Market Overview
The USA supersonic jet market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady development activity and controlled commercialization momentum. During the last two years, approximately ~ units progressed through testing, certification, and early deployment stages, driven by defense and private aviation demand. Flight testing hours exceeded ~ hours as programs advanced toward compliance milestones. Investment flows remained stable with funding concentrated on propulsion, materials, and noise mitigation technologies supporting near-term deployment readiness.
The market is primarily concentrated across California, Texas, and Florida due to aerospace clusters, testing infrastructure, and favorable regulatory ecosystems. These regions benefit from established aerospace supply chains, skilled labor pools, and proximity to federal research agencies. Demand is supported by defense procurement activity, private aviation operators, and technology developers. Policy frameworks encouraging sustainable aviation and advanced manufacturing further reinforce regional dominance and ecosystem maturity.
Market Segmentation
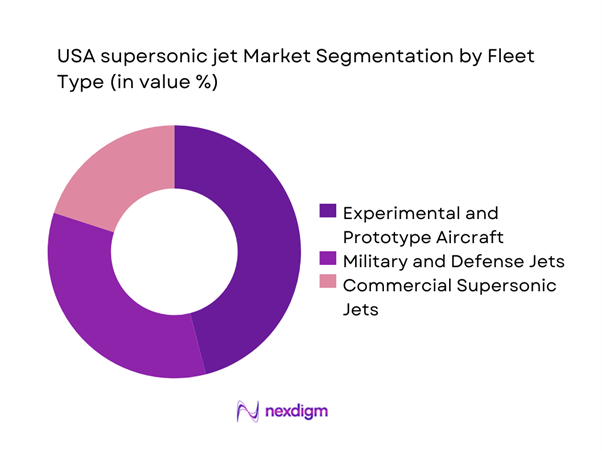
By Fleet Type
The market is currently dominated by experimental and prototype aircraft, reflecting the ongoing development and validation phase of supersonic platforms. Military and defense jets maintain a strong presence due to consistent funding cycles and strategic relevance. Commercial supersonic jets are emerging gradually, supported by regulatory progress and private sector interest. Fleet composition remains influenced by certification timelines, infrastructure readiness, and long-term fleet replacement strategies across defense and civil aviation stakeholders.
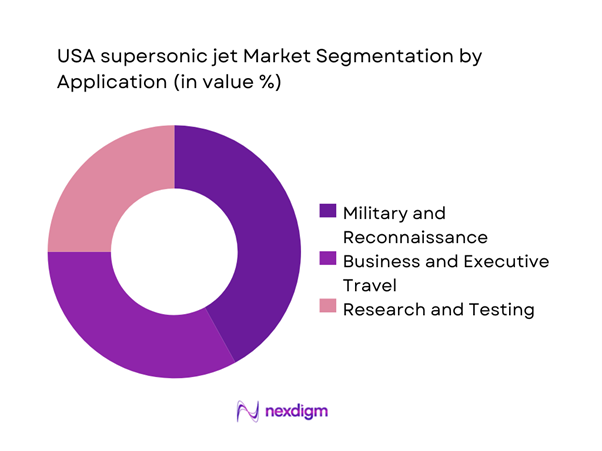
By Application
Military and reconnaissance applications dominate current usage due to established operational requirements and budget allocations. Business and executive travel applications are gaining traction as operators seek time-efficient alternatives to conventional aviation. Research and testing applications remain critical, supporting aerodynamic validation, propulsion testing, and regulatory compliance activities. The segmentation reflects a transition phase where experimental usage gradually supports commercial viability.
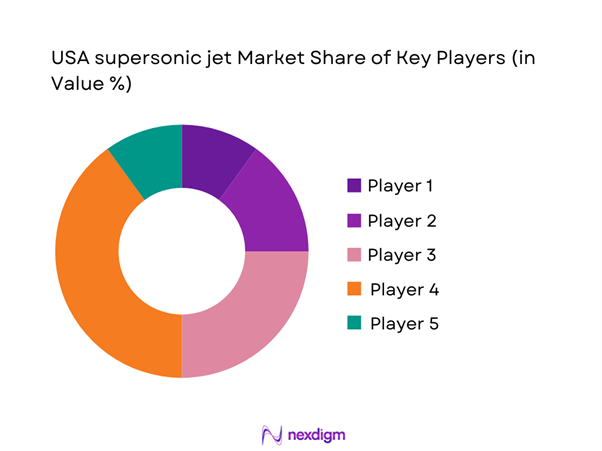
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by a limited number of technologically advanced manufacturers supported by specialized suppliers and research organizations. Competition centers on propulsion efficiency, noise reduction capabilities, certification readiness, and platform scalability. Strategic partnerships, government contracts, and technology demonstrations play a crucial role in shaping competitive positioning across the domestic ecosystem.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Boom Supersonic | 2014 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Northrop Grumman | 1939 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hermeus Corporation | 2018 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing Defense | 1916 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA supersonic jet Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising demand for reduced long-haul travel time
Rising demand for faster intercontinental travel is reshaping expectations for premium aviation efficiency and time-sensitive mobility needs. Corporate travel requirements increasingly prioritize time optimization, encouraging investment in high-speed aircraft alternatives. Defense mobility strategies also emphasize rapid deployment capabilities across long distances. Increased globalization of business operations sustains interest in reducing transit durations significantly. Airport congestion challenges further amplify the appeal of point-to-point supersonic connectivity. Operational efficiency improvements enhance feasibility for limited-route adoption. Advancements in navigation systems support safe high-speed operations. Passenger preference trends increasingly favor reduced travel duration over cost. Fleet planners evaluate supersonic options for strategic routing advantages. These combined factors steadily reinforce demand momentum.
Advancements in low-boom and noise reduction technologies
Technological progress in low-boom aerodynamics has significantly improved regulatory feasibility for supersonic operations. Advanced computational modeling enables optimized fuselage shaping to reduce sonic impact. Engine innovations contribute to quieter thrust profiles without compromising performance. Material science advancements allow lightweight structures supporting acoustic dampening. Flight testing programs demonstrate measurable reductions in ground-level noise perception. Regulatory bodies increasingly acknowledge validated noise mitigation data. Improved acoustic compliance enhances prospects for overland flight permissions. Public acceptance improves as environmental concerns are addressed. Investment flows increasingly target noise-reduction subsystems. These developments collectively accelerate commercialization potential.
Challenges
Stringent noise and emissions regulations
Regulatory frameworks impose strict limitations on permissible noise and emission levels for supersonic aircraft. Compliance requirements significantly extend certification timelines and testing complexity. Environmental scrutiny continues to intensify across aviation segments. Regulatory uncertainty delays investment decisions and program commitments. Variability across federal and state regulations complicates operational planning. Emission thresholds require continuous technological refinement. Policy alignment remains inconsistent across jurisdictions. Approval processes demand extensive documentation and validation cycles. These constraints elevate development risk profiles. Overall regulatory stringency remains a major barrier.
High development and certification costs
Supersonic aircraft development requires substantial capital allocation across engineering and testing phases. Certification procedures involve extensive simulation, flight testing, and documentation requirements. Specialized materials and propulsion systems increase engineering expenditures. Limited production volumes restrict economies of scale realization. Extended development timelines elevate financial exposure for developers. Infrastructure adaptation further increases program costs. Risk mitigation strategies demand additional investment layers. Financial barriers restrict participation to well-capitalized entities. Cost recovery timelines remain prolonged. These factors collectively constrain market entry.
Opportunities
Commercial supersonic passenger revival
Renewed interest in premium air travel creates opportunities for limited-capacity supersonic services. High-net-worth and corporate travelers demonstrate willingness to adopt faster alternatives. Route optimization enables targeted deployment on high-demand corridors. Airline partnerships support gradual integration into existing fleets. Cabin comfort innovations enhance value propositions. Market acceptance improves through sustainability initiatives. Brand differentiation drives early adoption potential. Operational learnings reduce scalability risks. Demand forecasting accuracy continues improving. This revival supports long-term commercial viability.
Government-backed aerospace R&D programs
Public funding initiatives significantly support early-stage supersonic research and validation. Collaborative programs reduce financial burdens for private developers. Access to government testing infrastructure accelerates development cycles. Research grants promote innovation in propulsion and materials. Policy alignment strengthens long-term industry confidence. Defense-oriented research indirectly benefits commercial platforms. Technology transfer mechanisms enhance industry-wide capabilities. Government participation reduces investment risk exposure. Sustained funding encourages continuous innovation. These programs form a critical growth catalyst.
Future Outlook
The USA supersonic jet market is expected to transition from experimental development toward limited commercial deployment over the coming years. Regulatory alignment, technological maturity, and infrastructure readiness will shape adoption rates. Continued collaboration between government agencies and private developers will remain essential. Advancements in sustainability and noise mitigation will further influence market acceptance.
Major Players
- Boom Supersonic
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Boeing Defense
- Hermeus Corporation
- Raytheon Technologies
- General Electric Aerospace
- Pratt & Whitney
- L3Harris Technologies
- Kratos Defense
- Virgin Galactic
- NASA Aeronautics
- Sierra Nevada Corporation
- Aerojet Rocketdyne
- Collins Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Commercial aircraft manufacturers
- Defense procurement agencies
- Private aviation operators
- Aerospace component suppliers
- Government and regulatory bodies including FAA and NASA
- Airport infrastructure developers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Aviation technology integrators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope, platform classifications, and application areas were defined through industry frameworks and regulatory benchmarks. Key performance indicators and operational parameters were established to guide data collection.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was analyzed using bottom-up and top-down approaches integrating production activity, testing programs, and deployment trends across the United States.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through expert consultations, technical reviews, and alignment with regulatory developments and program milestones.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated through triangulation, ensuring consistency across qualitative and quantitative indicators before final report preparation.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for civil and defense supersonic aircraft, platform and configuration-based segmentation logic, bottom-up and top-down fleet and revenue estimation approach, program-level revenue attribution and contract value mapping, primary validation through OEMs regulators and aerospace experts, triangulation using flight test data order books and regulatory filings)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission profiles
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and manufacturing flow
- Regulatory and certification environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising demand for reduced long-haul travel time
Advancements in low-boom and noise reduction technologies
Increased defense modernization budgets
Revival of commercial supersonic travel programs
Public and private investment in next-generation aviation - Challenges
Stringent noise and emissions regulations
High development and certification costs
Limited airport infrastructure compatibility
Fuel efficiency and sustainability concerns
Long development and commercialization timelines - Opportunities
Commercial supersonic passenger revival
Government-backed aerospace R&D programs
Export potential for defense-grade platforms
Integration of sustainable aviation fuels
Advancements in digital flight control systems - Trends
Development of low-boom supersonic designs
Increased use of composite materials
Digital twin and simulation-based testing
Public-private partnerships in aerospace
Growing focus on sustainable supersonic flight - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Commercial supersonic jets
Military and defense supersonic jets
Experimental and prototype aircraft - By Application (in Value %)
Business and executive travel
Military combat and reconnaissance
Research and test flight programs - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Turbojet and low-bypass turbofan
Advanced afterburning turbofan
Hybrid propulsion and low-boom configurations - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Commercial aviation
Defense and homeland security
Aerospace research organizations - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Satellite-based communication systems
Line-of-sight and ground-based communication
Integrated avionics connectivity systems - By Region (in Value %)
West Coast
Midwest
Southern United States
Northeast United States
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology maturity, fleet size, program funding, regulatory progress, pricing strategy, manufacturing capability, partnership ecosystem, geographic presence)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Boom Supersonic
Lockheed Martin Corporation
Northrop Grumman Corporation
Boeing Defense Space & Security
Raytheon Technologies
General Electric Aerospace
Rolls-Royce North America
Pratt & Whitney
NASA Aeronautics
Hermeus Corporation
Spike Aerospace
Aerion Supersonic
Virgin Galactic
Kratos Defense & Security Solutions
L3Harris Technologies
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


