity constraints, and the need for faster diagnosis-to-intervention cycles. Remote diagnosis functions as a foundational layer within virtual care ecosystems, directly influencing cost efficiency, clinical outcomes, and patient access while reinforcing data-driven and value-based care models.
Within the country, major metropolitan regions dominate adoption due to dense provider networks, advanced digital infrastructure, and high patient volumes. These regions host large integrated delivery networks and academic medical centers that act as early adopters of advanced diagnostic technologies. They also attract technology vendors and innovation partners due to reimbursement sophistication and clinical research activity. Technology influence is shaped by global medical technology and digital health innovation hubs that define diagnostic algorithms, interoperability standards, and platform architectures. Their leadership accelerates diffusion of advanced tools across domestic healthcare systems.
Market Segmentation
By Clinical Application Area
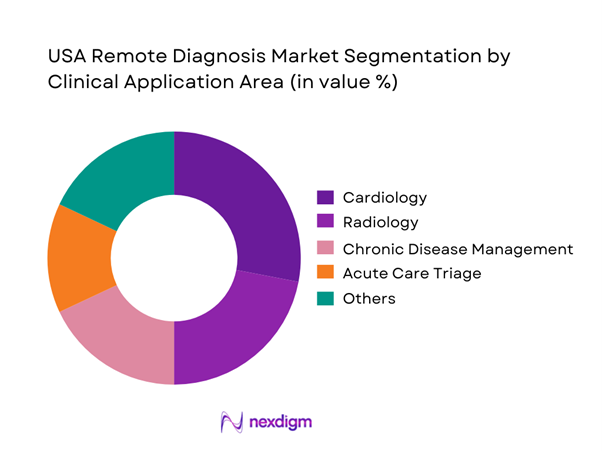
Cardiology-related remote diagnosis dominates due to the high prevalence of cardiovascular conditions and the strong clinical value of continuous and near-real-time diagnostic monitoring. Remote ECG interpretation, arrhythmia detection, and heart failure monitoring enable earlier intervention and reduce acute hospitalization risk. Providers prioritize cardiology because outcomes are directly measurable, reimbursement pathways are relatively mature, and diagnostic accuracy benefits significantly from algorithmic support. Integration with wearable and implantable devices further strengthens adoption, allowing longitudinal data analysis rather than episodic assessment. As cardiovascular care increasingly shifts toward outpatient and home settings, cardiology remains the anchor application driving platform investment and clinical acceptance across broader diagnostic domains.
By Care Setting
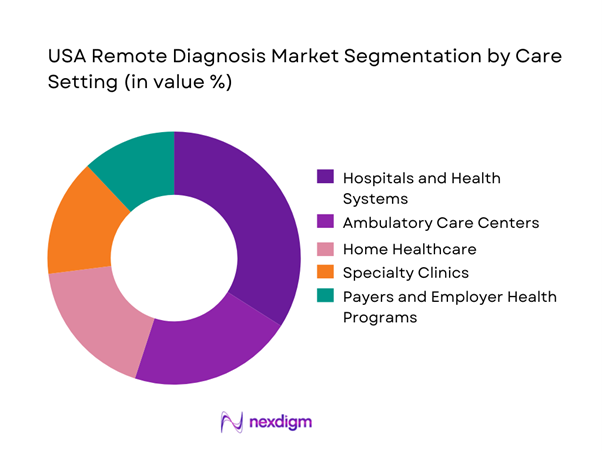
Hospitals and health systems represent the dominant care setting due to their role as diagnostic hubs and their financial capacity to deploy enterprise-grade platforms. Remote diagnosis solutions are embedded into hospital workflows to manage bed capacity, reduce diagnostic delays, and extend specialist expertise across satellite locations. These organizations value platforms that integrate with existing clinical systems and support multidisciplinary collaboration. Hospitals also influence adoption across affiliated clinics and home care programs, creating downstream demand. Their procurement scale and regulatory readiness make them the primary commercial anchor for solution providers, reinforcing their dominance in overall market value.
Competitive Landscape
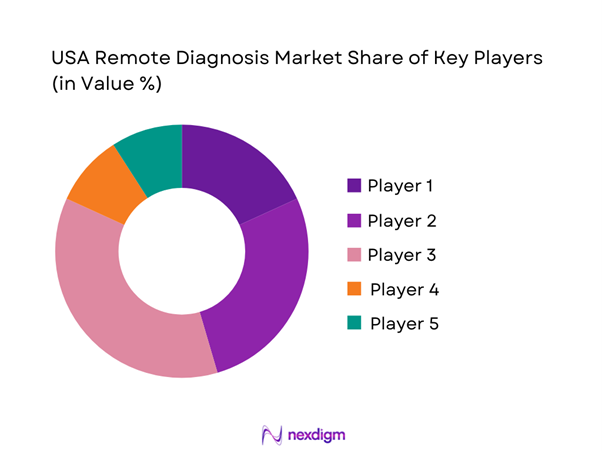
The USA remote diagnosis market is dominated by a few major players, including Teladoc Health and global or regional brands like Philips Healthcare, GE HealthCare, and Siemens Healthineers. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | Primary Remote Diagnosis Focus | Modality Coverage Depth | AI / Automation Layer | Integration Surface | Coverage Model | Differentiation |
| vRad (Virtual Radiologic) | 1999 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Radiology Partners | 2012 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Philips Healthcare | 1891 | Netherlands | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Siemens Healthineers | 1847 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GE HealthCare | 1994 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Remote Diagnosis Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of virtual care pathways
The expansion of virtual care pathways has repositioned remote diagnosis from a supporting capability to a foundational clinical function. As care delivery increasingly occurs across outpatient, home-based, and hybrid settings, providers require diagnostic workflows that operate independent of physical facilities. Remote diagnosis enables timely clinical decision-making, continuity across transitions of care, and scalable access to subspecialists without geographic constraints. Integration of diagnostics into virtual care platforms also reduces unnecessary in- person encounters and optimizes clinician utilization. Over time, standardized remote diagnostic workflows reinforce clinical confidence, embed diagnostic decision support into routine care, and establish remote diagnosis as an integral component of modern care delivery models.
Rising chronic disease burden
The rising prevalence of chronic conditions is shifting diagnostic demand from episodic testing toward continuous and longitudinal assessment models. Conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory disorders require frequent monitoring to detect early signs of deterioration and therapy non-adherence. Remote diagnosis platforms enable ongoing evaluation through connected diagnostics, trend analysis, and automated alerts, supporting proactive clinical intervention. This approach helps reduce avoidable acute episodes and downstream complications while supporting population-scale disease management. For providers and payers, remote diagnostics offer a mechanism to balance quality outcomes with operational efficiency, making adoption increasingly essential for chronic care strategies.
Challenges
Clinical data interoperability gaps
Clinical data fragmentation remains a significant barrier to effective remote diagnosis deployment. Patient information is often distributed across disparate electronic health records, imaging systems, laboratory platforms, and legacy infrastructure, limiting diagnostic context. Inconsistent data standards and variable interoperability maturity increase integration complexity, prolong implementation timelines, and elevate total cost of ownership. Without unified data access, remote diagnostic insights lack clinical completeness, reducing physician confidence and limiting scalability across multi-site organizations. Addressing interoperability gaps requires investment in standardized data exchange frameworks, governance alignment, and system modernization, all of which slow adoption despite strong clinical demand for remote diagnostic capabilities.
Physician trust and adoption resistance
Physician acceptance is critical to remote diagnosis success and remains uneven across specialties and care settings. Resistance often emerges when diagnostic outputs are perceived as opaque, insufficiently validated, or disruptive to established clinical workflows. Concerns around accountability, diagnostic accuracy, and over-reliance on automated insights can further delay adoption. Building trust requires rigorous clinical validation, transparent decision logic, and alignment with existing reporting and documentation processes. Structured training, phased deployment, and demonstrable improvements in turnaround time and diagnostic consistency are essential to overcoming skepticism and achieving sustained clinician engagement.
Opportunities
AI-driven diagnostic augmentation
Artificial intelligence presents a significant opportunity to enhance remote diagnosis by augmenting clinician decision-making rather than replacing it. AI-enabled tools can prioritize high-risk cases, identify subtle patterns across large datasets, and standardize interpretation across distributed care teams. When integrated into diagnostic workflows, these capabilities improve productivity, reduce cognitive burden, and support consistent clinical quality. As explainability and validation frameworks mature, clinician confidence in AI-assisted diagnostics continues to increase. This creates opportunities for providers to scale diagnostic capacity, improve turnaround performance, and deploy limited specialist resources more effectively across enterprise networks.
Home-based acute care models
The expansion of home-based acute care models is creating sustained demand for reliable diagnostic capabilities beyond hospital walls. Programs such as hospital-at-home require continuous clinical assessment, rapid escalation pathways, and dependable diagnostic insight to ensure patient safety. Remote diagnosis enables real-time monitoring, virtual specialist review, and timely intervention without physical admission. This model supports cost containment, capacity optimization, and improved patient experience while maintaining clinical oversight. As healthcare systems expand decentralized care delivery, remote diagnostics become a critical infrastructure layer supporting safe, scalable, and clinically robust home-based acute care programs.
Future Outlook
The USA Remote Diagnosis market will evolve toward deeper integration, standardized enterprise deployment, and expanded use across preventive and acute care pathways. Strategic focus will center on interoperability, clinical trust, and scalable AI augmentation, positioning remote diagnosis as a foundational healthcare infrastructure component rather than a discrete service.
Major Players
- Teladoc Health
- Philips Healthcare
- GE HealthCare
- Siemens Healthineers
- Oracle Health
- Epic Systems
- Cerner
- Medtronic
- Abbott
- Boston Scientific
- Amwell
- iRhythm Technologies
- Masimo
Key Target Audience
- Hospitals and integrated delivery networks
- Ambulatory care providers
- Home healthcare organizations
- Health insurance payers
- Employer health benefit managers
- Digital health platform providers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies (country-specific)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core variables included clinical application scope, care setting adoption, technology integration depth, and regulatory considerations. Data points were defined to capture both clinical and commercial dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
The market structure was developed by mapping diagnostic workflows, value-chain participation, and revenue attribution across use cases and care settings.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through structured interviews with clinicians, healthcare administrators, and technology providers to ensure practical relevance.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into a cohesive framework emphasizing strategic insights, market structure, and decision-oriented analysis.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Inclusions/Exclusions, Abbreviations, Topic-Specific Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Revenue Attribution Logic Across Use Cases or Care Settings, Primary Interview Program Design, Data Triangulation and Validation, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Remote Diagnosis Usage and Care-Continuum Mapping
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- USA Healthcare Service and Digital Delivery Architecture
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of virtual care pathways
Rising chronic disease burden
Integration of AI and clinical analytics
Hospital capacity optimization pressures
Consumer demand for home-based care
Value-based care reimbursement models - Challenges
Clinical data interoperability gaps
Regulatory and compliance complexity
Physician trust and adoption resistance
Cybersecurity and data privacy risks
Fragmented reimbursement structures
Technology integration costs - Opportunities
AI-driven diagnostic augmentation
Home-based acute care models
Enterprise health system standardization
Employer-sponsored virtual diagnostics
Advanced imaging and waveform analytics
Preventive and population health programs - Trends
Multi-Modal Diagnostics
Ambient Clinical Intelligence
Workflow-Embedded Diagnosis - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Service Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Revenue per Diagnostic Interaction, 2019–2024
- By Clinical Application Area (in Value %)
Cardiology
Radiology
Chronic Disease Management
Acute Care Triage
Post-Acute and Home Care
Preventive and Wellness Diagnostics - By Care Setting (in Value %)
Hospitals and Health Systems
Ambulatory Care Centers
Home Healthcare
Specialty Clinics
Payers and Employer Health Programs - By Technology / Platform Type (in Value %)
AI-enabled diagnostic platforms
Remote patient monitoring integrated diagnosis
Imaging and waveform analytics
EHR-integrated diagnostic tools
Standalone virtual diagnosis software - By Deployment / Delivery Model (in Value %)
Cloud-based platforms
Hybrid cloud and on-premise
Fully on-premise systems - By End-Use Customer Type (in Value %)
Large hospital groups
Independent hospitals
Physician networks
Home healthcare providers
Payers and managed care organizations
Employers and corporate health programs - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Competition ecosystem overview
- Cross Comparison Parameters (clinical integration depth, AI diagnostic accuracy, interoperability standards, regulatory compliance readiness, scalability across care settings, cybersecurity posture, analytics reporting sophistication, clinician workflow alignment)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and commercial model benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Teladoc Health
Philips Healthcare
GE HealthCare
Siemens Healthineers
Oracle Health
Epic Systems
Cerner
Medtronic
Abbott
Boston Scientific
Amwell
BioTelemetry
iRhythm Technologies
Masimo
Koninklijke Philips
- Buyer personas and decision-making units
- Procurement and contracting workflows
- KPIs used for evaluation
- Pain points and adoption barriers
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Service Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Revenue per Diagnostic Interaction, 2025–2030


