Market Overview
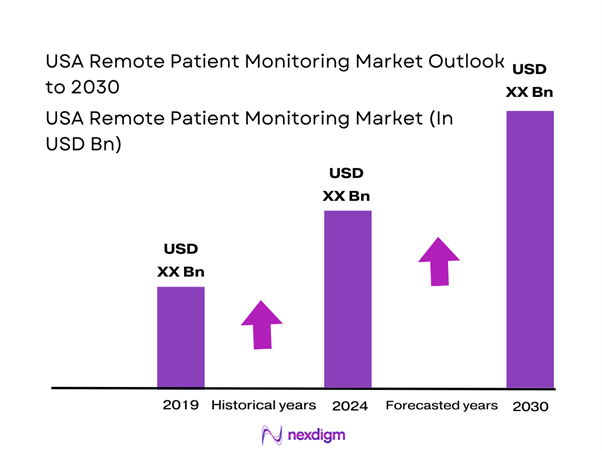
The USA remote patient monitoring market is valued at USD ~ billion, supported by reimbursement-driven program expansion, rising home-based care models, and rapid device/platform adoption across chronic and post-acute pathways. A commonly used national reference point is the USA RPM estimate (USD ~ billion) and its growth trajectory toward USD ~ billion, which reflects scaling adoption across devices, software, and clinical services layers.
The market’s operational dominance concentrates in large, digitally mature care ecosystems—especially metro clusters that combine high chronic-disease panels, major IDNs/academic medical centers, and payer density. Cities and regions anchored by large health systems and digital health procurement capacity (e.g., California metros, the Northeast corridor, Texas metros, Florida) lead RPM program rollouts because they can fund clinical monitoring teams, integrate RPM into EHR workflows, and negotiate payer contracts at scale, accelerating enterprise-wide deployment.
Market Segmentation
By Offering
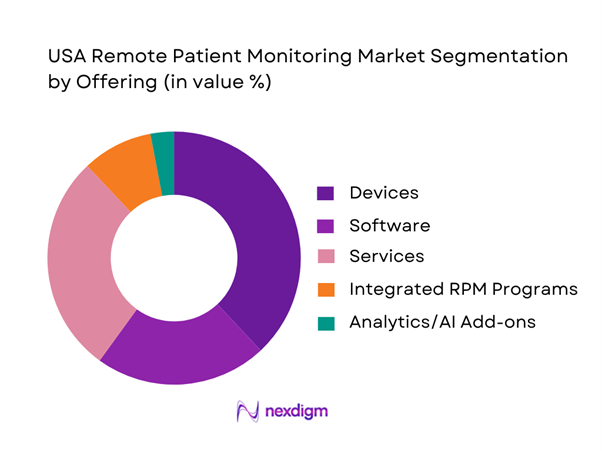
USA RPM is segmented by offering into devices, software, services, integrated RPM programs, and analytics/AI add-ons. Devices dominate because RPM adoption typically begins with reimbursable physiologic data capture—BP cuffs, CGMs, ECG patches, pulse oximeters—paired to a transmission and dashboard layer. The USA RPM market is segmented into devices, software, and services, with devices highlighted as a major share driver in the USA context. Devices also create the “activation moment” (enrollment + setup), after which services (clinical monitoring, escalation, patient coaching) monetize per patient-month and software scales across panels. Integrated programs are increasingly preferred by mid-sized providers that lack staffing to run monitoring internally, while analytics/AI add-ons attach to high-acuity cohorts to reduce alert burden and prioritize escalations.
By Indication / Care Pathway
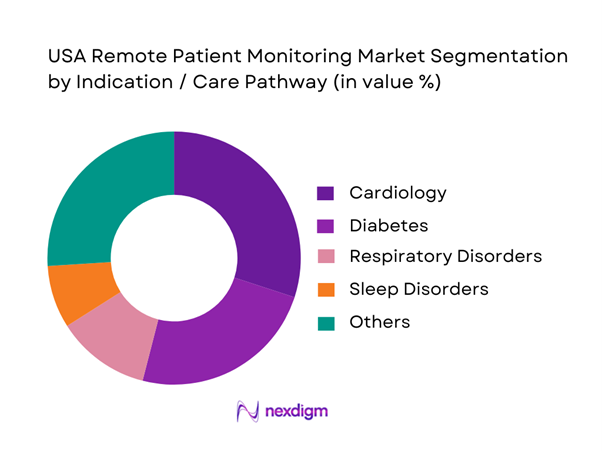
RPM is segmented into cardiology, diabetes, oncology, neurology, sleep disorders, wellness improvement, respiratory disorders, mental health, and others. Cardiology dominates because RPM aligns tightly with high-frequency vitals and arrhythmia surveillance and post-discharge monitoring, where clinicians value early deterioration detection and rapid escalation. Cardiology is identified as the largest share segment in the USA RPM market, citing cardiovascular disease burden and product advances that provide real-time cardiac data. Diabetes is also a major growth engine due to continuous glucose monitoring adoption and smartphone-linked biosensors, but cardiology remains the most systematized RPM pathway across IDNs because it is embedded into heart failure clinics, electrophysiology monitoring, and transitional care programs.
Competitive Landscape
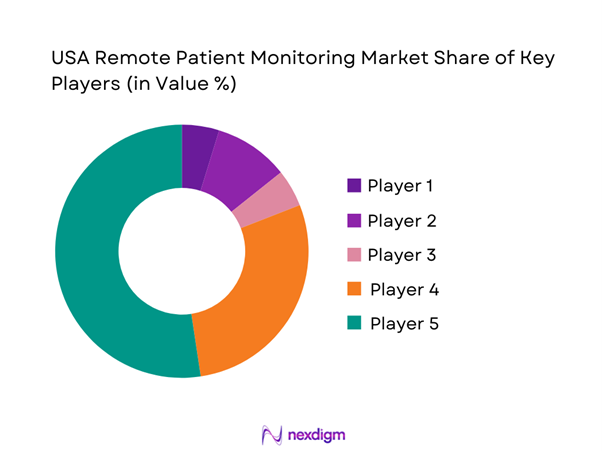
The USA RPM market is shaped by a mix of global medtech manufacturers, specialized monitoring companies, and full-stack RPM program operators. Large OEMs and platform firms increasingly partner with health systems and payers to deliver end-to-end programs—device provisioning, data transmission, triage workflows, and escalation pathways—while reimbursement rules and integration depth often determine vendor shortlists. Prominent USA RPM players reflect this blend of device leadership and service and platform scale.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | RPM Focus Area | Primary Indications | Device Modality Strength | Integration Approach | Deployment Model | Differentiation Lever |
| Philips (incl. BioTelemetry) | 1891 | Netherlands / USA ops | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Abbott | 1888 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Dexcom | 1999 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GE HealthCare | 1994 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| VitalConnect | 2011 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Remote Patient Monitoring Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Chronic Burden Addressability
Remote patient monitoring scales in the U.S. because the addressable chronic pool is structurally large and increasingly multi-morbid, making continuous physiologic tracking operationally valuable for cardiometabolic and cardio-respiratory pathways. Cardiovascular disease deaths in the U.S. are reported at ~, and mortality tables show ~ heart-disease deaths with ~ diabetes deaths in the same mortality release, reinforcing why RPM programs prioritize BP, ECG, weight, and glucose tracking to reduce decompensation risk signals between visits. At the macro layer, the U.S. GDP is listed at USD ~ trillion with a population of ~, which matters because higher absolute economic output and population scale sustain large insured and provider ecosystems that can operationalize longitudinal monitoring across millions of eligible patients. The RPM “why now” is also tied to chronic complexity, with about ~ people with diabetes and about ~ adults with prediabetes, enlarging the clinical and payer incentive for home-based tracking, escalation triage, and medication adherence support, especially when combined with hypertension and heart failure pathways.
Aging-at-Home Enablement
RPM expands fastest when older adults can remain safely at home while clinicians maintain visibility into vitals and deterioration risk, reducing avoidable acute utilization. Older-population resources are used by providers and payers to quantify the older adult base that drives demand for home monitoring, caregiver workflows, and fall- and frailty-adjacent care coordination. On the macro side, country indicators show the U.S. economy operating at USD ~ trillion GDP with ~ people, which correlates with large-scale Medicare and Medicare Advantage footprints, extensive home health capacity, and the digital infrastructure investment required for device provisioning, cellular connectivity, and monitoring operations. Aging-at-home is also constrained or enabled by broader labor and care availability. Registered nurse jobs are reported at ~, and RPM programs directly compete for nursing time to staff monitoring panels, escalate alerts, and coordinate interventions, making the absolute clinical workforce scale a key determinant of whether aging populations can be supported at home rather than via facility-based monitoring.
Challenges
Patient Adherence and Drop-offs
U.S. RPM outcomes depend on patients consistently transmitting physiologic data over sustained periods. Adherence gaps quickly degrade clinical signal quality and billing and documentation feasibility in reimbursement-linked programs. RPM is operationally constrained by Medicare coverage rules and documentation expectations; when patients stop transmitting, providers face both clinical blind spots and compliance and billing friction, which discourages scale. The patient pool is also inherently heterogeneous, with about ~ people with diabetes and about ~ adults with prediabetes, spanning wide socioeconomic and digital-literacy ranges that influence device setup success, daily measurement habits, and sustained engagement, making adherence a first-order operational risk for employers, payers, and provider programs. Macro constraints amplify the challenge. U.S. inflation is listed at ~ with a population of ~, implying that even small adherence failures can cascade into large absolute numbers of inactive devices, replacement cycles, and support tickets in nationwide programs, while inflationary pressure can increase the operational burden of patient support and outreach without referencing any RPM pricing or market-size statistics.
Alert Fatigue
RPM programs can generate high alert volumes, especially when thresholds are conservative, patients use devices inconsistently, or data quality is noisy, leading to alert fatigue that reduces clinician responsiveness and weakens care-team trust in the monitoring signal. Workforce realities shape this challenge, with registered nurse jobs reported at ~, and many RPM models depending on nursing teams to triage alerts, contact patients, and escalate to clinicians. When alerts overwhelm panels, the same RN base must cover both traditional care and RPM triage load, making fatigue a structural scaling constraint. Clinical urgency also comes from disease burden, with cardiovascular disease deaths reported at ~, which is why cardiology RPM pathways are built to be sensitive, yet high sensitivity increases alert volumes unless triage logic is tuned. Macro indicators add context, with U.S. GDP at USD ~ trillion and GDP per capita at USD ~, supporting broad adoption of connected devices and data streams. However, higher device penetration can also inflate alert volume in absolute terms, increasing the need for workflow automation and evidence-based alert stratification without citing any market size, CAGR, or pricing.
Opportunities
Hospital-at-Home Scaling
Hospital-at-home creates a direct expansion lane for RPM because acute-level care in the home requires continuous monitoring, escalation pathways, and tightly governed clinical workflows. Acute Hospital Care at Home discharges are reported at about ~ as of April, with ~ participating hospitals in that timeframe, demonstrating substantial real-world acute-at-home activity that relies on monitoring and rapid response capabilities. RPM becomes a care safety layer rather than a purely chronic tool. The opportunity is supported by federal capacity visibility priorities, with hospital capacity reporting and modernization work indicating continued system-level focus on optimizing inpatient capacity and moving appropriate care to the home with stronger data. Macro fundamentals reinforce scalability, with U.S. GDP at USD ~ trillion and GDP per capita at USD ~, enabling investment in home-based acute workflows such as devices, clinical operations, and integration across large health systems without relying on future projections or market-size claims.
AI-Enabled Clinical Triage
AI-enabled triage is a near-term RPM growth lever because the U.S. RPM challenge is not whether data can be collected, but whether data can be converted into actionable, low-burden clinical decisions. Alert fatigue and staffing constraints are already visible at national scale, with registered nurse jobs reported at ~, and RPM triage competing for that same finite RN pool. AI triage that reduces false positives and prioritizes true deterioration risk directly increases panel capacity per nurse without introducing pricing or market-size statistics. The clinical need is also quantifiable, with cardiovascular disease deaths reported at ~, which explains why cardiology RPM pipelines are tuned for sensitivity and why algorithmic risk stratification can materially reduce noise while preserving safety. Macro fundamentals support implementation, with U.S. GDP at USD ~ trillion and inflation at ~, which combined with labor-market pressure creates strong incentives to deploy automation that improves triage throughput and clinician productivity using current conditions rather than future projections.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the USA RPM market is expected to expand on the back of reimbursement-supported scale, higher acceptance of home-based care, and continued device innovation including wearables, patches, and multi-parameter kits. The USA RPM market is projected to rise from USD ~ billion to USD ~ billion, implying a CAGR of ~ over the period. Operationally, growth is expected to concentrate in programs that improve adherence and data capture, reduce alert fatigue through triage automation, and integrate tightly with EHR workflows to make RPM clinically native rather than an external dashboard.
Major Players
- Philips
- Medtronic
- Abbott
- Dexcom
- GE HealthCare
- Boston Scientific
- Masimo
- ResMed
- iRhythm Technologies
- VitalConnect
- Optum
- Biofourmis
- Current Health
- Health Recovery Solutions
Key Target Audience
- Hospitals & Integrated Delivery Networks
- Large Physician Groups / ACO Operators
- Home Health Agencies & Post-Acute Networks
- Health Insurers & Managed Care Organizations
- Employer Health & Benefits Buyers
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Pharmacy & Retail Health Buyers
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We construct an ecosystem map across device OEMs, RPM platforms, clinical monitoring service providers, payers, and provider buyers. Desk research consolidates reimbursement rules, device categories, and indication pathways, defining variables such as patient-month volume, device-day capture, adherence thresholds, and escalation intensity.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We model RPM revenues using a bottom-up patient-month framework, then reconcile with a top-down spend view across devices, software, and services. We stress-test assumptions using reimbursement logic to align operational reality with financial sizing.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate hypotheses via CATIs with RPM program operators, digital health leaders in provider systems, and vendor executives. Interviews focus on real- world enrollment conversion, adherence drop-offs, alert volumes, staffing ratios, integration timelines, and payer contracting patterns to refine segment weights and growth levers.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize findings into a validated market model and competitive benchmarking. Output includes segmentation and scenario-based outlooks tied to reimbursement stability, adoption by indication, and operational scalability, ensuring conclusions remain grounded in implementable program economics.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, RPM vs RTM Boundary Conditions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Bottom-Up Patient-Month and Device-Day Model, Top-Down Spend Reconciliation, Data Triangulation Framework, Primary Interview Approach, Validation via Claims and Reimbursement Logic, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution of RPM Programs
- Timeline of Technology Shifts
- Value Chain and Operating Model
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Growth Drivers
Chronic Burden Addressability
Aging-at-Home Enablement
Hospital Capacity Optimization
Reimbursement Pull
Device Innovation
Employer Care Navigation - Challenges
Patient Adherence and Drop-offs
Alert Fatigue
Workflow Integration Complexity
Clinician Staffing Constraints
Data Governance and Privacy
Interstate Operations
Device Logistics and Loss - Opportunities
Hospital-at-Home Scaling
AI-Enabled Clinical Triage
Multi-condition Monitoring Kits
Payer-Led RPM at Scale
Pharmacy-Enabled Enrollment
Rural and Underserved Reach - Trends
Cellular-First RPM
Patch-Based Monitoring
Consumer CGM Expansion
FHIR-Based Interoperability
Algorithmic Escalation
White-Label RPM Platforms - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Patient-Month Volume, 2019–2024
- By Device-Enabled Patient Coverage, 2019–2024
- By Average Revenue per Enrolled Patient-Month, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Devices
Software
Services
Integrated RPM Programs
Analytics and AI Add-ons - By Application (in Value %)
Wearables
Handheld Devices
Stationary and Home Hubs
Implantables
Patches - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Cardiology
Diabetes
Respiratory Disorders
Sleep Disorders
Oncology
Neurology - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Blood Pressure
Glucose
Pulse Oximetry
ECG and Heart Rhythm
Weight - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Hospitals and Integrated Delivery Networks
Physician Groups
Home Health Agencies
Post-Acute and Skilled Nursing Facilities
Payers - By Region (in Value %)
Chronic Care RPM
Post-Discharge RPM
Hospital-at-Home
Maternal and High-Risk Monitoring
Specialty Clinic RPM
- Competitive Map
- Cross Comparison Parameters (CMS RPM Billing Readiness, Device-Day Reliability, Patient Adherence Performance, Clinical Triage Throughput, EHR and Interoperability Depth, Fulfillment and Logistics Efficiency, Security and Compliance Posture, Outcomes and Contracting Evidence)
- Competitive Benchmarking Matrix
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Partner Ecosystem and Channel Strategy
- Company Profiles
Philips including BioTelemetry
Medtronic
Abbott
Dexcom
GE HealthCare
Boston Scientific
Masimo
ResMed
iRhythm Technologies
VitalConnect
Optum
Biofourmis
Current Health (Best Buy Health)
Health Recovery Solutions
- Provider Demand & Utilization
- Care Team Workflow Mapping
- Budget Ownership & Procurement
- Decision Drivers & Pain Points
- Implementation Readiness
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Patient-Month Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Revenue per Enrolled Patient-Month, 2025–2030


