Market Overview
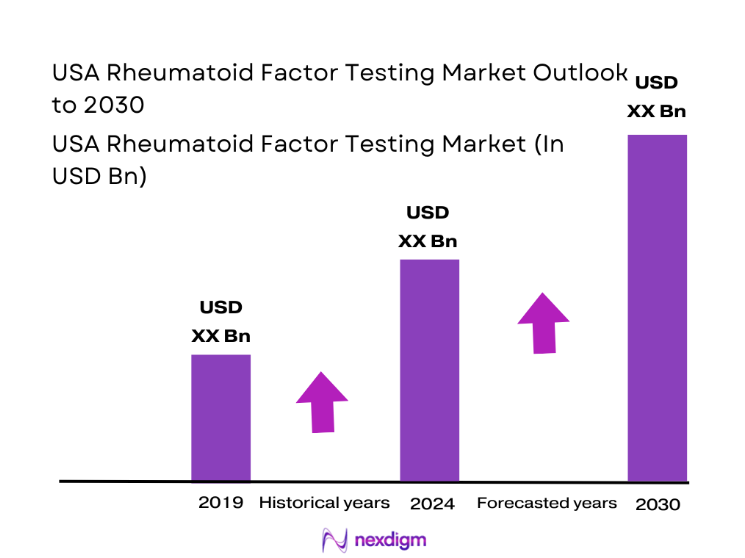
The USA Rheumatoid Factor Testing market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting strong diagnostic demand driven by autoimmune disease screening across hospitals and reference laboratories. Annual test throughput exceeds ~ million tests, supported by an installed base of ~ systems across clinical settings. Average revenue per test remains near USD ~, influenced by reimbursement structures and growing adoption of automated immunoassay platforms that improve turnaround time and workflow efficiency across high-volume diagnostic centers nationwide.
Market activity is concentrated in metropolitan healthcare clusters such as the Northeast corridor, Southern California, and major Midwestern cities, where dense hospital networks and integrated delivery systems accelerate test adoption. These regions benefit from advanced laboratory infrastructure, mature payer-provider ecosystems, and supportive policy environments that emphasize early diagnosis and chronic disease management. Strong specialist density and clinical trial activity further reinforce sustained demand for rheumatoid factor testing services.
Market Segmentation
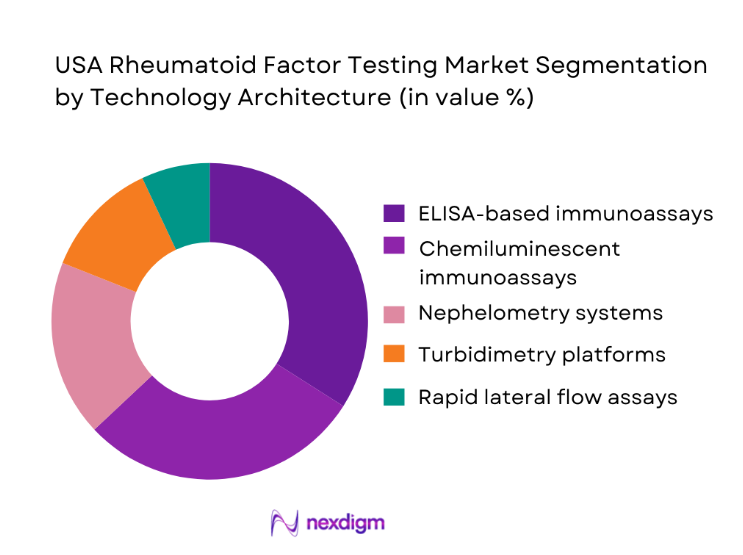
By Technology Architecture
ELISA-based and chemiluminescent immunoassays dominate testing workflows due to their balance of sensitivity, scalability, and operational efficiency in high-throughput laboratories. Nephelometry and turbidimetry continue to serve mid-volume facilities, while rapid lateral flow assays gain traction in outpatient clinics seeking faster decision support. The dominance of automated platforms is reinforced by rising test volumes exceeding ~ million annually and an expanding installed base of ~ systems in core laboratories. Continuous upgrades in assay precision and digital integration strengthen adoption across hospital networks, while standardized protocols in autoimmune diagnostics further consolidate technology leadership in this segment.
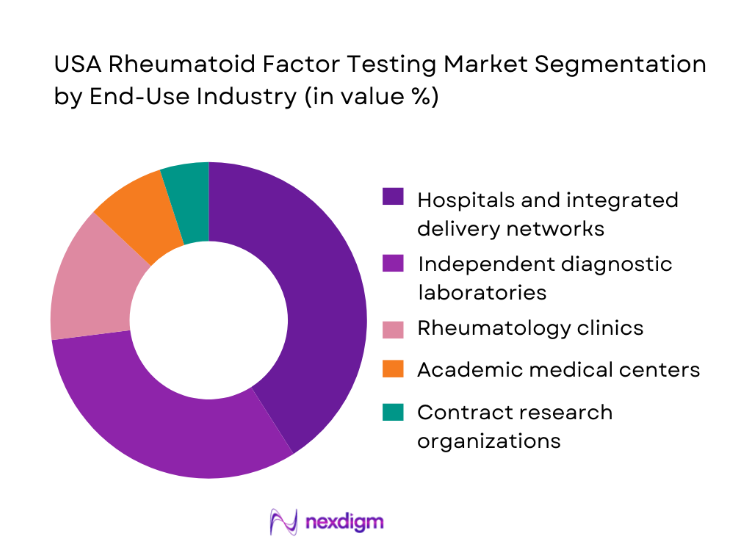
By End-Use Industry
Hospitals and integrated delivery networks lead demand, driven by centralized testing models handling ~ million samples annually. Independent diagnostic laboratories follow closely, leveraging scale efficiencies and broad physician outreach. Rheumatology clinics increasingly adopt in-house testing for faster patient management, supported by compact analyzers and simplified workflows. Academic medical centers and contract research organizations contribute through clinical trials and biomarker studies, sustaining steady test utilization. The dominance of hospital and reference lab segments is underpinned by higher budget allocations exceeding USD ~ million collectively for diagnostics infrastructure and a strong emphasis on standardized autoimmune disease pathways.
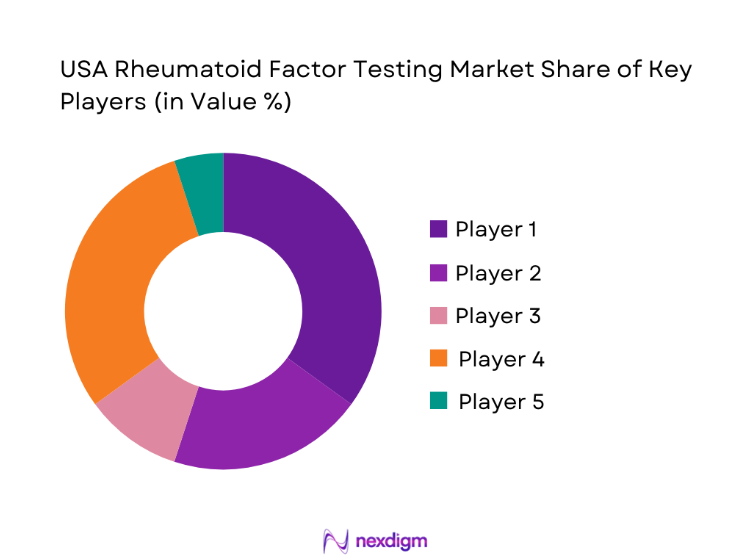
Competitive Landscape
The USA Rheumatoid Factor Testing market exhibits a moderately concentrated structure, with a handful of global diagnostics companies shaping technology standards while regional players compete on service reach and pricing flexibility. Market dynamics are defined by strong distribution networks, regulatory readiness, and long-term service contracts that influence procurement decisions across hospitals and laboratory chains.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Abbott Laboratories | 1888 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Roche Diagnostics | 1896 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Siemens Healthineers | 1847 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific | 1956 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bio-Rad Laboratories | 1952 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Rheumatoid Factor Testing Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune disorders
The growing patient pool has elevated annual diagnostic volumes beyond ~ million tests across major healthcare networks. Increased specialist referrals and chronic disease management programs are driving sustained utilization of rheumatoid factor testing in both hospital and outpatient settings. Healthcare systems allocate over USD ~ million annually toward autoimmune diagnostics infrastructure, supporting expanded analyzer deployments of ~ systems nationwide. This scale effect strengthens standardized testing pathways and reinforces demand for high-throughput platforms that can manage rising workloads efficiently.
Growing emphasis on early diagnosis and preventive care
Preventive healthcare strategies have accelerated test ordering frequency, with primary care and rheumatology clinics processing ~ million screening tests annually. Early detection initiatives supported by public health programs channel funding of approximately USD ~ million into diagnostic expansion, enabling faster patient triage and treatment planning. The shift toward proactive care models increases adoption of automated immunoassays and integrated reporting systems across ~ facilities, embedding rheumatoid factor testing as a routine component of chronic disease screening.
Challenges
Pricing pressure from reimbursement cuts and payer scrutiny
Reimbursement adjustments have constrained laboratory margins, reducing per-test returns to near USD ~ in several care settings. Diagnostic providers managing ~ million tests annually face tighter budget controls, limiting capital investments for new analyzers and upgrades. Hospitals reallocate funds of about USD ~ million toward higher-priority acute care needs, slowing replacement cycles for existing testing systems and intensifying cost-efficiency requirements across procurement strategies.
Variability in test accuracy across platforms and methodologies
Differences in assay sensitivity and calibration standards affect diagnostic confidence, leading to repeat testing volumes of ~ million annually. Healthcare providers incur additional operational costs approaching USD ~ million to manage confirmatory workflows and quality assurance programs. The lack of uniform performance benchmarks across ~ systems complicates purchasing decisions for smaller laboratories, slowing adoption of newer technologies despite rising clinical demand.
Opportunities
Adoption of high-throughput automated analyzers in core labs
Central laboratories processing ~ million samples annually are increasingly investing in automation to improve efficiency and turnaround time. Capital allocations exceeding USD ~ million support large-scale deployments of ~ systems that streamline workflow and reduce manual handling. These upgrades create opportunities for integrated platforms offering combined autoimmune panels, strengthening vendor engagement with hospital networks seeking scalable diagnostic solutions.
Expansion of point-of-care RF testing in outpatient settings
Outpatient clinics and ambulatory centers conduct ~ million visits annually for rheumatology care, creating demand for rapid testing solutions. Investments of approximately USD ~ million in compact analyzers enable near-patient diagnostics that enhance clinical decision speed. The growing footprint of ~ point-of-care sites supports broader market penetration, particularly in suburban and rural regions where access to centralized laboratories remains limited.
Future Outlook
The USA Rheumatoid Factor Testing market is positioned for steady expansion through the next decade, driven by preventive care models, automation in diagnostics, and integrated data ecosystems. Continued policy focus on early detection and chronic disease management will reinforce testing volumes across hospital and outpatient settings. Advancements in assay technology and digital connectivity are expected to further enhance efficiency, accuracy, and clinical value across the diagnostic continuum.
Major Players
- Abbott Laboratories
- Roche Diagnostics
- Siemens Healthineers
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Beckman Coulter
- Ortho Clinical Diagnostics
- DiaSorin
- QuidelOrtho
- Sekisui Diagnostics
- Trinity Biotech
- Werfen
- Sysmex Corporation
- Mindray Medical International
- Randox Laboratories
Key Target Audience
- Hospital procurement and laboratory management teams
- Independent diagnostic laboratory networks
- Rheumatology clinics and specialty care centers
- Integrated delivery networks and healthcare systems
- Investments and venture capital firms
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
- State health departments and public health agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market demand indicators, testing volumes, installed base estimates, and reimbursement dynamics were identified to frame the analytical scope. Key clinical pathways and technology adoption patterns were mapped across hospital and outpatient settings.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Quantitative models were developed using masked financial and volume benchmarks to estimate market scale and segment performance. Comparative analysis across regions and end-use industries shaped structural insights.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Clinical and operational assumptions were validated through structured consultations with laboratory managers and healthcare administrators. Feedback refined demand drivers, constraints, and opportunity pathways.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All findings were consolidated into a coherent market narrative, integrating quantitative indicators with strategic insights to deliver a consulting-grade assessment of the USA Rheumatoid Factor Testing market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, terminology and abbreviations, rheumatoid factor testing taxonomy across qualitative and quantitative methods, market sizing logic by test volume and reagent consumption, revenue attribution across assays analyzers calibrators and controls, primary interview program with rheumatologists labs hospitals and distributors, data triangulation and validation approach, assumptions limitations and data gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Care and diagnostic usage pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune disorders
Growing emphasis on early diagnosis and preventive care
Expansion of hospital and reference laboratory testing capacity
Technological advancements in immunoassay sensitivity and automation
Increasing test volumes driven by aging population
Integration of RF testing in broader autoimmune diagnostic panels - Challenges
Pricing pressure from reimbursement cuts and payer scrutiny
Variability in test accuracy across platforms and methodologies
Limited awareness in primary care settings about early RF testing
Operational constraints in smaller laboratories
Competition from emerging biomarker alternatives
Regulatory and compliance burden for diagnostic manufacturers - Opportunities
Adoption of high-throughput automated analyzers in core labs
Expansion of point-of-care RF testing in outpatient settings
Growth in bundled autoimmune disease panels
Partnerships between diagnostic firms and rheumatology networks
Development of digital diagnostics and AI-driven interpretation tools
Rising demand from clinical research and pharmaceutical trials - Trends
Shift from manual ELISA to fully automated immunoassay systems
Increasing use of combined RF and anti-CCP testing protocols
Growth of centralized testing models in large lab networks
Integration of RF testing data into electronic health records
Focus on faster turnaround times and workflow efficiency
Adoption of value-based diagnostic solutions - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Test Volume, 2019–2024
- By Installed Base, 2019–2024
- By Revenue per Test, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Hospital-based clinical laboratories
Independent reference laboratory networks
Physician office and clinic labs
Academic and research laboratories
Point-of-care testing sites - By Application (in Value %)
Rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis
Autoimmune disease screening
Disease activity monitoring
Therapy response assessment
Research and clinical trials - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
ELISA-based immunoassays
Nephelometry systems
Turbidimetry platforms
Chemiluminescent immunoassays
Rapid lateral flow assays - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Hospitals and integrated delivery networks
Independent diagnostic laboratories
Rheumatology clinics
Academic medical centers
Contract research organizations - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone analyzers
LIS-integrated systems
Cloud-enabled diagnostics platforms
Middleware-connected testing solutions
Remote monitoring and data reporting systems - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (test accuracy and sensitivity, assay turnaround time, automation level, instrument footprint, reagent cost per test, service and maintenance coverage, LIS connectivity, regulatory approvals)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Abbott Laboratories
Roche Diagnostics
Siemens Healthineers
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Bio-Rad Laboratories
Beckman Coulter
Ortho Clinical Diagnostics
DiaSorin
QuidelOrtho
Sekisui Diagnostics
Trinity Biotech
Werfen
Sysmex Corporation
Mindray Medical International
Randox Laboratories
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Test Volume, 2025–2030
- By Installed Base, 2025–2030
- By Revenue per Test, 2025–2030


